C++一本通基础算法:广度优先搜索(BFS)
tip:该算法将会疯狂使用队列,包括各种类型的队列
算法概述:先将起点入队,先向起点相邻的位置检索,如果满足条件,那么将这个位置入队。 然后将起点出队。再将所有与队首相邻且满足条件的位置入队,队首出队,知道队列为空。
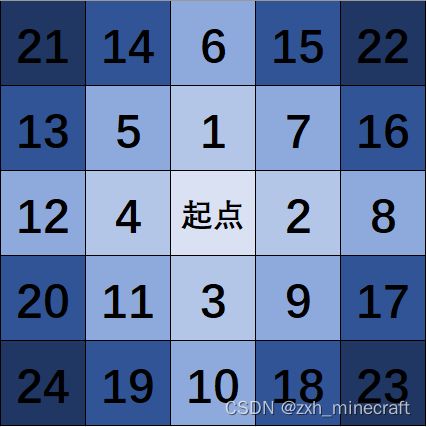
算法图像
如图所示,从起点检索,将1,2,3,4分别入队,起点出队,现在队列的队首为1,检索1周围的位置,将5,6,7分别入队,1出队,现在队首为2,检索2周围的位置,将8,9入队,……。直到24为队首时,周围不存在任何一个位置可以入队,且24已经为队列中唯一的元素,24出队,此时队列为空,搜索结束。
算法特点:需要用到大量的队列操作,可以解决很多的搜索问题,在求解最短路径问题且两个相邻的位置距离一定时,最先搜索到终点的路径长度就是最短路径。
广度优先搜索代码的一般形式
void bfs ( ) { //参数由解题需求决定
queue q; //类型自定,大概率为结构体
q.push(); //起点入队
//标记当前位置,避免重复访问
while (q.size()) { //只要队不为空
int t = q.front(); //取出队首元素
q.pop(); //队首出队
for ( ; ; ) { //循环用于检索队首的相邻位置
int xx , yy;
if ( ) { //如果这个位置满足条件
q.push(); //将这个位置入队
//标记当前位置
}
}
}
} 题目链接
信息学奥赛一本通(C++版)在线评测系统 (ssoier.cn)
分析:遍历矩阵,如果发现矩形中某一个元素为细胞,则细胞总数加1,则运用广搜将与这个细胞所相邻的所有细胞(包括这个细胞)都找出来并设置为非细胞元素,继续遍历。
心得:这道题在输入时用的是getchar,不管怎么改最终只能通过一个点,后来发现cin也可以输入单个字符,将getchar换成cin后,就可以通过了。
代码
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 10100;
int n,m,xy[4][2] = {1,0,0,1,-1,0,0,-1},ans = 0;
char a[N][N];
struct node {
int x,y;
};
void bfs (int x,int y) {
queue q;
q.push((node) {x,y});
a[x][y] = '0';
while (q.size()) {
// cout << q.front().x << " " << q.front().y << endl;
node k = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
int xx = k.x + xy[i][0],yy = k.y + xy[i][1];
if (xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m && a[xx][yy] != '0') {
// cout << xx << " b " << yy << endl;
a[xx][yy] = '0';
q.push((node){xx,yy});
}
}
}
}
int main () {
cin >> n >> m;
getchar();
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
for (int j = 1;j <= m;j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
// cout << a[i][j] << endl;
}
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
for (int j = 1;j <= m;j++) {
if (a[i][j] != '0') {
// cout << i << " " << j << endl;
bfs(i,j);
ans++;
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
} 题目链接
信息学奥赛一本通(C++版)在线评测系统 (ssoier.cn)
分析:经典的广搜走迷宫,设置4个偏移量再用广搜模板套即可。同时由于广搜是宽度优先,所以第一个搜索到的解即为最短路径解
心得:没什么好说的,一遍过。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
char a[N][N];
bool b[N][N];
int m,n,ans,sx,sy,ex,ey,xy[4][2]{1,0,0,1,-1,0,0,-1};
struct node {
int x,y,cnt;
};
void bfs (int x,int y) {
// cout << endl;
queue q;
q.push((node){x,y,0});
b[x][y] = 1;
while (q.size()) {
node t = q.front();
if (t.x == ex && t.y == ey) {
ans = t.cnt;
return;
}
q.pop();
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
int xx = t.x + xy[i][0],yy = t.y + xy[i][1];
// cout << xx << " " << yy << endl;
if (xx >= 1 && xx <= m && yy >= 1 && yy <= n && !b[xx][yy] && a[xx][yy] != '#') {
b[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push((node){xx,yy,t.cnt + 1});
}
}
}
}
int main () {
while (cin >> m >> n) {
if (m == 0 && n == 0) break;
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
ans = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++) {
for (int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
if (a[i][j] == '@') {
sx = i;
sy = j;
}
if (a[i][j] == '*') {
ex = i;
ey = j;
}
}
}
// cout << sx << " " << sy << endl;
bfs (sx,sy);
if (ans == 0) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}