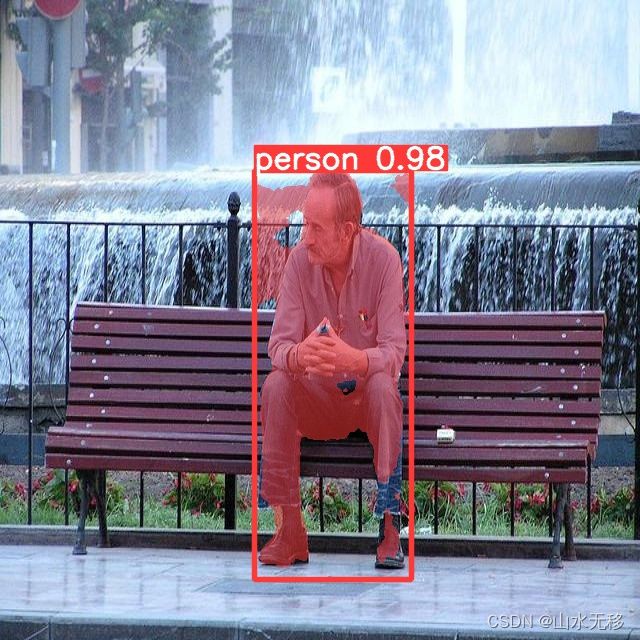
yolov8seg 瑞芯微RKNN芯片、地平线Horizon芯片、TensorRT部署
特别说明:参考官方开源的yolov8代码、瑞芯微官方文档、地平线的官方文档,如有侵权告知删,谢谢。
模型、测试图像、测试结果、完整代码,放在github上,参考链接 模型和代码。
由于之前写了三篇yolov8检测部署板端芯片相关的博文,有网友让写一篇yolov8seg部署博客,一直迟迟未行动,最近忙中借闲匆匆对yolov8seg进行了梳理,尝试了对yolov8seg进行部署验证和仿真测试。总体感受,yolov8的检测由于使用DFL,使得(检测+后处理)相对慢不少,如果把DFL模块相关的放模型里做导致模型慢不少,如果放后处理中做后处理慢(到底是放模型中做还是放后处理中做,根据整个系统的资源合理放置,本示例中是放在模型中进行的);yolov8seg 还需处理mask系数,同时分割结果还需乘以系数,使得对板端部署不是很友好。
特别说明:本示例中模型的训练使用的数据并不是很多,模型效果无法保证,只是用来测试部署用的,如果换一张图像可能存在检测不到属于正常现象。分割相关的后处理可能对板端部署还不是很优化,欢迎共同探讨优化。
1 模型和训练
训练代码参考官方开源的yolov8seg 训练代码,由于SiLU在有些板端芯片上还不支持,因此将其改为ReLU,训练数据集是coco的一部分训练的,主要是用来测试流程用,模型效果无法保证,换一张图像测试检测不到正常。
2 导出 yolov8seg 的 onnx
本实例提供的导出onnx方式只适配本示例对应仓库的代码,如果用官方导出的onnx,请自行写后处理代码。谢谢
后处理中有些算在板端芯片上效率低或者不支持,导出 onnx 需要将板端芯片不友好或不支持算子规避掉。导出onnx修改的部分。
第一步:
将pt只保存权重值,增加代码如下图。

# 保存权重值
import torch
self.model.fuse()
self.model.eval()
torch.save(self.model.state_dict(), './weights/yolov8n-seg_relu_80class_dict.pt')
修改后运行以下代码(在weights文件夹下生成yolov8n-seg_relu_80class_dict.pt):
model = YOLO('./weights/yolov8n-seg_relu_80class.pt')
result = model(task='segment', mode='predict', source='./images/test.jpg', line_width=3, show=True, save=True, device='cpu')
第二步:
导出onnx,去除不需要的算子。修改代码如下。
(1)修改检测头
修改该模块的完整代码:
class Detect(nn.Module):
"""YOLOv8 Detect head for detection models."""
dynamic = False # force grid reconstruction
export = False # export mode
shape = None
anchors = torch.empty(0) # init
strides = torch.empty(0) # init
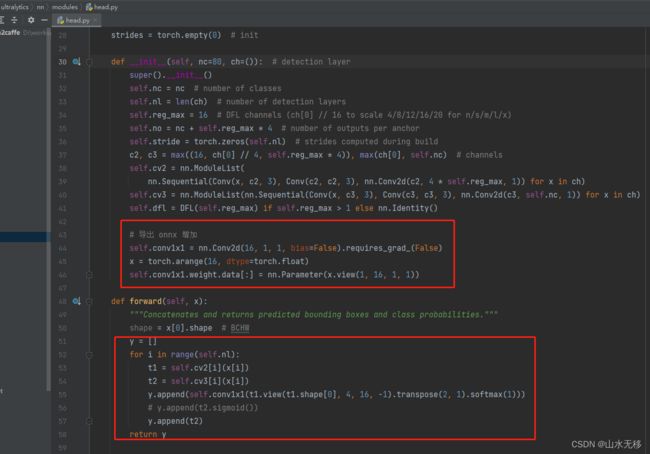
def __init__(self, nc=80, ch=()): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.nl = len(ch) # number of detection layers
self.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)
self.no = nc + self.reg_max * 4 # number of outputs per anchor
self.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during build
c2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], self.nc) # channels
self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(
nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2, 4 * self.reg_max, 1)) for x in ch)
self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)
self.dfl = DFL(self.reg_max) if self.reg_max > 1 else nn.Identity()
# 导出 onnx 增加
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(16, 1, 1, bias=False).requires_grad_(False)
x = torch.arange(16, dtype=torch.float)
self.conv1x1.weight.data[:] = nn.Parameter(x.view(1, 16, 1, 1))
def forward(self, x):
"""Concatenates and returns predicted bounding boxes and class probabilities."""
shape = x[0].shape # BCHW
y = []
for i in range(self.nl):
t1 = self.cv2[i](x[i])
t2 = self.cv3[i](x[i])
y.append(self.conv1x1(t1.view(t1.shape[0], 4, 16, -1).transpose(2, 1).softmax(1)))
# y.append(t2.sigmoid())
y.append(t2)
return y
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i])), 1)
if self.training:
return x
elif self.dynamic or self.shape != shape:
self.anchors, self.strides = (x.transpose(0, 1) for x in make_anchors(x, self.stride, 0.5))
self.shape = shape
x_cat = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2)
if self.export and self.format in ('saved_model', 'pb', 'tflite', 'edgetpu', 'tfjs'): # avoid TF FlexSplitV ops
box = x_cat[:, :self.reg_max * 4]
cls = x_cat[:, self.reg_max * 4:]
else:
box, cls = x_cat.split((self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1)
dbox = dist2bbox(self.dfl(box), self.anchors.unsqueeze(0), xywh=True, dim=1) * self.strides
y = torch.cat((dbox, cls.sigmoid()), 1) # 官方代码
# y = torch.cat((self.dfl(box), cls.sigmoid()), 1) # 导出本实例的onnx使用
return y if self.export else (y, x)
def bias_init(self):
"""Initialize Detect() biases, WARNING: requires stride availability."""
m = self # self.model[-1] # Detect() module
# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1
# ncf = math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # nominal class frequency
for a, b, s in zip(m.cv2, m.cv3, m.stride): # from
a[-1].bias.data[:] = 1.0 # box
b[-1].bias.data[:m.nc] = math.log(5 / m.nc / (640 / s) ** 2) # cls (.01 objects, 80 classes, 640 img)
class Segment(Detect):
"""YOLOv8 Segment head for segmentation models."""
def __init__(self, nc=80, nm=32, npr=256, ch=()):
"""Initialize the YOLO model attributes such as the number of masks, prototypes, and the convolution layers."""
super().__init__(nc, ch)
self.nm = nm # number of masks
self.npr = npr # number of protos
self.proto = Proto(ch[0], self.npr, self.nm) # protos
self.detect = Detect.forward
c4 = max(ch[0] // 4, self.nm)
self.cv4 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c4, 3), Conv(c4, c4, 3), nn.Conv2d(c4, self.nm, 1)) for x in ch)
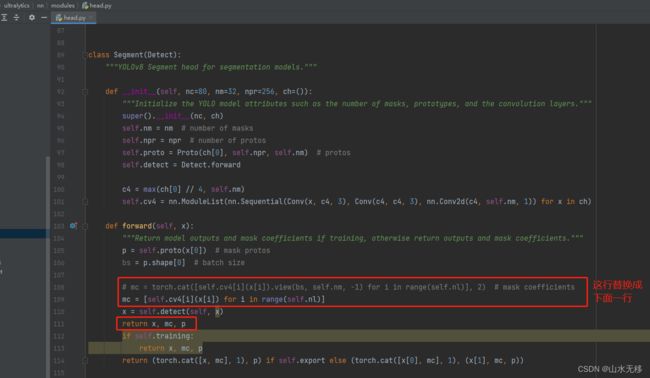
def forward(self, x):
"""Return model outputs and mask coefficients if training, otherwise return outputs and mask coefficients."""
p = self.proto(x[0]) # mask protos
bs = p.shape[0] # batch size
# mc = torch.cat([self.cv4[i](x[i]).view(bs, self.nm, -1) for i in range(self.nl)], 2) # mask coefficients
mc = [self.cv4[i](x[i]) for i in range(self.nl)]
x = self.detect(self, x)
return x, mc, p
if self.training:
return x, mc, p
return (torch.cat([x, mc], 1), p) if self.export else (torch.cat([x[0], mc], 1), (x[1], mc, p))
def _new(self, cfg: str, task=None, verbose=True):
"""
Initializes a new model and infers the task type from the model definitions.
Args:
cfg (str): model configuration file
task (str) or (None): model task
verbose (bool): display model info on load
"""
cfg_dict = yaml_model_load(cfg)
self.cfg = cfg
self.task = task or guess_model_task(cfg_dict)
self.model = TASK_MAP[self.task][0](cfg_dict, verbose=verbose and RANK == -1) # build model
self.overrides['model'] = self.cfg
# Below added to allow export from yamls
args = {**DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, **self.overrides} # combine model and default args, preferring model args
self.model.args = {k: v for k, v in args.items() if k in DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS} # attach args to model
self.model.task = self.task
import torch
self.model.fuse()
self.model.eval()
self.model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./weights/yolov8n-seg_relu_80class_dict.pt', map_location='cpu'), strict=False)
print("=========== onnx =========== ")
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640)
input_names = ["data"]
output_names = ["cls1", "reg1", "cls2", "reg2", "cls3", "reg3", "mc1", "mc2", "mc3", "seg"]
torch.onnx.export(self.model, dummy_input, "./weights/yolov8n-seg_relu_80class.onnx", verbose=False, input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names, opset_version=11)
print("======================== convert onnx Finished! .... ")
修改完以上三块,运行以下代码(生成onnx模型):
model = YOLO('./ultralytics/models/v8/yolov8-seg.yaml')
注意:以上修改顺序一定不能错,两次运行的代码也不一样,请注意,请注意,请注意。
3 yolov8seg 的pytoch 和onnx 测试结果
4 瑞芯微rknn和地平线horizon仿真测试参考
瑞芯微环境搭建和详细步骤参考 【瑞芯微RKNN模型转换和PC端仿真】。
地平线环境搭建和详细步骤参考【地平线Horizon模型转换和PC端仿真测试】。
5 相关链接
yolov8 检测瑞芯微RKNN和地平线Horizon芯片仿真测试部署
yolov8 瑞芯微 RKNN 的 C++部署
yolov8 导出官方模型进行瑞芯微RKNN和地平线Horizon芯片仿真测试部署