springIoc以及注解的使用
注解
注解的定义
注解(Annotation)是一种在 Java 程序中以元数据的形式对代码进行标记和说明的机制。它可以被添加到类、方法、字段、参数等程序元素上,用于提供额外的信息和指示。
也就是说注解是一种标记
注解怎么生效呢?
通过扫描的方式生效,spring容器进行指定包下的文件扫描,然后根据注解进行后续操作
注解的类型
- 内置注解(Built-in Annotations):Java语言提供了一些内置的注解,用于标记和处理特定的场景和行为。例如:
- @Override:用于标记方法覆盖父类方法。
- @Deprecated:用于标记已过时的方法、类或字段。
- @SuppressWarnings:用于抑制编译器警告信息。
- 元注解(Meta-Annotations):元注解是用于定义和处理注解本身的注解。它们可以用于 自定义注解,指定注解的行为、作用范围等。常见的元注解包括:
- @Target:指定注解可应用的目标元素类型(类、方法、字段等)。
- @Retention:指定注解的保留策略(源代码、编译时、运行时)。
- @Documented:指定注解是否包含在API文档中。
- 自定义注解(Custom Annotations):
- 开发者可以根据需要自定义自己的注解,以实现特定的功能和逻辑。自定义注解需要使用元注解来进行配置,并通过反射机制来获取注解信息。自定义注解可以应用于类、方法、字段等代码元素,并可以根据注解信息做出相应的处理。
简单来说内置注解就是 Java语言提供的一些注解,不需要导依赖和导包使用。元注解也就是注解的注解 专门用来标注注解,自定义注解 ,开法者根据需要自定义自己的注解,也就是自己做的一些规定,通常需要导包进行使用。
配置包扫描
<context:component-scan base-package="包名"/>
排除包下的一些信息
<context:exclude-filter type="annotion" expression="类的全限定符"/>
指定包含内容
<context:include-filter type="annotion" expression="类的全限定符"/>
type="annotation" 表示使用注解作为过滤器的类型,它会匹配带有特定注解的类进行组件扫描。
bean的作用域和周期方法注解
定义
作用域指的是在Spring容器中管理的Bean对象的生命周期范围和可见性。不同的作用域决定了在容器中创建的Bean实例的行为方式。
可以使用注解的形式进行规定
在Spring框架中,常见的Bean作用域(scope)包括:
- Singleton(单例):
在整个应用程序中只存在一个Bean实例,由Spring容器管理。每次请求该Bean时,都会返回同一个实例。 - Prototype(原型):每次请求该Bean时,容器都会创建一个新的Bean实例,并返回该实例。
- Request(请求):每个HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean实例,该实例仅在当前请求中有效。
- Session(会话):每个用户会话都会创建一个新的Bean实例,该实例在整个会话期间有效。
- GlobalSession(全局会话):仅适用于Portlet环境,表示全局会话作用域。
常用的生命周期方法注解包括:
周期的定义
周期(Lifecycle)指的是对象的创建、初始化、使用和销毁过程中的各个阶段。在Spring框架中,可以通过声明周期方法注解来定义在Bean的生命周期中执行的特定方法。
- @PostConstruct:在Bean的初始化阶段,即依赖注入完成后调用的方法上添加该注解。该方法会在构造函数执行之后、任何自动装配发生之前被调用。
- @PreDestroy:在Bean销毁之前调用的方法上添加该注解。该方法会在Bean被容器销毁之前被调用。
这两个就类似于前面说到的bean中的init-method 和destroy-method方法
注解Autowired的使用
它是spring框架的注解,用于自动装配bean,使用Autowired注解可以简化依赖注入。当创建一个Bean时,会自动检测该Bean所需要的依赖,将其注入到Bean中
- 构造方法注入:
在构造方法上使用 @Autowired的话,spring会尝试通过匹配类型或名称来自动注入构造方法所需的依赖项
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired
public MyBean(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
}
在上述示例中,MyBean 类的构造方法使用了 @Autowired 注解,告诉 Spring 自动注入 DependencyBean 对象。 自动注入也就是说会创建这个实例
- 成员变量注入:在成员变量上使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 将会自动注入与该成员变量类型匹配的 Bean 对象。
public class MyBean {
@Autowired
private DependencyBean dependency;
}
- Setter 方法注入:
在 Setter 方法上使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 将会自动注入与该 Setter 方法参数类型匹配的 Bean 对象。
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired
public void setDependency(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
}
- 方法注入:在普通方法上使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 将会自动注入与方法参数类型匹配的 Bean 对象。
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired
public void injectDependency(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
}
在上述示例中,MyBean 类的 injectDependency() 方法使用了 @Autowired 注解,告诉 Spring 自动注入与 DependencyBean 类型匹配的 Bean 对象。
举例帮助理解
我们来学习一下上面这部分内容的实际用处,以及为什么这样做
- 构造方法注入:
我们此时面临一个场景,我想要在一个类中使用另一个类的实例,比如说在动物类中,使用鸟类的飞行方法,那么我可以在动物类中创建一个鸟类的引用,通过Autowired注解注入,以达到在此类中实现鸟类的飞行方法。
如:我定义一个注入的类 三个私有化属性 一个重写的toString方法
@Component
public class DependencyBean {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DependencyBean{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
使用Autowired注解进行注入
@Component
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired //TODO 这个用法是什么呢?
public MyBean(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
public String sing(){
dependency.setAddress("地球");
dependency.setAge(50);
dependency.setName("张三");
return dependency.toString();
}
}
注入之后进行使用
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
MyBean bean = applicationContext.getBean(MyBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
System.out.println(bean.sing());
}
}
结果:我可以不用创建这个注入的类的对象,使用Autowired会自动帮助我创建
2. 成员变量的注入:其余不改,仅更改MyBean内容
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Autowired
private DependencyBean dependency;
public String sing(){
dependency.setAddress("地球");
dependency.setAge(50);
dependency.setName("张三");
return dependency.toString();
}
}
我们执行之后得到的结果,可以发现注入的话会自动创建一系列内容。相当于得到了实例
- setter方法的注入
@Component
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired
public void setDependency(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
public String sing(){
dependency.setAddress("地球");
dependency.setAge(50);
dependency.setName("张三");
return dependency.toString();
}
}
- 在普通方法上使用
@Component
public class MyBean {
private DependencyBean dependency;
@Autowired
public void injectDependency(DependencyBean dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
public String sing() {
dependency.setAddress("地球");
dependency.setAge(50);
dependency.setName("张三");
return dependency.toString();
}
}
结果仍一样
我们需要明白Autowired会根据你规定或者是表明的内容进行注入,从而得到对应的bean对象或者是bean实例。这样做的话简化了操作,让我们实现起来更加的方便。
使用注解实现ioc容器管理
dao层,持久化储存
package com.dao;
import com.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {
List<Student> queryAll();
}
实现
package com.dao;
import com.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
// 这个位置不可以直接使用注解 需要使用的时 bean的依赖注入
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public List<Student> queryAll() {
String sql = "select * from students ";
List<Student> students = jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Student.class));
return students;
}
}
这里我们主要明确,由于JdbcTemplate这个内容并不是我们创建的,这是根据需求导入的jar包,我们并不清楚它的标注是什么,这里仍然需要配置bean,先创建druid 进行配置后,注入依赖到JdbcTemplate中
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbcTemplate.properties"/>
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${atguigu.url}">property>
<property name="password" value="${atguigu.password}">property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${atguigu.driver}">property>
<property name="username" value="${atguigu.username}">property>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
这样的话,我们先配置号bean对象,当spring扫描的时候,扫描到Autowired的时候,会自动装配。只要保证bean的填写正确,后续的实例spring会帮助进行
Service层
接口
package com.service;
import com.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentService {
List<Student> queryAll();
}
实现类
package com.service.impl;
import com.dao.StudentDaoImpl;
import com.pojo.Student;
import com.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class StudentsServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDaoImpl studentDao;
@Override
public List<Student> queryAll() {
List<Student> students= studentDao.queryAll();
System.out.println("service层的内容"+students);
return students;
}
}
constroller层内容
package com.Constroller;
import com.pojo.Student;
import com.service.impl.StudentsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class StudentsConstroller {
@Autowired
private StudentsServiceImpl studentsService;
public List<Student> findAll(){
List<Student> student = studentsService.queryAll();
return student;
}
}
代码书写完毕之后,我们需要配置扫描,否则,spring的注解就没有任何效果了。先扫描才可以创建,不扫描的话出现这个错误
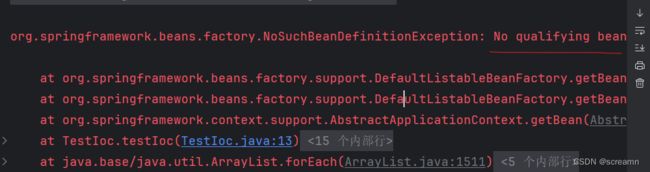
<context:component-scan base-package="加注解的包名"/>
测试
public class TestIoc {
@Test
void testIoc(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
StudentsConstroller bean = applicationContext.getBean(StudentsConstroller.class);
List<Student> studentList = bean.findAll();
System.out.println(studentList);
}
}
仍然是老套路,先创建根据配置文件创建ioc容器,创建完成之后,扫描注解进行bean对象的实例,然后执行对应的内容。
怎么执行呢?
通过Autowired进行关联,我们可以将依赖看成不同的模块,A模块调用B怎么调用?,那就是创建B模块的实例,在A中进行使用,而在这个位置,我们是通过注解的形式进行注入,相当于注解的效果是实现B模块的实例

使用ioc容器获取控制层对象,使用控制层的对象执行后续的内容。
前面我们提到的bean对象的配置,哪里使用的注入是通过指定property的ref进行关联的

如有错误,请指正。本文的内容来源于尚硅谷2023年ssm视频教程,对文中的内容有进一步补充和讲解。
