C++进阶--红黑树模拟实现STL中的map和set
红黑树模拟实现STL中的map和set
- 一、红黑树模板参数的控制
- 二、红黑树结点当中存储的数据
- 三、模板参数中仿函数的增加
- 四、正向迭代器的实现
- 五、set的模拟实现
- 六、map的模拟实现
- 七、完整代码
-
- 7.1 RBTree.h
- 7.2 set.h
- 7.3 map.h
- 7.4 test.cpp
一、红黑树模板参数的控制
set是K模型的容器,而map是KV模型的容器,那我们如何用一棵KV模型的红黑树同时实现map和set呢?
这里就需要控制map和set传入底层红黑树的模板参数,为了与原红黑树的模板参数进行区分,我们将红黑树第二个模板参数的名字改为T
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
T模板参数可能只是键值Key,也可能是由Key和Value共同构成的键值对,最后的参数KeyOfT表示传入的是set还是map容器。
如果是set容器,那么它传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是Key和Key
template<class K>
class set
{
//...
private:
RBTree<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
如果是map容器,那么它传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是Key以及Key和Value构成的键值对
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
//...
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
第一个拿到单独K的类型,因为find、erase这些接口函数的参数是K
第二个模板参数决定了树的结点里面存什么?–K 或 K/V
二、红黑树结点当中存储的数据
现在红黑树的模板参数变成了K和T,那么红黑树结点当中存储的应该是什么呢?
由于上层容器的不同,底层红黑树当中的K和T也是不同的:
- set容器:K和T都代表键值Key
- map容器:K代表键值Key,T代表Key和Value构成的键值对
对于set容器来说,底层红黑树结点当中存储K和T都是一样的,但是对于map容器来说,底层红黑树就只能存储T了。
这样一来,当上层容器是set的时候,结点当中存储的是键值Key;当上层容器是map的时候,结点当中存储的就是
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template <class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
三、模板参数中仿函数的增加
由于结点当中存储的是T,这个T可能是Key,也可能是
键值对。当我们需要进行结点的键值比较时,应该如何获取结点的键值呢?
当上层容器是set的时候T就是键值Key,直接用T进行比较即可,当上层容器时map的时候就不行了,此时我们需要从
因此,上层容器map需要向底层红黑树提供一个仿函数,用于获取T当中的键值Key,这样一来,当底层红黑树当中需要比较两个结点的键值时,就可以通过这个仿函数来获取T当中的键值了。
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
但是对于底层红黑树来说,它并不知道上层容器是map还是set,因此需要进行两个结点键值的比较时,底层红黑树都会通过传入的仿函数来获取键值Key,进而进行两个结点键值的比较。
因此,set容器也需要向底层传入一个仿函数。
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
此时,set容器传入底层红黑树的就是set的仿函数,map容器传入底层红黑树的就是map的仿函数
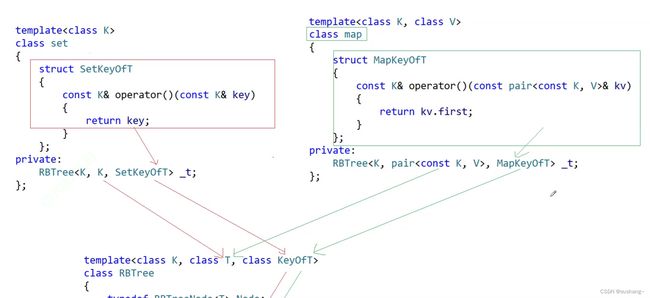
这样一来,当底层红黑树需要进行两个结点之间的键值的比较时,都会通过传入的仿函数来获取相应结点的键值,然后再进行比较
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
四、正向迭代器的实现
红黑树的正向迭代器实际上就是对结点指针进行了封装,因此在正向迭代器当中实际上就只有一个成员变量,那就是正向迭代器所封装结点的指针
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator <T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
};
因此,通过一个结点的指针就可以构造出一个正向迭代器
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//1. typedef __RBTreeIterator iterator; 拷贝构造
//2. typedef __RBTreeIterator const_iterator;
// 支持普通迭代器构造const迭代器的构造函数
__RBTreeIterator(const __RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*>& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
当对正向迭代器进行解引用操作时,直接返回对应结点数据的引用即可
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
当对正向迭代器进行->操作时,直接返回对应结点数据的指针即可
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
正向迭代器还需要重载==和!=运算符,直接判断两个迭代器所封装的结点是否是同一个即可
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
主要是+ +和- -运算符的重载
实现红黑树的正向迭代器时,一个结点的正向迭代器进行+ +操作后,应该根据红黑树中序遍历找到当前结点的下一个结点。
具体步骤如下
1.如果当前结点的右子树不为空,则+ +操作后应该找到其右子树当中的最左结点。
2.如果当前结点的右子树为空,则+ +操作后应该在该结点的祖先结点中,找到孩子是父亲左的那个祖先。
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
//1.右不为空,下一个就是右子树的最左结点
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
else
{
//2.右为空,沿着到根的路径,找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
实现红黑树的正向迭代器时,一个结点的正向迭代器进行- -操作后,应该根据红黑树中序遍历的序列找到当前结点的前一个结点。
具体逻辑如下
1.如果当前结点的左子树不为空,则- -操作后应该找到其左子树当中的最右结点。
2.如果当前结点的左子树为空,则- -操作后应该在该结点的祖先结点中,找到孩子是父亲右的那个祖先。
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left)
{
//1.左不为空,找左子树最右结点
Node* subRight = _node->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_node = subRight;
}
else
{
//2.左为空,孩子是父亲的右的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
正向迭代器实现后,我们需要在红黑树的实现当中进行迭代器类型的typedef。需要注意的是,为了让外部能够使用typedef后的正向迭代器类型iterator,需要在public区域进行typedef
然后在红黑树当中实现成员函数begin和end:
- begin函数返回中序序列当中第一个结点的正向迭代器,即最左结点
- end函数返回中序序列当中最后一个结点下一个位置的正向迭代器,这里直接使用空指针构造一个正向迭代器
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
private:
Node* _root=nullptr;
};
五、set的模拟实现
完成上述操作后,set的模拟实现也就很简单了,其中的成员函数都是调用底层红黑树的对应接口就行了,只不过需要注意将插入函数和查找函数返回值当中的结点指针改为迭代器即可
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace zl
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_set1()
{
int a[] = { 16,3,7,11,9,26,18,14,15 };
set<int> s;
/*s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);*/
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
//*it = 1;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
六、map的模拟实现
map的模拟实现也是相同的道理,其成员函数也是调用底层红黑树的杜对应接口,但是对于map来说,除了将插入函数和查找函数返回值当中的结点指针改为迭代器之外,还需要实现[ ]运算符的重载函数
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace zl
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_map1()
{
/*map m;
m.insert(make_pair(1,1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));*/
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
dict.insert(make_pair("count", "计数"));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "(字符串)"));
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
//it->first = "111"; //不能修改
//it->second = "111"; //可以修改
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& kv : dict)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_map2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜",
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
}
七、完整代码
7.1 RBTree.h
#pragma once
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template <class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator <T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//1. typedef __RBTreeIterator iterator; 拷贝构造
//2. typedef __RBTreeIterator const_iterator;
// 支持普通迭代器构造const迭代器的构造函数
__RBTreeIterator(const __RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*>& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
//1.右不为空,下一个就是右子树的最左结点
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
else
{
//2.右为空,沿着到根的路径,找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left)
{
//1.左不为空,找左子树最右结点
Node* subRight = _node->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_node = subRight;
}
else
{
//2.左为空,孩子是父亲的右的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
};
//仿函数
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
~RBTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
pair < iterator, bool > Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root),true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况2+3: u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色(p变黑,g变红)
{
// g
// p u
// c
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
//parent->_col = RED;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else // (grandfather->_right == parent)
{
// g
// u p
// c
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //情况2+3:u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色
{
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode),true);
}
/*void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}*/
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED)
{
cout << "根结点颜色是红色" << endl;
return false;
}
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
++benchmark;
cur = cur->_left;
}
//连续红色结点
return _Check(_root,0,benchmark);
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
private:
void _Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftH = _Height(root->_left);
int rightH = _Height(root->_right);
return leftH > rightH ? leftH + 1 : rightH + 1;
}
bool _Check(Node* root,int blackNum,int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (benchmark != blackNum)
{
cout << "某条路径黑色结点的数量不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
//cout << blackNum << endl;
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
++blackNum;
}
if (root->_col == RED
&& root->_parent
&& root->_parent->_col==RED)
{
cout << "存在连续的红色结点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _Check(root->_left,blackNum,benchmark)
&& _Check(root->_right,blackNum,benchmark);
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
/*void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}*/
Node* _root=nullptr;
};
//void Test_RBTree1()
//{
// //int a[] = { 16,3,7,11,9,26,18,14,15 };
// int a[] = { 4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14 };
// RBTree t1;
// for (auto e : a)
// {
// t1.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
// //cout << e << "插入:" << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
// }
// t1.InOrder();
// cout << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
//}
//void Test_RBTree2()
//{
// srand(time(0));
// const size_t N = 100000;
// RBTree t;
// for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
// {
// size_t x = rand()+i;
// t.Insert(make_pair(x, x));
// //cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
// }
// //t.InOrder();
//
// cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
// cout << t.Height() << endl;
//}
7.2 set.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace zl
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_set1()
{
int a[] = { 16,3,7,11,9,26,18,14,15 };
set<int> s;
/*s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);*/
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
//*it = 1;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
7.3 map.h
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace zl
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_map1()
{
/*map m;
m.insert(make_pair(1,1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));*/
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
dict.insert(make_pair("count", "计数"));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "(字符串)"));
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
//it->first = "111"; //不能修改
//it->second = "111"; //可以修改
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& kv : dict)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_map2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜",
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
}
7.4 test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include