408数据结构知识点——第三章 栈、队列和数组(一)
文章目录
-
-
- 栈
-
- 栈的定义
- 顺序栈的实现
- 共享栈
- 链栈的实现
- 队列
-
- 队列的定义
- 队列的顺序实现
- 队列的链式实现
- 双端队列
-
注:内容参考王道2024考研复习指导以及《数据结构》
栈
栈的定义
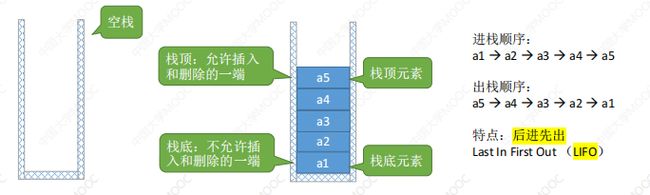
栈(Stack)是只允许在一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
逻辑结构与普通的线性表相同;插入、删除操作有区别。
名词:空栈、栈顶、栈顶元素、栈底、栈底元素
常考题型:
进栈顺序: a → b → c → d → e a \rightarrow b \rightarrow c \rightarrow d \rightarrow e a→b→c→d→e有哪些合法的出栈顺序?
n个不同元素进栈,出栈元素不同排列的个数为卡特兰(Catalan)数 1 n + 1 C 2 n n \frac{1}{n+1}C^n_{2n} n+11C2nn
顺序栈的实现
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct{//顺序栈的定义
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;//此处top指示真正的栈顶元素之上的下标地址
}SqStack;
//初始化栈
void InitStack(SqStack &S){
S.top=0;
}
//栈的判空操作
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S){
return (S.top==0);
}
//进栈操作
bool Push(SqStack &S,ElemType x){
if(top==MaxSize){
return false;
}
S.data[S.top++]=x;
return true;
}
//出栈操作
bool Pop(SqStack &S,ElemType &x){
if(top==0){
return false;
}
x=S.data[--S.top];
return true;
}
//取栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack &S,ElemType &x){
if(top==0){
return false;
}
x=S.data[S.top];//读取栈顶元素不需要指针下移
return true;
}
共享栈
两个栈共享同一片空间,栈满条件为 t o p 0 + 1 = t o p 1 top0+1=top1 top0+1=top1。
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct{//顺序栈的定义
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top0;
int top1;
}SqStack;
//初始化栈
void InitStack(SqStack &S){
S.top0=-1;
S.top1=MaxSize;
}
链栈的实现
typedef struct LinkNode{//链栈的定义
ElemType data;
struct LinkNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkStack;
//初始化操作(不带头结点)
void InitStack(LinkStack &S){
S=NULL;
}
//进栈操作
bool Push(LinkStack &S,ElemType x){
LNode *p=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (!p) {
return false; // 内存分配失败
}
p->data=x;
p->next=NULL;
if(S==NULL){
S=p;
return true;
}
p->next=S;
S=p;
return true;
}
//出栈操作
bool Pop(LinkStack &S,ElemType &x){
if(S==NULL){
return false;
}
LNode *p=S;
x=p->data;
S=p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//取栈顶元素
bool GetTop(LinkStack &S,ElemType &x){
if(S==NULL){
return false;
}
x=S->data;
return true;
}
队列
队列的定义
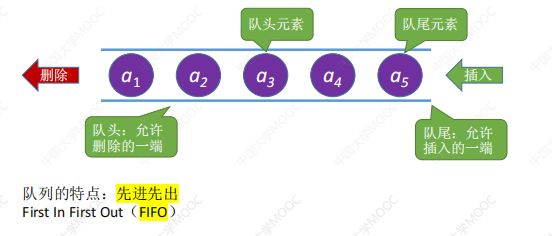
队列(Queue)是只允许在一端进行插入,在另一端删除操作的线性表。
名词:队头、队头元素、队尾、队尾元素、空队列
队列的顺序实现
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
//初始化操作
void InitQueue(SqQueuq &Q){
Q.front=Q.rear;
}
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q){
return (Q.front==Q.rear);
}
//入队操作
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q,ElemType x){
if((Q.rear+1)%MaxSize==Q.front){
return false;
}
Q.data[Q.rear]=x;
Q.rear=(Q.rear+1)%MaxSize;//循环队列处理方式
return true;
}
//出队操作
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q,ElemType &x){
if(Q.front==Q.rear){
return false;
}
x=Q.data[Q.front];
Q.front=(Q.front+1)%MaxSize;
return true;
}
bool GetHead(SqQueue Q,ElemType &x){
if(Q.front==Q.rear){
return false;
}
x=Q.data[Q.front];
return true;
}
判断队列已满/已空的方案(循环队列):
- 舍弃一个存储空间,如上图代码中所示进行判断,此时队列元素个数 = ( r e a r + M a x S i z e − f r o n t ) % M a x S i z e =(rear+MaxSize-front) \% MaxSize =(rear+MaxSize−front)%MaxSize。
- 在定义队列结构时,加入一个size指标,记录队列长度,队满条件为 s i z e = = M a x S i z e size==MaxSize size==MaxSize,此时队列元素个数 = s i z e =size =size。
- 在定义队列结构时,加入一个tag指标(每次删除成功,tag=0;每次插入成功,tag=1),此时队满条件为 f r o n t = = r e a r & & t a g = 1 front==rear\&\& tag=1 front==rear&&tag=1。
其他出题方式:
改变队头和队尾指针的指向,面对不同的指向,如何判空和判满,此时如何计算队列中元素的个数。
队列的链式实现
typedef struct LinkNode{//链队列的定义
ElemType data;
struct LinkNode *next;
}LNode;
typedef struct {
LNode *front;
LNode *rear;
}LinkQueue;
//初始化操作(带头结点)
void InitStack(LinkQueue &Q){
Q.front=Q.rear=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
q.font->next=NULL;
}
bool QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q){
return (Q,.front==Q.rear);
}
//入队
void EnQueue(LinkQueue %Q,ELemType x){
LNode *p=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
p->data=x;
p->next=NULL;
Q.rear->next=p;
Q.rear=p;
}
//出队
void DeQueue(LinkQueue %Q,ELemType &x){
if(Q.front==Q.rear){
return false;
}
LNode *p=Q.ftont->next;
x=p->data;
Q.front->next=p->next;
if(Q.rear==p){
Q.rear=Q.front;
}
free(p);
return true;
}
双端队列
只允许从两端插入、两端删除的线性表。
若只使用其中一端的插入、删除操作,则效果等同于栈。
受限的双端队列:
考点:判断输出序列的合法性(注:在栈中合法的输出序列,在端队列中必定合法)。