ICASSP 2024丨上海交通大学跨媒体语言智能实验室14篇入选论文分享
近日,2024年IEEE声学、语音与信号处理国际会议(2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2024)发布录用通知,上海交通大学跨媒体语言智能实验室有14篇论文被录用。
论文方向涵盖语音识别、语音合成、音色转换、情感识别、音频生成、关键词检测、数字人生成、口语语义理解、对话状态跟踪、声音事件检测等。
01 A BiRGAT Model for Multi-intent Spoken Language Understanding with Hierarchical Semantic Frames
作者:许洪深,曹瑞升,朱苏,蒋胜,张晗翀,陈露,俞凯
简介:先前关于口语语言理解(SLU)的研究主要集中在单一意图的情境下,其中每个输入的话语仅包含一个用户意图。这种配置显著限制了用户话语的表面形式和输出语义的容量。在这项工作中,我们首先提出了一个来自实际车载对话系统(称为MIVS)的多意图数据集。目标语义框架搭建了多层次结构组织,以解决多意图情况下的对齐和分配问题。此外,我们设计了一个BiRGAT模型来编码本体条目的层次结构,其骨干是一个双重关系图注意网络。结合三路指针生成器解码器,我们的方法在很大程度上优于传统的序列标记和基于分类的方案。在迁移学习设置中进行的消融研究进一步揭示了当前模型在多意图情况下的较差泛化能力。
项目仓库:https://github.com/X-LANCE/MIVS_BIRGAT
02 A Detailed Audio-Text Data Simulation Pipeline using Single-Event Sounds
作者:徐薛楠,徐晓航,谢泽宇,张平越,吴梦玥,俞凯
简介:Recently, there has been an increasing focus on audio-text cross-modal learning. However, most of the existing audio-text datasets contain only simple descriptions of sound events. Compared with classification labels, the advantages of such descriptions are significantly limited. In this paper, we first analyze the detailed information that human descriptions of audio may contain beyond sound event labels. Based on the analysis, we propose an automatic pipeline for curating audio-text pairs with rich details. Leveraging the property that sounds can be mixed and concatenated in the time domain, we control details in four aspects: temporal relationship, loudness, speaker identity, and occurrence number, in simulating audio mixtures. Corresponding details are transformed into captions by large language models. Audio-text pairs with rich details in text descriptions are thereby obtained. We validate the effectiveness of our pipeline with a small amount of simulated data, demonstrating that the simulated data enables models to learn detailed audio captioning.
03 Leveraging Speech PTM, Text LLM, and Emotional TTS for Speech Emotion Recognition
作者:马子阳,吴雯,郑之胜,郭奕玮,陈谦,张仕良,陈谐
简介:In this paper, we explored how to boost speech emotion recognition (SER) with the state-of-the-art speech pre-trained model (PTM), data2vec, text generation technique, GPT-4, and speech synthesis technique, Azure TTS. First, we investigated the representation ability of different speech self-supervised pre-trained models, and we found that data2vec has a good representation ability on the SER task. Second, we employed a powerful large language model (LLM), GPT-4, and emotional text-to-speech (TTS) model, Azure TTS, to generate emotionally congruent text and speech. We carefully designed the text prompt and dataset construction, to obtain the synthetic emotional speech data with high quality. Third, we studied different ways of data augmentation to promote the SER task with synthetic speech, including random mixing, adversarial training, transfer learning, and curriculum learning. Experiments and ablation studies on the IEMOCAP dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, compared with other data augmentation methods, and data augmentation with other synthetic data.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.10294
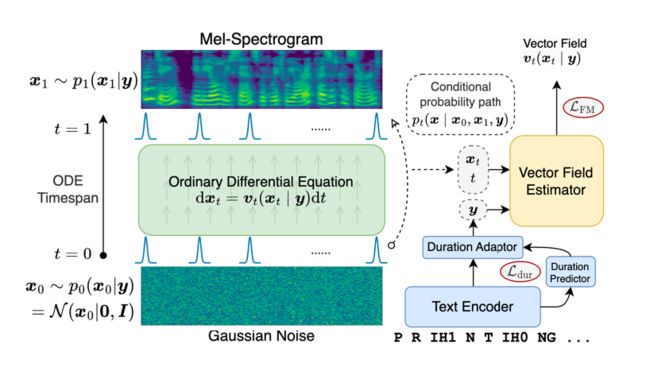
04 VoiceFlow: Efficient Text-To-Speech with Rectified Flow Matching
作者:郭奕玮,杜晨鹏,马子阳,陈谐,俞凯
简介:Although diffusion models in text-to-speech have become a popular choice due to their strong generative ability, the intrinsic complexity of sampling from diffusion models harms their efficiency. Alternatively, we propose VoiceFlow, an acoustic model that utilizes a rectified flow matching algorithm to achieve high synthesis quality with a limited number of sampling steps. VoiceFlow formulates the process of generating mel-spectrograms into an ordinary differential equation conditional on text inputs, whose vector field is then estimated. The rectified flow technique then effectively straightens its sampling trajectory for efficient synthesis. Subjective and objective evaluations on both single and multi-speaker corpora showed the superior synthesis quality of VoiceFlow compared to the diffusion counterpart. Ablation studies further verified the validity of the rectified flow technique in VoiceFlow.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.05027
项目仓库:https://github.com/X-LANCE/VoiceFlow-TTS
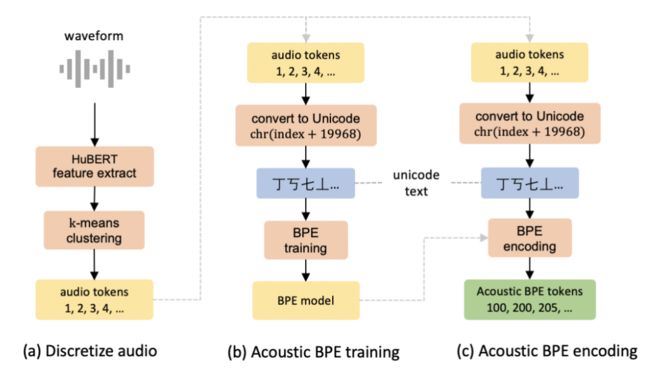
05 Acoustic BPE for Speech Generation with Discrete Tokens
作者:沈飞宇,郭奕玮,杜晨鹏,陈谐,俞凯
简介:Discrete audio tokens derived from self-supervised learning models have gained widespread usage in speech generation. However, current practice of directly utilizing audio tokens poses challenges for sequence modeling due to the length of the token sequence. Additionally, this approach places the burden on the model to establish correlations between tokens, further complicating the modeling process. To address this issue, we propose acoustic BPE which encodes frequent audio token patterns by utilizing byte-pair encoding. Acoustic BPE effectively reduces the sequence length and leverages the prior morphological information present in token sequence, which alleviates the modeling challenges of token correlation. Through comprehensive investigations on a speech language model trained with acoustic BPE, we confirm the notable advantages it offers, including faster inference and improved syntax capturing capabilities. In addition, we propose a novel rescore method to select the optimal synthetic speech among multiple candidates generated by rich-diversity TTS system. Experiments prove that rescore selection aligns closely with human preference, which highlights acoustic BPE's potential to other speech generation tasks.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.14580
06 Semantic-Enhanced Supervised Contrastive Learning
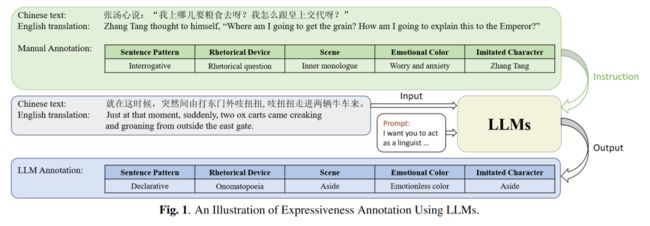
07 StoryTTS: A Highly Expressive Text-to-Speech Dataset with Rich Textual Expressiveness Annotations
作者:刘森,郭奕玮,陈谐,俞凯
简介:While acoustic expressiveness has long been studied in expressive text-to-speech (ETTS), the inherent expressiveness in text lacks sufficient attention, especially for ETTS of artistic works. In this paper, we introduce StoryTTS, a highly ETTS dataset that contains rich expressiveness both in acoustic and textual perspective, from the recording of a Mandarin storytelling show. A systematic and comprehensive labeling framework is proposed for textual expressiveness. We analyze and define speech-related textual expressiveness in StoryTTS to include five distinct dimensions through linguistics, rhetoric, etc. Then we employ large language models and prompt them with a few manual annotation examples for batch annotation. The resulting corpus contains 61 hours of consecutive and highly prosodic speech equipped with accurate text transcriptions and rich textual expressiveness annotations. Therefore, StoryTTS can aid future ETTS research to fully mine the abundant intrinsic textual and acoustic features. Experiments are conducted to validate that TTS models can generate speech with improved expressiveness when integrating with the annotated textual labels in StoryTTS.
项目仓库:https://github.com/X-LANCE/StoryTTS
08 DiffDub: Person-generic Visual Dubbing Using Inpainting Renderer with Diffusion Auto-encoder
作者:刘涛,杜晨鹏,樊帅,陈飞龙,俞凯
简介:Generating high-quality and person-generic visual dubbing remains a challenge. Recent innovation has seen the advent of a two-stage paradigm, decoupling the rendering and lip synchronization process facilitated by intermediate representation as a conduit. Still, previous methodologies rely on rough landmarks or are confined to a single speaker, thus limiting their performance. In this paper, we propose DiffDub: Diffusion-based dubbing. We first craft the Diffusion auto-encoder by an inpainting renderer incorporating a mask to delineate editable zones and unaltered regions. This allows for seamless filling of the lower-face region while preserving the remaining parts. Throughout our experiments, we encountered several challenges. Primarily, the semantic encoder lacks robustness, constricting its ability to capture high-level features. Besides, the modeling ignored facial positioning, causing mouth or nose jitters across frames. To tackle these issues, we employ versatile strategies, including data augmentation and supplementary eye guidance. Moreover, we encapsulated a conformer-based reference encoder and motion generator fortified by a cross-attention mechanism. This enables our model to learn person-specific textures with varying references and reduces reliance on paired audio-visual data. Our rigorous experiments comprehensively highlight that our ground-breaking approach outpaces existing methods with considerable margins and delivers seamless, intelligible videos in person-generic and multilingual scenarios.
09 TDT-KWS: Fast And Accurate Keyword Spotting Using Token-and-duration Transducer
作者:奚彧, 李豪, 杨宝琛, 李浩宇, 许海南, 俞凯
简介:Designing an efficient keyword spotting (KWS) system that delivers exceptional performance on resource-constrained edge devices has long been a subject of significant attention. Existing KWS search algorithms typically follow a frame-synchronous approach, where search decisions are made repeatedly at each frame despite the fact that most frames are keyword-irrelevant. In this paper, we propose TDT-KWS, which leverages token-and-duration Transducers (TDT) for KWS tasks. We also propose a novel KWS task-specific decoding algorithm for Transducer-based models, which supports highly effective frame-asynchronous keyword search in streaming speech scenarios. With evaluations conducted on both the public Hey Snips and self-constructed LibriKWS-20 datasets, our proposed KWS-decoding algorithm produces more accurate results than conventional ASR decoding algorithms. Additionally, TDTKWS achieves on-par or better wake word detection performance than both RNN-T and traditional TDT-ASR systems while achieving significant inference speed-up. Furthermore, experiments show that TDT-KWS is more robust to noisy environments compared to RNN-T KWS.
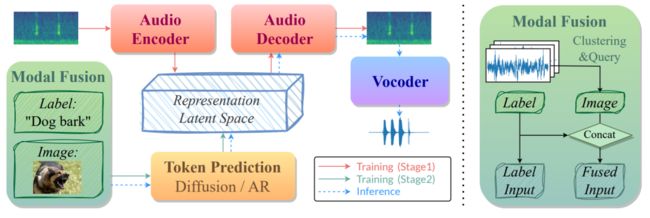
10 Enhancing Audio Generation Diversity with Visual Information
作者:谢泽宇,李柏涵,徐薛楠,吴梦玥,俞凯
简介:Audio and sound generation has garnered significant attention in recent years, with a primary focus on improving the quality of generated audios. However, there has been limited research on enhancing the diversity of generated audio, particularly when it comes to audio generation within specific categories. Current models tend to produce homogeneous audio samples within a category. This work aims to address this limitation by improving the diversity of generated audio with visual information. We propose a clustering-based method, leveraging visual information to guide the model in generating distinct audio content within each category. Results on seven categories indicate that extra visual input can largely enhance audio generation diversity.
11 SEF-VC: Speaker Embedding Free Zero-Shot Voice Conversion with Cross Attention
作者:李俊杰,郭奕玮,陈谐,俞凯
简介:Zero-shot voice conversion (VC) aims to transfer the source speaker timbre to arbitrary unseen target speaker timbre, while keeping the linguistic content unchanged. Although the voice of generated speech can be controlled by providing the speaker embedding of the target speaker, the speaker similarity still lags behind the ground truth recordings. In this paper, we propose SEF-VC, a speaker embedding free voice conversion model, which is designed to learn and incorporate speaker timbre from reference speech via a powerful position-agnostic cross-attention mechanism, and then reconstruct waveform from HuBERT semantic tokens in a non-autoregressive manner. The concise design of SEF-VC enhances its training stability and voice conversion performance. Objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate the superiority of SEF-VC to generate high-quality speech with better similarity to target reference than strong zero-shot VC baselines, even for very short reference speeches.
12 Contrastive Learning With Audio Discrimination For Customizable Keyword Spotting In Continuous Speech
作者:奚彧, 杨宝琛, 李豪, 郭嘉琪, 俞凯
简介:Customizable keyword spotting (KWS) in continuous speech has attracted increasing attention due to its real-world application potential. While contrastive learning (CL) has been widely used to extract keyword representations, previous CL approaches all operate on pre-segmented isolated words and employ only audio-text representations matching strategy. However, for KWS in continuous speech, co-articulation and streaming word segmentation can easily yield similar audio patterns for different texts, which may consequently trigger false alarms. To address this issue, we propose a novel CL with Audio Discrimination (CLAD) approach to learning keyword representation with both audio-text matching and audio-audio discrimination ability. Here, an InfoNCE loss considering both audio-audio and audio-text CL data pairs is employed for each sliding window during training. Evaluations on the open-source LibriPhrase dataset show that the use of sliding-window level InfoNCE loss yields comparable performance compared to previous CL approaches. Furthermore, experiments on the continuous speech dataset LibriSpeech demonstrate that, by incorporating audio discrimination, CLAD achieves significant performance gain over CL without audio discrimination. Meanwhile, compared to two-stage KWS approaches, the end-to-end KWS with CLAD achieves not only better performance, but also significant speed-up.
13 Label-aware Auxiliary Learning for Dialogue State Tracking
作者:刘韫聪,陈露,俞凯
简介:
Dialogue State Tracking (DST) is an essential part of taskoriented dialogue systems. Many existing methods try to utilize external dialogue datasets to improve the performance of DST models. Instead of previous methods, in this paper, we propose Label-Aware Auxiliary Learning for DST (LALDST) which focuses on exploiting the abundant internal information of the target DST dataset to improve the performance. We design label-aware auxiliary tasks, in which we apply noising functions to either the dialogue history or the belief state label and take the concatenation of them as input. The goal of each task is to restore the corrupted context. During the training process, we first further train the large pretrained language model on the auxiliary tasks, then fine-tune it on DST. Through the experimental results, we empirically show the effect of LAL-DST by the performance improvements it brings to MultiWOZ2.0 and WOZ.
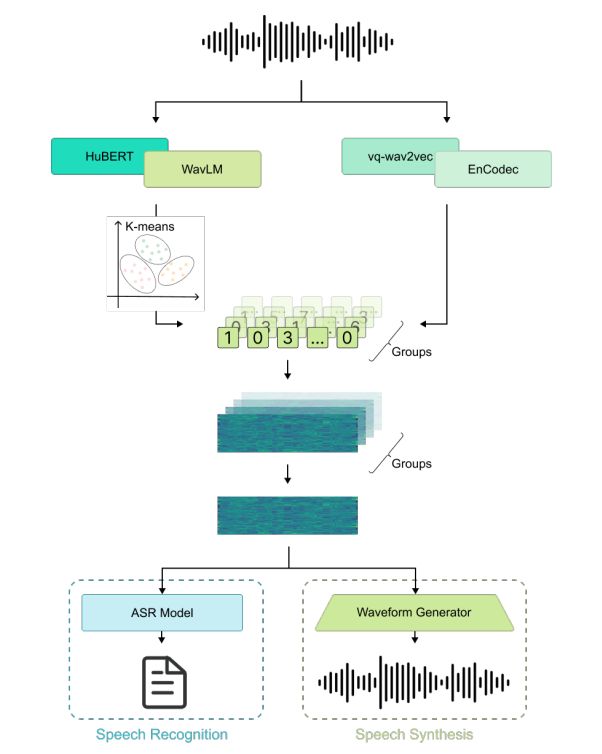
14 Towards Universal Speech Discrete Tokens: A Case Study for ASR and TTS
作者:杨亦凡,沈飞宇,杜晨鹏,马子阳,俞凯,Daniel Povey,陈谐
简介:Self-supervised learning (SSL) proficiency in speech-related tasks has driven research into utilizing discrete tokens for speech tasks like recognition and translation, which offer lower storage requirements and great potential to employ natural language processing techniques. However, these studies, mainly single-task focused, faced challenges like overfitting and performance degradation in speech recognition tasks, often at the cost of sacrificing performance in multi-task scenarios. This study presents a comprehensive comparison and optimization of discrete tokens generated by various leading SSL models in speech recognition and synthesis tasks. We aim to explore the universality of speech discrete tokens across multiple speech tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that discrete tokens achieve comparable results against systems trained on FBank features in speech recognition tasks and outperform mel-spectrogram features in speech synthesis in subjective and objective metrics. These findings suggest that universal discrete tokens have enormous potential in various speech-related tasks. Our work is open-source and publicly available to facilitate research in this direction.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.07377