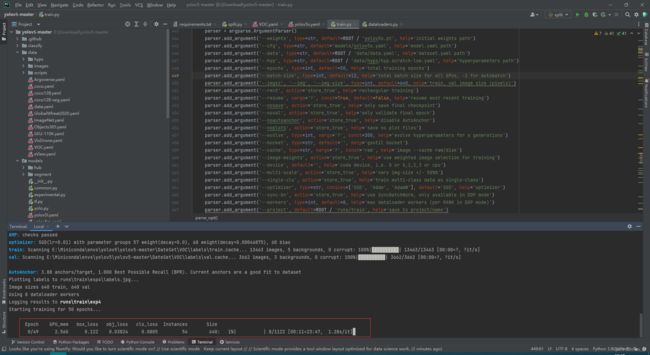
YOLOV5训练标准数据集
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、安装cuda和miniconda
-
- 1.安装cuda
- 2.安装miniconda并配置环境变量
-
- 1) 安装miniconda
- 2) miniconda环境变量配置
- 二、创建虚拟环境和安装Pytorch
-
- 1. 创建虚拟环境
- 2. 安装pytorch
- 三、 Pycharm和yolov5模型环境配置
-
- 1. PyCharm下载
- 2. yolov5模型环境配置
- 四、 VOC数据集的划分以及参数文件配置
-
- 1. VOC数据集划分
- 2. 权重文件下载
- 3. 参数文件配置
前言
第一次接触Yolov5有点懵,对于小白的我根本不知道从何入手,上网查阅了大量资料和视频,才勉强使用Yolov5训练出了VOC标准数据集的结果,在Yolov5环境搭建的过程中出现了很多问题,在这里我将自己获得的经验分享给大家,电脑显卡为GTX 1650 4GB。
一、安装cuda和miniconda
1.安装cuda
使用win+r快捷键打开运行窗口,输入cmd调出命令提示符,在命令提示符窗口中输入以下命令查看自己的电脑支持的最高cuda版本。
nvidia-smi

我的电脑最高支持cuda12.2,但是由于到目前为止pytorch稳定版支持的最高cuda版本为11.8,因此在这里我下载的版本为cuda11.8。
以下为cuda11.8的下载地址:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-11-8-0-download-archive
安装路径以及安装选项选择默认即可;安装完成以后使用在命令提示符窗口中输入nvcc-V可以查看安装版本。
2.安装miniconda并配置环境变量
1) 安装miniconda
打开miniconda下载地址:https://docs.conda.io/projects/miniconda/en/latest/,
下载Python3.8版本对应的miniconda windows安装包,安装时可以选择默认路径也可以自定义路径。
2) miniconda环境变量配置
win+i 搜索高级系统设置,打开环境变量。

在系统变量中的Path下添加以下三个路径:

在这里我将miniconda安装在了E盘的Miniconda下,需要根据自己的安装路径进行更改。
二、创建虚拟环境和安装Pytorch
1. 创建虚拟环境
在开始菜单中找到anaconda Prompt并打开,输入以下命令创建Python3.8版本的虚拟环境,yolov5为虚拟环境的名称。
conda create -n yolov5 python==3.8
使用“activate+环境名”激活虚拟环境。
activate yolov5
使用以下命令可以查看Python环境,激活后的环境前会被✳号标记。
conda env list
2. 安装pytorch
打开pytorch的下载地址:https://pytorch.org/ ,按照相应的cuda版本进行选择

复制以下命令在 Anaconda Prompt命令窗口中跳转到虚拟环境下运行安装pytorch
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url http://download.pytorch.org
三、 Pycharm和yolov5模型环境配置
1. PyCharm下载
下载Pycharm安装包,安装在c盘以外的文件夹。
以下的选项全部勾上,点击 Next 等待安装完成并激活。
2. yolov5模型环境配置
yolov5模型代码下载地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v5.0
yolov5下载完成以后解压,右键选择PyCharm打开

打开以后右键点击右下角python版本,选择添加解释器

将虚拟环境yolov5下的python.exe添加到项目解释器中,点击OK等待添加完成。


添加完成以后可以看到右下角显示带有虚拟环境的python版本

将yolov5-master中的requirements.txt文件复制到虚拟环境yolov5根目录下,在PyCharm终端窗口中使用cd命令跳转到虚拟环境所在位置,运行pip install -r requirements.txt,安装环境运行所依赖的包,等待安装完成。
四、 VOC数据集的划分以及参数文件配置
1. VOC数据集划分
VOC标准数据集下载地址:https://pjreddie.com/projects/pascal-voc-dataset-mirror/
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fX4auvyyZh_7qe0YUca7cA?pwd=akky 提取码:akky
将下载好的VOC数据放到yolov5目录下,对以下代码主要修改以下两个路径
in_file = open('E:/Download/yolov5-master/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations/%s.xml' % image_id) # xml路径
out_file = open('E:/Download/yolov5-master/VOCdevkit//VOC2012/YOLOLabels/%s.txt' % image_id, 'w')
数据集划分完整代码如下:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import random
from shutil import copyfile
classes = ['aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog',
'horse', 'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor'] # 划分的类别,依实际情况而定
# classes=["ball"]
TRAIN_RATIO = 80 # 训练集与数据集划分的比例
def clear_hidden_files(path):
dir_list = os.listdir(path)
for i in dir_list:
abspath = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(path), i)
if os.path.isfile(abspath):
if i.startswith("._"):
os.remove(abspath)
else:
clear_hidden_files(abspath)
def convert(size, box): # 边界框的转换
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('E:/Download/yolov5-master/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Annotations/%s.xml' % image_id) # xml路径
out_file = open('E:/Download/yolov5-master/VOCdevkit//VOC2012/YOLOLabels/%s.txt' % image_id, 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
in_file.close()
out_file.close()
wd = os.getcwd()
wd = os.getcwd()
data_base_dir = os.path.join(wd, "VOCdevkit/")
if not os.path.isdir(data_base_dir):
os.mkdir(data_base_dir)
work_sapce_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "VOC2012/")
if not os.path.isdir(work_sapce_dir):
os.mkdir(work_sapce_dir)
annotation_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "Annotations/")
if not os.path.isdir(annotation_dir):
os.mkdir(annotation_dir)
clear_hidden_files(annotation_dir)
image_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "JPEGImages/")
if not os.path.isdir(image_dir):
os.mkdir(image_dir)
clear_hidden_files(image_dir)
yolo_labels_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "YOLOLabels/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolo_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolo_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolo_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "images/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_dir)
yolov5_labels_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "labels/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, "train/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_train_dir)
yolov5_images_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, "val/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_test_dir)
yolov5_labels_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, "train/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
yolov5_labels_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, "val/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_train.txt"), 'w')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_val.txt"), 'w')
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_train.txt"), 'a')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_val.txt"), 'a')
list_imgs = os.listdir(image_dir) # list image files
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probability: %d" % prob)
for i in range(0, len(list_imgs)):
path = os.path.join(image_dir, list_imgs[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
image_path = image_dir + list_imgs[i]
voc_path = list_imgs[i]
(nameWithoutExtention, extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))
(voc_nameWithoutExtention, voc_extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(voc_path))
annotation_name = nameWithoutExtention + '.xml'
annotation_path = os.path.join(annotation_dir, annotation_name)
label_name = nameWithoutExtention + '.txt'
label_path = os.path.join(yolo_labels_dir, label_name)
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probability: %d" % prob)
if (prob < TRAIN_RATIO): # train dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
train_file.write(image_path + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_train_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_train_dir + label_name)
else: # test dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
test_file.write(image_path + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_test_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_test_dir + label_name)
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
数据集划分代码来自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53001080/article/details/130731845
2. 权重文件下载
权重文件下载地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1g-MPFF9AozVIusGI5BmXKA?pwd=40n4 提取码:40n4
在选择所需要的权重文件进行下载,在这里我选择的是yolov5s.pt,下载并移动到yolov5-master目录下
3. 参数文件配置
1)在yolov5-master/data目录下新建data.yaml,配置 训练集和验证集图片的路径,以及图片的分类标签。
data.yaml代码如下:
# train images (relative to 'path') 16551 images
train: E:/Miniconda/envs/yolov5/yolov5-master/DateSet/VOC/images/train
# val images (relative to 'path') 4952 images
val: E:/Miniconda/envs/yolov5/yolov5-master/DateSet/VOC/images/val
# Classes
names: ['aeroplane','bicycle','bird','boat','bottle','bus','car','cat','chair','cow','diningtable',
'dog','horse','motorbike','person','pottedplant','sheep','sofa',': train','tvmonitor']
2)修改models目录下的的yolov5s.yaml模型参数,只需要修改NC参数,NC为图片分类个数

3)配置train.py,主要修改以下参数
–weight: 权重
–cfg: 训练模型配置
–data: 训练数据配置
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default= 'yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='models/yolov5s.yaml', help='model.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default= 'data/data.yaml', help='dataset.yaml path')
batch-size默认值为16,运行过程出现显卡内存不足时可以设置为“-1”,让程序自动选择批量处理大小。
–epochs: 训练轮次
–batch-size: 批量处理大小
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=50, help='total training epochs')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=-1, help='total batch size for all GPUs, -1 for autobatch')
配置完成以后在PyCharm终端中运行以下代码激活虚拟环境并运行train.py函数进行模型训练,没有激活虚拟环境的话,训练过程不会调用GPU
activate yolov5
python train.py