2024.1.23 寒假训练记录(6)
记录一个训练赛踩的大坑:往函数里传vector一定要加引用!犯了三次的错误还是记不住,服了,一道题调了一个小时。
文章目录
- CF 1490E Accidental Victory
- CF 1753B Factorial Divisibility
- CF 1454E Number of Simple Paths
- AT ARC148A mod M
- CF 1854B Earn or Unlock
- CF 1055A Metro
- CF 460C Present
- CF 894A QAQ
CF 1490E Accidental Victory
题目链接
从后往前看,每个数加上前面的所有数能不能超过后一个数,一旦有一个数不行了就直接输出前面的数即可(注意开longlong啊啊啊)
#include CF 1753B Factorial Divisibility
题目链接
太毒瘤了这题赛时想了老半天
先记录下分子上每个数字出现的次数然后合并,比如说3个2!就合并成一个3!这样,看最后能不能都合并成x!的倍数即可
#include CF 1454E Number of Simple Paths
题目链接
晚上补题的时候发现比想象中简单,好可惜赛时没做这题啊
n个顶点n条边的图我们叫做基环树,可以想象它长这样:
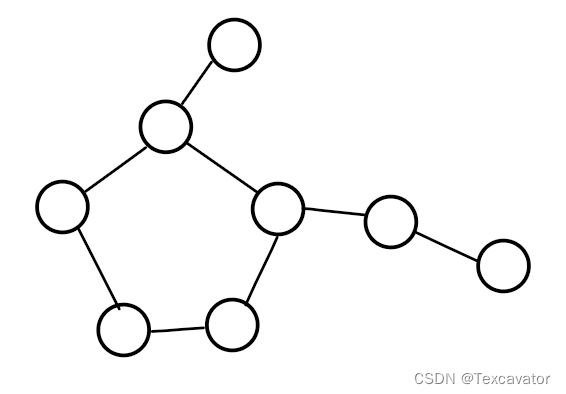
我们先记录环上的点,每个环上的点引出去的子树中,两点之间都只有一条路径,然后子树和其他点之间都有两条路径(因为有个环),可以循环计算每个子树,答案累加即可
#include AT ARC148A mod M
题目链接
受到之前cf有场div2的启发,当xy模mod余数相同,等价于x与y之差是mod的倍数
所以首先判断是否全为偶数,如果全是偶数直接除以2就可以
如果不是偶数,最差的情况是除以2,有的是1有的是0,然后再看一下能不能让所有数全部相同,我们就计算相邻两数之差取gcd,如果gcd是1就不能让所有数全相同,不是1直接除以那个gcd就可以让所有数全相同了
#include CF 1854B Earn or Unlock
题目链接
dp+bitset优化
如果我们可以到第 i 张牌,那我们得到的积分就是 a[1] + a[2] + … + a[i] - (i - 1),为什么是这么多呢,因为前面 i 张牌得到的积分是 a[1] 加到 a[i],然后我们为了到第 i 张,还需要花费 i - 1(第一张思免费送给我们的)
现在问题就变成了判断能否到 i 的位置,用bitset记录,如果可以到 i 的位置就把 dp[i] 赋为 1,到第 i 位就更新ans,要注意更新完之后要把 dp[i] 恢复成 0(因为有后效性,如果不清空,后面的操作就会把当前位的1往后挪)
#include CF 1055A Metro
题目链接
用Dijkstra做的,dfs应该也可以
#include CF 460C Present
题目链接
二分+树状数组
#include CF 894A QAQ
题目链接
大水题
#include