浅议-动态范围控制(DRC)
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 一、Dynamic Range Control
- 二、静态曲线Static curve
-
- 1.静态曲线如下图
- 2.matlab的DRC系统如下图所示:
- 3. 静态曲线方程
-
- 3.1 NT拐点计算
- 3.2 ET 计算
- 3.3 CT 计算
- 3.4 LT计算
- 4 增益计算
- 5 Xsc(dB)的计算:
-
- 1.Threshold-阈值
- 2. Ratio 压缩比
- 3. KneeWidth -拐点宽度
- 6. Gain Smoothing-增益平滑
-
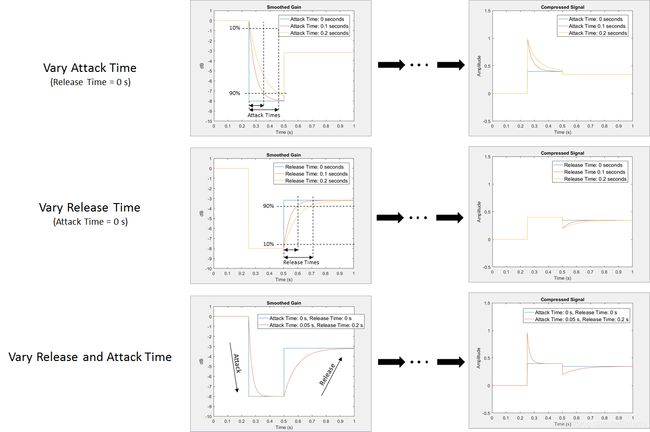
- Gain Smoothing 的attack time, release time如下图所示
- 三、参考文献
一、Dynamic Range Control
参见matlab:https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/audio/ug/dynamic-range-control.html
Dynamic range control is the adaptive adjustment of the dynamic range of a signal. The dynamic range of a signal is the logarithmic ratio of maximum to minimum signal amplitude specified in dB.
You can use dynamic range control to:
- Match an audio signal level to its environment
- Protect AD converters from overload
- Optimize information
- Suppress low-level noise
Types of dynamic range control include:
- Dynamic range compressor –– Attenuates the volume of loud sounds that
cross a given threshold. They are often used in recording systems to
protect hardware and to increase overall loudness. - Dynamic range limiter –– A type of compressor that brickwalls sound
above a given threshold. - Dynamic range expander –– Attenuates the volume of quiet sounds below
a given threshold. They are often used to make quiet sounds even
quieter. - Noise gate –– A type of expander that brickwalls sound below a given
threshold.
动态范围控制可以自动调整信号的动态范围;(信号的动态范围是信号的最大幅值与最小幅值比值的对数,使用dB作为单位) 动态范围控制功能:
a.根据环境匹配音频信号电平;也就是杜比volume leveler的作用;
b.保护ADC使其不会过载;在广播信号发送时,发送器有峰值限制,超过这个峰值会使得发送器过载。动态范围控制可以压缩原始信号的动态,使发送信号的动态范围满足发送器的要求。在音频领域,将数字音频信号送到DAC之前,音频智能功放算法中的DRC可以实现扬声器振幅保护;
c.优化信息;也就是使音频信号使用到满幅的动态范围;
d.压制低电平的噪声;DRC的噪声门有一定的降噪效果;
动态范围控制的类型
a.动态范围压缩器(Dynamic range compressor)–减弱超过给定阈值的大声信号的音量;可以保护硬件,增加整体响度;
b.动态范围限幅器(Dynamic range limiter)–是压缩器的一种,可以限制超过给定阈值的信号;
c.动态范围扩展器(Dynamic range expander)–减弱低于给定阈值的小声信号的音量;可以使得小信号听起来更加小声;
d.噪声门(Noise gate)–是扩展器的一种,可以限制低于给定阈值的信号。
二、静态曲线Static curve
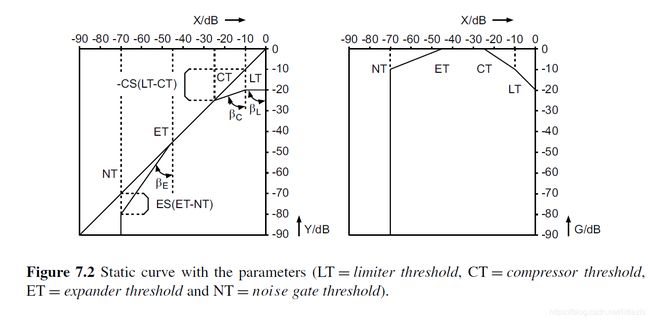
1.静态曲线如下图
参见《Digital Audio Signal Processing》第七章:
2.matlab的DRC系统如下图所示:
This tutorial shows how to implement dynamic range control systems using the compressor, expander, limiter, and noiseGate System objects from Audio System Toolbox™. The tutorial also provides an illustrated example of dynamic range limiting at various stages of a dynamic range limiting system.
The diagram depicts a general dynamic range control system.
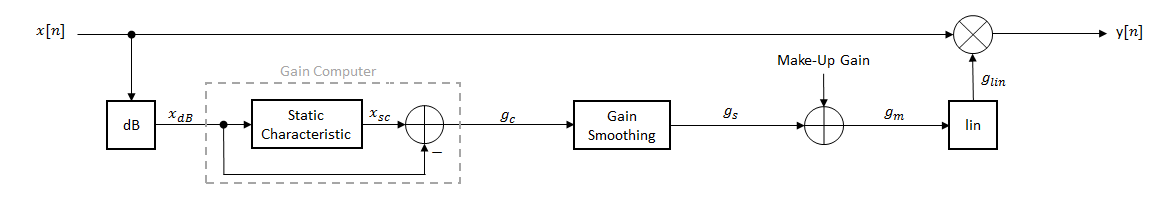
计算步骤如下:
- 线性到dB转换:x→Xd B
xdB=20log10(x).
- 将dB信号通过静态特性方程式,然后求出差值来进行增益计算: gc=xsc−xdB
- 随时间推移进行平滑处理:gc→gs
- 补充增益(仅适用 compressors 和 limiters): gs→gm
- dB到线性转换:gm→glin
- 将计算出的增益信号于原始音频信号相乘:y=glin × x
3. 静态曲线方程
3.1 NT拐点计算
NT = -70
NT没有softknee,有holdtime
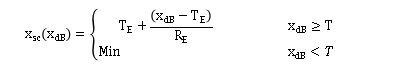
3.2 ET 计算
expander
Threshold: -10
Ratio: 5
KneeWidth: 0
AttackTime: 0.0500
ReleaseTime: 0.2000
HoldTime: 0.0500
SampleRate: 44100
ET = -45
有softknee,有holdtime
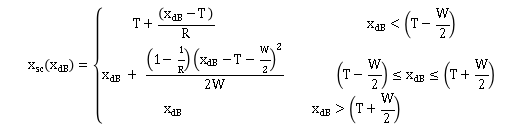
3.3 CT 计算
compressor 具有属性:
Threshold: -10
Ratio: 5
KneeWidth: 0
AttackTime: 0.0500
ReleaseTime: 0.2000
MakeUpGainMode: 'Property'
MakeUpGain: 0
SampleRate: 44100
CT = -25
有softknee,有MakeUpGain
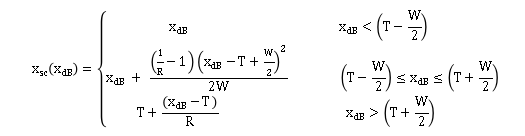
3.4 LT计算
Threshold (dB) — Operation threshold
–10 (default) | scalar in the range –50 to 0
Knee width (dB) — Transition area in the limiter characteristic
0 (default) | scalar in the range 0 to 20
View static characteristic — Open static characteristic plot of the dynamic range limiter
button
Attack time (s) — Time it takes applied gain to ramp up
0 (default) | scalar in the range 0 to 4
Release time (s) — Time it takes applied gain to ramp down
0.2 (default) | scalar in the range 0 to 4
Make-up gain mode — Make-up gain mode
Property (default) | Auto
Make-up gain (dB) — Applied make-up gain
0 (default) | scalar in the range –10 to 24
Inherit sample rate from input — Specify source of input sample rate
on (default) | off
Input sample rate (Hz) — Specify input sample rate
44100 (default) | positive scalar
L T= -10,
有softknee ,有MakeUpGain
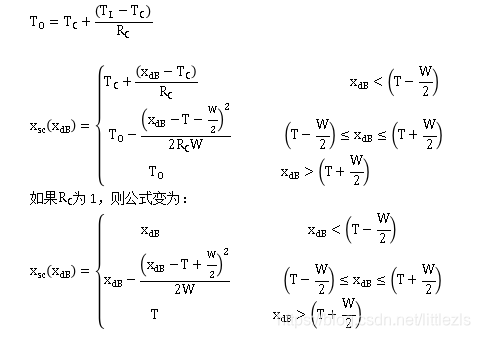
4 增益计算
增益计算单元进行增益信号的初步预估,增益计算单元的核心模块是静态特征,每一种类型的DRC有不同的静态特征,包括了可调的属性参数:
a.阈值threshold–所有的静态特性都有一个阈值,在阈值的一边,输入信号没有被修改,在阈值的另一边,输入信号被压缩、扩展以及限幅;
b.压缩比率Ratio–扩展器和压缩器的静态特征模块在计算增益时依赖用户提供的输入/输出的压缩比;
c.kneewidth-- 扩展器Expanders、压缩器compressors以及限幅器limiters的静态特征模块可以调整拐点的宽度;拐点宽度包含在阈值中,拐点宽度越大,阈值附近的过渡越平滑。如果拐点没有提供过度,则是硬拐点;如果拐点附近有大于0的拐点宽度值,则是软拐点。noiseGate只有硬拐点;
d.在计算信号增益要进行电平检测,电平检测使用递归一阶滤波器获取原始信号的电平;有基于Peak和基于RMS两种方法;Peak是生成信号电平的峰值包络,RMS是计算前N个样本的RMS值作为当前样本的电平。电平检测的作用是对于一个在原点波动的信号,DRC关心的是信号的峰值或者RMS值,而不关心信号的振荡情况;
e.Hold time 是应用增益之前的延迟时间;
f.电平检测一阶递归滤波器,使用Attack time或者release time作为滤波器的系数进行Gain Smoothing-增益平滑控制。
5 Xsc(dB)的计算:
1.Threshold-阈值
Expanders, compressors, limiters,noiseGate都有阈值
2. Ratio 压缩比
3. KneeWidth -拐点宽度
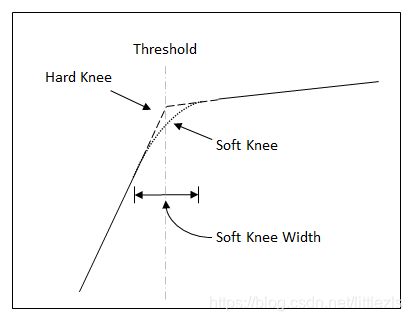
Expanders, compressors, 和 limiters可以调整静态特征的拐点宽度,当soft knee width 为0就变成硬拐点(Hard Knee)
noiseGate只有硬拐点(Hard Knee)
6. Gain Smoothing-增益平滑
所有动态范围控制器都提供随时间变化的增益平滑。增益平滑会减少所施加增益的急剧跳变,这可能会导致伪影和不自然的声音。您可以将增益平滑概念化为在增益信号中增加阻抗。
expander 和 noiseGate使用有相同的平滑方程,因为noise gate是 expander.的一个类型。
limiter和compressor使用有相同的平滑方程,因为 limiter是 compressor.的一个类型。
增益平滑的类型由attack time, release time和 hold time的组合指定。attack time, release time对应于增益信号从其最终值的10%变为90%所花费的时间。Hold time 是应用增益之前的延迟时间
具体增益平滑方程如下:
expander and noiseGate平滑方程:
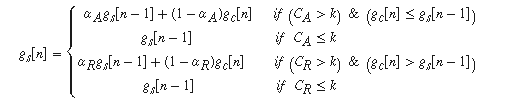
其中αA 和 αR 有下式得到::

- k 是指定的hold time的换算的采样点数
- CA , CR 是 attack , release的采样点数
compressor and limiter平滑方程:
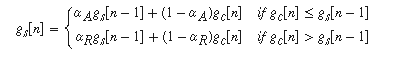
αA 和 αR 参见expander and noiseGate获取方程
Gain Smoothing 的attack time, release time如下图所示
三、参考文献
https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/audio/ug/dynamic-range-control.html
(2008.2nd_edition)Digital Audio Signal Processing - Zolzer.pdf
参考网址:
https://blog.csdn.net/houxiaoni01/article/details/112790209
https://blog.csdn.net/book_bbyuan/article/details/72458688
https://www.woaifaming.net/doc/68750.html
https://blog.csdn.net/cyz_2014/article/details/84718528