【OJ】链表刷题
个人主页 : zxctsclrjjjcph
文章封面来自:艺术家–贤海林
如有转载请先通知
题目
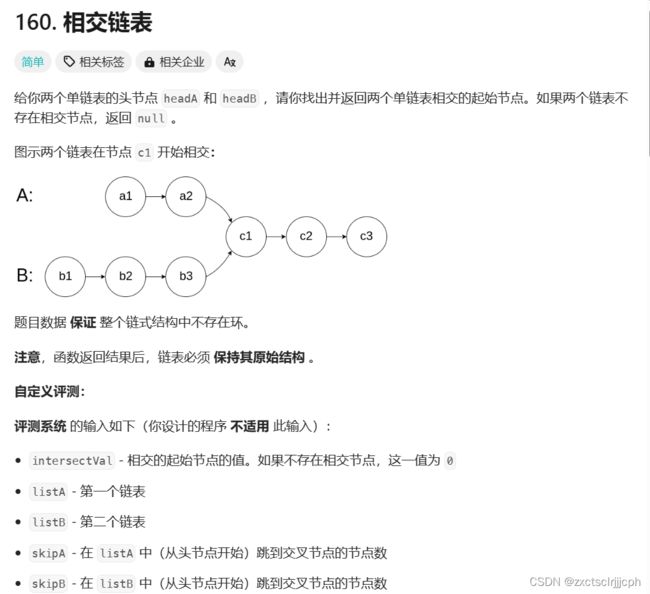
- 1. 相交链表(160)
-
- 1.1 暴力求解
-
- 1.1.1 分析
- 1.1.2 代码实现
- 1.2 优化后求解
-
- 1.2.1 分析
- 1.2.2 代码实现
- 2. 随机链表的复制(138)
-
- 2.1 分析
- 2.2 代码实现
1. 相交链表(160)
1.1 暴力求解
1.1.1 分析
题目中描述既要判断是否相交,还要找交点。
把A链表中的所有节点依次在B中找一边。
为了防止在遍历链表时头节点丢失,先记录一下AB头节点:
struct ListNode* begin1 = headA;
struct ListNode* begin2 = headB;
先取A的节点,在B链表中遍历一遍,判断B中节点与A是否相交,如果相交,直接返回A的节点,如果不相交,B节点继续往后走。

当A的第一个节点在B中没有找到相交时,A节点就往后走,继续像第一个节点判断方式一样。不过这里得注意一下,再次访问B链表时候,B的走的节点又得从头节点开始begin2 = headB。
当A链表中所有节点都访问完了后,B都没有与之相交的,就返回NULL。
1.1.2 代码实现
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB) {
struct ListNode* begin1 = headA;
struct ListNode* begin2 = headB;
while (begin1)
{
begin2 = headB;
while (begin2)
{
if (begin1 == begin2)
return begin1;
begin2 = begin2->next;
}
begin1 = begin1->next;
}
return NULL;
}
1.2 优化后求解
暴力求解虽然简单,但是时间复杂度太高为O(n^2),优化一下代码,使得时间复杂度到O(n)。
1.2.1 分析
可以先判断是否相交,如果A和B两个链表的尾节点的地址都相同,那么就A和B两个链表相交。如果如果A和B两个链表的尾节点的地址不相同,那么就A和B两个链表不相交。
如果相交那么交点怎么求呢?
先求出A和B两个链表的长度,
while(begin1->next)
{
lenA++;
begin1=begin1->next;
}
while(begin2->next)
{
lenB++;
begin2=begin2->next;
}
让长的链表先走两个链表相查的节点数,
while(n--)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
}
两个链表再同时走,第一个相同的就是交点。
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
1.2.2 代码实现
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode *begin1=headA;
struct ListNode *begin2=headB;
int lenA=1;
int lenB=1;
while(begin1->next)
{
lenA++;
begin1=begin1->next;
}
while(begin2->next)
{
lenB++;
begin2=begin2->next;
}
if(begin1!=begin2)
{
return NULL;
}
int n=abs(lenA-lenB);
struct ListNode *longlist=headA;
struct ListNode *shortlist=headB;
if(lenA<lenB)
{
longlist=headB;
shortlist=headA;
}
while(n--)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
}
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}
2. 随机链表的复制(138)
2.1 分析
这里链表里面包含单链表和随机指针,而随机指针指向链表任意节点或者为空。
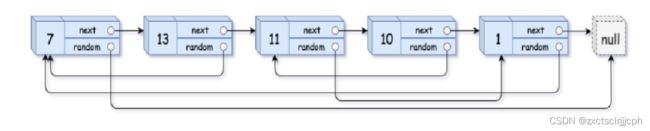
对于节点的拷贝就是申请节点放原节点值任何尾插就行,复制链表倒是容易的。这里主要就是考虑随机指针怎么处理。
如果记录值让随机指针指向,可能会有多个相同的值。所以这里可以记录这个random出现的位置,看看是第几个用i记录,这样就不会出现多个随机指针指向同一个节点。如果每次复制节点都要找第i个,每个找random都是N,那么时间复杂度就是O(N^2)。时间复杂度太高了,优化一下。

第一步:可以把拷贝的节点都放在原节点的后面,也就是这样:
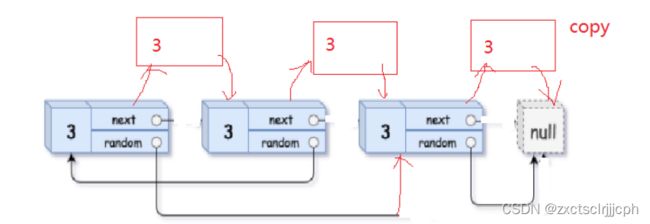
这样能方便找到原节点与random的关系。
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=copy->next;
}

第二步:处理copy节点的random。
再从头开始走第二遍,copy节点每次都等于cur节点的next。
如果cur的random为空,copy节点的random也为空。
如果不是空,copy的random就是cur的random的next。
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=copy->next;
}

第三步:copy节点解下来尾插
出现申请一个新头节点,任何将copy节点一个一个取下来尾插,最后返回新的头节点。
struct Node* newhead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
struct Node* next=copy->next;
if(tail==NULL)
{
newhead=tail=copy;
}
else
{
tail->next=copy;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur->next=next;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
2.2 代码实现
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=copy->next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=copy->next;
}
struct Node* newhead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
struct Node* next=copy->next;
if(tail==NULL)
{
newhead=tail=copy;
}
else
{
tail->next=copy;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur->next=next;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
}