最新百度 阿里 华为 腾讯 谷歌面试笔试题及解析
原文地址:http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/panfengyun12345/12618453
-
- 8月15日,百度2道面试题:
1、来自《编程之美》的概率题:一个桶里面有白球、黑球各100个,现在按下述规则取球:的
i 、每次从通里面拿出来两个球;
ii、如果取出的是两个同色的求,就再放入一个黑球;
ii、如果取出的是两个异色的求,就再放入一个白球。
问:最后桶里面只剩下一个黑球的概率是多少?
2、算法题:给你一个自然数N,求[6,N]之内的所有素数中,两两之和为偶数的那些偶数。 - 9月5日,华为2014校园招聘的机试题目
通过键盘输入一串小写字母(a~z)组成的字符串。请编写一个字符串压缩程序,将字符串中连续出席的重复字母进行压缩,并输出压缩后的字符串。
压缩规则:
1、仅压缩连续重复出现的字符。比如字符串"abcbc"由于无连续重复字符,压缩后的字符串还是"abcbc"。
2、压缩字段的格式为"字符重复的次数+字符"。例如:字符串"xxxyyyyyyz"压缩后就成为"3x6yz"。
要求实现函数:
void stringZip(const char *pInputStr, long lInputLen, char *pOutputStr);
输入pInputStr: 输入字符串lInputLen: 输入字符串长度
输出 pOutputStr: 输出字符串,空间已经开辟好,与输入字符串等长;
注意:只需要完成该函数功能算法,中间不需要有任何IO的输入输出
示例
输入:“cccddecc” 输出:“3c2de2c”
输入:“adef” 输出:“adef”
输入:“pppppppp” 输出:“8p” - 9月6日,网新恒天2014校园招聘笔试编程题
已知memcpy的函数为: void* memcpy(void *dest , const void* src , size_t count)其中dest是目的指针,src是源指针。不调用c++/c的memcpy库函数,请编写memcpy。
点评:老题,参考答案如下-
//copyright@July 2013/9/24 void* memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t count) { //安全检查 assert( (dst != NULL) && (src != NULL) ); unsigned char *pdst = (unsigned char *)dst; const unsigned char *psrc = (const unsigned char *)src; //防止内存重复 assert(!(psrc<=pdst && pdst<psrc+count)); assert(!(pdst<=psrc && psrc<pdst+count)); while(count--) { *pdst = *psrc; pdst++; psrc++; } return dst; }
-
- 9月9日,迅雷2014校招笔试编程题:
已知集合A和B的元素分别用不含头结点的单链表存储,函数difference()用于求解集合A与B的差集,并将结果保存在集合A的单链表中。例如,若 集合A={5,10,20,15,25,30},集合B={5,15,35,25},完成计算后A={10,20,30}。
链表结点的结构类型定义如下:
请完成函数void difference(node** LA , node* LB)-
struct node { int elem; node* next; };
点评:参考答案或更多题目请参见:http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/11482103。 -
- 9月10日,美团网2014校招研发笔试哈尔滨站
1、链表翻转。给出一个链表和一个数k,比如链表1→2→3→4→5→6,k=2,则翻转后2→1→4→3→6→5,若k=3,翻转后3→2→1→6→5→4,若k=4,翻转后4→3→2→1→5→6,用程序实现
点评:类似编程艺术第1章左旋转字符串,见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6322882。
2、一个m*n的矩阵,从左到右从上到下都是递增的,给一个数elem,求是否在矩阵中,给出思路和代码
点评:杨氏矩阵查找,见编程艺术第23章:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7085669。 - 9月14日,阿里巴巴2014校招笔试哈尔滨站
1、宿舍内5个同学一起玩对战游戏。每场比赛有一些人作为红方,另一些人作为蓝方。请问至少需要多少场比赛,才能使任意两个人之间有一场红方对蓝方和蓝方对红方的比赛?答案为4场,参考如下图,作者doc_sgl: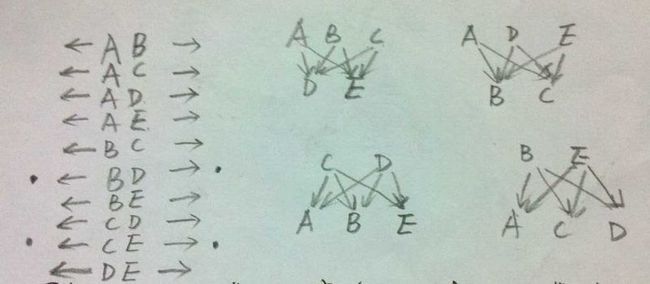
点评:其余题目请参见:http://blog.csdn.net/doc_sgl/article/details/11695671。
2、一个有10亿条记录的文本文件,已按照关键字排好序存储。请设计算法,可以快速的从文件中查找指字关键字的记录。 - 9月14日,阿里巴巴-系统工程师-北京站

- 9月16日,创新工场2014校招笔试题

点评:上面第3题还是杨氏矩阵查找,见编程艺术第23章:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7085669。既然这么多公司都喜欢考杨氏矩阵查找,那么再给出杨氏矩阵查找一题的扩展:给定 n×n 的实数矩阵,每行和每列都是递增的,求这 n^2 个数的中位数,分析详见:http://zhiqiang.org/blog/science/computer-science/median-algorithm-of-ordered-matrix.html。 - 9月21日,百度2014校招-济南站

- 9月21日,腾讯2014软件开发校招-简答题-广州

点评:这里有一关于上面2题的题解:http://blog.csdn.net/thebestdavid/article/details/12056293,可以参考。 - 9月22日,人人校招笔试题

点评:上述第1题寻找满足条件的两个数,见编程艺术第5章:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6419466;上述第2题见编程艺术第21章:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6890054。 - 9月22日,阿里巴巴北邮站



点评:这里有一朋友关于上述3题的题解:http://blog.csdn.net/thebestdavid/article/details/11975809,大家可以参考。 - 9月23日,网易电商部-社招面试
HashMap与HashTable区别
点评:HashMap基于Hashtable实现,不同之处在于HashMap是非同步的,并且允许null,即null value和null key,Hashtable则不允许null,详见:http://oznyang.iteye.com/blog/30690。此外,记住一点:hashmap/hashset等凡是带有hash字眼的均基于hashtable实现,没带hash字眼的如set/map均是基于红黑树实现,前者无序,后者有序,详见此文第一部分:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7382693。 - 9月24日,去哪儿网2014校招西安站笔试题
给定一个200MB的文本文件,里面存的是IP地址到真实地址信息的映射信息,例如:211.200.101.100北京
然后给你6亿个IP地址,请设计算法快速的打印出所对应的真实地址信息。 - 9月25日,阿里巴巴二面
指针/数组区别,决策树训练原理,SVM原理,网络协议,堆排序,字符串转换成整数,设计一款拼音输入法等等..
点评:字符串转换成整数看似简单,实则很多坑,要写好并不容易,具体分析和实现见编程艺术第30章:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/9024123;决策树见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7577684;SVM原理见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7624837。
总结:此次面试的这位同学面的还是堆排/快排/atoi等典型问题,实际上:①面试看基础算法编程能力,和准备是否充分;②不论结果如何,跟4年前高考一 样,高考和面试都只是人生路上的其中一站。你的真正核心竞争力不是进哪所名校哪所名企,而是存在你骨子里的上进心或热爱钻研技术的态度。 - 9月28日,微软2014校招笔试题最后一道

点评:上题形式上类似编程艺术第35章完美洗牌算法http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/10212493#t8,但因给定的是链表,所以相对来说,简单了不少;微软2014校招其它题目见:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoerlyl/article/details/12126807。 - 9月28日,百度2014校招-武汉站-系统分析师

- 10月2日,暴风影音2014校招笔试
1、合并两个已经排序的单链表为一个排序的单链表,相同内容只保留一个
如:单链表a:1->2->3->4
单链表b:3->4->5
输出:1->2->3->4->5
2、编写程序,在原字符串中把尾部m个字符移动到字符串的头部,要求:长度为n字符串操作时间复杂度为O(n),时间复杂度为O(1)。
如:原字符串为”Ilovebaofeng”,m=7,输出结果:”baofengIlove”。
点评:还是类似编程艺术第1章左旋字符串:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6322882。
3、暴风影音的片源服务器上保存着两个文件a和b,各存放50亿条URL,每条URL占用64字节,内存限制是4G,让你找出a,b文件共同的URL。要求:算法设计。
点评:上述第3题等海量数据处理面试题,请参见此文第第一部分第6题:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7382693。 - 关于linux内核的几个面试问题:
1、Linux中主要有哪几种内核锁?
2、Linux中的用户模式和内核模式是什么含意?
3、用户进程间通信主要哪几种方式?
4、有哪几种内存分配函数? - 微软一面:输入两个数,相加求和,二进制输出。
9月11日, 京东:
谈谈你对面向对象编程的认识
- 8月15日,百度2道面试题:
- 8月20日,金山面试,题目如下:
数据库1中存放着a类数据,数据库2中存放着以天为单位划分的表30张(比如 table_20110909,table_20110910,table_20110911),总共是一个月的数据。表1中的a类数据中有一个字段 userid来唯一判别用户身份,表2中的30张表(每张表结构相同)也有一个字段userid来唯一识别用户身份。如何判定a类数据库的多少用户在数据 库2中出现过?
来源:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20120820/23/C6B16CCF-EE15-47C0-9B15-77497291F2B9.html。 - 百度实习笔试题(2012.5.6)
1、一个单词单词字母交换,可得另一个单词,如army->mary,成为兄弟单词。提供一个单词,在字典中找到它的兄弟。描述数据结构和查询过程。评点:同去年9月份的一道题,见此文第3题:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6803368。
2、线程和进程区别和联系。什么是“线程安全”
3、C和C++怎样分配和释放内存,区别是什么
4、算法题1
一个url指向的页面里面有另一个url,最终有一个url指向之前出现过的url或空,这两种情形都定义为null。这样构成一个单链表。给两条这样单链表,判断里面是否存在同样的url。url以亿级计,资源不足以hash。
5、算法题2
数组al[0,mid-1] 和 al[mid,num-1],都分别有序。将其merge成有序数组al[0,num-1],要求空间复杂度O(1)
6、系统设计题
百度搜索框的suggestion,比如输入“北京”,搜索框下面会以北京为前缀,展示“北京爱情故事”、“北京公交”、“北京医院”等等搜索词,输入“结构之”,会提示“结构之法”,“结构之法 算法之道”等搜索词。
请问,如何设计此系统,使得空间和时间复杂度尽量低。
评点:①直接上Trie树「Trie树的介绍见:从Trie树(字典树)谈到后缀树」 + TOP K「hashmap+堆,hashmap+堆 统计出如10个近似的热词,也就是说,只存与关键词近似的比如10个热词,详细方法可参看此文第2个题的讲解:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7382693」?
②or Double-array trie tree?同时,StackOverflow上也有两个讨论帖子:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2901831/algorithm-for-autocomplete,http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1783652/what-is-the-best-autocomplete-suggest-algorithm-datastructure-c-c。
③此外,这里有一篇关于“拼写错误检查”问题的介绍,或许对你有所启示:http://blog.afterthedeadline.com/2010/01/29/how-i-trie-to-make-spelling-suggestions/。。 - 人搜笔试1. 快排每次以第一个作为主元,问时间复杂度是多少?(O(N*logN))
2. T(N) = N + T(N/2)+T(2N), 问T(N)的时间复杂度是多少? 点评:O(N*logN) or O(N)?
3. 从(0,1)中平均随机出几次才能使得和超过1?(e)
4.编程题:
一棵树的节点定义格式如下:
struct Node{ Node* parent; Node* firstChild; // 孩子节点 Node* sibling; // 兄弟节点 }
要求非递归遍历该树。
思路:采用队列存储,来遍历节点。
5. 算法题:
有N个节点,每两个节点相邻,每个节点只与2个节点相邻,因此,N个顶点有N-1条边。每一条边上都有权值wi,定义节点i到节点i+1的边为wi。
求:不相邻的权值和最大的边的集合。 - 人搜面试,所投职位:搜索研发工程师:面试题回忆
1、删除字符串开始及末尾的空白符,并且把数组中间的多个空格(如果有)符转化为1个。
2、求数组(元素可为正数、负数、0)的最大子序列和。
3、链表相邻元素翻转,如a->b->c->d->e->f-g,翻转后变为:b->a->d->c->f->e->g
4、链表克隆。链表的结构为:
typedef struct list { int data; //数据字段 list *middle; //指向链表中某任意位置元素(可指向自己)的指针 list *next;//指向链表下一元素 } list;
5、100万条数据的数据库查询速度优化问题,解决关键点是:根据主表元素特点,把主表拆分并新建副表,并且利用存储过程保证主副表的数据一致性。(不用写代码)
6、求正整数n所有可能的和式的组合(如;4=1+1+1+1、1+1+2、1+3、2+1+1、2+2)。点评:这里有一参考答案:http://blog.csdn.net/wumuzi520/article/details/8046350。
7、求旋转数组的最小元素(把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小 元素。例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1)
8、找出两个单链表里交叉的第一个元素
9、字符串移动(字符串为*号和26个字母的任意组合,把*号都移动到最左侧,把字母移到最右侧并保持相对顺序不变),要求时间和空间复杂度最小
10、时间复杂度为O(1),怎么找出一个栈里的最大元素
11、线程、进程区别
12、static在C和C++里各代表什么含义
13、const在C/C++里什么意思
14、常用linux命令
15、解释Select/Poll模型 - 网易有道二面:
判断一个数字序列是BST后序遍历的结果,现场写代码。
来源:http://blog.csdn.net/hopeztm/article/category/1201028; - 8月30日,网易有道面试题
var tt = 'aa'; function test() { alert(tt); var tt = 'dd'; alert(tt); } test();
- 8月31日,百度面试题:不使用随机数的洗牌算法,详情:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20120831/10/C837A419-DFD4-4326-897C-669909BD2086.html;
- 9月6日,阿里笔试题:平面上有很多点,点与点之间有可能有连线,求这个图里环的数目。
- 9月7日,一道华为上机题:
题目描述: 选秀节目打分,分为专家评委和大众评委,score[] 数组里面存储每个评委打的分数,judge_type[] 里存储与 score[] 数组对应的评委类别,judge_type == 1,表示专家评委,judge_type == 2,表示大众评委,n表示评委总数。打分规则如下:专家评委和大众评委的分数先分别取一个平均分(平均分取整),然后,总分 = 专家评委平均分 * 0.6 + 大众评委 * 0.4,总分取整。如果没有大众评委,则 总分 = 专家评委平均分,总分取整。函数最终返回选手得分。
函数接口 int cal_score(int score[], int judge_type[], int n)
上机题目需要将函数验证,但是题目中默认专家评委的个数不能为零,但是如何将这种专家数目为0的情形排除出去。
来源:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20120907/15/c30eead8-9e49-41c2-bd11-c277030ad17a.html; - 9月8日,腾讯面试题:
假设两个字符串中所含有的字符和个数都相同我们就叫这两个字符串匹配,
比如:abcda和adabc,由于出现的字符个数都是相同,只是顺序不同,
所以这两个字符串是匹配的。要求高效!
又是跟上述第3题中简单题一的兄弟节点类似的一道题,我想,你们能想到的,这篇blog里:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6347454都已经有了。 - 阿里云,搜索引擎中5亿个url怎么高效存储;
- 一道C++笔试题,求矩形交集的面积:
在一个平面坐标系上,有两个矩形,它们的边分别平行于X和Y轴。
其中,矩形A已知, ax1(左边), ax2(右边), ay1(top的纵坐标), ay2(bottom纵坐标). 矩形B,类似,就是 bx1, bx2, by1, by2。这些值都是整数就OK了。
要求是,如果矩形没有交集,返回-1, 有交集,返回交集的面积。
int area(rect const& a, rect const& b)
{
...
}
点评:
healer_kx:
补齐代码,最好是简洁的,别用库。你可以写你的辅助函数,宏定义,代码风格也很重要。
ri_aje:
下面是一个简短的证明。-
struct rect { // axis alignment assumed // bottom left is (x[0],y[0]), top right is (x[1],y[1]) double x [2]; double y [2]; }; template <typename T> T const& min (T const& x, T const& y) { return x<y ? x : y; } template <typename T> T const& max (T const& x, T const& y) { return x>y ? x : y; } // return type changed to handle non-integer rects double area (rect const& a, rect const& b) { // perfectly adjacent rects are considered having an intersection of 0 area double const dx = min(a.x[1],b.x[1]) - max(a.x[0],b.x[0]); double const dy = min(a.y[1],b.y[1]) - max(a.y[0],b.y[0]); return dx>=0&&dy>=0 ? dx*dy : -1; }
对于平行于坐标轴的矩形 r,假设其左下角点坐标为 (rx0,ry0),右上角点坐标为 (rx1,ry1),那么由 r 定义的无限有界点集为:{(x,y)|x in [rx0,rx1] && y in [ry0,ry1]}。
根据交集的定义,则任意二维点 (x,y) 在矩形 a,b 的交集内等价于
{(x,y)|(x,y) in a 并且 (x,y) in b} <==>
{(x,y)|x in [ax0,ax1] && x in [bx0,bx1] 并且 y in [ay0,ay1] && y in [by0,by1]} <==>
{(x,y)|x in [max(ax0,bx0),min(ax1,bx1)] 并且 y in [max(ay0,by0),min(ay1,by1)]}
因此,交集矩形的边长分别为 min(ax1,bx1)-max(ax0,bx0) 和 min(ay1,by1)-max(ay0,by0)。注意当交集为空时(a,b 不相交),则经此法计算出来的交集边长为负值,此事实可用于验证 a,b 的相交性。
鉴于笛卡尔积各个维度上的不相关性,此方法可扩展到任意有限维线性空间,比如,三维空间中平行于坐标轴的长方体的交集体积可以用类似的方法计算。
来源:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20120913/18/bc669d60-b70a-4008-be65-7c342789b925.html。 -
- 2012年创新工场校园招聘最后一道笔试题:工场很忙
创新工场每年会组织同学与项目的双选会,假设现在有M个项目,编号从1到M,另有N名同学,编号从1到N,每名同学能选择最多三个、最少一个感兴趣的项 目。选定之后,HR会安排项目负责人和相应感兴趣的同学一对一面谈,每次面谈持续半小时。由于大家平时都很忙,所以咱们要尽量节约时间,请你按照以下的条 件设计算法,帮助HR安排面试。
1)同学很忙。项目负责 人一次只能与一名同学面谈,而同学会在自己第一个面试开始时达到工场,最后一个面试结束后离开工场,如果参加一个项目组的面试后不能立即参加下一个项目组 的面试,就必须在工场等待。所以请尽可能让同学的面试集中在某一时间段,减少同学在工场等待的时间。
2)项目负责人很忙。众所周知,创业团队的负责人会有很多事情要做,所以他们希望能够将自己参与的面试集中在某一段时间内,请在保证1)的情况下,使得项目负责人等待的时间最少。
3)HR很忙。从第一轮面试开始以后,所有HR都必须等到最后一轮面试结束,所以需要在保证1)和2)的同时,也能尽快解放掉所有的HR,即让第一轮面试到最后一轮面试之间持续的时间最短。
输入(以文件方式输入,文件名为iw,例如iw.in):
第1行...第n行:同学的编号 项目的编号
样例(数据间用空格隔开,两个0表示输入结束):
1 1
12
1 3
2 1
3 1
3 2
0 0
表示M=3,N=3,编号为1的同学选择了项目1,2和3,编号为2的同学选择了项目1,编号为3的同学选了项目1和2
输出(以文件方式输出,文件名为iw,例如iw.out):
第1行:编号为1的项目依次面试新同学的编号序列
第2行:编号为2的项目依次面试新同学的编号序列
...
第n行:编号为n的项目依次面试新同学的编号序列
样例(数据间用空格隔开,0表示没有面试):
13 2
3 1 0
0 0 1
表示编号为1的项目在第一轮面试编号为1的同学,第二轮面试编号为3的同学,第三轮面试编号为2的同学
编号为2的项目在第一轮面试编号为3的同学,第二轮面试编号为1的同学,第二轮不用面试
编号为3的项目在第一轮和第二轮都不用面试,第三轮面试编号为1的同学
链接:http://t.qq.com/p/t/108332110988802; -
4**9 的笔试题,比较简单:
1.求链表的倒数第二个节点
2.有一个整数数组,求数组中第二大的数 -
阿里巴巴二道题第一道:
对于给定的整数集合S,求出最大的d,使得a+b+c=d。a,b,c,d互不相同,且都属于S。集合的元素个数小于等于2000个 ,元素的取值范围在[-2^ 28,2^ 28 - 1 ],假定可用内存空间为100MB,硬盘使用空间无限大,试分析时间和空间复杂度,找出最快的解决方法。
点评:
@绿色夹克衫:两两相加转为多项式乘法,比如(1 2 4 6) + (2 3 4 5) => (x + x^2 + x^4 + x^6)*(x^2 + x^3 + x^4 + x^5) 。更多思路请见这 :http://www.51nod.com/answer/index.html#!answerId=569 。阿里巴巴第二道(研发类)
笔试题1,原题大致描述有一大批数据,百万级别的。数据项内容是:用户ID、科目ABC各自的成绩。其中用户ID为0~1000万之间,且是连续的,可以唯一标识一条记录。科目ABC成绩均在0~100之间。有两块磁盘,空间大小均为512M,内存空间64M。
1) 为实现快速查询某用户ID对应的各科成绩,问磁盘文件及内存该如何组织;
2) 改变题目条件,ID为0~10亿之间,且不连续。问磁盘文件及内存该如何组织;
3) 在问题2的基础上,增加一个需求。在查询各科成绩的同时,获取该用户的排名,问磁盘文件及内存该如何组织。
笔试题2: 代码实现计算字符串的相似度。
点评: 和计算两字符串的最长公共子序列相似。
设Ai为字符串A(a1a2a3 … am )的前i个字符(即为a1,a2,a3 … ai )
设Bj为字符串B(b1b2b3 … bn )的前j个字符(即为b1,b2,b3 … bj)
设 L(i , j)为使两个字符串和Ai和Bj相等的最小操作次数。
当ai等于bj时 显然L(i, j)=L(i-1, j-1)
当ai不等于bj时
若将它们修改为相等,则对两个字符串至少还要操作L(i-1, j-1)次
若删除ai或在Bj后添加ai,则对两个字符串至少还要操作L(i-1, j)次
若删除bj或在Ai后添加bj,则对两个字符串至少还要操作L(i, j-1)次
此时L(i, j)=min( L(i-1, j-1), L(i-1, j), L(i, j-1) ) + 1
显然,L(i, 0)=i,L(0, j)=j, 再利用上述的递推公式,可以直接计算出L(i, j)值。具体代码请见这:http://blog.csdn.net/flyinghearts/article/details/5605996。 - 9月14日,小米笔试,给一个浮点数序列,取最大乘积子序列的值,例如 -2.5,4,0,3,0.5,8,-1,则取出的最大乘积子序列为3,0.5,8。
点评:
解法一、
或许,读者初看此题,自然会想到最大乘积子序列问题类似于最大子数组和问题:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6444021,然实则具体处理起来诸多不同,为什么呢,因为乘积子序列中有正有负也还可能有0。
既如此,我们可以把问题简化成这样:数组中找一个子序列,使得它的乘积最大;同时找一个子序列,使得它的乘积最小(负数的情况)。因为虽然我们只要一个 最大积,但由于负数的存在,我们同时找这两个乘积做起来反而方便。也就是说,不但记录最大乘积,也要记录最小乘积。So,
我们让maxCurrent表示当前最大乘积的candidate,
minCurrent反之,表示当前最小乘积的candidate。
(用candidate这个词是因为只是可能成为新一轮的最大/最小乘积),
而maxProduct则记录到目前为止所有最大乘积candidates的最大值。
由于空集的乘积定义为1,在搜索数组前,maxCurrent,minCurrent,maxProduct都赋为1。
假设在任何时刻你已经有了maxCurrent和minCurrent这两个最大/最小乘积的candidates,新读入数组的元素x(i)后,新的最 大乘积candidate只可能是maxCurrent或者minCurrent与x(i)的乘积中的较大者,如果x(i)<0导致 maxCurrent<minCurrent,需要交换这两个candidates的值。
当任何时候maxCurrent<1,由于1(空集)是比maxCurrent更好的candidate,所以更新maxCurrent为1,类 似的可以更新minCurrent。任何时候maxCurrent如果比最好的maxProduct大,更新maxProduct。
具体代码如下:
解法二、-
template <typename Comparable> Comparable maxprod( const vector<Comparable>&v) { int i; Comparable maxProduct = 1; Comparable minProduct = 1; Comparable maxCurrent = 1; Comparable minCurrent = 1; //Comparable t; for( i=0; i< v.size() ;i++) { maxCurrent *= v[i]; minCurrent *= v[i]; if(maxCurrent > maxProduct) maxProduct = maxCurrent; if(minCurrent > maxProduct) maxProduct = minCurrent; if(maxCurrent < minProduct) minProduct = maxCurrent; if(minCurrent < minProduct) minProduct = minCurrent; if(minCurrent > maxCurrent) swap(maxCurrent,minCurrent); if(maxCurrent<1) maxCurrent = 1; //if(minCurrent>1) // minCurrent =1; } return maxProduct; }
本题除了上述类似最大子数组和的解法,也可以直接用动态规划求解(其实,上述的解法一本质上也是动态规划,只是解题所表现出来的具体形式与接下来的解法二不同罢了。这个不同就在于下面的解法二会写出动态规划问题中经典常见的状态转移方程,而解法一是直接求解)。具体解法如下:
假设数组为a[],直接利用动归来求解,考虑到可能存在负数的情况,我们用Max[i]来表示以a[i]结尾的最大连续子序列的乘积值,用Min[i]表示以a[i]结尾的最小的连续子序列的乘积值,那么状态转移方程为:
Max[i]=max{a[i], Max[i-1]*a[i], Min[i-1]*a[i]};
Min[i]=min{a[i], Max[i-1]*a[i], Min[i-1]*a[i]};
初始状态为Max[1]=Min[1]=a[1]。代码如下:
变种-
/* 给定一个整数数组,有正有负数,0,正数组成,数组下标从1算起 求最大连续子序列乘积,并输出这个序列,如果最大子序列乘积为负数,那么就输出-1 用Max[i]表示以a[i]结尾乘积最大的连续子序列 用Min[i]表示以a[i]结尾乘积最小的连续子序列 因为有复数,所以保存这个是必须的 */ void longest_multiple(int *a,int n){ int *Min=new int[n+1](); int *Max=new int[n+1](); int *p=new int[n+1](); //初始化 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ p[i]=-1; } Min[1]=a[1]; Max[1]=a[1]; int max_val=Max[1]; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ Max[i]=max(Max[i-1]*a[i],Min[i-1]*a[i],a[i]); Min[i]=min(Max[i-1]*a[i],Min[i-1]*a[i],a[i]); if(max_val<Max[i]) max_val=Max[i]; } if(max_val<0) printf("%d",-1); else printf("%d",max_val); //内存释放 delete [] Max; delete [] Min; }
此外,此题还有另外的一个变种形式,即给定一个长度为N的整数数组,只允许用乘法,不能用除法,计算任意(N-1)个数的组合中乘积最大的一组,并写出算法的时间复杂度。
我们可以把所有可能的(N-1)个数的组合找出来,分别计算它们的乘积,并比较大小。由于总共有N个(N-1)个数的组合,总的时间复杂度为O(N2),显然这不是最好的解法。
OK,以下解答来自编程之美
解法1

解法2
此外,还可以通过分析,进一步减少解答问题的计算量。假设N个整数的乘积为P,针对P的正负性进行如下分析(其中,AN-1表示N-1个数的组合,PN-1表示N-1个数的组合的乘积)。
1.P为0 那么,数组中至少包含有一个0。假设除去一个0之外,其他N-1个数的乘积为Q,根据Q的正负性进行讨论:
Q为0
说明数组中至少有两个0,那么N-1个数的乘积只能为0,返回0;
Q为正数
返回Q,因为如果以0替换此时AN-1中的任一个数,所得到的PN-1为0,必然小于Q;
Q为负数
如果以0替换此时AN-1中的任一个数,所得到的PN-1为0,大于Q,乘积最大值为0。2. P为负数
根据“负负得正”的乘法性质,自然想到从N个整数中去掉一个负数,使得PN-1为一个正数。而要使这个正数最大,这个被去掉的负数的绝对值必须是数组中最小的。我们只需要扫描一遍数组,把绝对值最小的负数给去掉就可以了。
3. P为正数
类似地,如果数组中存在正数值,那么应该去掉最小的正数值,否则去掉绝对值最大的负数值。
上面的解法采用了直接求N个整数的乘积P,进而判断P的正负性的办法,但是直接求乘积在编译环境下往往会有溢出的危险(这也就是本题要求不使用除法的潜在 用意),事实上可做一个小的转变,不需要直接求乘积,而是求出数组中正数(+)、负数(-)和0的个数,从而判断P的正负性,其余部分与以上面的解法相 同。
在时间复杂度方面,由于只需要遍历数组一次,在遍历数组的同时就可得到数组中正数(+)、负数(-)和0的个数,以及数组中绝对值最小的正数和负数,时间复杂度为O(N)。 -
- 9月15日,中兴面试:
小端系统
输出结果为?(答案:32 20)-
union{ int i; unsigned char ch[2]; }Student; int main() { Student student; student.i=0x1420; printf("%d %d",student.ch[0],student.ch[1]); return 0; }
-
- 一道有趣的Facebook面试题:
给一个二叉树,每个节点都是正或负整数,如何找到一个子树,它所有节点的和最大?
点评:
@某猛将兄:后序遍历,每一个节点保存左右子树的和加上自己的值。额外一个空间存放最大值。
@陈利人:同学们,如果你面试的是软件工程师的职位,一般面试官会要求你在短时间内写出一个比较整洁的,最好是高效的,没有什么bug的程序。所以,光有算法不够,还得多实践。
写完后序遍历,面试官可能接着与你讨论,a). 如果要求找出只含正数的最大子树,程序该如何修改来实现?b). 假设我们将子树定义为它和它的部分后代,那该如何解决?c). 对于b,加上正数的限制,方案又该如何?总之,一道看似简单的面试题,可能能变换成各种花样。
比如,面试管可能还会再提两个要求:第一,不能用全局变量;第一,有个参数控制是否要只含正数的子树。其它的,随意,当然,编程风格也很重要。 - 谷歌面试题:
有几百亿的整数,分布的存储到几百台通过网络连接的计算机上,你能否开发出一个算法和系统,找出这几百亿数据的中值?就是在一组排序好的数据中居于中间的数。显然,一台机器是装不下所有的数据。也尽量少用网络带宽。 - 小米,南京站笔试(原第20题):
一个数组里,数都是两两出现的,但是有三个数是唯一出现的,找出这三个数。
点评:
3个数唯一出现,各不相同。由于x与a、b、c都各不相同,因此x^a、x^b、x^c都不等于0。具体答案请参看这两篇文章:1、http://blog.csdn.net/w397090770/article/details/8032898,2、http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/25411174201283084246412/。 - 9月19日,IGT面试:你走到一个分叉路口,有两条路,每个路口有一个人,一个说假话,一个说真话,你只能问其中一个人仅一个问题,如何问才能得到正确答案?点评:答案是,问其中一个人:另一个人会说你的路口是通往正确的道路么?
- 9月19日,创新工厂笔试题:
给定一整型数组,若数组中某个下标值大的元素值小于某个下标值比它小的元素值,称这是一个反序。
即:数组a[]; 对于i < j 且 a[i] > a[j],则称这是一个反序。
给定一个数组,要求写一个函数,计算出这个数组里所有反序的个数。
点评:
归并排序,至于有的人说是否有O(N)的时间复杂度,我认为答案是否定的,正如老梦所说,下限就是nlgn,n个元素的数组的排列共有的排列是nlgn,n!(算法导论里面也用递归树证明了:O(n*logn)是最优的解法,具体可以看下这个链接:)。然后,我再给一个链接,这里有那天笔试的两道题目:http://blog.csdn.net/luno1/article/details/8001892。 - 9月20日,创新工厂南京站笔试:
已知字符串里的字符是互不相同的,现在任意组合,比如ab,则输出aa,ab,ba,bb,编程按照字典序输出所有的组合。
点评:非简单的全排列问题(跟全排列的形式不同,abc 全排列的话,只有6个不同的输出:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6879101)。本题可用递归的思想,设置一个变量表示已输出的个数,然后当个数达到字符串长度时,就输出。-
//假设str已经有序,from 一直很安静 void perm(char *str, int size, int resPos) { if(resPos == size) print(result); else { for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { result[resPos] = str[i]; perm(str, size, resPos + 1); } } }
-
- 9月21日,小米,电子科大&西安交通大学笔试题:
 问:最后程序输出是多少?点评:此题有陷阱,答题需谨慎!
问:最后程序输出是多少?点评:此题有陷阱,答题需谨慎!-
void fun() { unsigned int a = 2013; int b = -2; int c = 0; while (a + b > 0) { a = a + b; c++; } printf("%d", c); }



点评:
针对上述第3题朋友圈的问题,读者@互联网的飞虫提供的解法及代码如下(有任何问题,欢迎指正,多谢):-
#include <STDIO.H> #include <WINDOWS.H> int Friends(int n, int m , int* r[]); int main(int argc,char** argv) { int r[5][2] = {{1,2},{4,3},{6,5},{7,8},{7,9}}; printf("有%d个朋友圈。\n",Friends(0,5,(int**)r)); return 0; } int Friends(int n, int m, int* r[]) // 注意这里的参数很奇葩 { int *p = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*m*3); memset(p,0,sizeof(int)*m*3); int i = 0; int iCount = 0; int j = 0; int * q = (int*)r; // 这里很巧妙 将二维指针 强转为一维指针 for (i=0;i<m;++i) { for (j=0;j<2;++j) { p[i*3+j]=q[i*2+j]; // 注意这里二维数组向一维数组的转换 } p[i*3+j] = 0; } bool bFlag = false; for (i=0;i<m;++i) { bFlag = false; if (p[i*3+2]==1) { bFlag = true; } p[i*3+2] = 1; for (j=0;j<m;++j) { if (i==j) { continue; } if (p[i*3]==p[j*3] || p[i*3] == p[j*3+1] || p[i*3+1] == p[j*3+0] || p[i*3+1] == p[j*3+1]) { if (p[j*3+2]==1) { bFlag = true; } p[j*3+2] = 1; } } if (!bFlag) { ++iCount; } } free(p); return iCount; }
-
- 9月21日晚,海豚浏览器笔试题:
1、有两个序列A和B,A=(a1,a2,...,ak),B=(b1,b2,...,bk),A和B都按升序排列,对于1<=i,j<=k,求k个最小的(ai+bj),要求算法尽量高效。
2、输入:
L:“shit”“fuck”“you”
S:“shitmeshitfuckyou”
输出:S中包含的L一个单词,要求这个单词只出现一次,如果有多个出现一次的,输出第一个这样的单词
怎么做? - 9月22日上午,百度西安站全套笔试题如下:

点评:上述的系统设计题简单来讲,是建立起按键号码数字到人名(手机号)的映射关系,具体讲,步骤解法如下图所示:
3.算法与程序设计
第一题:
某个公司举行一场羽毛球赛,有1001个人参加,现在为了评比出“最厉害的那个人”,进行淘汰赛,请问至少需要进行多少次比赛。
第二题
有100个灯泡,第一轮把所有灯泡都开启,第二轮把奇数位的灯泡灭掉,第三轮每隔两个灯泡,灭一个,开一个,依此类推。求100轮后还亮的灯泡。
点评:完全平方数,本人去58面试时,也遇到过与此类似的题。
第三题
有20个数组,每个数组里面有500个数组,降序排列,每个数字是32位的unit,求出这10000个数字中最大的500个。
点评:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=647。
4.系统设计题
类似做一个手机键盘,上面有1到9个数字,每个数字都代表几个字母(比如1代表abc三个字母,z代表wxyz等等),现在要求设计当输入某几个数字的组合时,查找出通讯录中的人名及电话号码。
其它的还有三道简答题,比如线程的死锁,内存的管理等等。最后,附一讨论帖子:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20120923/18/7fd148b2-c000-4326-93a6-cb3bb8675702.html。 - 9月22日,微软笔试:
T(n)=1(n<=1),T(n) = 25*T(n/5) + n^2,求算法的时间复杂度。更多题目请参见:http://blog.csdn.net/wonderwander6642/article/details/8008209。 - 9月23日,腾讯校招部分笔试题(特别提醒:下述试卷上的答案只是一考生的解答,非代表正确答案.如下面第11题答案选D,第12题答案选C,至于解释可看这里:http://coolshell.cn/articles/7965.html):


点评:根号九说,不过最后两道大的附加题,全是秒杀99%海量数据处理面试题里的:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7382693,太感谢July了。 - 9月23日,搜狗校招武汉站笔试题:
一、已知计算机有以下原子操作
1、 赋值操作:b = a;
2、 ++a和a+1;
3、for( ){ ***}有限循环;
4、操作数只能为0或者正整数;
5、定义函数
实现加减乘操作
二、对一个链表进行排序,效率越高越好,LinkedList<Integer>.
附:9月15日,搜弧校招笔试题:http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/8015964。 - 搜狗校招笔试题:
100个任务,100个工人每人可做一项任务,每个任务每个人做的的费用为t[100][100],求一个分配任务的方案使得总费用最少。
点评:匈牙利算法,可以看看这篇文章:http://www.byvoid.com/blog/hungary/,及这个链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=641。 - 9月24日,Google南京等站全套笔试题如下:





点评:
谷歌的笔试从易到难,基础到复杂,涵盖操作系统 网络 数据结构 语言 数学思维 编程能力 算法能力,基本上能把一个人的能力全面考察出来。
至于上述2.1寻找3个数的中位数,请看读者sos-phoenix给出的思路及代码:
最坏情况下的比较次数:3 (次)-
2.1 // 采用两两比较的思路(目前没想到更好的) if (a <= b) { if (b <= c) return b; else { if (a <=c) return c; else return a; } } else { if (a <= c) return a; else { if (b <= c) return c; else return b; } }
平均情况下的比较次数:(2×2 + 4*3)/6 = 8/3 (次)
此外这题,微博上的左耳朵耗子后来也给出了一个链接:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1582356/fastest-way-of-finding-the-middle-value-of-a-triple,最后是微博上的梁斌penny的解答:http://weibo.com/1497035431/yFusm7obQ。其余更多参考答案请看本文评论下第93楼。 -
- 读者来信,提供的几个hulu面试题:
9月19号,hulu电面:
问题1 两个骰子,两个人轮流投,直到点数和大于6就停止,最终投的那个人获胜。问先投那个人获胜概率?
问题2 平面上n个圆,任意两个都相交,是否有一条直线和所有的圆都有交点。
9月22号,上午hulu面试
问题1 100个人,每人头上戴一顶帽子,写有0..99的一个数,数可能重复,每个人都只能看到除自己以外其他人的帽子。每个人需要说出自己的帽子的数,一个人说对就算赢。点评:参考答案请看这个链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=642。
问题2 n台机器,每台有负载,以和负载成正比的概率,随机选择一台机器。「原 题是希望设计O(1)的算法(预处理O(n)不可少,要算出每台机器的比例),因为非O(1)的话,就trivial了:可以产生随机数例如[0,1)然 后,根据负载比例,2分或者直接循环检查落入哪个区间,决定机器。 面试官想问,有没更好的办法,避免那种查找。即能否多次(常数次)调用随机函数,拟合出一个概率分布」
问题3 行列都递增的矩阵,求中位数。点评:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=643,http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7085669(杨氏矩阵查找问题)。 - 西安百度软件研发工程师:
一面(2012.9.24):
问的比较广,涉及操作系统、网络、数据结构。比较难的就2道题。
(1)10亿个int型整数,如何找出重复出现的数字;
(2)有2G的一个文本文档,文件每行存储的是一个句子,每个单词是用空格隔开的。问:输入一个句子,如何找到和它最相似的前10个句子。(提示:可用倒排文档)。
二面(2012.9.25):
(1)一个处理器最多能处理m个任务。现在有n个任务需要完成,每个任务都有自己完成所需的时间。此外每个任务之间有依赖性,比如任务A开始执行的前提是任务B必须完成。设计一个调度算法,使得这n这任务的完成时间最小;
(2)有一个排序二叉树,数据类型是int型,如何找出中间大的元素;
(3)一个N个元素的整形数组,如何找出前K个最大的元素。
(4)给定一个凸四边形,如何判断一个点在这个平面上。
点评:本题的讨论及参考答案请见这:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=669。
运维部(2012.9.27):
(1)堆和栈的区别;
(2)问如何数出自己头上的头发。 - 9月25日,人人网笔试题:

点评:参考答案请见,http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=671。 - 9月25日晚,创新工场校园招聘北邮站笔试:




- 9月25日,小米大连站笔试题:
1一共有100万,抽中的2万,每月增加4万,问20个月能抽中的概率为:?
2 for(int i=0;i<strlen(s);i++){n+=I;}时间复杂度O(n)
3 手机wifi(A)….wifi ap….局域网(B)…..路由器…ADSL(C)…..互联网…..服务器
断掉上述ABC哪些点TCP链接会立刻断掉?
4 12345入栈,出栈结果 21543 31245 43215 12534 可能的为?(第一个和第三个)
5 x^n+a1x^n-1+…+an-1x+an,最少要做—乘法?题目中a1,a2,an为常数。 - 9月26日,百度一二面:
1、给定一数组,输出满足2a=b(a,b代表数组中的数)的数对,要求时间复杂度尽量低。
2、搜索引擎多线程中每个线程占用多少内存?如果搜索引擎存储网页内存占用太大怎么解决?
3、有很多url,例如*.baidu.com,*.sina.com ......
现在给你一个sports.sina.com 快速匹配出是*.sina.com。点评:老题,此前blog内曾整理过。
4、找出字符串的编辑距离,即把一个字符串s1最少经过多少步操作变成编程字符串s2,操作有三种,添加一个字符,删除一个字符,修改一个字符(只要听过编辑距离,知道往动态规划上想,很快就可以找到解法)。
点评:请看链接:http://blog.csdn.net/Lost_Painting/article/details/6457334。
5、编程实现memcopy,注意考虑目标内存空间和源空间重叠的时候。
6、实现简单的一个查找二叉树的深度的函数。
- 9月26日晚,优酷土豆笔试题一道:
优酷是一家视频网站,每天有上亿的视频被观看,现在公司要请研发人员找出最热门的视频。
该问题的输入可以简化为一个字符串文件,每一行都表示一个视频id,然后要找出出现次数最多的前100个视频id,将其输出,同时输出该视频的出现次数。
1.假设每天的视频播放次数为3亿次,被观看的视频数量为一百万个,每个视频ID的长度为20字节,限定使用的内存为1G。请简述做法,再写代码。
2.假设每个月的视频播放次数为100亿次,被观看的视频数量为1亿,每个视频ID的长度为20字节,一台机器被限定使用的内存为1G。
点评:有关海量数据处理的题目,请到此文中找方法(无论题目形式怎么变,基本方法不变,当然,最最常用的方法是:分而治之/Hash映射 + Hash统计 + 堆/快速/归并排序):http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7382693。注:上题第二问文件太大,则可如模1000,把整个大文件映射为1000个小文件再处理 .... - 9月26日,baidu面试题:
1.进程和线程的区别
2.一个有序数组(从小到大排列),数组中的数据有正有负,求这个数组中的最小绝对值
3.链表倒数第n个元素
4.有一个函数fun能返回0和1两个值,返回0和1的概率都是1/2,问怎么利用这个函数得到另一个函数fun2,使fun2也只能返回0和1,且返回0的概率为1/4,返回1的概率为3/4。(如果返回0的概率为0.3而返回1的概率为0.7呢)
5.有8个球,其中有7个球的质量相同,另一个与其他球的质量不同(且不知道是比其他球重还是轻),请问在最坏的情况下,最少需要多少次就能找出这个不同质量的球
6.数据库索引
7.有一个数组a,设有一个值n。在数组中找到两个元素a[i]和a[j],使得a[i]+a[j]等于n,求出所有满足以上条件的i和j。
8.1万个元素的数组,90%的元素都是1到100的数,10%的元素是101--10000的数,如何高效排序。 - 小米的web开发笔试题:
一场星际争霸比赛,共8个人,每个人的实力用分数表示,要分成两队,如何保证实力最平均?给定一个浮点数的序列,F1,F2,……,Fn(1<=n<=1000),定义P(s,e)为子序列Fi(s<=i<=e)的积,求P的最大值。 - 9月27日,趋势科技面试题:
马路口,30分钟内看到汽车的概率是95%,那么在10分钟内看不到汽车的概率是? - 9月27日晚,IGT笔试题:
给定一个字符串里面只有"R" "G" "B" 三个字符,请排序,最终结果的顺序是R在前 G中 B在后。
要求:空间复杂度是O(1),且只能遍历一次字符串。
点评:本质是荷兰国旗问题,类似快排中partition过程,具体思路路分析及代码可以参考此文第8节:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6211155。 - 9月27日,人人两面:
一面
1 实现atoi
2 单链表变形 如 1 2 3 4 5 变为 1 3 5 4 2 如1 2 3 4 变为 1 3 4 2
(就是拆分链表 把偶数为反过来接在奇数位后面)
二面
1 二叉树查找不严格小于一个值的最大值(返回节点)。
2 有序数组里二分查找一个数(如果有相同的找最后一次出现的)。
3 等价于n*n的矩阵,填写0,1,要求每行每列的都有偶数个1 (没有1也是偶数个),问有多少种方法。
评论:开始以为是算法题,想了狂搜,递推(dp,可以用xor表示一行的列状态,累加),分治,(拆两半,然后上半段下半段的列有相同的奇偶性)。后来,自己算了几个发现n = 1 n = 2 n = 3 的结果,他告诉了我n = 4是多少,然后发现f(n) = 2^((n - 1) ^2) 。最后我给出了一个巧妙的证明。然后发现如果是m*n的矩阵也是类似的答案,不局限于方阵。此外,题目具体描述可以看看这里:http://blog.himdd.com/?p=2480。
9月27日,小米两面:
一面:
除了聊研究,就一道题
1 数组里找到和最接近于0的两个值。
二面:
1 行列有序的矩阵查找一个数
2 直方图最大矩形。点评:这里有此题的具体表述及一份答案:http://blog.csdn.net/xybsos/article/details/8049048。
3 next_permutation
4 字符串匹配 含有* ? (写代码)
5 实现strcpy memmove (必须写代码)更多,还可以参见此文第三节节末:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6417600,或此文:http://www.360doc.com/content/11/0317/09/6329704_101869559.shtml。-
//void * memmove ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );) //是<string.h>的标准函数,其作用是把从source开始的num个字符拷贝到destination。 //最简单的方法是直接复制,但是由于它们可能存在内存的重叠区,因此可能覆盖了原有数据。 //比如当source+count>=dest&&source<dest时,dest可能覆盖了原有source的数据。 //解决办法是从后往前拷贝。 //对于其它情况,则从前往后拷贝。 void* memmove(void* dest, void* source, size_t count) { void* ret = dest; if (dest <= source || dest >= (source + count)) { //正向拷贝 //copy from lower addresses to higher addresses while (count --) *dest++ = *source++; } else { //反向拷贝 //copy from higher addresses to lower addresses dest += count - 1; source += count - 1; while (count--) *dest-- = *source--; } return ret; }
6 读数 (千万亿,百万亿……)变为数字 (说思路即可,字符串查找,填写各个权值的字段,然后判断是否合法,读前面那些×权值,累加)。 -
- 9月27日,Hulu 2013北京地区校招笔试题
填空题:
1、中序遍历二叉树,结果为ABCDEFGH,后序遍历结果为ABEDCHGF,那么前序遍历结果为?
2、对字符串HELL0_HULU中的字符进行二进制编码,使得字符串的编码长度尽可能短,最短长度为?
3、对长度12的有序数组进行二分查找,目标等概率出现在数组的每个位置上,则平均比较次数为?
4、一副扑克(去王),每个人随机的摸两张,则至少需要多少人摸牌,才能保证有两个人抽到同样的花色。
5、x个小球中有唯一一个球较轻,用天平秤最少称量y次能找出这个较轻的球,写出y和x的函数表达式y=f(x)
6、3的方幂及不相等的3的方幂的和排列成递增序列1,3,4,9,10,12,13……,写出数列第300项
7、无向图G有20条边,有4个度为4的顶点,6个度为3的顶点,其余顶点度小于3,则G有多少个顶点
8、桶中有M个白球,小明每分钟从桶中随机取出一个球,涂成红色(无论白或红都涂红)再放回,问小明将桶中球全部涂红的期望时间是?
9、煤矿有3000吨煤要拿到市场上卖,有一辆火车可以用来运煤,火车最多能装1000吨煤,且火车本身需要烧煤做动力,每走1公里消耗1吨煤,如何运煤才能使得运到市场的煤最多,最多是多少?
10、1,2,3,4…..n,n个数进栈,有多少种出栈顺序,写出递推公式(写出通项公式不得分)
11、宇宙飞船有100,000位的存储空间,其中有一位有故障,现有一种Agent可以用来检测故障,每个Agent可以同时测试任意个位数,若都没有 故障,则返回OK,若有一位有故障,则失去响应。如果有无限多个Agent可供使用,每个Agent进行一次检测需要耗费1小时,现在有2个小时时间去找 出故障位,问最少使用多少个Agent就能找出故障。
(总共12道填空题,还有一道太复杂,题目很长,还有示意图,这里没有记录下来)
大题:
1、n个数,找出其中最小的k个数,写出代码,要求最坏情况下的时间复杂度不能高于O(n logk)
2、写程序输出8皇后问题的所有排列,要求使用非递归的深度优先遍历
3、有n个作业,a1,a2…..an,作业aj的处理时间为tj,产生的效益为pj,最后完成期限为dj,作业一旦被调度则不能中断,如果作业aj在dj前完成,则获得效益pj,否则无效益。给出最大化效益的作业调度算法。点评:参考答案请看这个链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=645。 - 有道的一个笔试题,1-9,9个数组成三个三位数,且都是完全平方数(三个三位数 占据 9个数)求解法。点评@林晚枫&归云见鸿:
(a*10+b)(a*10+b)
100a^2+20ab+b^2
a 属于 [1,2,3]
a=3,b=1 31 961,
a=2,b=3 23 529 400+40b+b^2
25 625
27 729
28 784
29 841
a=1,b=3 13 169 100+20b+b^2
14 196
16 256
17 289
18 324
19 361
=>最终唯一解 529 784 361
具体代码如下(3个for循环,然后hash):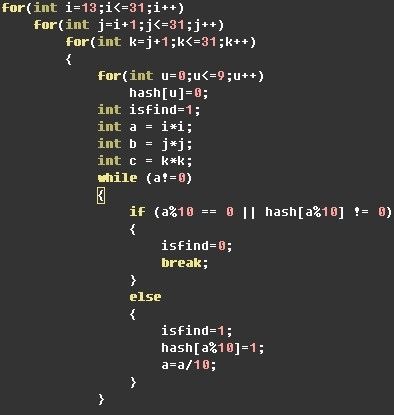
- 9月28日,大众点评北京笔试题目:
1.一个是跳台阶问题,可以1次一级,1次两级,1次三级,求N级的跳法一共多少种?
点评:老题,参考答案请见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6879101。
2.一个文件有N个单词,每行一个,其中一个单词出现的次数大于N/2,怎么样才能快速找出这个单词?
点评:还是老题,参见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6890054。
大众点评前面还有30道逻辑题,15道文字推理,15道数学推理,一共只给20min。 - 9月28日,网易笔试题:
1、英雄升级,从0级升到1级,概率100%。
从1级升到2级,有1/3的可能成功;1/3的可能停留原级;1/3的可能下降到0级;
从2级升到3级,有1/9的可能成功;4/9的可能停留原级;4/9的可能下降到1级。
每次升级要花费一个宝石,不管成功还是停留还是降级。
求英雄从0级升到3级平均花费的宝石数目。
点评:题目的意思是,从第n级升级到第n+1级成功的概率是(1/3)^n(指数),停留原级和降级的概率一样,都为[1-(1/3)^n]/2)。
2、将一个很长的字符串,分割成一段一段的子字符串,子字符串都是回文字符串。
有回文字符串就输出最长的,没有回文就输出一个一个的字符。
例如:
habbafgh
输出h,abba,f,g,h。
点评:编程艺术第十五章有这个回文问题的解答,参见:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/6712171。此外,一般的人会想到用后缀数组来解决这个问题,其余更多的方法请见:http://dsqiu.iteye.com/blog/1688736。最后,还可以看下这个链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=672。 - 10月9日,腾讯一面试题:
有一个log文件,里面记录的格式为:
QQ号: 时间: flag:
如123456 14:00:00 0
123457 14:00:01 1
其中flag=0表示登录 flag=1表示退出
问:统计一天平均在线的QQ数。
点评:类似于此文中:http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/7348968,第8题后的腾讯面试题,读者可以参看之。 - 10月9日,腾讯面试题:
1.有一亿个数,输入一个数,找出与它编辑距离在3以内的书,比如输入6(0110),找出0010等数,数是32位的。
2.每个城市的IP段是固定的,新来一个IP,找出它是哪个城市的,设计一个后台系统。 - 10月9日,YY笔试题:
1 输出一个字符串中没有重复的字符。如“baaca”输出“bac”。
2 对于一个多叉树,设计TreeNode节点和函数,返回先序遍历情况下的下一个节点。
函数定义为TreeNode* NextNode(TreeNode* node)
3 分割字符串。
对于一个字符串,根据分隔符seperator,把字符串分割,如果存在多个分隔符连在一起,则当做一个分隔符。如果分隔符出现在" "符号之间,则不需要分割" "之间的字符。
比如a++abc ,分隔符为+,输出a abc
a+"hu+" 输出a hu+
a++"HU+JI 输出a "HU JI。
请根据上述需求完成函数:void spiltString(string aString,char aSeperator)。
- 10月9日,赶集网笔试

- 10月9日,阿里巴巴2013校园招聘全套笔试题(注:下图中所标答案不代表标准答案,有问题,欢迎留言评论)



上述第15题,填空:lower+ (upper-lower)/2
lower midupper
0612
7912
778
888
比较4次
上述第16题,解答如下图所示:
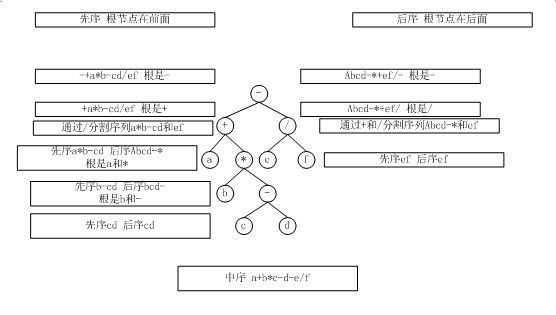
上述第17题,解答如下图所示:

18、甲包8个红球 2个蓝球,乙包2个红球 8个蓝球。抛硬币决定从哪个包取球,取了11次,7红4蓝。注,每次取后还放进去,只抛一次硬币。问选的是甲包的概率?
点评:
贝叶斯公式 + 全概率公式作答(参看链接:http://www.doc88.com/p-132711202556.html)。具体解答如下图所示:

注:上述第15~18的解答全部来自读者Lei Lei来信给出的解答,他的博客地址是:http://blog.csdn.net/nwpulei,特此感谢。有任何问题,欢迎随时讨论&指正,同时,更欢迎其他朋友也一起来做这些题目(你的答案一经选用,我可以根据你的要求,贴出你的个人主页或微博地址或博客地址)。
19、已知一个n个元素的数组,第i个元素在排序后的位置在[i-k,i+k]区间,k<<n .让你设计一个算法对数组排序,要求时间复杂度最小,O (nlogn)不得分,O(nk)得2分,如下图所示:

读者twtsa毛遂自荐,这是他给出的上述第19~20题的个人题解:http://blog.csdn.net/twtsa/article/details/8055143。有任何问题,欢迎随时讨论&指正。 - 10月10日,暴风影音笔试:
都是非常基础的题目,这是其中一道:一个整数转换成二进制后,问里面有多少个1。 - 10月10日,2013亚马逊在线笔试题目
题目及参考答案请见这:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26750075-id-3370694.html。(感谢读者freeloki来信提供)。 -
10月10日人人网面试题
第一面:
1、(1)++i 和 i++,那个效率高?
(2)++++i,i++++,哪个是合法的?
(3)实现int型的++i 和 i++操作。
2、一段程序,求输出。(考察静态变量和模版类)3、(1)实现二进制转十进制。-
int g = 0; template<typename T> class B { public: int static fun() { static int value = ++g; return value; } }; int main() { cout << B<int>::fun() << endl; cout << B<char>::fun() << endl; cout << B<float>::fun() << endl; cout << B<int>::fun() << endl; cout << B<long>::fun() << endl; return 0; }
(2)如果有下面这种能直接求二进制转十进制的代码,是怎么实现的?
binary<1>::value; // 结果为1
binary<11>::value; // 结果为3
4、volatile、explicit、mutable表示的含义。
5、求整形数组的一个子数组,使得该子数组所有元素的和的绝对值最大。
6、(1)写求单链表是否有环的算法。
(2)如果有环,如何找出环的第一个结点。
7、实现单例模式。
二面:
1、一个文本,一万行,每行一个词,统计出现频率最高的前10个词(词的平均长度为Len)。并分析时间复杂度。
2、求数组中最长递增子序列。 -
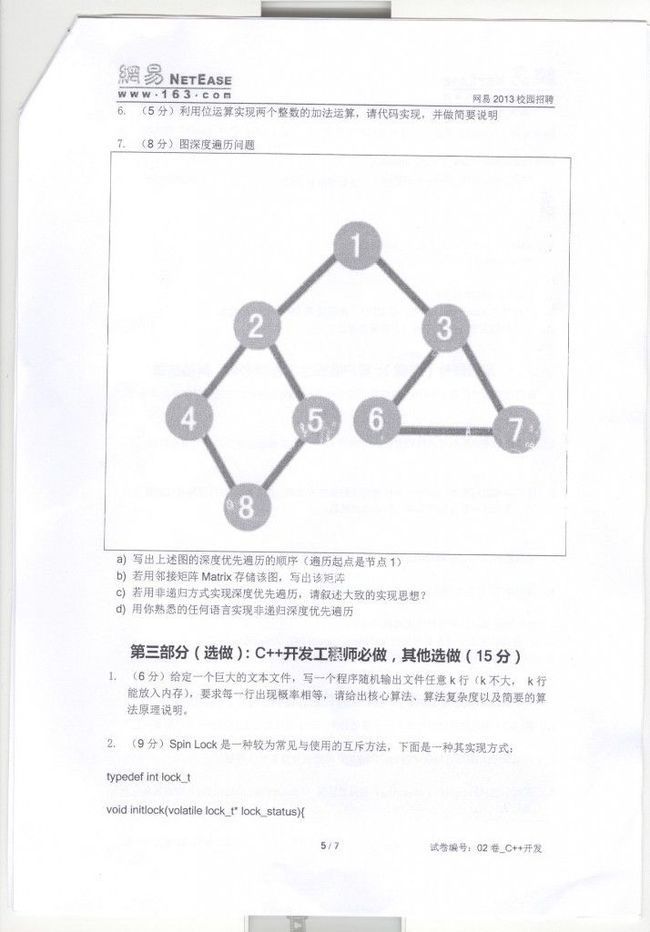
- 10月10日,网易2013校园招聘全套笔试题:






- 10月10日,网易,数据挖掘工程师:
1,简述你对数据与处理的认识;
2,简述你对中文分词的理解,说明主要难点和常用算法;
3,常见的分类算法有哪些;
4,简述K-MEANS算法;
5,设计一个智能的商品推荐系统;
6,简述你对观点挖掘的认识。
点评:其它题目与上述第56题第一部分(http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/8060917)所述相同。 - 10月11日,阿里巴巴笔试部分题目:
1. 甲乙两个人上街,捡到一张10块钱的购物卡,两人就想出一个办法来分配这张卡。两个分别将自己出的价格写在纸上,然后看谁出的价高就给谁,并且那个出价高的人要把出的钱给对方。现在甲有6块钱,乙有8块钱。问谁获得的钱多。(多选)
A 甲多 B 乙多 C 一样多 D 有可能出现有人赔钱的情况
2. 有一个怪物流落到一个荒岛上,荒岛上有n条鳄鱼。每条鳄鱼都有实力单独吃掉怪物。但是吃掉怪物是有风险的,会造成体力值下降,然后会有可能被掉其他鳄鱼吃。问,最后那个怪物是危险的还是安全的?
3. 算法题:
A[i]是一个有序递增数组,其中所有的数字都不相等,请设计一种算法,求出其中所有的A[i]=i的数字并分析时间复杂度,不分析复杂度不得分。
4. 大题
你在浏览器中输入网址:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v,按下回车键后,会发生什么事情,请一一描述(20分)。包括浏览器,网络,服务器等等发生的事情,及各项关键技术。
点评:这样的题考过很多次,参考答案如下图所示:
- 10月11日,华为一面:
1、将一个普通的二叉树转换为二叉排序树?
2、随便写一个排序算法。 - 10月11日,完美笔试题:
1.为什么析构函数应该设为虚函数
2.大数字乘法问题
3.双向链表模拟队列操作push pop find
4.求 a/3 不能用除法
5.多核下多线程同步问题,使用锁应该注意什么
6.三个宝箱有一个里面有珠宝,现在拿第一宝箱,然后打开第二个宝箱后发现没有珠宝,用概率论原理解释为什么现在拿第三个宝箱,里面有珠宝的概率比拿第一个宝箱高。 - 10月11日,搜狐畅游旗下第七大道笔试题:
算法题
1.一个数是否是另一个数的平方。
2.N进制换成M进制
3.设计一个大数乘法
综合题
1.N个数,出栈有几种情况
2.进程死锁原因及条件. - 腾迅一个非常有意思的面试题:
N个数组,每个数组中的元素都是递增的顺序,现在要找出这N个数组中的公共元素部分,如何做? 注:不能用额外辅助空间。
点评:
讨论了半天:http://weibo.com/1580904460/z08mT0aFj,没个好的结果,发现还是上午想到的N个指针逐步向后移动,辅以二分,然后N路归并更靠谱,类似这里的第5题所述的办法:http://www.cnblogs.com/BeyondAnyTime/archive/2012/07/17/2593224.html。若读者有更好的思路,欢迎赐教。 - 10月12日,迅雷2013校园招聘「广州站」C++方向全套笔试题
(注:若照片看不清楚,请右键点击“图片另存为”到桌面,然后再打开图片,便可以随意放大缩小图片拉)






- 10月12日晚,微策略北京站笔试题(根据读者回忆整理):
1、魔术定义:整数N以基数B表示,如21以基数3表示为210,那么21是基数3的一个魔术,210三个位的值都不一样。设计函数,输入参数N和B(B介于2到10之间),返回是否为魔术。
2、斐波那契数列的变形,一个贼每次上楼梯1或者2,一个27层的楼梯需要多少种方法,记住贼不能经过5,8,13层,否则会被抓住。点评:还是可以用斐波那契来推算,f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2),只是f(5) f(8) f(13) = 0,http://www.51nod.com/answer/index.html#!answerId=596。
3、给定一棵树根节点,每个节点里面的值都不相同,查找iKEY的节点,并使用一个给定的节点将查找到的节点替换掉。节点内有两个孩子节点和一个父节点。
4、字符串数组S,全是0和1表示的,字符串都是n位的,且1的个数小于等于l,返回index的字符串。(这个比较奇怪,如果S中字符串都是符合1的个数小于等于l,则直接可以得到index的字符串啊,难道是要先求这个字符串数组?那就比较麻烦了)
5、降序排列的数组,找到其中两个不同的值,其乘积最接近一个给定的值M,感觉和加法求和很类似。
6、序列123...N,N介于3和9之间,在其中加入+-或者空格,使其和为0,
如123456 1-2 3-4 5+6 7 等价于1-23-45+67=0。请问,如何获得所有组合? - 10月12日,大众点评笔试一题:

- 读者私信,昨日(12号)美团的笔试题:
1、一副扑克52张(去了大小王),洗牌,求最顶一张和最底一张是A的概率
2、知道两个数的异或以及这两个数的和,问可以确定这对数吗?为什么?给出推理过程
3、A、B两个文件各存50亿个商品名称,每个50个字符,求这两个文件中相同名称的商品名,内存限制4G(看过您的《教你如何迅速秒杀掉:99%的海量数据处理面试题》中的第6题,无压力,非常感谢)
4、给一个二叉树的后序遍历和中序遍历,画出这颗二叉树,写出前序遍历结果,并给出推理过程
5、一个有序数组array,给一个数x,可重复,求这个数在array中出现的区间,算法思路和代码实现
6、一个映射文件中存了ip地址区间和城市名称,形如:
10.0.0.1 10.0.1.27 北京
10.0.2.1 10.0.2.27 北京
201.0.1.12 201.0.2.124 上海
给你一个ip地址,获取城市名称,要求:1)给出算法思想 2)代码实现。 - 10月12日晚,360 2013校招部分笔试题(注:图中所标答案不代表正确答案):

int main()
{
fork()||fork();
return 0;
}
问,上述程序创建了几个进程?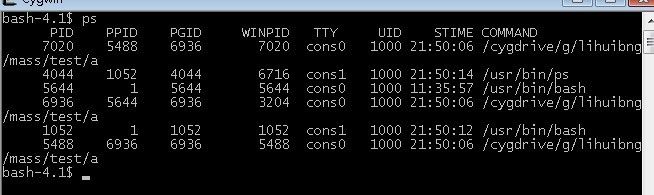
编程题、传教士人数m,野人c,m≥c,开始都在岸左边,
①船只能载两人,传教士和野人都会划船,当然必须有人划船
②两岸边保证野人人数不能大于传教士人数
把所有人都送过河,设计一方案,要求编程实现。
点评:
读者huangxy10于本文评论下第169楼提供了一种解法:http://blog.csdn.net/huangxy10/article/details/8066408。再附一个讨论帖子:http://topic.csdn.net/u/20121012/22/70226713-A669-4F03-80B7-BFFF12A330EB.html。 - 10月13日,百度2013校招北京站笔试题:
一、简答题(30分)
1、用简单语句描述数据库操作的步骤
2、写出TCP/IP的四层结构
3、什么是MVC结构,并描述各层结构的作用
二、算法与程序设计题(40分)
1、字母a-z,数字0-9,现需要其中任意3个作为密码,请输出所有可能组合。(伪码\C\C++\JAVA)(10分)
点评:如本文评论下第198楼所述,即从26+10=36个不同字符中选取3个字符的组合,用递归及非递归两种方法,可以参照以下链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/wumuzi520/article/details/8087501(从n个数中选取m个数的组合数),主要代码如下:
2、实现字符串反转函数(10分)-
//copyright @wumuzi520 //从n个数中选取m个数的组合数 void Combination(int arr[], int nLen, int m, int out[], int outLen) { if(m == 0) { for (int j = 0; j < outLen; j++) { cout << out[j] << "\t"; } cout << endl; return; } for (int i = nLen; i >= m; --i) //从后往前依次选定一个 { out[m-1] = arr[i-1]; //选定一个后 Combination(arr,i-1,m-1,out,outLen); // 从前i-1个里面选取m-1个进行递归 } } void PrintCombination(int arr[], int nLen, int m) { int* out = new int[m]; Combination(arr,nLen,m,out,m); delete [] out; }
3、给定字符函数a、插入 b、删除 c、替换
例如字符串A=acegf,字符串B=adef,最少需要2步操作将A转换为B,
即第一步将c替换为d,第二步将g删除;
(1)请问将字符串A=gumbo转换为字符串B=gambol,最少需要几步操作,列出如何操作(2分)
(2)任意字符串A和字符串B,如何计算最小操作次数,计算思路,并给出递归公式(3分)
(3)实现代码(注意代码风格与效率)(15分)
点评:请参看上文第38题第4小题:9月26日,百度一二面试题。
三、系统设计题(30分)
RSA SecurID安全系统
应用场景:这是一种用户登录验证手段,例如银行登录系统,这个设备显示6位数字,每60秒变一次,再经过服务器认证,通过则允许登录。问How to design this system?
1)系统设计思路?服务器端为何能有效认证动态密码的正确性?
2)如果是千万量级永固,给出系统设计图示或说明,要求子功能模块划分清晰,给出关键的数据结构或数据库表结构。
考虑用户量级的影响和扩展性,用户密码的随机性等,如果设计系统以支持这几个因素.
3)系统算法升级时,服务器端和设备端可能都要有所修改,如何设计系统,能够使得升级过程(包括可能的设备替换或重设)尽量平滑? -
- 10月13日,百度移动开发笔试题
一、 1、什么是RISC;
2、通过后序、中xu求前序
3、重写与重载的区别
二、
1、反转链表
2、判断两个数组中是否有相同的数字
3、1000瓶水中找 出有毒的那瓶,毒性一周后发作,一周内最少需要多少只老鼠
三、系统设计 email客户端,支持多账户和pop3等协议
1、请写出可能的至少5个用例;
2、使用sqlite存储帐户、已收信息、已发信息、附件、草稿,请设计合理的表结构
3、pop3等协议等接口已完成,请给出email客户端的模块设计图。 - 10月13日,人搜2013 校招北京站部分笔试题(读者回忆+照片):


1,二重歌德巴赫猜想
所有大于等于6的偶数都可以表示成两个(奇)素数之和。
给定1-10000,找到可以用两个素数之和表示每一个偶数的两个素数,然后输出这两个素数,如果有多对,则只需要输出其中之一对即可。
要求:复杂度较低,代码可运行。
2,城市遍历
某人家住北京,想去青海玩,可能会经过许多城市,
现已知地图上的城市连接,求经过M个城市到达青海的路线种类。
城市可以多次到达的,比如去了天津又回到北京,再去天津,即为3次。北京出发不算1次。
输入:
N M S
N为城市总数,北京为0,青海为N-1;
M为经过的城市数目;
S为之后有S行
i j
表示第i个城市可以去第j个城市,是有方向的。
输出:
N
表示路径种类。
3,分布式系统设计
有1000亿个URL,其中大约有5亿个site。每天的更新大约2%-5%。设计一个系统来解决存储和计算下面三个问题。可用分布式系统。
URL:http///site[port]*(key==?;key==?)
site:[*].domain
URL:http://www.baidu.com/baidu?word=%E5%AE%A3%E8%AE%B2%E4%BC%9A&ie=utf-8
site::www.baidu.com
domain::baidu.com
key=baidu?word
a>检测每个域名下的site数目,以及每个site下的URL数目,输出site变化超过一定阈值的域名以及URL数目变化剧烈的site。找出泛域。
泛域:该域下的site数目超过500个,且每个site下的URL数目超过100个。
b>提取URL中key的特征,对site进行聚类;
(每个site下面有多个URL,这些URL中有许多key,可以获取这些key作为site的特征,对site进行聚类,不过这应该是多机器联合的)
c>对于给定的domain,输出该domain下的所有site。 - 10月13日,创新工场笔试:
第一个,快排最坏情况下是O(n^2),问如何优化?
第二个,怎么样求一个数的根号
点评:你是不是会想到一系列有关数学的东西,什么泰勒级数啊,什么牛顿法啊,具体编程可以如下代码所示:链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=660。-
static void Main(string[] args) { double k = 5; double n = 2, m = k; while (n != m) { m = k / n; n = (m + n) / 2; } }
第三个,4个数字,用四则元素求结果能否为24。写出这个判断的函数。 -
- 10月14日,思科网讯旗下公司笔试题:
1、海量数据中,寻找最小的k个数。
请分情况,给出时间复杂度最优,或空间复杂度最优的方案,或时间复杂度/空间复杂度综合考虑的可行方案。
点评:参见:第三章、寻找最小的k个数。
2、有两座桥,其中一座可能是坏的,两个守桥人分别守在这两座桥的入口。他们一个总是会说实话,一个总是说谎话。
你现在需要找出哪一座桥可以通过。
1),请问最少需要问守桥人几个问题,可以找出可以通过的桥?如何问?
2),请编程解决。 - 10月14日,腾讯杭州站笔试题:
1、http服务器会在用户访问某一个文件的时候,记录下该文件被访问的日志,网 站管理员都会去统计每天每文件被访问的次数。写一个小程序,来遍历整个日志 文件,计算出每个文件被访问的访问次数
1)请问这个管理员设计这个算法
2)该网站管理员后来加入腾讯从事运维工作,在腾讯,单台http服务器不够用的 ,同样的内容,会分布在全国各地上百台服务器上。每台服务器上的日志数量, 都是之前的10倍之多,每天服务器的性能更好,之前他用的是单核cpu,现在用的 是8核的,管理员发现在这种的海量的分布式服务器,基本没法使用了,请重新设计一个算法。
2、腾讯的qq游戏当中,最多人玩的游戏就是斗地主了,每一句游戏开始时,服务 器端都要洗牌,以保证发牌的时每个人拿的牌都是随机的,假设用1-54来表示54 张不同的拍,请你写一个洗牌算法,保证54张牌能随机打散!
选择题:
1)、下列RAID技术无法提高可靠性的是:
A:RAID0 B:RAID1 C:RAID10 D:RAID5
2)、长度为1的线段,随机在其上选择两点,将线段分为三段,问这3个字段能组成一 个三角形的概率是:
1/2,1/3,1/4,1/8
3)、下面那种标记的包不会在三次握手的过程中出现()
A:SYN B:PSH C:ACK D:RST - 10月14日,搜狗2013 校招笔试题:
1、有n*n个格子,每个格子里有正数或者0,从最左上角往最右下角走,只能向下和向右,一共走两次(即从左上角走到右下角走两趟),把所有经过的格子的数加起来,求最大值SUM,且两次如果经过同一个格子,则最后总和SUM中该格子的计数只加一次。
点评:@西芹_new,一共搜(2n-2)步,每一步有四种走法,考虑不相交等条件可以剪去很多枝,代码如下「http://blog.csdn.net/huangxy10/article/details/8071242」:
@绿色夹克衫:跟这个问题:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=487 ,是同一个问题。-
西芹_new<[email protected]> 0:55:40 // 10_15.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; #define N 5 int map[5][5]={ {2,0,8,0,2}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,3,2,0,0}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {2,0,8,0,2}}; int sumMax=0; int p1x=0; int p1y=0; int p2x=0; int p2y=0; int curMax=0; void dfs( int index){ if( index == 2*N-2){ if( curMax>sumMax) sumMax = curMax; return; } if( !(p1x==0 && p1y==0) && !(p2x==N-1 && p2y==N-1)) { if( p1x>= p2x && p1y >= p2y ) return; } //right right if( p1x+1<N && p2x+1<N ){ p1x++;p2x++; int sum = map[p1x][p1y]+map[p2x][p2y]; curMax += sum; dfs(index+1); curMax -= sum; p1x--;p2x--; } //down down if( p1y+1<N && p2y+1<N ){ p1y++;p2y++; int sum = map[p1x][p1y]+map[p2x][p2y]; curMax += sum; dfs(index+1); curMax -= sum; p1y--;p2y--; } //rd if( p1x+1<N && p2y+1<N ) { p1x++;p2y++; int sum = map[p1x][p1y]+map[p2x][p2y]; curMax += sum; dfs(index+1); curMax -= sum; p1x--;p2y--; } //dr if( p1y+1<N && p2x+1<N ) { p1y++;p2x++; int sum = map[p1x][p1y]+map[p2x][p2y]; curMax += sum; dfs(index+1); curMax -= sum; p1y--;p2x--; } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { curMax = map[0][0]; dfs(0); cout <<sumMax-map[N-1][N-1]<<endl; return 0; }
1、用动态规划可以求解,大概思路就是同时DP 2次所走的状态。先来分析一下这个问题,为了方便讨论,先对矩阵做一个编号,且以5*5的矩阵为例(给这个矩阵起个名字叫M1):M10 1 2 3 41 2 3 4 52 3 4 5 63 4 5 6 74 5 6 7 8从左上(0)走到右下(8)共需要走8步(2*5-2)。为了方便讨论,我们设所走的步数为s。因为限定了只能向右和向下走,因此无论如何走,经过8步后(s = 8)都将走到右下。而DP的状态也是依据所走的步数来记录的。再来分析一下经过其他s步后所处的位置,根据上面的讨论,可以知道经过8步后,一定处于右下角(8),那么经过5步后(s = 5),肯定会处于编号为5的位置。3步后肯定处于编号为3的位置......。s = 4的时候,处于编号为4的位置,对于方格中,共有5(相当于n)个不同的位置,也是所有编号中最多的。推广来说 n*n的方格,总共需要走2n - 2步,当s = n - 1时,编号为n个,也是编号最多的。如果用DP[s,i,j]来记录2次所走的状态获得的最大值,其中s表示走s步,i表示s步后第1次走所处的位置,j表示s步后第2次走所处的位置。为了方便讨论,再对矩阵做一个编号(给这个矩阵起个名字叫M2):2、N个整数(数的大小为0-255)的序列,把它们加密为K个整数(数的大小为0-255).再将K个整数顺序随机打乱,使得可以从这乱序的K个整数中解码出原序列。设计加密解密算法,且要求K<=15*N.M20 0 0 0 01 1 1 1 12 2 2 2 23 3 3 3 34 4 4 4 4M10 1 2 3 41 2 3 4 52 3 4 5 63 4 5 6 74 5 6 7 8经过6步后,肯定处于M1中编号为6的位置。共有3个编号为6的,分别对应M2中的2 3 4。假设第1次经过6步走到了M2中的2,第2次经过6步走到了M2中的4,DP[s,i,j] 则对应 DP[6,2,4]。由于s = 2n - 2,0 <= i<= <= j <= n,所以这个DP共有O(n^3)个状态。M10 1 2 3 41 2 3 4 52 3 4 5 63 4 5 6 74 5 6 7 8再来分析一下状态转移,以DP[6,2,3]为例( 就是上面M1中加粗的部分),可以到达DP[6,2,3]的状态包括DP[5,1,2],DP[5,1,3],DP[5,2,2],DP[5,2,3],加粗表示位置DP[5,1,2] DP[5,1,3] DP[5,2,2] DP[5,2,3] ( 加红表示要达到的状态DP[6,2,3])0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6
3 4 5 6 7 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 5 6 7
4 5 6 7 8 4 5 6 7 8 4 5 6 7 8 4 5 6 7 8因此, DP[6,2,3] = Max(DP[5,1,2] ,DP[5,1,3],DP[5,2,2],DP[5,2,3]) + 6,2和6,3格子中对应的数值 (式一)2、上面(式一)所示的这个递推看起来没有涉及:“如果两次经过同一个格子,那么该数只加一次的这个条件”,讨论这个条件需要换一个例子,以DP[6,2,2]为例。DP[6,2,2]可以由DP[5,1,1],DP[5,1,2],DP[5,2,2]到达,但由于i = j,也就是2次走到同一个格子,那么数值只能加1次。
所以 当i = j时,DP[6,2,2] = Max(DP[5,1,1],DP[5,1,2],DP[5,2,2]) + 6,2格子中对应的数值 (式二)
3、故,综合上述的(式一),(式二)最后的递推式就是if(i != j)DP[s, i ,j] = Max(DP[s - 1, i - 1, j - 1], DP[s - 1, i - 1, j], DP[s - 1, i, j - 1], DP[s - 1, i, j]) + W[s,i] + W[s,j]elseDP[s, i ,j] = Max(DP[s - 1, i - 1, j - 1], DP[s - 1, i - 1, j], DP[s - 1, i, j]) + W[s,i]其中W[s,i]表示经过s步后,处于i位置,位置i对应的方格中的数字。复杂度分析:状态转移最多需要统计4个变量的情况,看做是O(1)的。共有O(n^3)个状态,所以总的时间复杂度是O(n^3)的。空间上可以利用滚动数组优化,由于每一步的递推只跟上1步的情况有关,因此可以循环利用数组,将空间复杂度降为O(n^2)。OK,上述这个方法可能不算最优解法,但相对比较容易想一些。希望大家能够提供更好的想法,也欢迎大家补充程序。链接: http://www.51nod.com/answer/index.html#!answerId=598。
如果是:
1,N<=16,要求K<=16*N.
2,N<=16,要求K<=10*N.
3,N<=64,要求K<=15*N.
点评:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=659。 -
- 人人网面试,只面一道题,要求5分钟出思路,10分钟出代码
面试题是:
两个无序数组分别叫A和B,长度分别是m和n,求中位数,要求时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(1) 。 -
10月15日,网新恒天笔试题
1.不要使用库函数,写出void *memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t count),其中dst是目标地址,src是源地址。
点评:下面是nwpulei写的代码:-
void* memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t count) { assert(dst != NULL); assert(src != NULL); unsigned char *pdst = (unsigned char *)dst; const unsigned char *psrc = (const unsigned char *)src; assert(!(psrc<=pdst && pdst<psrc+count)); assert(!(pdst<=psrc && psrc<pdst+count)); while(count--) { *pdst = *psrc; pdst++; psrc++; } return dst; }
链接:http://blog.csdn.net/nwpulei/article/details/8090136。
2.给定一个字符串,统计一下哪个字符出现次数最大。
3.我们不知道Object类型的变量里面会出现什么内容,请写个函数把Object类型转换为int类型。 -
- 10月15日,Google 2013 校招全套笔试题:





1.写一个函数,输出前N个素数,函数原型:void print_prime(int N); 不需要考虑整数的溢出问题,也不需要使用大数处理算法。
2.长度为N的数组乱序存放着0带N-1.现在只能进行0与其他数的swap操作,请设计并实现排序,必须通过交换实现排序。
3.给定一个源串和目标串,能够对源串进行如下操作:
1.在给定位置上插入一个字符
2.替换任意字符
3.删除任意字符
写一个程序,返回最小操作数,使得对源串进行这些操作后等于目标串,源串和目标串的长度都小于2000。
点评:
1、此题反复出现,如上文第38题第4小题9月26日百度一二面试题,10月9日腾讯面试题第1小题,及上面第69题10月13日百度2013校招北京站笔试题第二大道题第3小题,同时,还可以看下这个链接:http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=662。2、补充:上述问题类似于编程之美上的下述一题「以下内容摘自编程之美第3.3节」:- //动态规划:
- //f[i,j]表示s[0...i]与t[0...j]的最小编辑距离。
- f[i,j] = min { f[i-1,j]+1, f[i,j-1]+1, f[i-1,j-1]+(s[i]==t[j]?0:1) }
- //分别表示:添加1个,删除1个,替换1个(相同就不用替换)。
许多程序会大量使用字符串。对于不同的字符串,我们希望能够有办法判断其相似程度。我们定义了一套操作方法来把两个不相同的字符串变得相同,具体的操作方法为:
1.修改一个字符(如把“a”替换为“b”);
2.增加一个字符(如把“abdd ”变为“aebdd ”);
3.删除一个字符(如把“travelling”变为“traveling”)。
比如,对于“abcdefg”和“abcdef ”两个字符串来说,我们认为可以通过增加/减少一个“g”的方式来达到目的。上面的两种方案,都仅需要一次操作。把这个操作所需要的次数定义为两个字符串 的距离,而相似度等于“距离+1”的倒数。也就是说,“abcdefg”和“abcdef”的距离为1,相似度为1 / 2 = 0.5。
给定任意两个字符串,你是否能写出一个算法来计算出它们的相似度呢?
这样,很快就可以完成一个递归程序,如下所示:-
Int CalculateStringDistance(string strA, int pABegin, int pAEnd, string strB, int pBBegin, int pBEnd) { if(pABegin > pAEnd) { if(pBBegin > pBEnd) return 0; else return pBEnd – pBBegin + 1; } if(pBBegin > pBEnd) { if(pABegin > pAEnd) return 0; else return pAEnd – pABegin + 1; } if(strA[pABegin] == strB[pBBegin]) { return CalculateStringDistance(strA, pABegin + 1, pAEnd, strB, pBBegin + 1, pBEnd); } else { int t1 = CalculateStringDistance(strA, pABegin, pAEnd, strB, pBBegin + 1, pBEnd); int t2 = CalculateStringDistance(strA, pABegin + 1, pAEnd, strB,pBBegin, pBEnd); int t3 = CalculateStringDistance(strA, pABegin + 1, pAEnd, strB,pBBegin + 1, pBEnd); return minValue(t1,t2,t3) + 1; } }
上面的递归程序,有什么地方需要改进呢?在递归的过程中,有些数据被重复计算了。比如,如果开始我们调用CalculateStringDistance(strA,1, 2, strB, 1, 2),下图是部分展开的递归调用。
可以看到,圈中的两个子问题被重复计算了。为了避免这种不必要的重复计算,可以把子问题计算后的解存储起来。如何修改递归程序呢?还是DP!请看此链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/yujunyong/articles/2004724.html。
BTW,群友braveheart89也整理了这套笔试题:http://blog.csdn.net/braveheart89/article/details/8074657。
3、此外,关于这个“编辑距离”问题的应用:搜索引擎关键字查询中拼写错误的提示,可以看下这篇文章:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2012/10/spelling_corrector.html。「关于什么是“编辑距离”:一个快速、高效的Levenshtein算法实现,这个是计算两个字符串的算法,Levenshtein距离又称为“编辑距离”,是指两个字符串之间,由一个转换成另一个所需的最少编辑操作次数。当然,次数越小越相似。这里有一个BT树的数据结构,挺有意思的:http://blog.notdot.net/2007/4/Damn-Cool-Algorithms-Part-1-BK-Trees」
最后,Lucene中也有这个算法的实现(我想,一般的搜索引擎一般都应该会有此项拼写错误检查功能的实现):http://www.bjwilly.com/archives/395.html。
4、扩展:面试官还可以继续问下去:那么,请问,如何设计一个比较两篇文章相似性的算法?(这个问题的讨论可以看看这里:http://t.cn/zl82CAH) - 10月16日,UC的笔试题目:
1、有个长度为2n的数组{a1,a2,a3,...,an,b1,b2,b3,...,bn},希望排序后{a1,b1,a2,b2,....,an,bn},要求时间复杂度o(n),空间复杂度0(1)。
点评:@绿色夹克衫:完美洗牌问题「关于洗牌算法:http://blog.csdn.net/gogdizzy/article/details/4917488」,解决这个问题的关键在于如何解决置换群中的环。方法是微软员工那篇论文中写的:http://user.qzone.qq.com/414353346/blog/1243343118#!app=2&via=QZ.HashRefresh&pos=1243343118,大概意思是,用3的幂来弄:链接:1,http://www.51nod.com/question/index.html#!questionId=278;2、这里也有一参考答案:http://blog.csdn.net/yuan8080/article/details/5705567。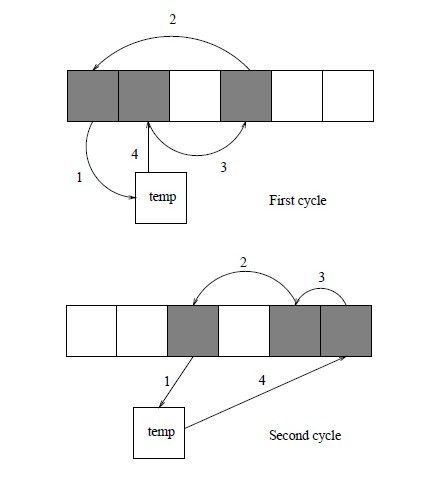
@方程:
- int index = arr.length / 2;
- int temp = arr[index];
- while(index != 1){
- int tempIndex = (index + (index % 2) * (arr.length - 1)) / 2;
- arr[index] = arr[tempIndex];
- index = tempIndex;
- }
- arr[1] = temp;
- 10月17日,创新工场电话面试:
1,如何删除一个搜索二叉树的结点;
2,如何找到一个数组中的两个数,他们的和为0;
3,如何判断两条二维平面上的线段是否相交。 - 网易2013 校招笔试题:



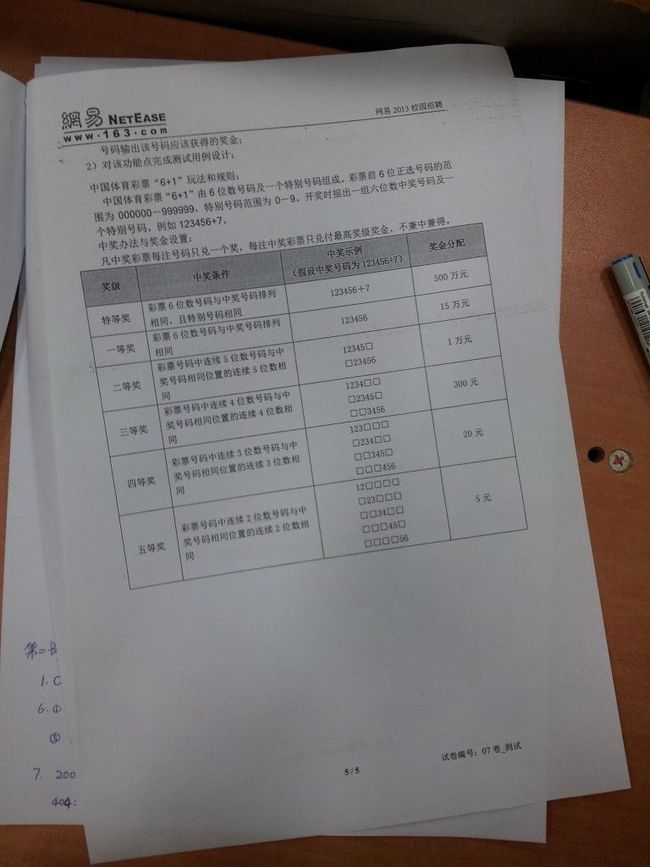
- 10月19日,百度研发三面题:
百度地图里的路线查询:给定两个站点,如果没有直达的路线,如何找到换乘次数最少的路线?
点评:蚂蚁算法?还是广搜,或A*算法? - 10月20日,baidu广州站笔试算法题:
1. 有一箱苹果,3个一包还剩2个,5个一包还剩3个,7个一包还剩2个,求N个满足以上条件的苹果个数。
2. 用递归算法写一个函数,求字符串最长连续字符的长度,比如aaaabbcc的长度为4,aabb的长度为2,ab的长度为1。
3. 假设一个大小为100亿个数据的数组,该数组是从小到大排好序的,现在该数组分成若干段,每个段的数据长度小于20「也就是说:题目并没有说每段数据的size 相同,只是说每个段的 size < 20 而已」,然后将每段的数据进行乱序(即:段内数据乱序),形成一个新数组。请写一个算法,将所有数据从小到大进行排序,并说明时间复杂度。
点评:
思路一、如@四万万网友所说:维护一个20个元素大小的小根堆,然后排序,每次pop取出小根堆上最小的一个元素(log20),然后继续遍历原始数组后续的(N-20)个元素,总共pop (N-20)次20个元素小根堆的log20的调整操作。
思路二@飘零虾、如果原数组是a[],那么a[i+20]>=a[i]恒成立(因为每段乱序区间都是小于20的,那么向后取20,必然是更大的区间的元素)。
第一个数组:取第0、20、40、60、80...
第二个数组:取第1、21、41、61、81...
...
第20个数组:取第19、39、59、79... (上述每个数组100亿/20 个元素)
共计20个数组,每个数组100亿/20 个元素「注:这5亿个元素已经有序,不需要再排序」,且这20个数组都是有序的,然后对这20个数组进行归并,每次归并20个元素。时间复杂度跟上述思路一一样,也是N*logK(N=100亿,K=20)。
此外,读者@木叶漂舟直接按每组20个排序,将排好的20个与前20个调整拼接,调整两端接头处的元素,写了个简单地demo: http://t.cn/zlELAzs。不过,复杂度有点高,目前来说中规中矩的思路还是如上文中@四万万网友 所说思路一「@张玮-marihees按照思路一:http://weibo.com/1580904460/z1v5jxJ9P,写了一份代码:http://codepad.org/T5jIUFPG,欢迎查看」。 - 10月21日,完美笔试算法题「同时,祝自己生日快乐!」:
1. 请设计一个算法,当给出在2D平面中某个三角形ABC的顶点坐标时能输出位于该三角形内的一个随机点(需要满足三角形内均匀随机),无需写出实现,只要能清楚地描述算法即可。
2. 请自己用双向链表实现一个队列,队列里节点内存的值为int,要求实现入队,出队和查找指定节点的三个功能。
3. 实现一个无符号任意大整数的类,实现两个无符号超大整数的乘法。 - 10月22日,CSR掌微电子笔试题:
5.给定两个字符串s1和s2,要求判定s2是否能够被通过s1做循环移位(rotate)得到字符串包含。例如,S1=AABCD和s2=CDAA,返回true;给定s1=ABCD和s2=ACBD,返回false。用伪代码或流程图叙述解法。
点评:老题,类似:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6322882。其余题目见:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3eb9f72801016llt.html。 - 10月23日,去哪儿网笔试:
1.将IPV4转换成整数
2.定义一个栈的数据结构,实现min函数,要求push,pop,min时间复杂度是0(1);
点评:这是2010年整理的微软100题的第2题,http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6057286,答案见此文第2题:http://blog.csdn.net/v_JULY_v/article/details/6126406。
3.数组a[n]里存有1到n的所有树,除了一个数removed,找出这个missing的树。
4.找出字符串中的最长子串,要求子串不含重复字符,并分析时间复杂度。 -
10月28日,微软三面题「顺祝,老妈明天生日快乐!」:
找一个点集中与给定点距离最近的点,同时,给定的二维点集都是固定的,查询可能有很多次,时间复杂度O(n)无法接受,请设计数据结构和相应的算法。
类似于@陈利人:附近地点搜索,就是搜索用户附近有哪些地点。随着GPS和带有GPS功能的移动设备的普及,附近地点搜索也变得炙手可热。在庞大的地理数 据库中搜索地点,索引是很重要的。但是,我们的需求是搜索附近地点,例如,坐标(39.91, 116.37)附近500米内有什么餐馆,那么让你来设计,该怎么做?
点评:R树「从B树、B+树、B*树谈到R 树」还是KD树「从K近邻算法、距离度量谈到KD树、SIFT+BBF算法」? - 11月10日,百度笔试题:
1、20个排序好的数组,每个数组500个数,按照降序排序好的,让找出500个最大的数。
2、一在线推送服务,同时为10万个用户提供服务,对于每个用户服务从10万首歌的曲库中为他们随机选择一首,同一用户不能推送重复的,设计方案,内存尽可能小,写出数据结构与算法。