2024.1.5 IO进程线程 作业
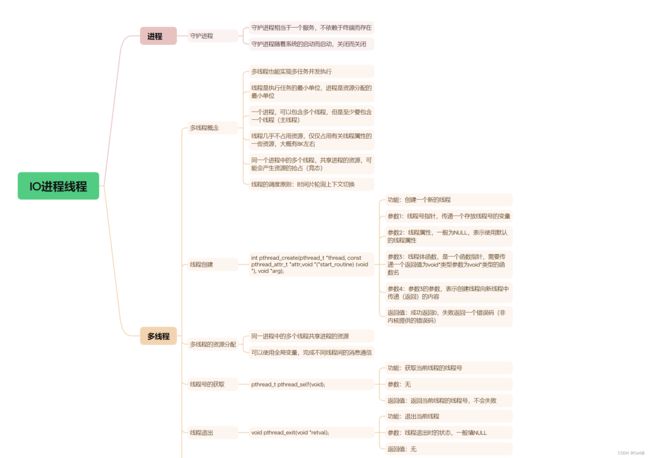
思维导图
 练习题
练习题
1>将互斥机制代码实现
#include
//全局临界资源buf
char buf[1024];
//创建互斥锁,控制线程,避免多个线程同时访问临界资源
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//分支线程
void *task(void *arg)
{
while (1)
{
//获取锁资源
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("分支线程:%s\n",buf);
strcpy(buf,"hello world\n");
//释放锁资源
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//定义线程变量
pthread_t tid;
//互斥锁初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//创建线程
if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("error");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("主线程:%s\n",buf);
strcpy(buf,"nihao shijie\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
//释放线程资源
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
//销毁互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
2>将同步机制代码实现
#include
//创建无名信号量
sem_t sem;
//分支线程1
void *task1(void *arg)
{
while (1)
{
sleep(2);
printf("生产\n");
//释放资源
sem_post(&sem);
}
}
//分支线程2
void *task2(void *arg)
{
while (1)
{
//申请资源,如果资源为0,则等待
sem_wait(&sem);
printf("消费\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//定义线程变量
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化无名信号量
//第2个参数0表示线程之间的通信
//第3个参数表示初始资源value为0
sem_init(&sem, 0, 0);
//创建线程1、2
if (pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("create tid1 error");
return -1;
}
if (pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("create tid2 error");
return -1;
}
//主线程回收资源
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
//销毁无名信号量
sem_destroy(&sem);
return 0;
}

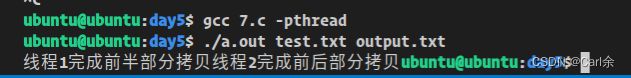
3>使用三个线程完成两个文件的拷贝,线程1完成拷贝前一半,线程2完成拷贝后一半,主线程回收两个分支线程的资源
#include
//创建无名信号量
sem_t sem;
//创建文件相关结构体
typedef struct File
{
const char *src_file;
const char *dest_file;
off_t start;
off_t end;
} * fileStruct;
//获取文件字符长度
int length(const char *srcfile, const char *destfile)
{
//打开原文件和目标文件
int srcfd = open(srcfile, O_RDONLY);
int destfd = open(destfile, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);
if (srcfd == -1 || destfd == -1)
{
perror("open file error");
return -1;
}
//光标从头到尾,返回字符个数
int len = lseek(srcfd, 0, SEEK_END);
//关闭文件
close(srcfd);
close(destfd);
return len;
}
//文件拷贝函数
int copy_file(const char *srcfile, const char *destfile, int start, int end)
{
int srctd, desttd;
//打开原文件和目标文件
int srcfd = open(srcfile, O_RDONLY);
//在计算字符长度函数中已经创建过文件,所以只需要写
int destfd = open(destfile, O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC);
if (srcfd == -1 || destfd == -1)
{
perror("open file error");
return -1;
}
//重新定位光标到文件开头
lseek(srcfd, start, SEEK_SET);
lseek(destfd, start, SEEK_SET);
//搬运工
char buffer[1] = "";
int res_read = 0;
int res_write = 0;
//拷贝字符到创建的文件中去
//当前光标位置在目标光标位置前,则写入
while (start < end)
{
res_read = read(srcfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (res_read <= 0)
break;
res_write = write(destfd, buffer, res_read);
start += res_write;
}
//关闭文件
close(srcfd);
close(destfd);
}
void *task1(void *arg)
{
fileStruct fStruct = (fileStruct)arg;
copy_file(fStruct->src_file, fStruct->dest_file, fStruct->start, fStruct->end);
// 完成前一半拷贝,释放资源
sem_post(&sem);
free(fStruct); // 释放传入的结构体内存
printf("线程1完成前半部分拷贝");
}
void *task2(void *arg)
{
//等待线程tid1写入前一半,然后申请
sem_wait(&sem);
fileStruct fStruct=(fileStruct)arg;
copy_file(fStruct->src_file,fStruct->dest_file,fStruct->start,fStruct->end);
free(fStruct);
printf("线程2完成前后部分拷贝");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//定义两个线程
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化无名信号量,要在创建线程前初始化
sem_init(&sem, 0, 0);
//获取返回的字符长度
int len = length(argv[1], argv[2]);
//创建结构体变量,并赋值
fileStruct arg1 = (fileStruct)malloc(sizeof(struct File));
fileStruct arg2 = (fileStruct)malloc(sizeof(struct File));
arg1->src_file = argv[1];
arg1->dest_file = argv[2];
arg1->start = 0;
arg1->end = len / 2;
arg2->src_file = argv[1];
arg2->dest_file = argv[2];
arg2->start = len / 2;
arg2->end = len;
if (pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, arg1) != 0)
{
printf("create pthread1 error\n");
return -1;
}
if (pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, arg2) != 0)
{
printf("create pthread2 error\n");
return -1;
}
//线程资源回收
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
//销毁无名信号量
sem_destroy(&sem);
return 0;
}
4>使用三个线程完成:线程1输出字符A线程2输出字符B线程3输出字符C要求输出结果为:ABCABCABCABCABC...
#include
//创建互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//定义计数器 0=A 1=B 2=C
int count = 0;
void *task1(void *arg) {
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (count % 3 == 0) {
printf("A");
count++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void *task2(void *arg) {
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (count % 3 == 1) {
printf("B");
count++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void *task3(void *arg) {
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if (count % 3 == 2) {
printf("C");
count++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
usleep(1000);// 添加一些延迟
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//定义线程变量
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
//创建线程1、2、3
if (pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("create tid1 error");
return -1;
}
if (pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("create tid2 error");
return -1;
}
if (pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, task3, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("create tid2 error");
return -1;
}
//主线程回收资源
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
//销毁互斥锁
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}