Django项目部署到云服务器
Django项目部署到云服务器
1.购买阿里云服务器,用xshell进行连接
记得要开启相应的端口
2.上传代码至git仓库
git init
git add .
git commit -m "first commit"
git push origin master
3.在服务器拉取相应代码
git clone xxxx
4.根据requirement.txt安装依赖
在开发机上导出
pip3 freeze > requirements.txt
查看依赖
cat requirenment.txt
上传服务器,然后在服务器安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
查看已安装的依赖
pip list
5.修改settings.py中的数据库参数
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'house',
'HOST': '121.41.89.89',
'PORT': 3306,
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': 'xxxxxxx'
}
}
6.访问
python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:80
访问实例的公网IP地址~就可以看到你的网站啦
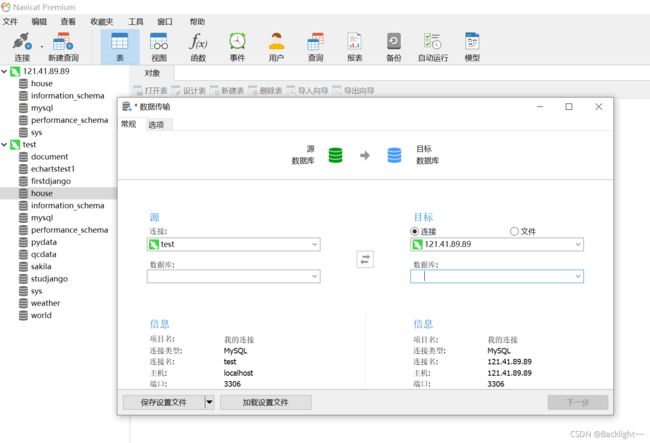
7.数据库
在服务器上下载安装mysql
使用Navicat连接mysql
在工具里面找到数据传输
可以直接将本地的数据库传到服务器的数据库上
8.Gunicorn
下载Gunicorn
pip install gunicorn
测试Gunicorn是否能启动你的项目服务
# gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 项目名.wsgi:application
如果报错
-bash: gunicorn: command not found
原因:未配置环境变量
解决:我安装gunicorn用的pip3,所以找到python3的bin目录,将入环境变量即可
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/python3/bin
也可以用守护进程的方式运行 (一直在后台运行)
# gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 -D 项目名.wsgi:application
查看gunicorn是否成功启动
ps - ef | grep python
netstat -tpln | grep 端口号
如果发现进程被占用,使用
kill -9 进程号
杀死进程,然后重新启动
9.nginx
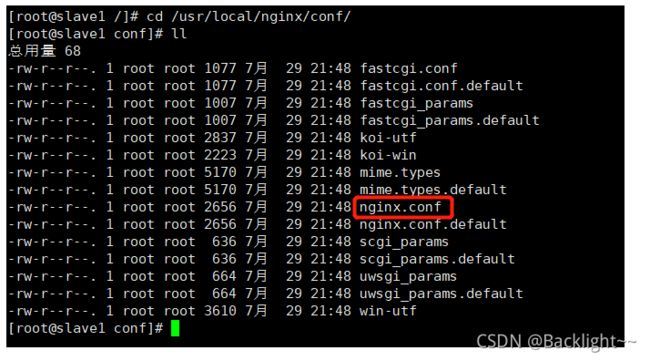
编辑Nginx配置文件
nginx 安装目录下,其默认的配置文件都放在这个目录的 conf 目录下,而 主配置文件
nginx.conf 也在其中,后续对 nginx 的使用基本上都是对此配置文件进行相应的修改
进入nginx配置目录后,打开nginx.conf
vim nginx.conf
整个配置文件如下:
user root;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name 121.41.89.89;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /static {
root /root/Program/test-demo;
autoindex on;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
autoindex on;
}
# }
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
主要修改地方在这里
server {
listen 80; # 这是nginx监听的端口
server_name 121.41.89.89; # 这是服务器的ip
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /static { # 这是静态资源 (动静分离)
root /root/Program/test-demo;
autoindex on;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000; # 转发的地址,意思是监听到80端口就转发到127.0.0.1:8000端口(反向代理)
autoindex on;
}
配置完成后保存退出
在/usr/local/nginx/sbin 目录下执行
./nginx-s reload
命令总结:
进入nginx的目录 /usr/local/nginx/sbin
1.查看nginx的版本号
./nginx -v
2.查看nginx进程是否启动
ps -ef | grep nginx
3.启动nginx
./nginx
4.关闭nginx
./nginx -s stop
5.重新加载nginx
配置文件更改之后,需要重新加载
./nginx -s reload
更多nginx的知识可以查看我之前的博客https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45730790/article/details/120047185
10.完成
现在就可以通过公网访问了
例如http://121.41.89.89/houtai/to_login/
如果还有项目要部署也是之前的操作,在nginx配置的时候多加一个server即可
**如果这篇文章对您有帮助,麻烦点赞、收藏或者关注一波哦!**