练习1,推断是否为素数:
// ConsoleAppIsPrime1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // /* *函数功能:推断一个输入的数是否为素数 *函数原形:bool Prime( int x ) *參数:int x:将要推断的数 *返回值:bool型变量,推断是否是素数 *备注:须要包括头文件 "< // /* *问题描写叙述:将十进制转换成二进制或者八进制,16进制 *问题演示样例:输入50 2。输出110010 *函数功能: *函数原形:void HexadecimalTrans(int n, int d) *參数:int n,十进制整数 int d,进制数 *返回值:无 *时间复杂度: *备注:无 *日期:2014/11/30 *算法描写叙述: */ #include "stdafx.h" #include // /* *问题描写叙述:暴力搜索遍历查找。从100个随机函数中(100-999)查找指定数字的位置 *问题演示样例: *函数功能:查找指定的数 *函数原形:int FindNum(int num[], int x) *參数:int num[]。要查找的数组, int x。要查找的数 *返回值:数字的位置 *时间复杂度:O() *备注:无 *日期:2014/7/30 *算法描写叙述: */ #include "stdafx.h" #include // /* *问题描写叙述:二分法遍历查找。从100个随机函数中(100-999)查找指定数字的位置 *问题演示样例: *函数功能:二分查找法查找指定的数 *函数原形:int SpecialFindNum(int num[], int x, int low, int high) *參数: int num[]。要查找的数组, int x。要查找的数 int low, 查找的起始位置 int high,查找的末端位置 *返回值:数字的位置 *时间复杂度:O() *备注:无 *日期:2014/7/30 *算法描写叙述: */ #include "stdafx.h" #include // /* *问题描写叙述:输入字符串。将其逆序输出 *问题演示样例:输入,asdfgh。输出hgfdsa *函数功能:逆序输出字符串的内容 *函数原形:void Reverse( char* s, int left, int right ); *參数: char *,欲逆序的字符串。 int left, 逆序的左起点 int right。逆序的右尾点 *返回值:无 *时间复杂度:O(n) *备注:无 *日期:2014/7/30 *算法描写叙述: */ #include "stdafx.h" #include // /* *问题描写叙述:输入两个字符串,推断相互之间字符串是否包括 *问题演示样例:输入,asdfgh,输出asd。结果。包括! *函数功能:推断两个字符串是否包括 *函数原形:bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB); *參数: char *pStrA, 第一个字符串 char *pStrB,第二个字符串 *返回值:布尔变量 *时间复杂度:O(n) *备注:无 *日期:2014/7/30 *算法描写叙述: */ #include "stdafx.h" #include "iostream" using namespace std; bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB); int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { char a[10],b[10]; bool flag; while(true) { cout<<"Please Enter characters A:"< 比方3位的全部格雷码: 000 代码例如以下: N个人围成一圈,从第一个開始报数,第M个将出局,最后剩下一个,其余人都将出局。 比如N=6。M=5。被出局的顺序是:5,4,6,2,3。1。 (1)CircleList.h的代码例如以下: (2)主測试代码: // #include "stdafx.h" #include "CircleList.h" using namespace std; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { int nlen=10; LinkList 汉诺塔递归问题: 婚礼上的谎言 定义:二进制长度就是最高位1的下标值+1(下标从0開始),比方16 = 10000。则长度是5, 2= 0010。长度为2 碾转相除法:如果f(a,b)是a,b的最大公约数,则f(b。a%b)=f(a。b)。即f(b,a%b)相同也是其最大公约数
“括号配对”代码实现例如以下: // #include "stdafx.h" #include "iostream" using namespace std; void OddEvenSepar(int *num, int N) { for (int i = 0; i < N;i++) { int k = 1; while (k < num[i]) { if (k % 2 == 1) { cout << k << " "; } k++; } cout << endl; int kk = 1; while (kk < num[i]) { if (kk % 2 == 0) { cout << kk << " "; } kk++; } cout << endl; } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { system("color 0A"); int N = 0; cout << "请输入測试组数:" << endl; cin >> N; int *num = new int[N]; cout << "请输入相应个数的偶数" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < N;i++) { cin>>num[i]; } cout << endl; OddEvenSepar(num, N); delete[] num; num = NULL; system("pause"); return 0; } 难度:1。第31题 方法: 排序法。或者直接求取 “五个数求最值”代码实现例如以下: // #include "stdafx.h" #include "iostream" using namespace std; void getMinMax(int *num,int n) { int min = num[0], max = num[0]; for (int j = 0; j < n;j++) { if (min>num[j]) { min = num[j]; } if (max < num[j]) { max = num[j]; } } cout << "最小值为:" << min << endl; cout << "最大值为:" << max << endl; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { system("color 0A"); int num[5] = {0}; for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++) { cin >> num[i]; } getMinMax(num,5); system("pause"); return 0; } 比如,输入:2 4 5 难度1,第34题 方法: 暴力破解。遍历出答案 // #include "stdafx.h" #include "iostream" using namespace std; int HanXinCount(int *num); int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { system("color 0A"); int *num = new int[3]; cout << "请输入3种排列方式的队尾人数:"< 难度3。第32题 方法: DFS法,深度遍历型程序设计 “组合数”代码实现例如以下: PS:有的东西表面看上去公正、全面,实际可能走向极端的分立思维,很多客观事物不能简单均分,可能其内在具有复杂的联系。一旦坚持平分,结果倒失去了客观、全面的基础。 维基百科告诉我们要这样写:为什么呢? 一般二分法这样写: 将 所以解决问题的方法就是: mid = ((unsigned int)low + (unsigned int)high)) >> 1 ; 或者 mid = low+(high-low)/2; 构造函数是一个非常特殊的成员函数。当一个对象被创建时他将会自己主动被调用。 析构器也是一个非常特殊的成员函数,当对象在作用域结束时会被自己主动的隐式调用。当动态分配内存和销毁时也会调用这两个特殊的函数,即new和delete操作符! 进入正题,显式调用这两个特殊的函数: 当构造器被显式调用时,编译器立马创建了一个未命名的暂时对象。同一时候它也被立马销毁。这也是为什么输出中的第二行会是“析构器被运行”特别注意。假设对象时动态分配的内存。千万别显式调用析构器。由于delete会调用析构器。 类的成员函数也能调用析构器和构造器 最后再来分析一段程序: !。 非常少须要显式调用析构函数。 可是。对置于绝对地址的对象进行清理会非常实用。 这些对象通常使用採用位置參数的用户定义的 new 运算符进行分配。 delete 运算符不能释放该内存,由于它不是从自由存储区分配的(有关具体信息,请參阅 new 和 delete 运算符)。 可是。对析构函数的调用能够运行对应的清理。 若要显式调用 String 类的对象 s 的析构函数,请使用下列语句之中的一个: 能够使用对前面显示的析构函数的显式调用的表示法,不管类型是否定义了析构函数。 这同意您进行此类显式调用,而无需了解是否为此类型定义了析构函数。 显式调用析构函数。当中没有定义的析构函数无效。练习2,指定范围内的素数:
// ConsoleAppIsPrime.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*函数功能:推断指定范围内素数个数
*函数原形:int Primes( int n ,int m )
*參数:
int n:请输入想要确认的素数范围下限
int m:请输入想要确认的素数范围上限
*返回值:n到m范围内素数的个数
*备注:
*日期:2014/11/25
*原创:是
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:[email protected]
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "math.h"
using namespace std;
int Primes( int n ,int m );
bool Prime( int x );
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int countprimes=0;
int a=0;
int b=0;
while (true)
{
cout<<"请输入想要确认的素数范围上限:";
cin>> a ;
cout<<"请输入想要确认的素数范围下限:";
cin>> b;
countprimes=Primes(a,b);
cout<<"在 "<< a <<"到 "<< b <<"之间的素数个数为: "<< countprimes<练习3,某整数是否为2的次幂:
/*
*函数功能:推断一个整数是否为2的次幂
*函数原形:bool IsTwoN(int n);
*參数:int n,要推断的整数
*返回值:bool型变量,表征是与否
*时间复杂度:O(1)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/11/23
*原创:否
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:[email protected]
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "math.h"
using namespace std;
bool IsTwoN(int n);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
while(1)
{
bool flag;
int m;
cout<<"请输入一个整数:"<练习4。整数的二进制数中1的个数:
/*
*函数功能:求取整数相应二进制数中1的个数
*函数原形:int Count(int z);
*參数:int z,要计算的整数
*返回值:返回整数相应二进制数中1的个数
*时间复杂度:O(1)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/11/23
*原创:否
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:[email protected]
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int Count(int z);
int main()
{
int number;
int z;
char asn='n';
do
{
cout<<"请输入一个整数:"<
练习5。统计指定数据出现次数:
// ConsoleAppDigitCount.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描写叙述:用随机函数生成100个在100到999之间的整数,设计程序统计这些三位数中十位是各自是0-9出现次数
*问题演示样例:无
*函数功能:统计三位数中十位数0-9出现的次数
*函数原形:void DigitCount(int num[], int count[])
*參数:int num[], 欲统计的数组,int count[]存储统计结果
*返回值: 无
*时间复杂度:O(n)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/12/31
*算法描写叙述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include
![]()
练习6,进制的转换:
// ConsoleAppHexadecimalTrans.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。练习7,查找指定数据的位置(暴力搜索):
// ConsoleAppSpecifiedSearch.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。![]()
练习8,二分法查找指定数据位置:
// ConsoleAppSpecifiedSearch.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。练习9。字符串中指定数据出现次数
// ConsoleAppCharCount.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描写叙述:设计一个程序。统计随机给出的字符串的数字的个数。字母的个数,特殊字符的个数
*问题演示样例:123asd。数字3,字母3,特殊字符0
*函数功能:统计字符串中的数据
*函数原形:void CharCal(char *str, int count[])
*參数:char *str,欲统计的字符串, int count[],用于存储统计结果
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:O()
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描写叙述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
![]()
练习10,逆序输出字符串
// ConsoleAppCharTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
练习11。字符串包括推断
// ConsoleAppCharTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
练习12,打印随意位元的格雷码序列:
001
011
010
110
111
101
100// ConsoleAppGrayCode.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
bool GrayCode(int nBits);
int changeBit(int a);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int nBits=0;
cout<<"请输入位元长度:"<#include
练习14,约舍夫出局
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
templatetemplate
// Win32AppCircleOut.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
![]()
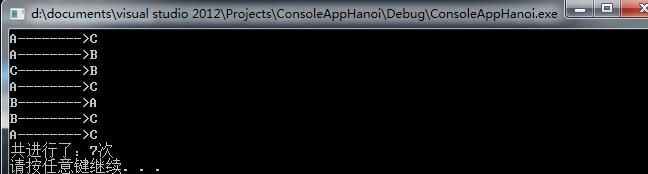
练习15,汉诺塔递归
// ConsoleAppHanoi.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int Hanoicount=0;
bool HanoiMove(int n,char a,char b,char c);//将n个盘从a借助b移动到c
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
HanoiMove(5,'A','B','C');
cout<<"共进行了:"<
练习。16求某年某月某日是当年的第几天
/ ConsoleAppRunNian.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
using namespace std;
int leap(int a) /*自己定义函数leap用来指定年份是否为闰年*/
{
if (a % 4 == 0 && a % 100 != 0 || a % 400 == 0) /*闰年判定条件*/
return 1; /*是闰年返回1*/
else
return 0; /*不是闰年返回0*/
}
int number(int year, int m, int d) /*自己定义函数number计算输入日期为该年第几天*/
{
if ( m>12 || d > 31 || d < 0 || m<0)
{
cerr<<"參数错误!"<
![]()
练习17,逻辑推理题
// ConsoleAppHunLi.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a, b, c;
for (a = 1; a <= 3; a++) /*穷举a的全部可能*/
for (b = 1; b <= 3; b++) /*穷举b的全部可能*/
for (c = 1; c <= 3; c++) /*穷举c的全部可能*/
if (a != 1 && c != 1 && c != 3 && a != b && a != c && b != c)
/*假设表达式为真,则输出结果。否则继续下次循环*/
{
cout<
![]()
练习18,二维数组转换为一维数组:
// ConsoleAppMatTrans.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
/******************
定义二维数组char array[x][y];
1.仅仅定义个一维的就能够了
char *array;
array = new char[x*y]; 这样的方式等价于char *array = new char[x*y];
訪问的时候*(array+i*y+j)表示array[i][j]
2.定义一个二维数组
char **array1
array1 = new char *[x];
for(i=0;i
![]()
练习19,求取一个二进制数的长度
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int BitLength(unsigned int n);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int count=0,a;
do
{
cout<<"请输入一个整数"<练习20,求两个正整数的最大公约数
#include "stdafx.h"
#include练习21,栈的顺序输出(STL库实现)
// ConsoleAppStackTest1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*函数功能:以 23 56 11 4 87 98入栈,以11 4 56 98 87 23出栈
*函数原形:无
*參数:无
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:无
*备注:无
*日期:2014/12/13
*原创:是
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:[email protected]
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
练习22,括号配对问题
描写叙述 如今。有一行括号序列。请你检查这行括号是否配对。
输入
3
[(])
(])
([[]()])
No
No
Yes
括号均指的是含圆括号和中括号)
1,假设为左型的括号(比方 “[” “(”)则入栈
2。假设为右型括号且栈为空或栈顶元素与之不配对则输出No,反之弹出栈顶元素
3,反复1和2步骤直到扫描结束,最后检查栈是否为空,若为空输出Yes反之输出No。
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
#include "stack"
using namespace std;
bool BracketMatch(const string srcStr);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int N = 0;
//申请内存
string src;
while (cin>>N)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> src;
if (BracketMatch(src))
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool BracketMatch(const string srcStr)
{
stack
练习23。奇偶数分离
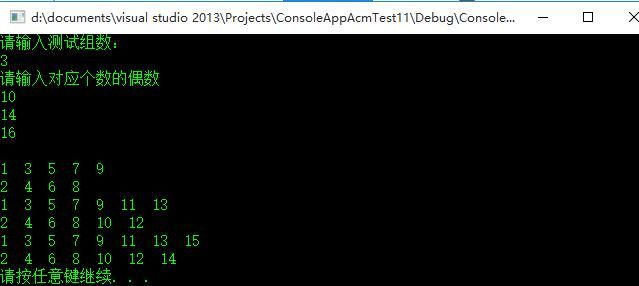
描写叙述 有一个整型偶数n(2<= n <=10000),你要做的是:先把1到n中的全部奇数从小到大输出,再把全部的偶数从小到大输出。
输入
每组有一个整型偶数n。
第二行输出全部的偶数
2
10
14
1 3 5 7 9
2 4 6 8 10
1 3 5 7 9 11 13
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
// ConsoleAppAcmTest11.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
练习24。五个数求最值
描写叙述 设计一个从5个整数中取最小数和最大数的程序
输入
1 2 3 4 5
1 5
// ConsoleAppAcmTest31.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。![]()
练习25,韩信点兵
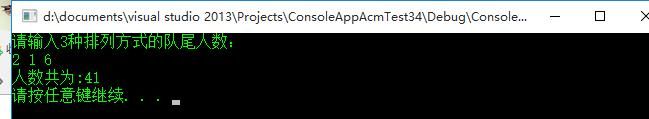
描写叙述 相传韩信才智过人。从不直接清点自己军队的人数,仅仅要让士兵先后以三人一排、五人一排、七人一排地变换队形,而他每次仅仅掠一眼队伍的排尾就知道总人数了。输入3个非负整数a,b,c ,表示每种队形排尾的人数(a<3,b<5,c<7)。输出总人数的最小值(或报告无解)。已知总人数不小于10。不超过100 。
输入
2 1 6
41
// ConsoleAppAcmTest34.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。练习26,组合数
描写叙述 找出从自然数1、2、... 、n(0
输入
特定顺序:每个组合中的值从大到小排列。组合之间按逆字典序排列。
5 3
543
542
541
532
531
521
432
431
421
321
// ConsoleAppAcmTest32.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[11];
bool visit[11];//存放数据被訪问否
void DFSCombiNum1(int n,int cur, int r);
void printNum(int *w, int r);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int n = 5;
int r = 3;
cout << "确定范围1到n:请输入n的详细值"<
![]()
练习27,计算超大数相乘:
编写两个超大数相乘,不用考虑负数
#include
![]()
练习28。单词的部分逆置
#include "string"
#include "vector"
#include
练习29。二分查找法存在的问题
![]() 。(n代表集合中元素的个数) 空间复杂度
。(n代表集合中元素的个数) 空间复杂度 ![]() 。虽以递归形式定义,可是尾递归。可改写为循环
。虽以递归形式定义,可是尾递归。可改写为循环
開始分析
以上看起来没事,除了一个非常微妙的东西,表达“m =(l+r)/ 2″。
它不能用于l和r特别大的时候,假设l和r的总和大于最大正int值(2的31次方–1)。
练习30,显式的调用析构器和构造器
s.String::~String(); // Nonvirtual call
ps->String::~String(); // Nonvirtual call
s.~String(); // Virtual call
ps->~String(); // Virtual call
练习31,调整数组结构
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
#include "fstream"
#include "algorithm"
using namespace wavelet;
using namespace std;
bool AdjustData(
double *pDetCoef,
const int height,
const int width
)
{
if (pDetCoef == NULL)
return false;
double *ptmpdet = new double[height / 2 * width];
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2 * width; i++)
ptmpdet[i] = pDetCoef[i];
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = height / 2 * width / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (j < width / 2)
pDetCoef[pos1++] = ptmpdet[i*width + j];
else
pDetCoef[pos2++] = ptmpdet[i*width + j];
}
}
delete[] ptmpdet;
ptmpdet = NULL;
return true;
}
bool IAdjustData(
double *pDetCoef,
const int height,
const int width
)
{
if (pDetCoef == NULL)
return false;
double *ptmpdet = new double[height / 2 * width];
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2 * width; i++)
ptmpdet[i] = pDetCoef[i];
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = height / 2 * width / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (j < width / 2)
pDetCoef[i*width + j] = ptmpdet[pos1++];
else
pDetCoef[i*width + j] = ptmpdet[pos2++];
}
}
delete[] ptmpdet;
ptmpdet = NULL;
return true;
}
int main()
{
system("color 0A");
double s[30] = {1,2,3,4,5,6, 2,3,4,5,6,7, 3,4,5,6,7,8, 4,5,6,7,8,9, 5,6,7,8,9,10};
int height = 5;
int width = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl; cout << endl;
AdjustData(s,height,width);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
IAdjustData(s, height, width);
cout << endl; cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
题源參考