射线与AABB相交检测
Box2D使用了一个叫做 slab 的碰撞检测算法。
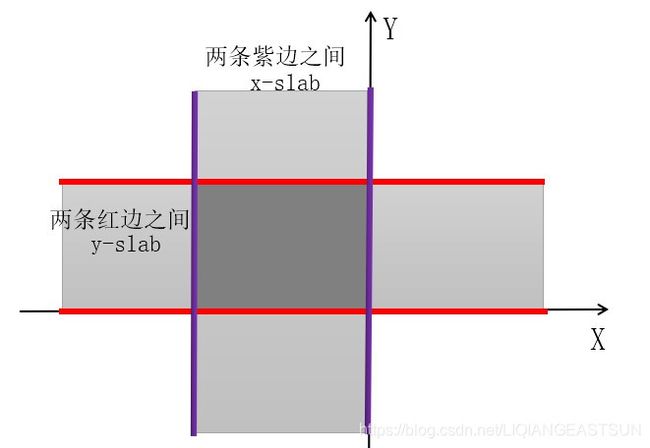
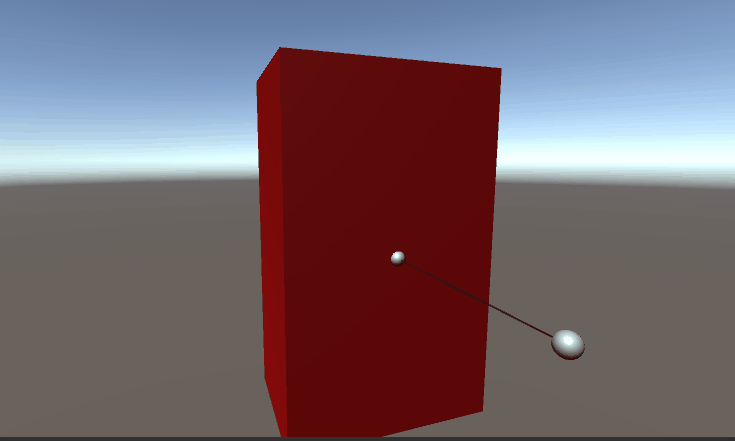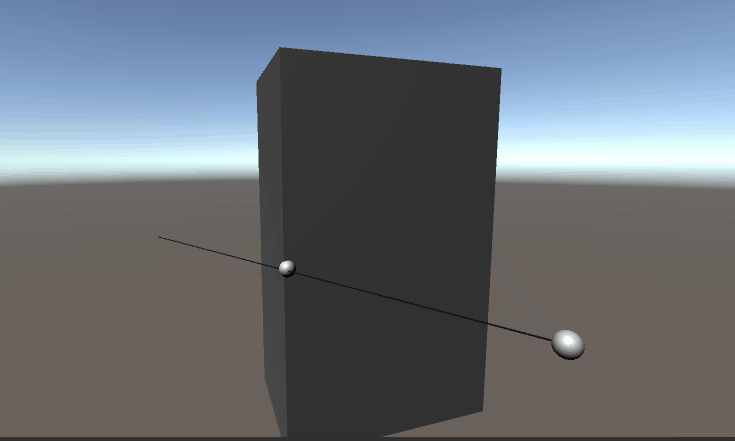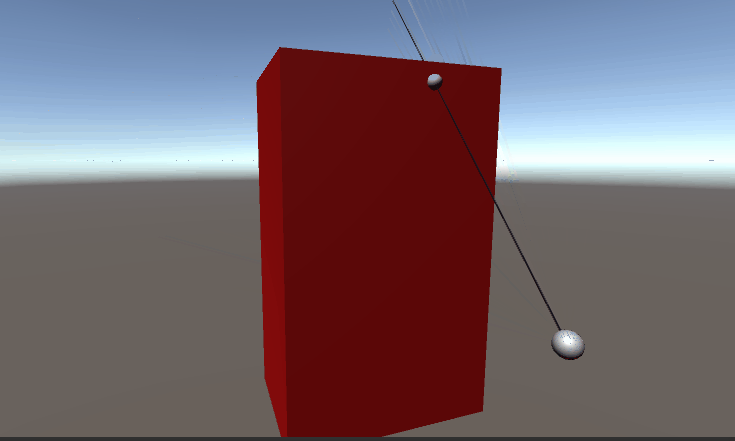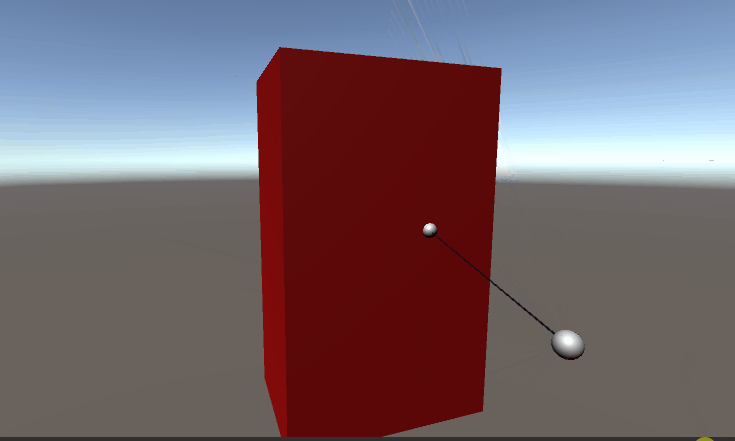
在2D中AABB是一个矩形边界框,slab 指的是矩形一组平行线之间的范围,所以在2D中矩形边界框四条边,两两一组,可以组成两个 slab。
如下图:
平行于Y轴的两条边(紫色线)之间的范围是 x-slab,范围无限长,宽度限制在两条紫色线之间
平行于X轴的两条边(红色线)之间的范围是 y-slab ,范围无限长,宽度限制在两条红色线之间
中间灰色比较深的部分就是矩形框,它是两个slab的重合部分,即属于x-slab 也属于 y-slab
则有下面几条规则:
2D 中
1.如果一个点在 AABB内,则该点必定同时在 x-slab、y-slab
2.如果一条射线和AABB相交,则这条射线和 两个 slab 相交部分必定有重合部分
3.同理在3D中 1、2 依然满足,因为3D AABB是六个面,有三对相互平行的面,每一对平行的面之间的范围就是一个 slab。因为 3D 不好绘制,下面依然用 2D讲述
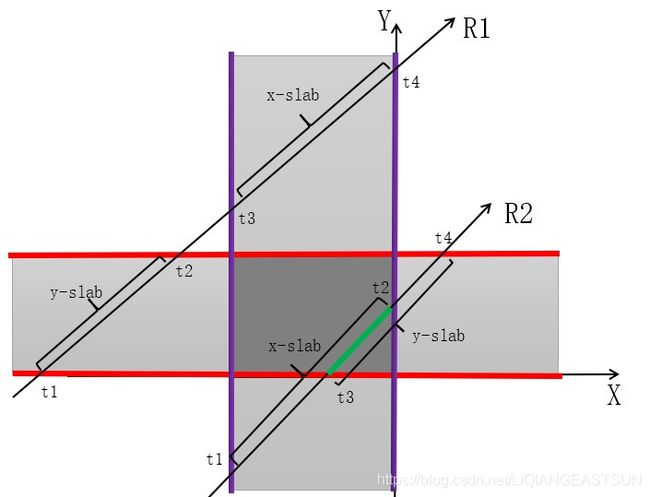
射线与AABB边界框相交情况如下图
射线R1
在 t1 位置进 y-slab
在 t2 位置出 y-slab
在 t3 位置进 x-slab
在 t4 位置出 x-slab
注:t1、t2、t3、t4 为从射线起点到各个交点的距离
但是 区间 (t1, t2) 和 (t3, t4) 没有重叠部分,则判定R1与AABB不相交
射线R2
在 t1 位置进 x-slab
在 t3 位置进 y-slab
在 t2 位置出 x-slab
在 t4 位置出 y-slab
区间 (t1, t2) 和 (t3, t4) 有重叠部分(图中绿色线条) t3 到 t2 部分,绿色线条部分既属于 x-slab,又属于 y-slab 部分,则判定射线 R2 与 AABB相交
由上得出结论,如果射线与AABB各个面相交的 t 区间 有重叠部分,则射线与AABB相交
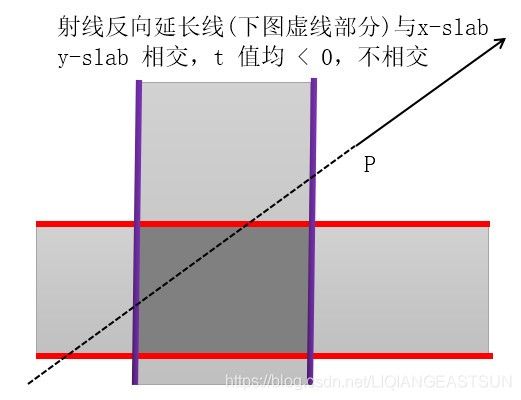
还有一种情况就是射线的反向延长线与 slab 相交,判定为相交无效
下面计算射线与AABB各个面的相交结果
令
射线与x-slab相交的t值为 (t1,t2),t1 < t2
射线与y-slab相交的t值为 (t3,t4),t3 < t4
射线与z-slab 相交的 t值为 (t5,t6),t5 < t6
只要满足区间 (t1,t2) ,(t3,t4),(t5,t6),在一维数轴上有重叠部分就说明射线与AABB相交,到此可以发现我们将 3D、2D 问题降维到了 1维 数轴上数值比较的问题了。
方法就是判断 t1、t3、t5中最大值 < t2、t4、t6中最小值
相交条件为:Max(t1, t3, t5 ) < Min(t2, t4,t6)
射线方程: p + t * rayDir
其中 p为 射线起点,rayDir 为射线的方向向量,t 为射线长度系数。
平面方程为 S * n = d
注:上边两个方程中 * 的作用
当用在 点 * 向量 或 向量 * 向量 时就是 向量点乘(Dot)
当用在 数值 * 向量 就是 数值乘 (X)
其中 S 为平面上的点,n为平面法向量,d为原点(0, 0, 0)到平面的距离。
如果射线与平面相交,令交点为 V,则点 V 即在射线上,也在平面上
代入射线方程中:V = p + t * rayDir
代入平面方程中:V * n = d,即 Dot( V , n ) = d
注:下面使用 Dot 表示点乘
将 V 展开为(p + t * rayDir)得到
Dot(( p + t * rayDir) , n) = d
Dot(p, n) + Dot(t * rayDir, n) = d
Dot(t * rayDir, n) = d - Dot(p, n)
t * Dot(rayDir, n) = d - Dot(p, n)
t = (d - Dot(p, n)) / Dot(rayDir, n)
射线与平面相交点距离射线起点距离t的距离公式为 t = (d - Dot(p, n)) / Dot(rayDir, n)
注意:Dot(rayDir, n), 射线向量与AABB某个面法向量点乘,当这两个向量垂直时,也就是射线平行于平面时,点乘结果为 0
AABB 以最小点 Min(x, y, z)、最大点Max(x, y, z) 表示
AABB 的六个面的方程满足
Dot(Min, normal) = d
Dot(Max, normal) = d
其中 normal 可分别表示为 AABB的三个轴向 (1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0),(0, 0, 1)
求射线与 x-slab 相交值为 t1,t2
令t1< t2,如果 t1 > t2 ,则 t1、t2值互换
求射线与 y-slab相交值为 t3,t4
令t3< t4,如果 t3 > t4 ,则t3、t4值互换
求射线与 z-slab相交值为 t5,t6
令t5< t6,如果 t5 > t6 ,则t5、t6值互换
(t1,t2) ,(t3,t4),(t5,t6) 如果有一组数据两个值都小于 0,如 (t1 = -1、t2 = -3) ,则射线与AABB不相交,
下一步:如果 t1、t2 、t3 、t4、 t5 、t6 有 小于 0 的,令其值 = 0
代码逻辑如下,关于图3的情况我还没有验证
AABB定义
public class AABB
{
public Vector3 min;
public Vector3 max;
public AABB(Vector3 min, Vector3 max)
{
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
}
}
逻辑代码
///
/// 射线与AABB相交检测
/// 下面方法是 射线与 3D AABB 相交的计算
/// 如果想计算 射线与 2D AABB 相交,则将下方关于 z 坐标的部分删除即可
///
public class RayAABBCollision
{
///
/// 判断射线与AABB是否相交
///
/// 射线起点
/// 射线方向
/// AABB
///
/// 判断射线与AABB是否相交
///
/// 射线起点
/// 射线方向
/// AABB
/// 射线与AABB交点坐标
///
/// 判断射线与AABB是否相交
///
/// 射线起点
/// 射线方向向量
/// AABB
/// 射线起点到相交点距离
///
/// 射线与平面相交计算
///
/// 射线起点
/// 射线方向向量
/// aabb
/// 平面法向量
/// t = (d - Dot(raySource, normal)) / Dot(rayDir, normal)
/// d = Dot(planePoint, normal)
/// t = (Dot(planePoint, normal) - Dot(raySource, normal)) / Dot(rayDir, normal)
/// t = Dot((planePoint - raySource), normal) / Dot(rayDir, normal)
private bool Calculate(Vector3 raySource, Vector3 rayDir, AABB aabb, Vector3 normal, ref float t1, ref float t2)
{
float p_sub_r_dot_n1 = Vector3.Dot(aabb.min - raySource, normal);
float p_sub_r_dot_n2 = Vector3.Dot(aabb.max - raySource, normal);
float r_dot_n = Vector3.Dot(rayDir, normal);
if (Math.Abs(r_dot_n) <= float.Epsilon) // 射线垂直于平面法向量,所以射线与平面平行
{
float dot1 = Vector3.Dot(aabb.min - raySource, normal);
float dot2 = Vector3.Dot(aabb.max - raySource, normal);
if (dot1 * dot2 > 0)
{
return false;
}
}
t1 = p_sub_r_dot_n1 / r_dot_n;
t2 = p_sub_r_dot_n2 / r_dot_n;
return true;
}
private bool CheckValue(ref float value1, ref float value2)
{
if (value1 < 0 && value2 < 0)
{
return false;
}
value1 = Mathf.Clamp(value1, 0, value1);
value2 = Mathf.Clamp(value2, 0, value2);
if (value1 > value2)
{
float temp = value1;
value1 = value2;
value2 = temp;
}
return true;
}
}测试结果,测试动画总AABB边红色为相交