二分查找(代码实现)
二分查找:
文章参考:二分查找(折半查找算法)
二分查找又称折半查找、二分搜索、折半搜索等,是在分治算法基础上设计出来的查找算法,对应的时间复杂度为O(logn)。
二 分 查 找 算 法 仅 适 用 于 有 序 序 列 , 它 只 能 用 在 升 序 序 列 或 者 降 序 序 列 中 查 找 目 标 元 素 。 \textcolor{Red}{二分查找算法仅适用于有序序列,它只能用在升序序列或者降序序列中查找目标元素。} 二分查找算法仅适用于有序序列,它只能用在升序序列或者降序序列中查找目标元素。
二分查找算法的实现思路
在有序序列中,使用二分查找算法搜索目标元素的核心思想是:不断地缩小搜索区域,降低查找目标元素的难度。
以在升序序列中查找目标元素为例,二分查找算法的实现思路是:
初始状态下,将整个序列作为搜索区域(假设为 [B, E]);
找到搜索区域内的中间元素(假设所在位置为 M),和目标元素进行比对。如果相等,则搜索成功;如果中间元素大于目标元素,表明目标元素位于中间元素的左侧,将 [B, M-1] 作为新的搜素区域;反之,若中间元素小于目标元素,表明目标元素位于中间元素的右侧,将 [M+1, E] 作为新的搜素区域;
重复执行第二步,直至找到目标元素。如果搜索区域无法再缩小,且区域内不包含任何元素,表明整个序列中没有目标元素,查找失败。
举个简单的例子,在下图所示的升序序列中查找元素 31。

图 1 中,所有元素的位置分别用 0~9 表示,中间元素的位置为 ⌊ 0 + (9 - 0) / 2 ⌋ = 4,如下图所示: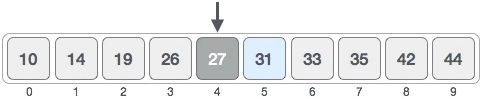
中间元素 27 < 31,可以断定 [0, 4] 区域内绝对没有 31,目标元素只可能位于 [5, 9] 区域内,如下图所示:

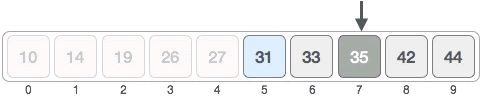
中间元素 35 > 31,可以断定 [7, 9] 区域内绝对没有 31,目标元素只可能位于 [5,6] 中,如下图所示:
- 在 [5, 6] 区域内,中间元素的位置为 ⌊ 5 + (6- 5) / 2 ⌋ = 5,中间元素就是 31,成功找到目标元素。
代码实现
C语言:
int search(int array[],int n,int target){
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
while(left<=right){
int middle = left + ((right - left)>>1);//防止溢出。>>1为向右移一位,比除以2速度更快
if(array[middle] > target){
right = middle - 1;//target在左区间。
}else if(array[middle] < target){
left = middle + 1;//target在右区间。
}else{
return middle;//tarfet在中间。
}
}
return -1;//没有找到该元素。
}
Java(简版):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class search {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean judge = true;
int[]array = new int[]{-22,-11,-1,0,11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99};
int target = 23;
int left = 0,right = array.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int middle = (left+right)/2;
if(target==array[middle]){
System.out.println("找到指定元素,位置为:"+(middle+1));
judge = false;
break;
}else if(array[middle]>target){
right = middle - 1;
} else if (array[middle]<target) {
left = middle + 1;
}
}
if(judge){
System.out.println("很抱歉,没有找到该元素!");
}
}
}
Java(最终):
//Java自带二分查找
//Java源码:
// Like public version, but without range checks.
/**
* Checks that {@code fromIndex} and {@code toIndex} are in
* the range and throws an exception if they aren't.
*/
static void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(fromIndex);
}
if (toIndex > arrayLength) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(toIndex);
}
}
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,long key) {
/**
* Searches a range of
* the specified array of longs for the specified value using the
* binary search algorithm.
* The range must be sorted (as
* by the {@link #sort(long[], int, int)} method)
* prior to making this call. If it
* is not sorted, the results are undefined. If the range contains
* multiple elements with the specified value, there is no guarantee which
* one will be found.
*
* @param a the array to be searched
* @param fromIndex the index of the first element (inclusive) to be
* searched
* @param toIndex the index of the last element (exclusive) to be searched
* @param key the value to be searched for
* @return index of the search key, if it is contained in the array
* within the specified range;
* otherwise, (-(insertion point) - 1). The
* insertion point is defined as the point at which the
* key would be inserted into the array: the index of the first
* element in the range greater than the key,
* or {@code toIndex} if all
* elements in the range are less than the specified key. Note
* that this guarantees that the return value will be >= 0 if
* and only if the key is found.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code fromIndex > toIndex}
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code fromIndex < 0 or toIndex > a.length}
* @since 1.6
*/
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
private static int binarySearch0(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,long key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
long midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}