rabbitmq基础教程(ui,java,springamqp)
概述:安装看我上篇文章Docker安装rabbitmq-CSDN博客
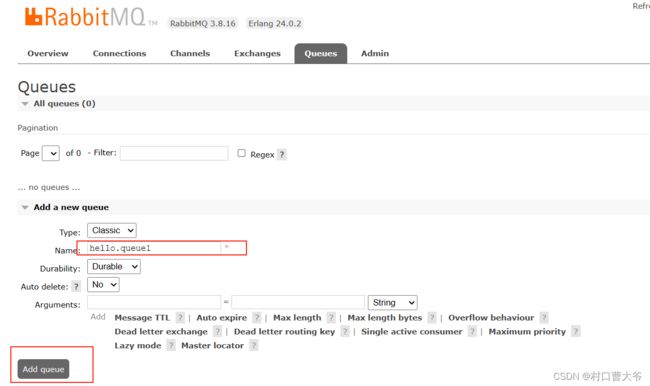
任务一
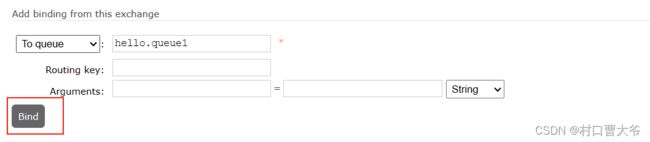
创建一个队列
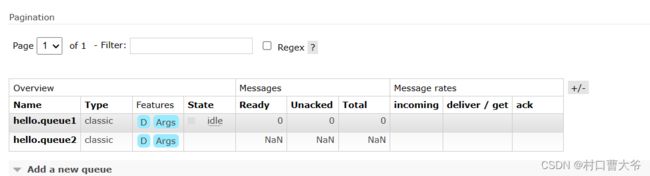
这样创建两个队列
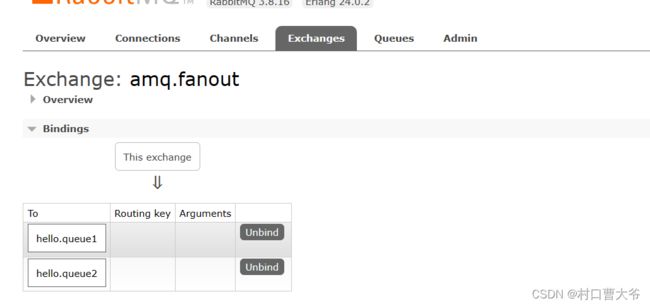
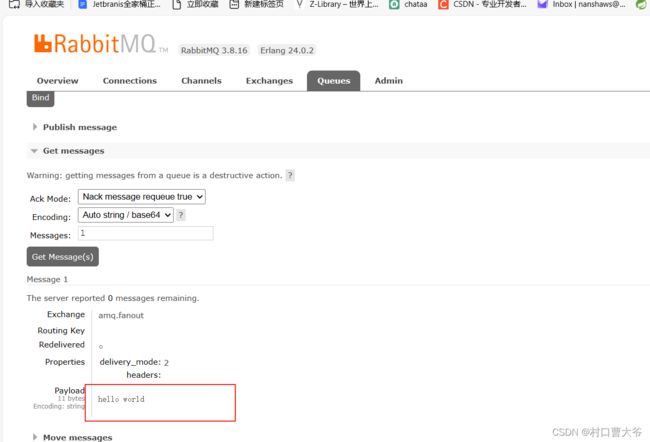
在amq.fanout交换机里面发送数据
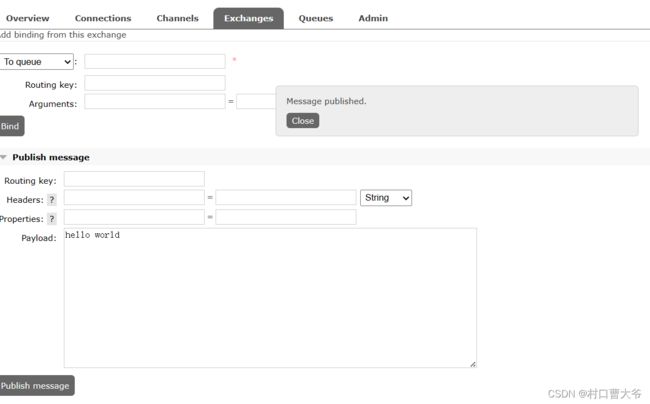
模拟发送数据
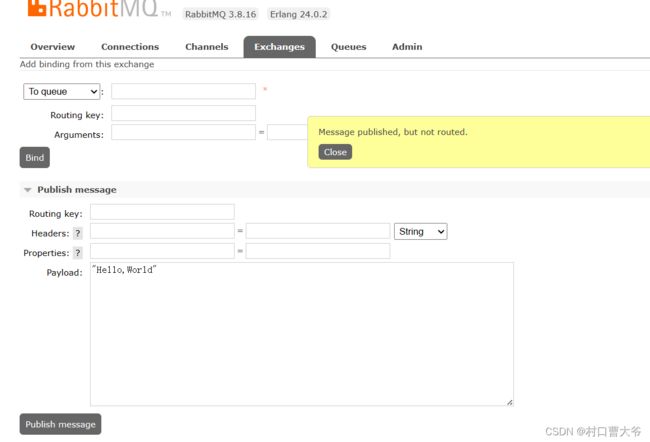
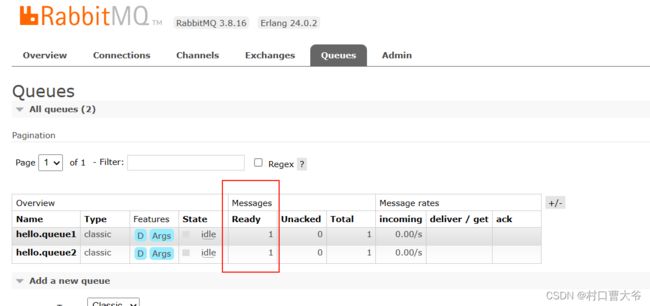
发送消息,发现一下信息:
所以得出理论,消息发送是先到交换机,然后由交换机路由到消息队列
交换机是负责路由和转发消息的,并没有存储的功能。
绑定队列
这时,再在交换机中发消息
查看结果:
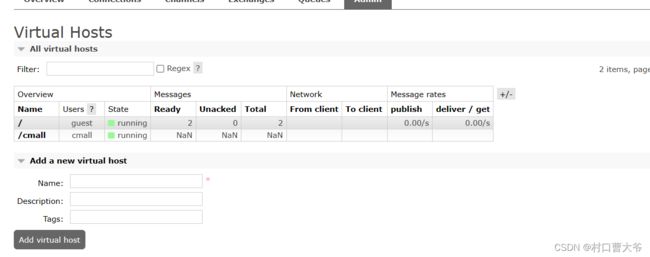
数据隔离
在rabbitmq中有虚拟主机的概念。
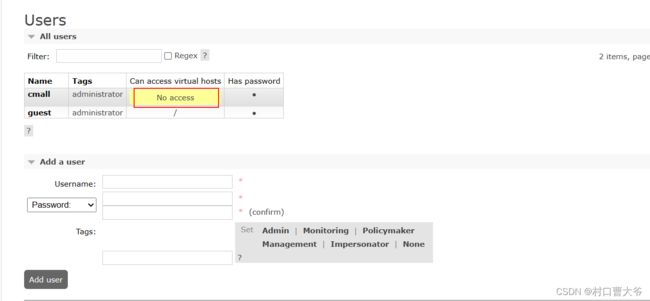
第一步:新添用户
添加成功后,发现没有虚拟主机,也就是说,我用这个用户登录后,是不可以操作上面的数据的。
又因为,我是超级管理员,所以我能看到这些
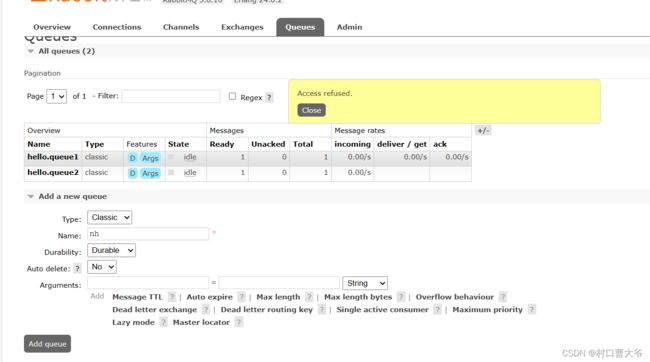
所以只能看,不能操作。
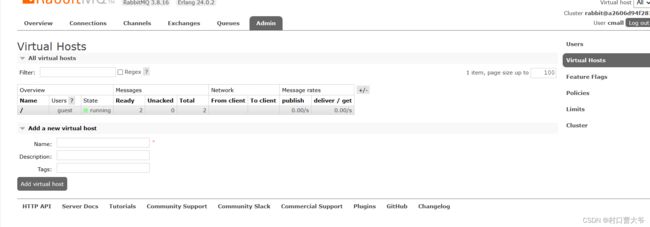
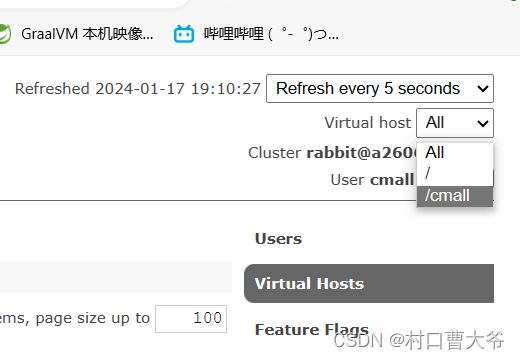
第二步:创立自己的虚拟主机
第三步:选自己的虚拟主机
选好后就只能看自己的了。
用Java代码操作
官网:RabbitMQ Tutorials — RabbitMQ
可以看到,官网上有案例,我们大多情况下用的是SpringAmqp,所以也就不讲那么多java简单调用的事情了。
用Spring AMQP操作
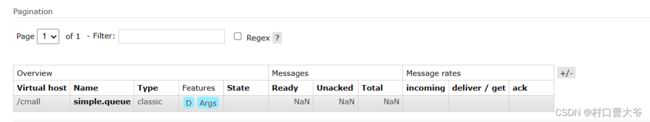
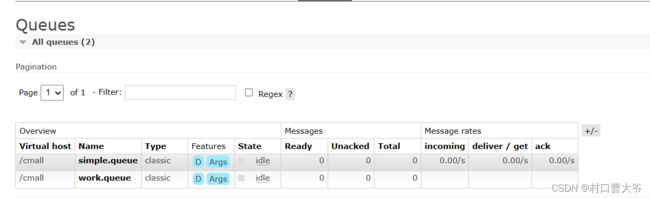
第一步:在控制台里面创建一个simple.queue队列
第二步:编写代码
pom文件
4.0.0
org.cyl
test09
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
test09
test09
1.8
UTF-8
UTF-8
2.6.13
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
com.rabbitmq
amqp-client
5.13.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
${spring-boot.version}
pom
import
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
3.8.1
1.8
1.8
UTF-8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
${spring-boot.version}
org.cyl.test09.Test09Application
true
repackage
repackage
配置mq服务端消息
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.56.10
port: 5672
virtual-host: /cmall
username: cmall
password: 123456发送方:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SendMessageService {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void testSimpleQueue(){
String queueName="simple.queue";
String message="hello,spring amqp!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
}
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}
接收方:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ReceiveMessageService {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void receiveMessage(String message) {
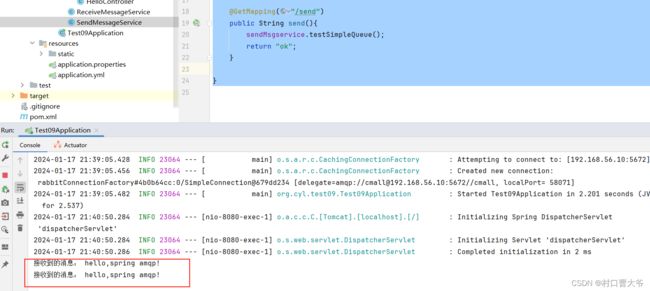
System.out.println("接收到的消息: " + message);
}
}
controller类:
package org.cyl.test09.demos.controller;
import org.cyl.test09.demos.ReceiveMessageService;
import org.cyl.test09.demos.SendMessageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
SendMessageService sendMsgservice;
@Autowired
ReceiveMessageService receiveMsgService;
@GetMapping("/send")
public String send(){
sendMsgservice.testSimpleQueue();
return "ok";
}
}
展示结果:
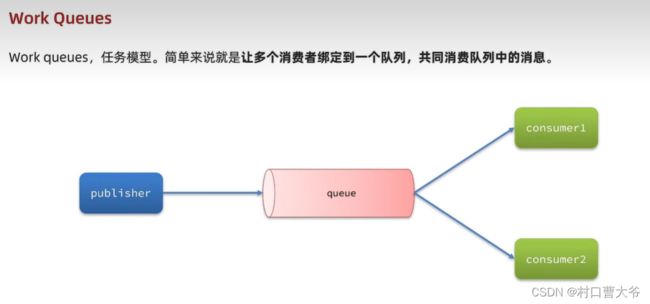
Work模型
第一步:创建一个队列
第二步:编写代码
发送:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SendMessageService {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void testSimpleQueue() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName="work.queue";
for (int i=1;i<50;i++){
String message="hello,spring amqp!_"+i;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}
接收:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ReceiveMessageService {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void receiveMessage1(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void receiveMessage2(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}
}
结果展示:
消费者一和消费者二是轮询效果。
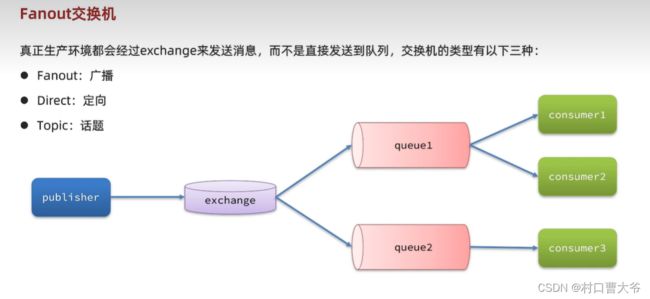
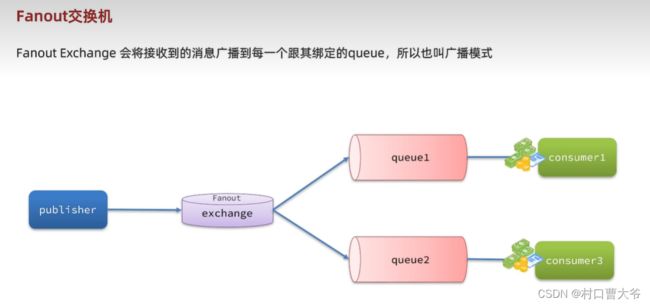
Fanout交换机
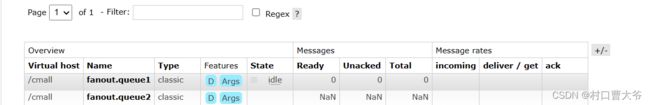
第一步:创建队列
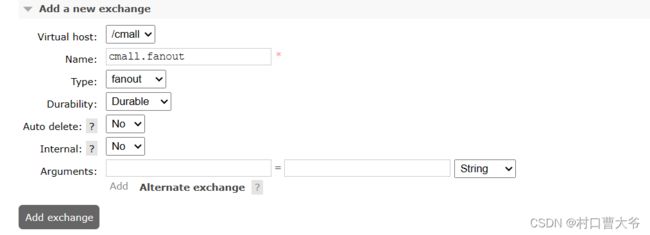
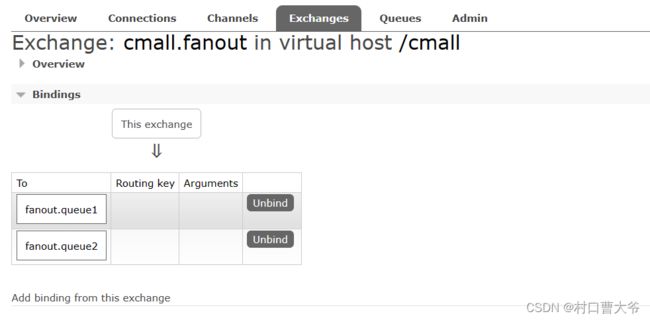
第二步:创建交换机并绑定
第三步:编写代码
发送端:
public void testFanout() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring everyone";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,null,message);
}接收端:
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
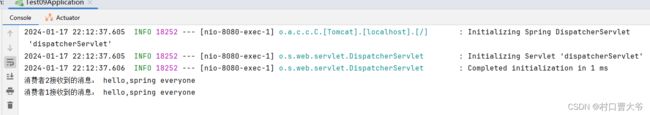
public void receiveMessage3(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void receiveMessage4(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}展示结果:
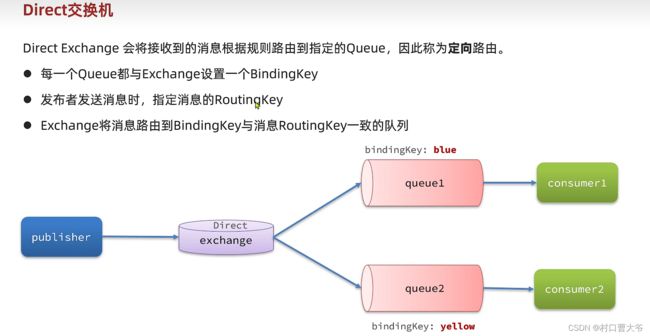
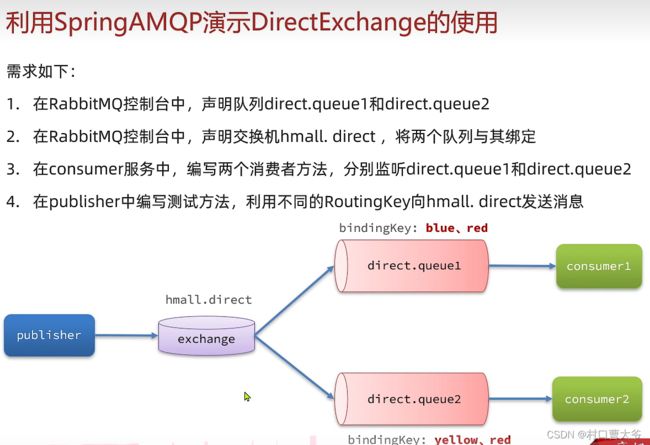
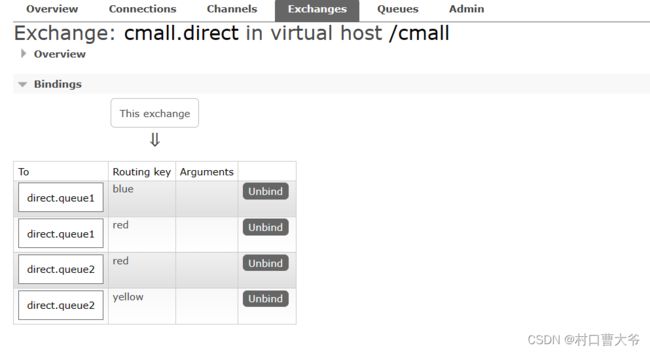
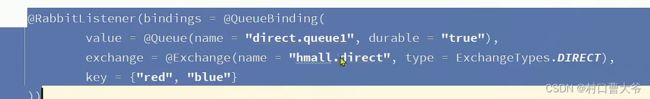
私发给不同的人:Direct交换机
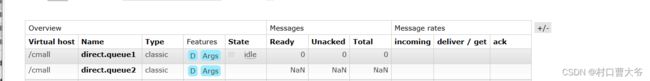
第一步:创建两个队列
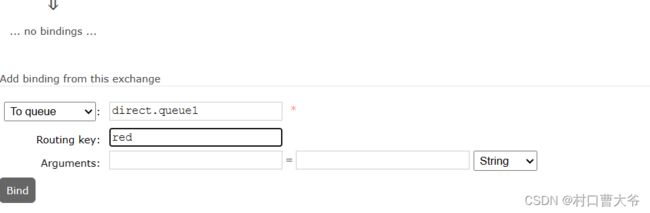
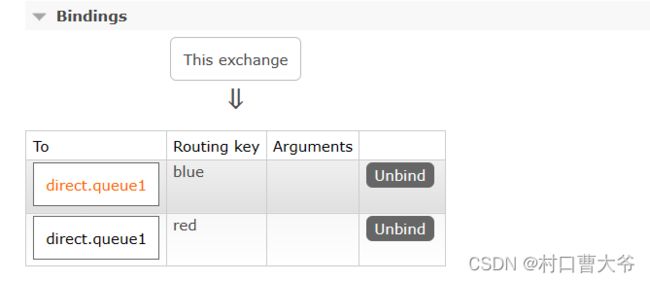
第二步:声明交换机并绑定
第三步:编写代码
接收方:
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void receiveMessage5(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void receiveMessage6(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}发送方:
public void testDirect1() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring everyone";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"red",message);
}
public void testDirect2() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring blue";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"blue",message);
}
public void testDirect3() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring yellow";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"yellow",message);
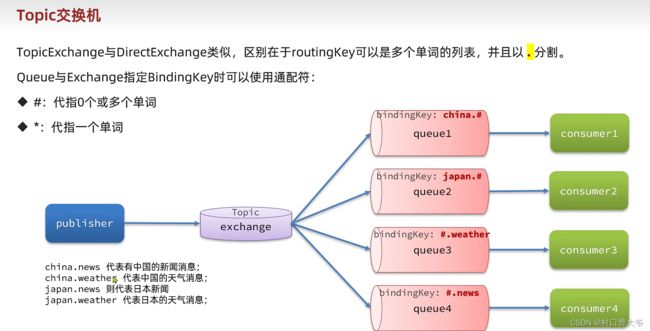
}Topic交换机
这个示例代码就懒得写了。
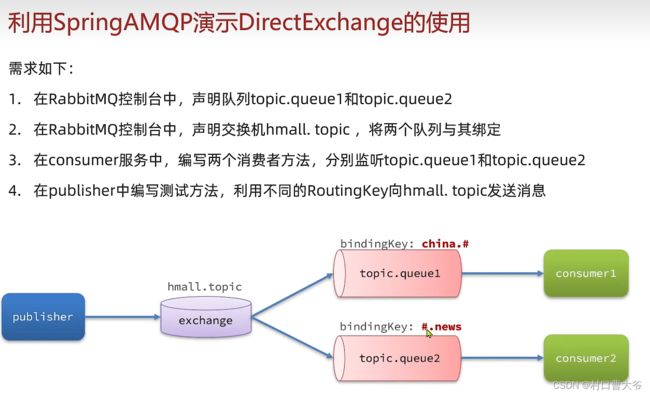
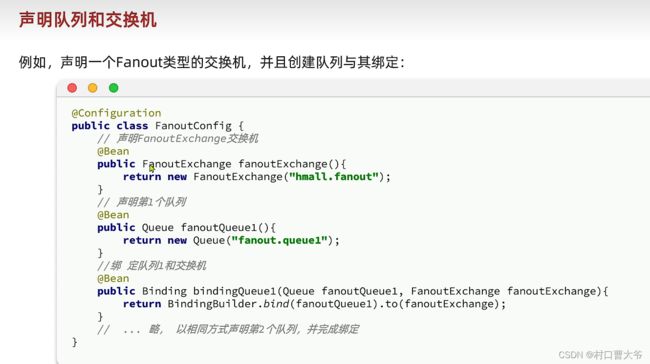
声明交换机和队列1
绑定队列到哪个交换机里面。
一般建立关系都是在消费者这边的。
声明交换机和队列2
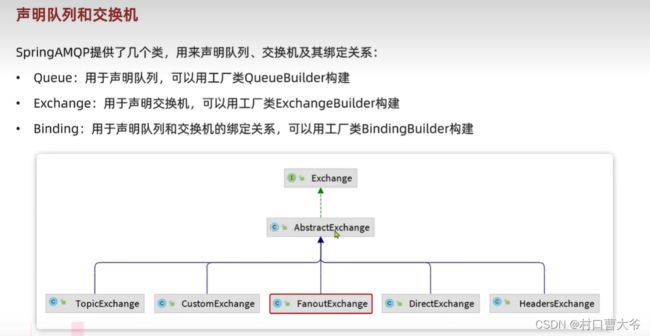
基于注解式声明队列和交换机。
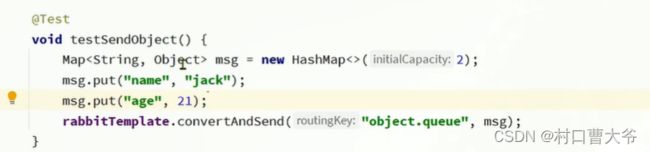
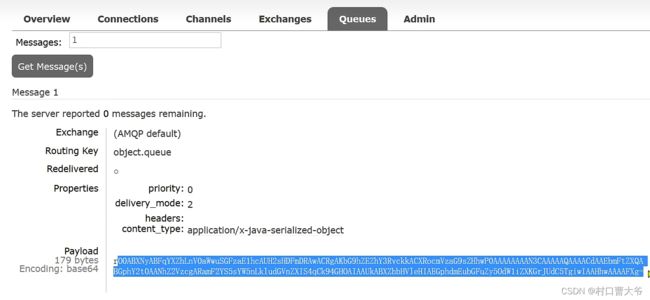
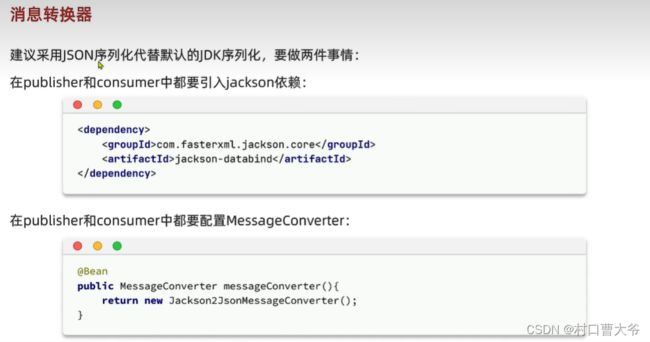
消息转换器
字节码可变,会有安全问题。
搞完以上东西,代码不用变,在发一次,即可为json。
好了,基础讲完。