Android CarService源码分析
文章目录
- 一、CarService的基本架构
-
- 1.1、Android Automative整体框架
- 1.2、Framework CarService
- 1.3、目录结构
-
- 1.3.1、CarService
- 1.3.2、Car APP
- 二、CarService的启动流程
-
- 2.1、系统启动后在SystemServer进程中启动CarServiceHelperService
- 2.2、CarService启动
- 三、CarService源码分析
-
- 3.1、CarService框架源码分析
- 3.2、CarAudioService源码分析
-
- 3.2.1、构造函数
- 3.2.2、setupDynamicRouting
- 3.2.3、AudioManager::registerAudioPolicy
- 3.2.4、AudioService::registerAudioPolicy
-
- 3.2.4.1、流程图
- 3.2.4.2、AudioService::registerAudioPolicy代码
- 3.2.4.3、AudioPolicyProxy构造函数
- 3.2.4.4、AudioPolicyProxy::setExtVolumeController
- 3.2.5、CarAudioService::setupVolumeGroups
-
- 3.2.5.1、这里通过CarVolumeGroupsHelper类加载car_volume_groups.xml文件
- 3.2.5.2、packages/services/Car/service/res/xml/car_volume_groups.xml文件
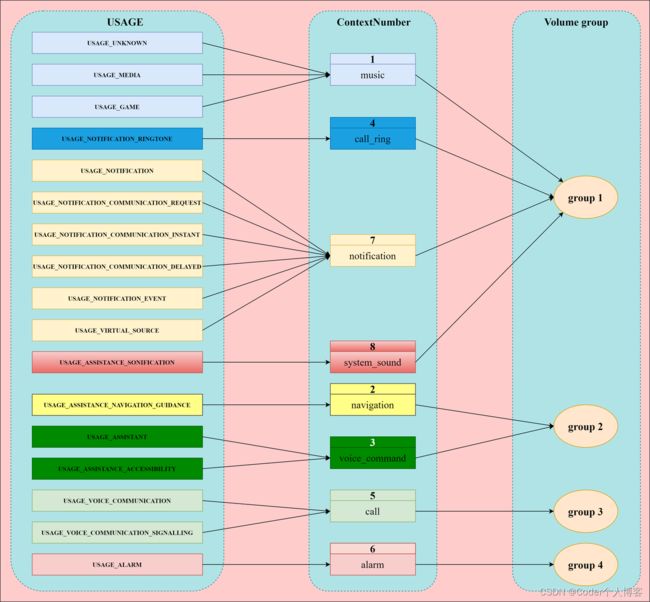
- 3.2.5.3、USAGE、ContextNumber和volumeGroups的关系
团队博客: 汽车电子社区
一、CarService的基本架构
1.1、Android Automative整体框架

从这幅图中我们可以看出,Android Automative是在原先Android的系统架构上增加了一些与车相关的(图中虚线框中绿色背景的)模块。
1. Car App:包括OEM和第三方开发的App
2. Car API:内有包含 CarSensorManager 在内的 API。位于 /platform/packages/services/Car/car-lib。
3. CarService:系统中与车相关的服务,位于 /platform/packages/services/Car/目录。
4. 车载 HAL:用于定义 OEM 可以实现的车辆属性的接口。包含属性元数据(例如,车辆属性是否为 int 以及允许使用哪些更改模式)。位于 hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/vehicle.h。如需了解基本参考实现,请参阅 hardware/libhardware/modules/vehicle/。
1.2、Framework CarService
Android O/P为Automotive场景提供了一系列的服务,这些服务统被称为CarService。它们与HAL层的VehicleHAL通信,进而通过车载总线(例如CAN总线)与车身进行通讯,同时它们还为应用层的APP提供接口,从而让APP能够实现对车身的控制与状态的显示。
 CarManage位于packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/hardware目录,
CarManage位于packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/hardware目录,
CarService位于packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car目录。
1.3、目录结构
1.3.1、CarService
├── Android.mk
├── apicheck.mk
├── apicheck_msg_current.txt
├── apicheck_msg_last.txt
├── car-cluster-logging-renderer //LoggingClusterRenderingService继承InstrumentClusterRenderingService
├── car-default-input-service //按键消息处理
├── car-lib //提供给汽车App特有的接口,许多定制的模块都在这里实现,包括Sensor,HVAC,Cabin,ActiveParkingAssiance,Diagnostic,Vendor等
├── car-maps-placeholder //地图软件相关
├── car_product //系统编译相关
├── car-support-lib //android.support.car
├── car-systemtest-lib //系统测试相关
├── car-usb-handler //开机自启,用于管理车机USB
├── CleanSpec.mk
├── evs
├── obd2-lib
├── PREUPLOAD.cfg
├── procfs-inspector
├── service //com.android.car是一个后台运行的组件,可以长时间运行并且不需要和用户去交互的,这里即使应用被销毁,它也可以正常工作
├── tests
├── tools //是一系列的工具,要提到的是里面的emulator,测试需要用到的。python写的,通过adb可以连接vehicleHal的工具,用于模拟测试
├── TrustAgent
└── vehicle-hal-support-lib
1.3.2、Car APP
Car APP的相关源码位于packages/apps/Car/目录,其中packages/services/Car/car_product/build/car.mk里面决定了需要编译哪些相关apk(system/priv-app)。
packages/services/Car/car_product/build/car.mk内容如下:
# Common make file for all car builds
PRODUCT_PUBLIC_SEPOLICY_DIRS += packages/services/Car/car_product/sepolicy/public
PRODUCT_PRIVATE_SEPOLICY_DIRS += packages/services/Car/car_product/sepolicy/private
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
Bluetooth \
CarActivityResolver \
CarDeveloperOptions \
CarSettingsIntelligence \
CarManagedProvisioning \
OneTimeInitializer \
CarProvision \
StatementService \
SystemUpdater
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
clatd \
pppd \
screenrecord
# This is for testing
ifneq (,$(filter userdebug eng, $(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT)))
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
DefaultStorageMonitoringCompanionApp \
EmbeddedKitchenSinkApp \
GarageModeTestApp \
ExperimentalCarService \
BugReportApp \
NetworkPreferenceApp \
SampleCustomInputService \
AdasLocationTestApp \
curl \
# SEPolicy for test apps / services
BOARD_SEPOLICY_DIRS += packages/services/Car/car_product/sepolicy/test
endif
# ClusterOsDouble is the testing app to test Cluster2 framework and it can handle Cluster VHAL
# and do some Cluster OS role.
ifeq ($(ENABLE_CLUSTER_OS_DOUBLE), true)
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += ClusterHomeSample ClusterOsDouble
else
# DirectRenderingCluster is the sample app for the old Cluster framework.
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += DirectRenderingCluster
endif # ENABLE_CLUSTER_OS_DOUBLE
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \
frameworks/av/media/libeffects/data/audio_effects.conf:system/etc/audio_effects.conf
PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \
persist.bluetooth.enablenewavrcp=false \
ro.carrier=unknown
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += \
config.disable_systemtextclassifier=true
###
### Suggested values for multi-user properties - can be overridden
###
# Enable headless system user mode
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += \
ro.fw.mu.headless_system_user?=true
# Enable user pre-creation
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += \
android.car.number_pre_created_users?=1 \
android.car.number_pre_created_guests?=1
# Enable User HAL integration
# NOTE: when set to true, VHAL must also implement the user-related properties,
# otherwise CarService will ignore it
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES += \
android.car.user_hal_enabled?=true
### end of multi-user properties ###
# Overlay for Google network and fused location providers
$(call inherit-product, device/sample/products/location_overlay.mk)
$(call inherit-product-if-exists, frameworks/webview/chromium/chromium.mk)
$(call inherit-product, packages/services/Car/car_product/build/car_base.mk)
# Overrides
PRODUCT_BRAND := generic
PRODUCT_DEVICE := generic
PRODUCT_NAME := generic_car_no_telephony
PRODUCT_IS_AUTOMOTIVE := true
PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES := \
ro.config.ringtone=Girtab.ogg \
ro.config.notification_sound=Tethys.ogg \
ro.config.alarm_alert=Oxygen.ogg \
$(PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES) \
PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \
keyguard.no_require_sim=true
# TODO(b/205189147): Remove the following change after the proper fix is landed.
# Uses the local KeyGuard animation to resolve TaskView misalignment issue after display-on.
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES += \
persist.wm.enable_remote_keyguard_animation=0
# Automotive specific packages
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
CarFrameworkPackageStubs \
CarService \
CarShell \
CarDialerApp \
CarRadioApp \
OverviewApp \
CarSystemUI \
LocalMediaPlayer \
CarMediaApp \
CarMessengerApp \
CarHTMLViewer \
CarMapsPlaceholder \
CarLatinIME \
CarSettings \
CarUsbHandler \
android.car \
car-frameworks-service \
com.android.car.procfsinspector \
libcar-framework-service-jni \
ScriptExecutor \
# RROs
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
CarPermissionControllerRRO \
# System Server components
# Order is important: if X depends on Y, then Y should precede X on the list.
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_SERVER_JARS += car-frameworks-service
# TODO: make the order optimal by appending 'car-frameworks-service' at the end
# after its dependency 'services'. Currently the order is violated because this
# makefile is included before AOSP makefile.
PRODUCT_BROKEN_SUBOPTIMAL_ORDER_OF_SYSTEM_SERVER_JARS := true
# Boot animation
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += \
packages/services/Car/car_product/bootanimations/bootanimation-832.zip:system/media/bootanimation.zip
PRODUCT_LOCALES := \
en_US \
af_ZA \
am_ET \
ar_EG ar_XB \
as_IN \
az_AZ \
be_BY \
bg_BG \
bn_BD \
bs_BA \
ca_ES \
cs_CZ \
da_DK \
de_DE \
el_GR \
en_AU en_CA en_GB en_IN en_XA \
es_ES es_US \
et_EE \
eu_ES \
fa_IR \
fi_FI \
fil_PH \
fr_CA fr_FR \
gl_ES \
gu_IN \
hi_IN \
hr_HR \
hu_HU \
hy_AM \
id_ID \
is_IS \
it_IT \
iw_IL \
ja_JP \
ka_GE \
kk_KZ \
km_KH km_MH \
kn_IN \
ko_KR \
ky_KG \
lo_LA \
lv_LV \
lt_LT \
mk_MK \
ml_IN \
mn_MN \
mr_IN \
ms_MY \
my_MM \
ne_NP \
nl_NL \
no_NO \
or_IN \
pa_IN \
pl_PL \
pt_BR pt_PT \
ro_RO \
ru_RU \
si_LK \
sk_SK \
sl_SI \
sq_AL \
sr_RS \
sv_SE \
sw_TZ \
ta_IN \
te_IN \
th_TH \
tr_TR \
uk_UA \
ur_PK \
uz_UZ \
vi_VN \
zh_CN zh_HK zh_TW \
zu_ZA
PRODUCT_BOOT_JARS += \
android.car
PRODUCT_HIDDENAPI_STUBS := \
android.car-stubs-dex
PRODUCT_HIDDENAPI_STUBS_SYSTEM := \
android.car-system-stubs-dex
PRODUCT_HIDDENAPI_STUBS_TEST := \
android.car-test-stubs-dex
# Disable Prime Shader Cache in SurfaceFlinger to make it available faster
PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += \
service.sf.prime_shader_cache=0
二、CarService的启动流程
2.1、系统启动后在SystemServer进程中启动CarServiceHelperService
 1. 在Android系统之后,系统首先会启动一个名为Zygote的进程,而Zygote进程又会启动SystemServer进程,这里我们先来看SystemServer的main方法。
1. 在Android系统之后,系统首先会启动一个名为Zygote的进程,而Zygote进程又会启动SystemServer进程,这里我们先来看SystemServer的main方法。
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
public final class SystemServer implements Dumpable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run(){
...代码省略...
// Start services.
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices(t);//启动引导服务
startCoreServices(t);//启动核心服务
startOtherServices(t);//启动其他服务
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
...代码省略...
}
}
main方法里启动了run方法,而在run方法中会调用了startOtherServices() 方法。
2. startOtherServices和CarService相关的关键代码如下所示。
public final class SystemServer implements Dumpable {
private static final String CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.internal.car.CarServiceHelperService";
private PackageManager mPackageManager;
private void startOtherServices() {
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
...代码省略...
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
t.traceBegin("StartCarServiceHelperService");
//如果有车机服务,则开启车机帮助服务
final SystemService cshs = mSystemServiceManager
.startService(CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS);
if (cshs instanceof Dumpable) {
mDumper.addDumpable((Dumpable) cshs);
}
if (cshs instanceof DevicePolicySafetyChecker) {
dpms.setDevicePolicySafetyChecker((DevicePolicySafetyChecker) cshs);
}
t.traceEnd();
}
...代码省略...
}
}
}
3. SystemServiceManager的startService方法如下所示。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
public class SystemServiceManager {
//存储了SystemServiceManager负责启动的各种服务
private final ArrayList<SystemService> mServices = new ArrayList<SystemService>();
public SystemService startService(String className) {
final Class<SystemService> serviceClass = loadClassFromLoader(className,this.getClass().getClassLoader());
return startService(serviceClass);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
...代码省略...
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
}
...代码省略...
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
}
因为前面我们传入的参数为com.android.internal.car.CarServiceHelperService,所以这里startService方法首先会通过反射创建CarServiceHelperService对象实例,然后将其存储在类型ArrayList的mServices中,紧接着会调用CarServiceHelperService的onStart方法。
4. CarServiceHelperService的onStart方法如下所示。
frameworks/opt/car/services/src/com/android/internal/car/CarServiceHelperService.java
public class CarServiceHelperService extends SystemService
implements Dumpable, DevicePolicySafetyChecker {
@Override
public void onStart() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CAR_HELPER_START);
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_REBOOT);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SHUTDOWN);
mContext.registerReceiverForAllUsers(mShutdownEventReceiver, filter, null, null);
mCarWatchdogDaemonHelper.addOnConnectionChangeListener(mConnectionListener);
mCarWatchdogDaemonHelper.connect();
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setPackage("com.android.car");
intent.setAction(CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE);
//通过bindService绑定车机服务CarService
if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, mCarServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
mHandler, UserHandle.SYSTEM)) {
Slogf.wtf(TAG, "cannot start car service");
}
loadNativeLibrary();
}
void loadNativeLibrary() {
System.loadLibrary("car-framework-service-jni");
}
}
packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/com/android/car/internal/common/CommonConstants.java
public final class CommonConstants {
// CarService Constants
public static final String CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE = "android.car.ICar";
}
CarServiceHelperService的onStart方法首先创建一个Action为android.car.ICar,包名为com.android.car的Intent,然后通过bindService的方式启动该Intent对应的服务,而这个服务正是车机模块才有的CarService服务。
2.2、CarService启动
1、系统关于CarService服务的声明如下所示。
packages/services/Car/service/AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:androidprv="http://schemas.android.com/apk/prv/res/android"
package="com.android.car"
coreApp="true"
android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system">
<!--...代码省略...-->
<application android:label="@string/app_title"
android:directBootAware="true"
android:allowBackup="false"
android:persistent="true">
<service android:name=".CarService"
android:singleUser="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.car.ICar"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
<!--...代码省略...-->
</application>
</manifest>
结合这个配置文件我们可以知道CarServiceHelperService最终所启动的,就是CarService这个服务。
2、CarService的onCreate方法如下所示。
public class CarService extends Service {
private ICarImpl mICarImpl;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
...代码省略...
mICarImpl = new ICarImpl(this,
mVehicle,
SystemInterface.Builder.defaultSystemInterface(this).build(),
mVehicleInterfaceName);
mICarImpl.init();
linkToDeath(mVehicle, mVehicleDeathRecipient);
//将ICarImpl存储到系统服务管理者ServiceManager中
ServiceManager.addService("car_service", mICarImpl);
SystemProperties.set("boot.car_service_created", "1");
super.onCreate();
initTiming.traceEnd(); // "CarService.onCreate"
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// keep it alive.
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mICarImpl;
}
}
CarService的onCreate方法会创建一个关键对象ICarImpl的实例,并将该实例赋值给mICarImpl属性变量,然后会调用该对象的init方法,之后还会将mICarImpl存储到ServiceManager中。另外结合CarService的onBind方法我们可以知道,CarServiceHelperService通过bindService方式开启CarService,CarService会返回mICarImpl对象,通过该Binder对象使二者建立双向跨进程通信。
三、CarService源码分析
3.1、CarService框架源码分析
当服务启动之后, 首先调用其onCreate方法. CarService的onCreate方法实现如下:
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(CarLog.TAG_SERVICE, "Service onCreate");
//获取通知管理NotificationManager对象
mCanBusErrorNotifier = new CanBusErrorNotifier(this /* context */);
mVehicle = getVehicle();
if (mVehicle == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Vehicle HAL service is not available.");
}
try {
mVehicleInterfaceName = mVehicle.interfaceDescriptor();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to get Vehicle HAL interface descriptor", e);
}
Log.i(CarLog.TAG_SERVICE, "Connected to " + mVehicleInterfaceName);
mICarImpl = new ICarImpl(this,
mVehicle,
SystemInterface.Builder.defaultSystemInterface(this).build(),
mCanBusErrorNotifier,
mVehicleInterfaceName);
mICarImpl.init();
linkToDeath(mVehicle, mVehicleDeathRecipient);
ServiceManager.addService("car_service", mICarImpl);
//设置SystemProperty属性 carService已创建
SystemProperties.set("boot.car_service_created", "1");
super.onCreate();
}
主要做了两件事情:
1. 获取mVehicle 车辆相关的HIDL Binder远程对象。
2. 创建了mICarImpl对象, 并将其添加到ServiceManager管理的服务列表中.
这里的ICarImpl起着创建并管理各个服务的作用。在它的构造函数中,创建了各个服务的实例,并添加到服务列表中,源码如下:
packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/ICarImpl.java
public ICarImpl(Context serviceContext, IVehicle vehicle, SystemInterface systemInterface,
CanBusErrorNotifier errorNotifier, String vehicleInterfaceName) {
mContext = serviceContext;
mSystemInterface = systemInterface;
mHal = new VehicleHal(vehicle);
mVehicleInterfaceName = vehicleInterfaceName;
//创建各种重要的服务
mUserManagerHelper = new CarUserManagerHelper(serviceContext);
final Resources res = mContext.getResources();
final int maxRunningUsers = res.getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_multiuserMaxRunningUsers);
mCarUserService = new CarUserService(serviceContext, mUserManagerHelper,
ActivityManager.getService(), maxRunningUsers);
mSystemActivityMonitoringService = new SystemActivityMonitoringService(serviceContext);
mCarPowerManagementService = new CarPowerManagementService(mContext, mHal.getPowerHal(),
systemInterface, mUserManagerHelper);
mCarPropertyService = new CarPropertyService(serviceContext, mHal.getPropertyHal());
....
//将重要的服务缓存到 CarLocalServices
CarLocalServices.addService(CarPowerManagementService.class, mCarPowerManagementService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarUserService.class, mCarUserService);
CarLocalServices.addService(CarTrustedDeviceService.class, mCarTrustedDeviceService);
// 将创建的服务对象依次添加到一个list中保存起来
List<CarServiceBase> allServices = new ArrayList<>();
allServices.add(mFeatureController);
allServices.add(mCarUserService);
.....
}
这些创建的服务就是上文介绍的汽车服务.。
3.2、CarAudioService源码分析
3.2.1、构造函数
这里读取配置文件audioUseDynamicRouting确定是否使用动态Routing。
public CarAudioService(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mTelephonyManager = (TelephonyManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
mAudioManager = (AudioManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
mUseDynamicRouting = mContext.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.audioUseDynamicRouting);
}
3.2.2、setupDynamicRouting
当mUseDynamicRouting为true时,将调用setupDynamicRouting函数;该函数里会创建一个AudioPolicy ,并通过mAudioManager.registerAudioPolicy函数注册该AudioPolicy。
private void setupDynamicRouting() {
final IAudioControl audioControl = getAudioControl();
if (audioControl == null) {
return;
}
AudioPolicy audioPolicy = getDynamicAudioPolicy(audioControl);
int r = mAudioManager.registerAudioPolicy(audioPolicy);
if (r != AudioManager.SUCCESS) {
throw new RuntimeException("registerAudioPolicy failed " + r);
}
mAudioPolicy = audioPolicy;
}
3.2.3、AudioManager::registerAudioPolicy
public int registerAudioPolicy(@NonNull AudioPolicy policy) {
if (policy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal null AudioPolicy argument");
}
final IAudioService service = getService();
try {
String regId = service.registerAudioPolicy(policy.getConfig(), policy.cb(),
policy.hasFocusListener(), policy.isFocusPolicy(), policy.isVolumeController());
if (regId == null) {
return ERROR;
} else {
policy.setRegistration(regId);
}
// successful registration
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
return SUCCESS;
}
【1】policy.isVolumeController()
这里mVolCb 的值就是通过setAudioPolicyVolumeCallback函数设置进来的,因此这里的 mVolCb 就是CarAudioService的mAudioPolicyVolumeCallback
public boolean isVolumeController() { return mVolCb != null; }
public Builder setAudioPolicyVolumeCallback(@NonNull AudioPolicyVolumeCallback vc) {
if (vc == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid null volume callback");
}
mVolCb = vc;
return this;
}
【2】这里的policy.cb()为IAudioPolicyCallback ,(这个很重要,后续将会用到)
public IAudioPolicyCallback cb() { return mPolicyCb; }
private final IAudioPolicyCallback mPolicyCb = new IAudioPolicyCallback.Stub() {
public void notifyAudioFocusGrant(AudioFocusInfo afi, int requestResult) {
sendMsg(MSG_FOCUS_GRANT, afi, requestResult);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyAudioFocusGrant: pack=" + afi.getPackageName() + " client="
+ afi.getClientId() + "reqRes=" + requestResult);
}
}
public void notifyAudioFocusLoss(AudioFocusInfo afi, boolean wasNotified) {
sendMsg(MSG_FOCUS_LOSS, afi, wasNotified ? 1 : 0);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyAudioFocusLoss: pack=" + afi.getPackageName() + " client="
+ afi.getClientId() + "wasNotified=" + wasNotified);
}
}
public void notifyAudioFocusRequest(AudioFocusInfo afi, int requestResult) {
sendMsg(MSG_FOCUS_REQUEST, afi, requestResult);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyAudioFocusRequest: pack=" + afi.getPackageName() + " client="
+ afi.getClientId() + " gen=" + afi.getGen());
}
}
public void notifyAudioFocusAbandon(AudioFocusInfo afi) {
sendMsg(MSG_FOCUS_ABANDON, afi, 0 /* ignored */);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyAudioFocusAbandon: pack=" + afi.getPackageName() + " client="
+ afi.getClientId());
}
}
public void notifyMixStateUpdate(String regId, int state) {
for (AudioMix mix : mConfig.getMixes()) {
if (mix.getRegistration().equals(regId)) {
mix.mMixState = state;
sendMsg(MSG_MIX_STATE_UPDATE, mix, 0/*ignored*/);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyMixStateUpdate: regId=" + regId + " state=" + state);
}
}
}
}
public void notifyVolumeAdjust(int adjustment) {
sendMsg(MSG_VOL_ADJUST, null /* ignored */, adjustment);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "notifyVolumeAdjust: " + adjustment);
}
}
};
3.2.4、AudioService::registerAudioPolicy
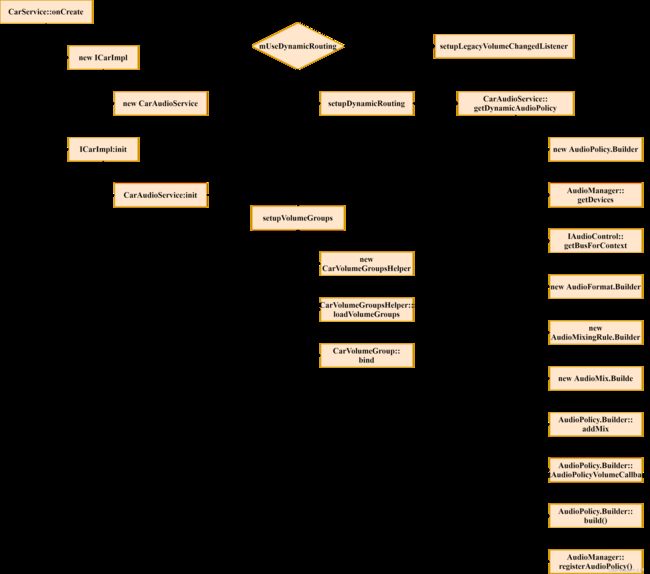
3.2.4.1、流程图
3.2.4.2、AudioService::registerAudioPolicy代码
AudioPolicyProxy app = new AudioPolicyProxy(policyConfig, pcb, hasFocusListener, isFocusPolicy, isVolumeController);
这里实例化了AudioPolicyProxy,并将registerAudioPolicy参数作为AudioPolicyProxy构造函数的参数。如上所述,isVolumeController的值就是policy.isVolumeController(),因此为true。
public String registerAudioPolicy(AudioPolicyConfig policyConfig, IAudioPolicyCallback pcb,
boolean hasFocusListener, boolean isFocusPolicy, boolean isVolumeController) {
AudioSystem.setDynamicPolicyCallback(mDynPolicyCallback);
String regId = null;
// error handling
boolean hasPermissionForPolicy =
(PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED == mContext.checkCallingPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING));
if (!hasPermissionForPolicy) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Can't register audio policy for pid " + Binder.getCallingPid() + " / uid "
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + ", need MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING");
return null;
}
mDynPolicyLogger.log((new AudioEventLogger.StringEvent("registerAudioPolicy for "
+ pcb.asBinder() + " with config:" + policyConfig)).printLog(TAG));
synchronized (mAudioPolicies) {
try {
if (mAudioPolicies.containsKey(pcb.asBinder())) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Cannot re-register policy");
return null;
}
AudioPolicyProxy app = new AudioPolicyProxy(policyConfig, pcb, hasFocusListener,
isFocusPolicy, isVolumeController);
pcb.asBinder().linkToDeath(app, 0/*flags*/);
regId = app.getRegistrationId();
mAudioPolicies.put(pcb.asBinder(), app);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// audio policy owner has already died!
Slog.w(TAG, "Audio policy registration failed, could not link to " + pcb +
" binder death", e);
return null;
}
}
return regId;
}
3.2.4.3、AudioPolicyProxy构造函数
AudioPolicyProxy(AudioPolicyConfig config, IAudioPolicyCallback token,
boolean hasFocusListener, boolean isFocusPolicy, boolean isVolumeController) {
super(config);
setRegistration(new String(config.hashCode() + ":ap:" + mAudioPolicyCounter++));
mPolicyCallback = token;
mHasFocusListener = hasFocusListener;
mIsVolumeController = isVolumeController;
if (mHasFocusListener) {
mMediaFocusControl.addFocusFollower(mPolicyCallback);
// can only ever be true if there is a focus listener
if (isFocusPolicy) {
mIsFocusPolicy = true;
mMediaFocusControl.setFocusPolicy(mPolicyCallback);
}
}
if (mIsVolumeController) {
setExtVolumeController(mPolicyCallback);
}
connectMixes();
}
3.2.4.4、AudioPolicyProxy::setExtVolumeController
这里设置mExtVolumeController 的值为类AudioPolicy中的IAudioPolicyCallback mPolicyCb。
private void setExtVolumeController(IAudioPolicyCallback apc) {
if (!mContext.getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_handleVolumeKeysInWindowManager)) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot set external volume controller: device not set for volume keys" +
" handled in PhoneWindowManager");
return;
}
synchronized (mExtVolumeControllerLock) {
if (mExtVolumeController != null && !mExtVolumeController.asBinder().pingBinder()) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot set external volume controller: existing controller");
}
mExtVolumeController = apc;
}
}
3.2.5、CarAudioService::setupVolumeGroups
3.2.5.1、这里通过CarVolumeGroupsHelper类加载car_volume_groups.xml文件
private void setupVolumeGroups() {
Preconditions.checkArgument(mCarAudioDeviceInfos.size() > 0,
"No bus device is configured to setup volume groups");
final CarVolumeGroupsHelper helper = new CarVolumeGroupsHelper(
mContext, R.xml.car_volume_groups);
mCarVolumeGroups = helper.loadVolumeGroups();
for (CarVolumeGroup group : mCarVolumeGroups) {
for (int contextNumber : group.getContexts()) {
int busNumber = mContextToBus.get(contextNumber);
group.bind(contextNumber, busNumber, mCarAudioDeviceInfos.get(busNumber));
}
// Now that we have all our contexts, ensure the HAL gets our intial value
group.setCurrentGainIndex(group.getCurrentGainIndex());
Log.v(CarLog.TAG_AUDIO, "Processed volume group: " + group);
}
// Perform validation after all volume groups are processed
if (!validateVolumeGroups()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid volume groups configuration");
}
}
3.2.5.2、packages/services/Car/service/res/xml/car_volume_groups.xml文件
<volumeGroups xmlns:car="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<group>
<context car:context="music"/>
<context car:context="call_ring"/>
<context car:context="notification"/>
<context car:context="system_sound"/>
</group>
<group>
<context car:context="navigation"/>
<context car:context="voice_command"/>
</group>
<group>
<context car:context="call"/>
</group>
<group>
<context car:context="alarm"/>
</group>
</volumeGroups>