C++语法复习笔记-9.C++STl、Boost库、多线程编程(进行中)
文章目录
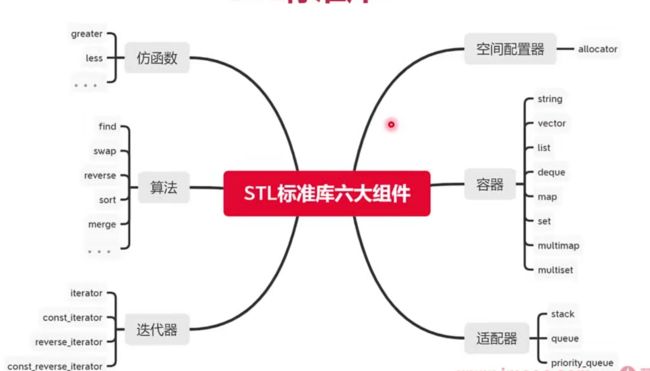
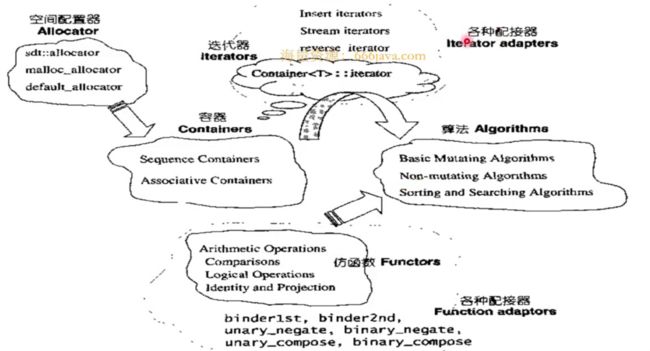
- 1. STL
-
- 1. 概览
- 2. 容器
-
- 2.1. 序列式容器vector、list、deque
-
- 初始化
- 遍历-for_each函数
- 2.2. 适配器stack、queue、priority_queue
-
- 初始化
- 访问方式
- 2.3. 关联型容器map、set
-
- 插入元素
- 遍历-仿函数
- 查询-find函数
- 删除-erase函数
-
- 用for循环
- 用find函数查找删除或直接删除
- 3. 仿函数
-
- 3.1 概念
- 3.2 排序代码示例
-
- C++ 原生函数
- C++ 泛型编程
- C++ 仿函数
- C++ 仿函数模板
- 4. 算法库
-
- 4.1 总览
- 4.2 `transform`和`lambda`表达式使用
- 4.3 容器统计与二分查找
-
- `count`统计指定元素出现次数
- `count_if`条件统计
-
- `binder2nd`&&`binder1st`比较函数
- `binary_search`二分查找
- `search`查找子序列
慕课网C++教程
1. STL
1. 概览
2. 容器
2.1. 序列式容器vector、list、deque
初始化
int iArr[] = { 1, 2,3,4,5 };
vector<int> iVector(iArr, iArr + 4); // 通过地址,初始化vector[1,2,3,4]
list<int> iList(iArr, iArr + 4);
deque<int> iDeque(iArr, iArr + 4);
遍历-for_each函数
// 显示-重载运算符-函数
struct Display {
void operator()(int i)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
};
int main() {
for_each( iVector.begin(), iVector.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
for_each(iList.begin(), iList.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
for_each(iDeque.begin(), iDeque.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2. 适配器stack、queue、priority_queue
初始化
int iArr[] = { 1, 2,3,4,5 };
// 序列式容器
vector<int> iVector(iArr, iArr + 4); // 通过地址,初始化vector[1,2,3,4]
list<int> iList(iArr, iArr + 4);
deque<int> iDeque(iArr, iArr + 4);
// 适配器
queue<int> iQueue(iDeque); // 队列 先进先出
stack<int> iStack(iDeque); // 栈 先进后出
priority_queue<int> iPQueue(iArr, iArr + 4); // 优先队列,按优先权
访问方式
// 遍历适配器
while ( !iQueue.empty() )
{
cout << iQueue.front() << " "; // 1 2 3 4
iQueue.pop();
}
cout << endl;
while (!iStack.empty())
{
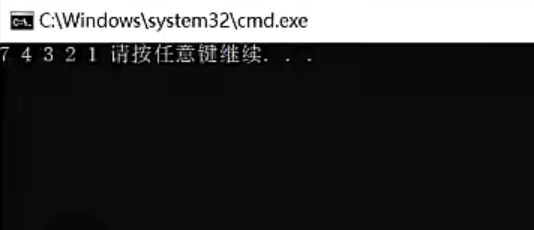
cout << iStack.top() << " "; // 4 3 2 1
iStack.pop();
}
cout << endl;
while (!iPQueue.empty())
{
cout << iPQueue.top() << " "; // 4 3 2 1
iPQueue.pop();
}
cout << endl;
2.3. 关联型容器map、set
插入元素
map<string, double> studentSocres;
// 插入元素
// 方式1:像数组一样操作
studentSocres["LiMing"] = 95.0;
studentSocres["LiHong"] = 98.5;
// 方式2:insert方法
studentSocres.insert(pair<string, double>("zhangsan", 100.0) );
studentSocres.insert(pair<string, double>("Lisi", 98.6));
studentSocres.insert(pair<string, double>("wangwu", 94.5));
// 方式3:value_type方法-指明插入数据的类型
studentSocres.insert(map<string, double>::value_type("zhaoliu", 95.5) );
遍历-仿函数
// 仿函数
struct Display
{
void operator()(pair<string, double> info)
{
cout << info.first << ": " << info.second << endl;
}
};
int main() {
for_each(studentSocres.begin(),studentSocres.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
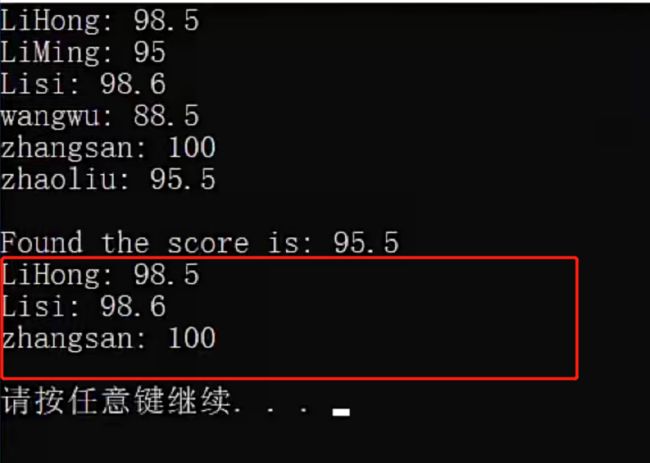
查询-find函数
// 查询操作-使用find函数完成查找工作
map<string, double>::iterator iter;
iter = studentSocres.find("zhaoliu");
if (iter != studentSocres.end())
{
cout << "Found the score is: " << iter->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Didn't find the key." << endl;
}
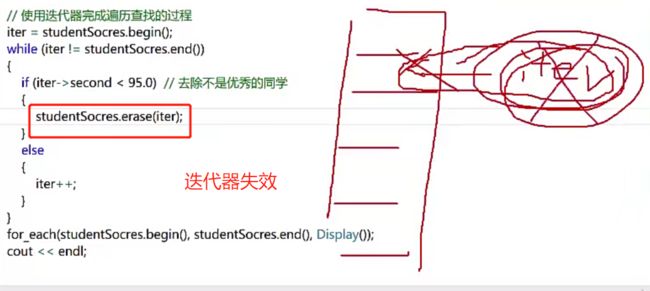
删除-erase函数
- 注意迭代器失效问题,删除迭代器指针后,迭代器要向下个位置移动一位,继续判断下个位置的key,value
- 即,先清除临时迭代器中的内容,再将迭代器指向下个位置的内容
studentSocres.erase(iter++);
// 使用迭代器完成遍历查找的过程
iter = studentSocres.begin();
while (iter != studentSocres.end())
{
if (iter->second < 98.0) // 去除不是优秀的同学
{
studentSocres.erase(iter++); // 注意:迭代器失效问题
}
else
{
iter++;
}
}
for_each(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
用for循环
// 用for循环进行迭代器的遍历
for (iter = studentSocres.begin(); iter != studentSocres.end(); iter++)
{
if (iter->second <= 98.5)
{
// 清除临时迭代器的值,函数返回时会指向下个迭代器,要有指针能够接收
iter = studentSocres.erase(iter);
}
}
for_each(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
用find函数查找删除或直接删除
// find得到迭代器并删除-避免由于循环导致迭代器失效问题
iter = studentSocres.find("LiHong");
studentSocres.erase(iter);
for_each(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end(), Display());
// 直接删除key
int n = studentSocres.erase("LiHong1");
cout << n << endl;
for_each(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end(), Display());
// 删除范围内的值
studentSocres.erase(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end());
for_each(studentSocres.begin(), studentSocres.end(), Display());
cout << endl;
3. 仿函数
3.1 概念
3.2 排序代码示例
C++ 原生函数
// 自定义排序函数
bool MySort(int a, int b)
{
return a < b; // a在前,a小,即从小到大排序
}
// 自定义输出函数
void Display(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main() {
// C++方式
int arr[] = { 4, 3, 2, 1, 7 };
sort(arr, arr + 5, MySort); // 起始位置,原生定义函数
for_each(arr, arr + 5, Display);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C++ 泛型编程
// 定义泛型函数
template<class T>
inline bool MySortT(T const& a, T const& b) // 用const& 优化性能
{
return a < b;
}
template<class T>
inline void DisplayT(T const& a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main() {
// C++泛型
int arr2[] = { 4, 3, 2, 1, 7 };
sort(arr2, arr2 + 5, MySortT<int>);
for_each(arr2, arr2 + 5, DisplayT<int>);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C++ 仿函数
// 定义仿函数
struct SortF
{
bool operator() (int a, int b)
{
return a < b;
}
};
struct DisplayF
{
void operator() (int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
};
int main() {
// C++仿函数
int arr3[] = { 4, 3, 2, 1, 7 };
sort(arr3, arr3 + 5, SortF());
for_each(arr3, arr3 + 5, DisplayF());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C++ 仿函数模板
// C++仿函数模板
template<class T>
struct SortTF
{
inline bool operator() (T const& a, T const& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
struct DisplayTF
{
inline void operator() (T const& a) const
{
cout << a << " ";
}
};
int main() {
// C++仿函数模板
int arr4[] = { 4, 3, 2, 1, 7 };
sort(arr4, arr4 + 5, SortTF<int>() );
for_each(arr4, arr4 + 5, DisplayTF<int>());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
4. 算法库
4.1 总览
4.2 transform和lambda表达式使用
// transform和lambda表达式
int ones[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int twos[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int results[5];
// 两个数组容器中的元素依次相加并返回
// 传入第一个容器开始结束位置,第二个容器开始位置,结果容器,处理函数
// 注意第二个容器和结果容器要能容纳第一个容器传入的大小
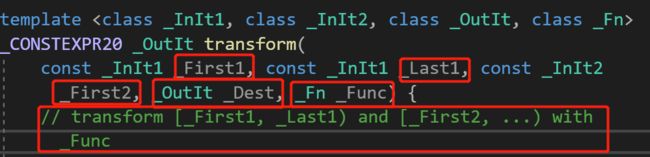
transform(ones, ones + 5, twos, results, std::plus<int>());
// lambda表达式(匿名函数)
// [] :可以传入外部定义的变量,例如外部变量int a, [a]
// () :接收自己函数中的参数
// ->类型:接收函数返回类型
// {}:函数的主体语句
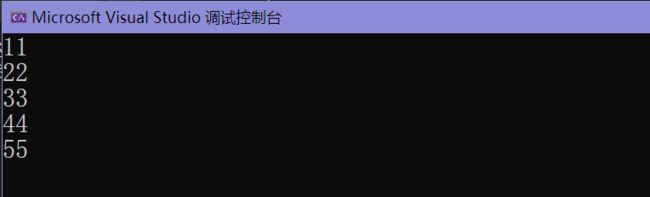
for_each(results, results + 5,
[ ](int a)->void {cout << a << endl; } );
cout << endl;
4.3 容器统计与二分查找
count统计指定元素出现次数
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// count:传入起始位置,要查找的数字,统计一共出现的次数
cout << count(arr, arr + len, 6) << endl; // 统计6的个数
count_if条件统计
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// count_if 条件查找
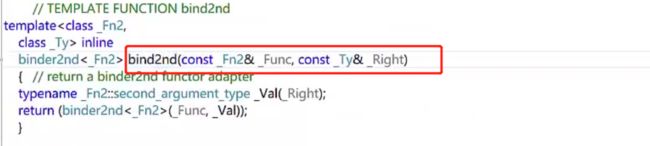
// bind2nd:数值在右边,函数是<,数值为7 ->表示 <7的个数
cout << count_if(arr, arr + len, bind2nd(less<int>(), 7) ) << endl; // <7的数:10个
// bind1st:数值在左边,函数是<,数值为7 ->表示 >7的个数
cout << count_if(arr, arr + len, bind1st(less<int>(), 7) ) << endl; // >7的数:1个
binder2nd&&binder1st比较函数
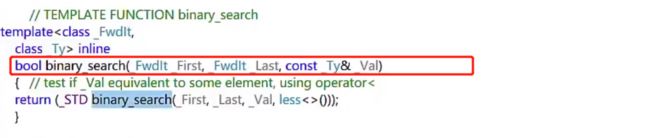
binary_search二分查找
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// binary_search二分查找指定元素是否存在
cout << binary_search(arr, arr + len, 9) << endl; // 返回0: 表示9找不到
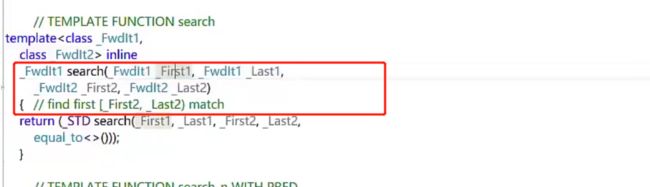
search查找子序列
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
vector<int> iA(arr + 2, arr + 6); // {2,3,3,4} // 创建子序列
vector<int> iA2;
iA2.push_back(1);
iA2.push_back(9); // {1, 9}
// 查找子序列
// 返回地址位置,进行解引用,可以取地址中的值:2,如果不存在,返回一个负值表不存在
cout << *search(arr, arr + len, iA.begin(), iA.end()) << endl; // 2
cout << *search(arr, arr + len, iA2.begin(), iA2.end()) << endl; // 一个负数