线程池执行流程以及拒绝策略
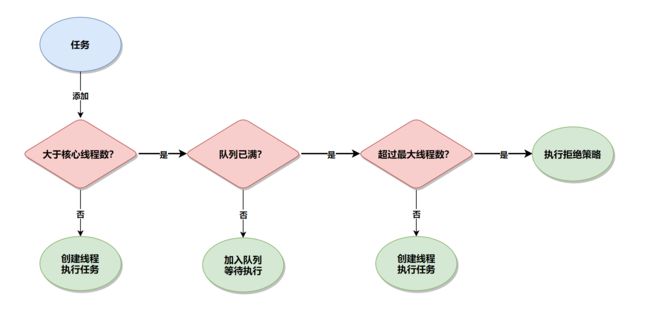
线程池的执行流程是:先判断当前线程数是否大于核心线程数?如果结果为 false,则新建线程并执行任务;如果结果为 true,则判断任务队列是否已满?如果结果为 false,则把任务添加到任务队列中等待线程执行,否则则判断当前线程数量是否超过最大线程数?如果结果为 false,则新建线程执行此任务,否则将执行线程池的拒绝策略,如下图所示:
线程池拒绝策略
当任务过多且线程池的任务队列已满时,此时就会执行线程池的拒绝策略,线程池的拒绝策略默认有以下 4 种:
- AbortPolicy:中止策略,线程池会抛出异常并中止执行此任务;
- CallerRunsPolicy:把任务交给添加此任务的(main)线程来执行;
- DiscardPolicy:忽略此任务,忽略最新的一个任务;
- DiscardOldestPolicy:忽略最早的任务,最先加入队列的任务。
默认的拒绝策略为 AbortPolicy 中止策略。
# DiscardPolicy拒绝策略
接下来我们以 DiscardPolicy 忽略此任务,忽略最新的一个任务为例,演示一下拒绝策略的具体使用,实现代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 任务的具体方法
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前任务被执行,执行时间:" + new Date() +
" 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
// 等待 1s
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 创建线程,线程的任务队列的长度为 1
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
100, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
// 添加并执行 4 个任务
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
// 线程池执行完任务,关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
}
以上程序的执行结果如下: 从上述执行结果可以看出,给线程池添加了 4 个任务,而线程池只执行了 2 个任务就结束了,其他两个任务执行了拒绝策略 DiscardPolicy 被忽略了,这就是拒绝策略的作用。
从上述执行结果可以看出,给线程池添加了 4 个任务,而线程池只执行了 2 个任务就结束了,其他两个任务执行了拒绝策略 DiscardPolicy 被忽略了,这就是拒绝策略的作用。
# AbortPolicy拒绝策略
为了和 DiscardPolicy 拒绝策略对比,我们来演示一下 JDK 默认的拒绝策略 AbortPolicy 中止策略,线程池会抛出异常并中止执行此任务,示例代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 任务的具体方法
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前任务被执行,执行时间:" + new Date() +
" 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
// 等待 1s
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 创建线程,线程的任务队列的长度为 1
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
100, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); // 显式指定拒绝策略,也可以忽略此设置,它为默认拒绝策略
// 添加并执行 4 个任务
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
// 线程池执行完任务,关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
}
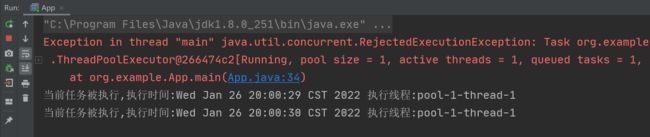
以上程序的执行结果如下:
从结果可以看出,给线程池添加了 4 个任务,线程池正常执行了 2 个任务,其他两个任务执行了中止策略,并抛出了拒绝执行的异常 RejectedExecutionException。
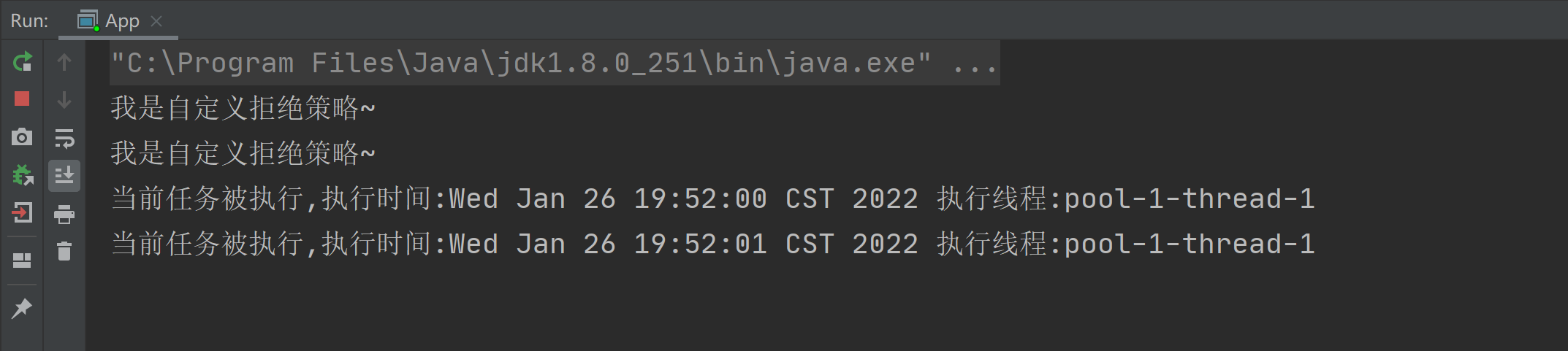
#自定义拒绝策略
当然除了 JDK 提供的四种拒绝策略之外,我们还可以实现通过 new RejectedExecutionHandler,并重写 rejectedExecution 方法来实现自定义拒绝策略,实现代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 任务的具体方法
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前任务被执行,执行时间:" + new Date() +
" 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
// 等待 1s
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 创建线程,线程的任务队列的长度为 1
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
100, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1),
new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
// 执行自定义拒绝策略的相关操作
System.out.println("我是自定义拒绝策略~");
}
});
// 添加并执行 4 个任务
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
}
以上程序的执行结果如下:
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
threadPool.execute(runnable);
}
以上程序的执行结果如下: