06 栈
目录
1.栈
2.实现
3.OJ题
1. 栈
1. 栈的概念和结构
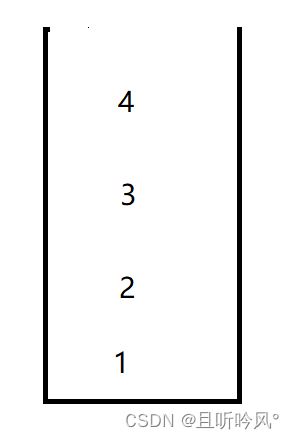
栈: 这一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则
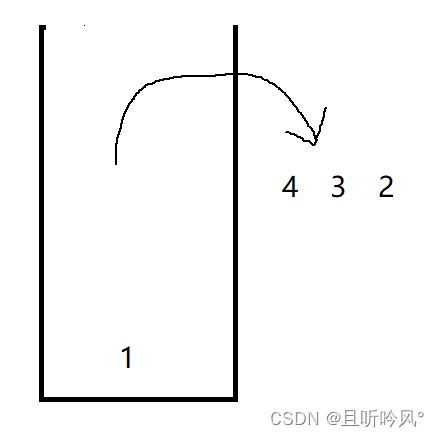
压栈: 栈的插入操作叫做压栈/入栈进栈,数据在栈顶
出栈: 栈的删除操作叫出栈,数据也在栈顶
第一个题依次入栈,那么出栈的顺序就是相反的,E是第一个,1是最后一个
第二题不可能的出栈顺序,想3先出栈,3前面的都得入栈,3出完栈后必须2出栈,所以C不可能
2. 实现
栈的实现可以用数组或者链表,相对而言数组的机构更优一些,因为数组尾插的代价更小
所以将数组的尾巴作为栈顶,0下标作为栈底
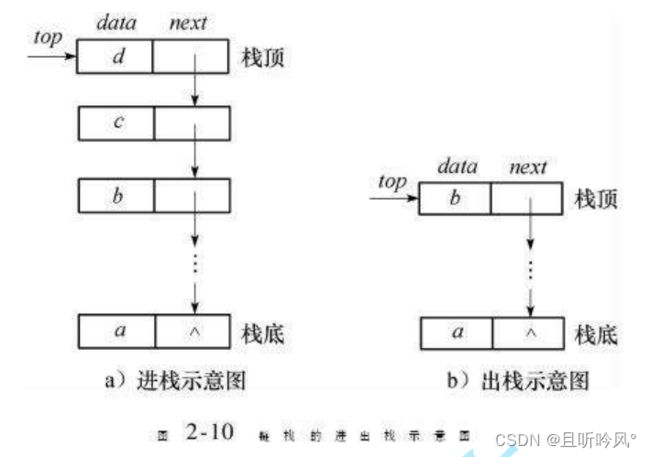
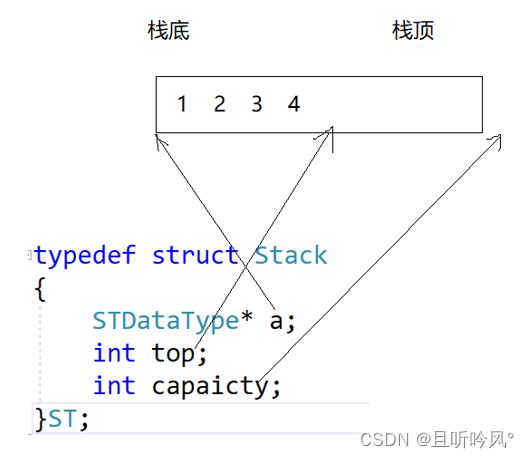
在结构体设计中,top代表栈顶的位置,初始化为0,代表下一个栈顶数据的位置。出栈和栈顶元素需要判断是不是空栈
头文件
#pragma once
#include 实现文件
#include "Stack.h"
#include 主文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include 3.OJ题
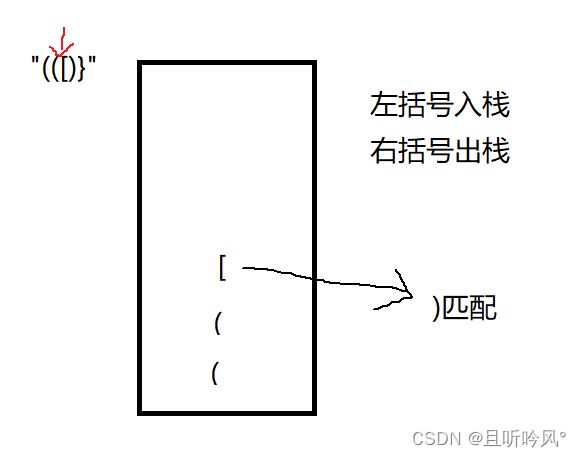
有效的括号: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/description/

思路
有两个不匹配,一个是数量不匹配,一个是内容不匹配。这个题可以利用栈结构,遇到左括号入栈,右括号出栈。出栈会自动匹配栈顶元素,也就是离的最近的括号,如果两个括号不匹配,说明不满足,也就是内容不匹配。如果出栈时栈为空或者字符串遍历完栈不为空,说明都是数量不匹配。C语言解决这个题最简单的方法就是先实现一个栈,直接调用栈结构,因为栈里面有栈顶、是否为空这些函数可以直接利用
#include