| 网页右边,向下滑有目录索引,可以根据标题跳转到你想看的内容 |
| 如果右边没有就找找左边 |
| 此文是学习尚硅谷Elasticsearch课程的笔记 |
- 全文检索引擎
- Lucene 是 Apache软件基金会Jakarta项目组的一个子项目,提供了简单却强大的应用程序接口,能够全文索引和搜索。Java开发环境中Lucene是成熟的免费开源工具,但Lucene只是一个提供全文搜索功能类库的核心工具包,而真正使用还需要完善的服务框架搭建起来进行应用
- 于是Elasticsearch 和 Solr出现了(两个都是用Lucene进行开发的,各有优点)
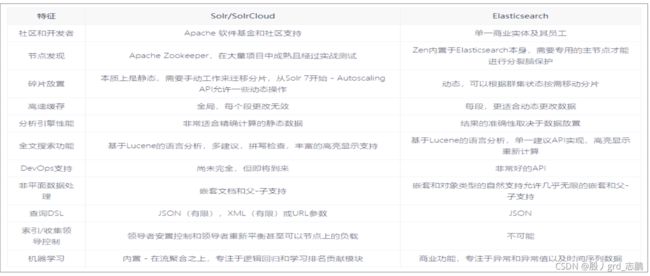
- 如果除了搜索文本外,还需要它来处理分析查询,Elasticsearch 是更好的选择,
- 需要分布式索引,良好的可伸缩性,Elasticsearch是更好的选择
- 如果需要监控和指标,Elasticsearch 暴露了更多关键指标,是更好的选择
- 其它方面,Slor是更好的选择,当然Solr对新手不太友好,相对较难
- The Elastic Stack,又称ELK Stack,ELK 技术栈,包括Elasticsearch、Kibana、Beats和Logstash,能够安全可靠的获取任何来源、任何格式的数据,然后实时地对数据进行搜索、分析和可视化。
- Elaticsearch简称ES,是一个开源的,高扩展的,分布式全文搜索引擎,整个ELK Static的核心,可以近乎实时的存储、检索数据;扩展性强,可以扩展到百台服务器,处理PB级的数据
一、入门
1. 下载安装windows和Linux版本
- 进入官网https://www.elastic.co/cn/,下载




- 解压
- 启动ES

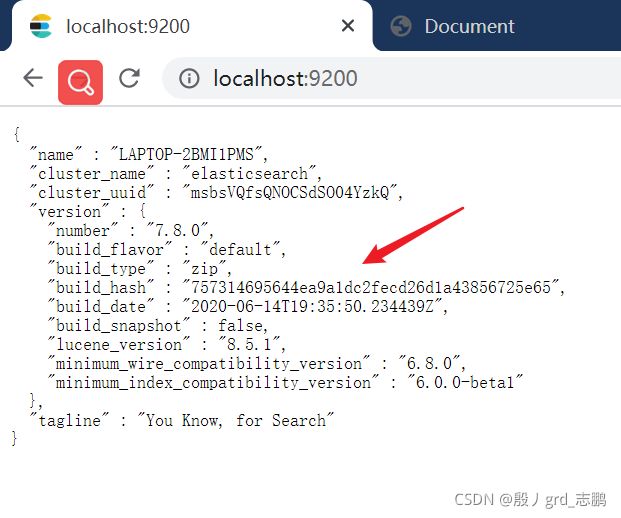
- cmd窗口中,会有两个端口号
9300端口为ES集群间组件的通信端口,9200端口是浏览器访问的http协议RESTful端口

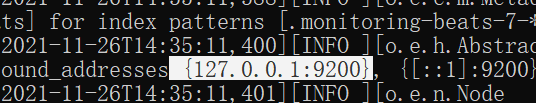
- 浏览器访问9200端口,出现如下内容,表示访问成功
2. 数据格式
- Elasticsearch 是面向文档型数据库,一条数据就是一个文档,如果你会Mysql,那么下面这张图是Mysql存储数据概念和Elasticsearch里存储文档数据的类比

- Index可以看做一个库,Types相当于表,Documents 相当于行,Fields相当于列
- Types概念已经被弱化了,ES 6.X中,一个index下已经只能包含一个type,7.X中Type的概念已经被删除
- 因为ES需要快速检索,我们需要快速通过索引检索到数据,而type的存在,与我们初心相违背,因此出现了
正排索引和倒排索引
- ES是为了提高搜索效率而出现的,比如,有这样一条数据id=1000,content = zhangsan
- 比如我们要找id为1000的数据,那么正排索引很有用,直接找到id为1000的数据
- 但是,当我们想要找到,content里面包含zhang,或者包含san,正排索引就不是很管用了
- 此时就需要使用倒排索引,key = zhang id = 1000,key = san id = 1000
- 可见,倒排索引,就是让关键字作为key,content中包含key的数据的id保存的value中,这样,当我们检索关键字zhang时,就可以快速找到相匹配的数据
3. 通过HTTPRestful操作ES
- ES向外暴露了很多httpRestFul风格的API,我们通过这些来快速入门,大家看看就好,这些不常用的
1. 索引
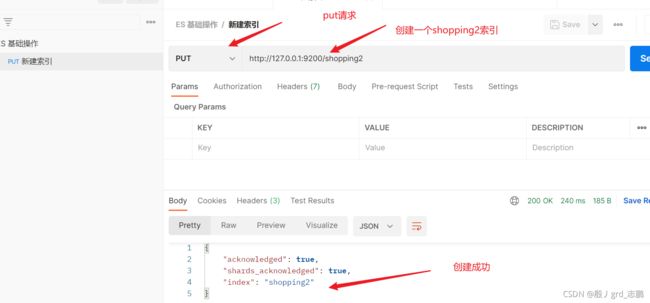
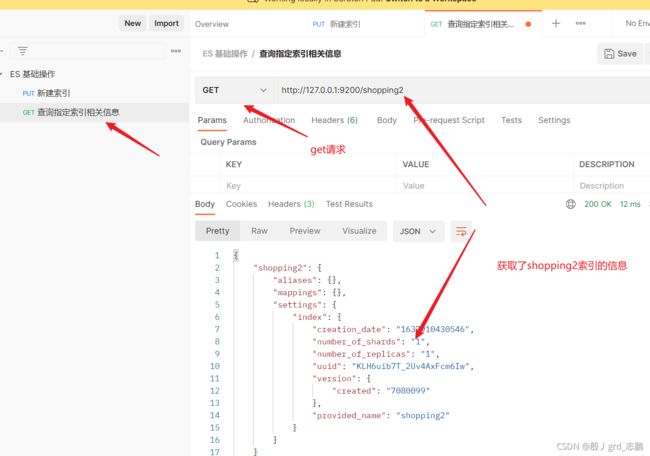
http://127.0.0.1:9200/_cat/indices?v


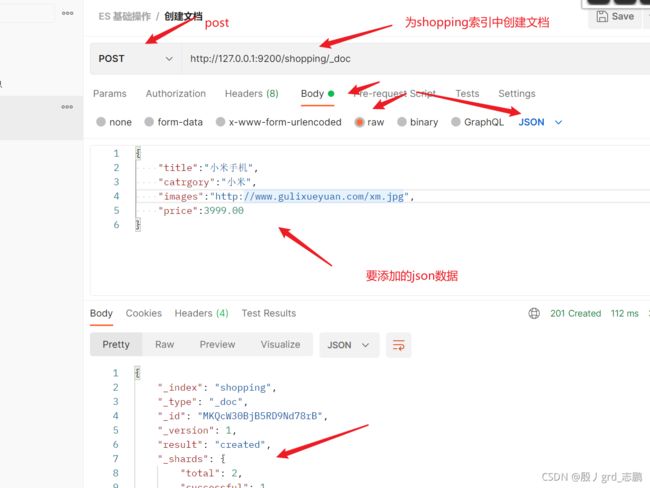
2. 文档
{
"title":"小米手机",
"catrgory":"小米",
"images":"http://www.gulixueyuan.com/xm.jpg",
"price":3999.00
}
- 随机生成id
- 自定义id

- 根据id查http://127.0.0.1:9200/shopping/_doc/1001

- 查询所有http://127.0.0.1:9200/shopping/_search

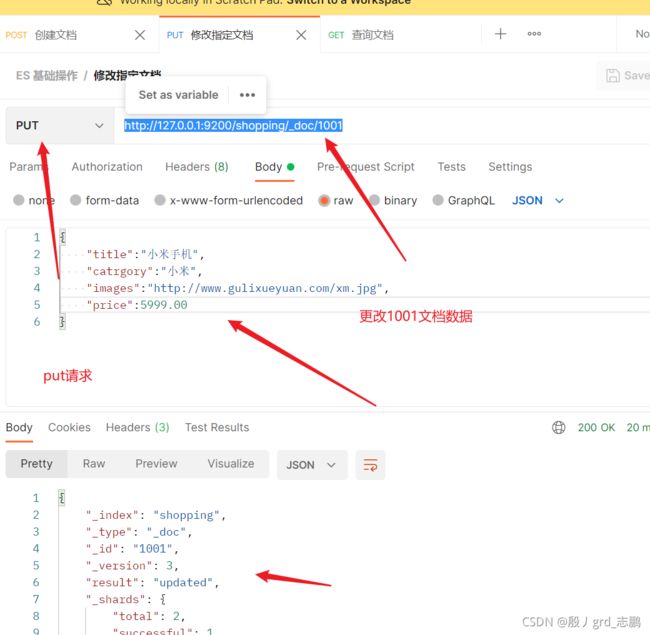
- 修改指定文档,全部内容

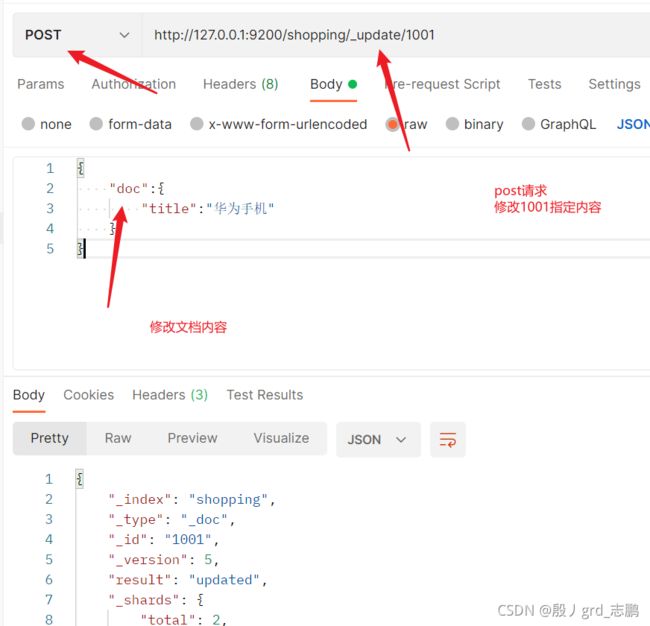
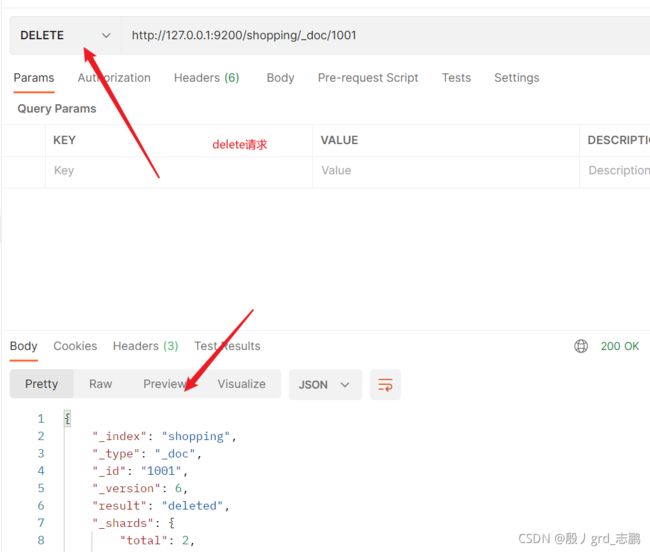
- 修改指定文档,指定内容

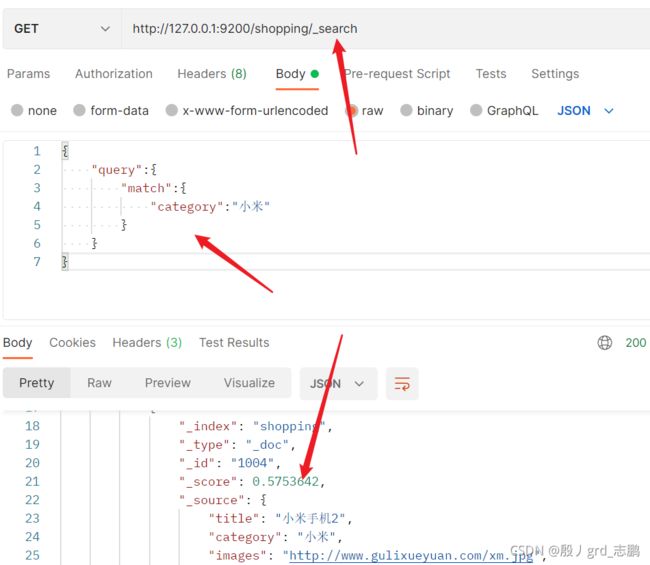
3. 复杂查询(先多添加点文档)
- 写在地址栏

- 使用json
{
"query":{
"match":{
"category":"小米"
}
}
}
| 2. 全部查询(后面都只给出json条件,因为url都一样),以及分页等参数的设置 |
{
"query":{
"match_all":{
}
},
"from":0,
"size":2,
"_source":[
"title",
"price"
],
"sort":{
"price":{
"order":"desc"
}
}
}
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{
"match":{
"catrgory":"小米"
}
},
{
"match":{
"price":"3999.0"
}
}
]
}
}
}
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{
"match":{
"catrgory":"小米"
}
},
{
"match":{
"catrgory":"华为"
}
}
]
}
}
}
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"range":{
"price":{
"gt":4000
}
}
}
}
}
}
4. 条件删除
- 发 POST 请求 :http://127.0.0.1:9200/shopping/_delete_by_query
- 请求参数
{
"query":{
"match":{
"price":4000.00
}
}
}
4. 匹配规则
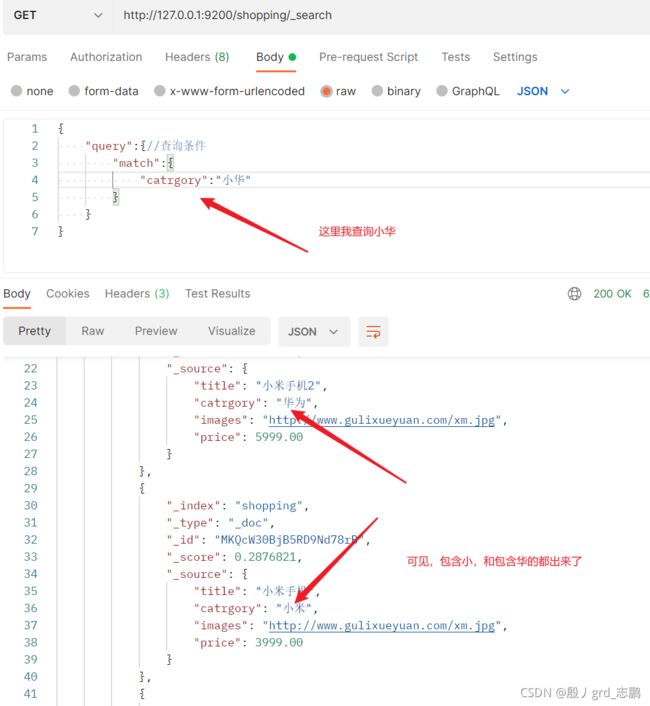
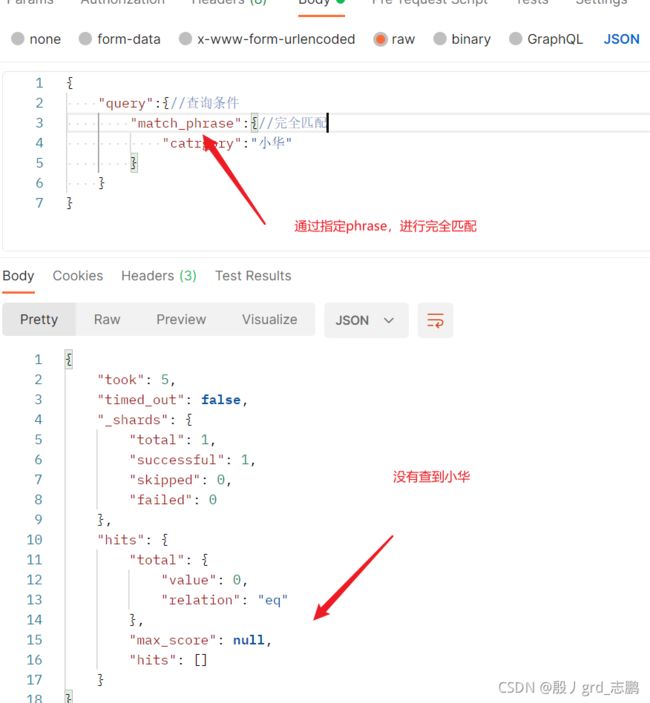
{
"query":{
"match_phrase":{
"catrgory":"小华"
}
}
}
5. 高亮

{
"query":{
"match":{
"catrgory":"小华"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"catrgory":{}
}
}
}
6. 聚合操作
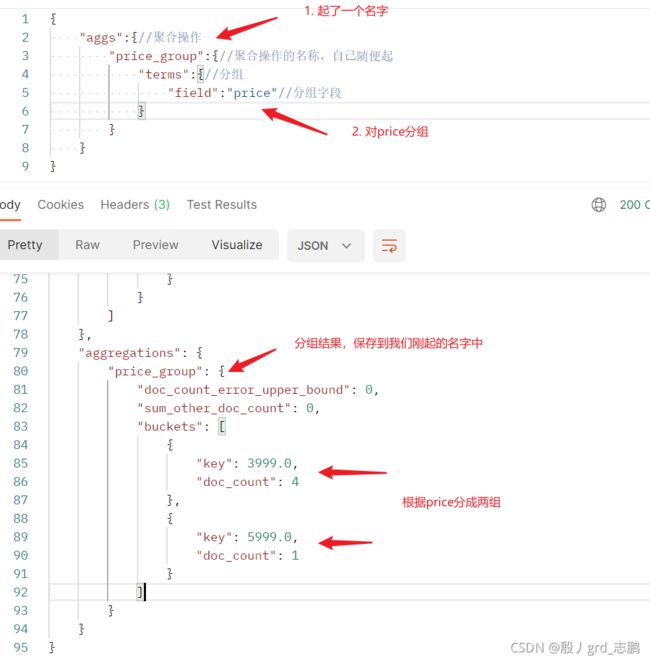
{
"aggs":{
"price_group":{
"terms":{
"field":"price"
}
}
},
}

{
"aggs":{
"price_group":{
"terms":{
"field":"price"
}
},
"price_avg":{
"avg":{
"field":"price"
}
}
},
"size":0
}
7. 映射
- 先新建一个索引
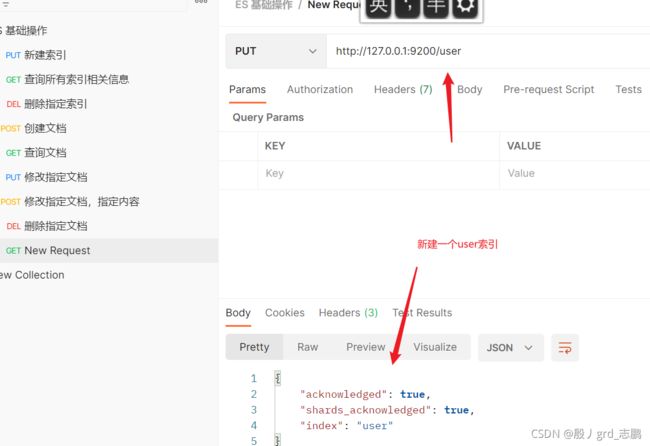
- 建立隐射http://127.0.0.1:9200/user/_mapping

{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text",
"index":true
},
"sex":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":true
},
"telphone":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":false
}
}
}
- 创建文档

- 查询
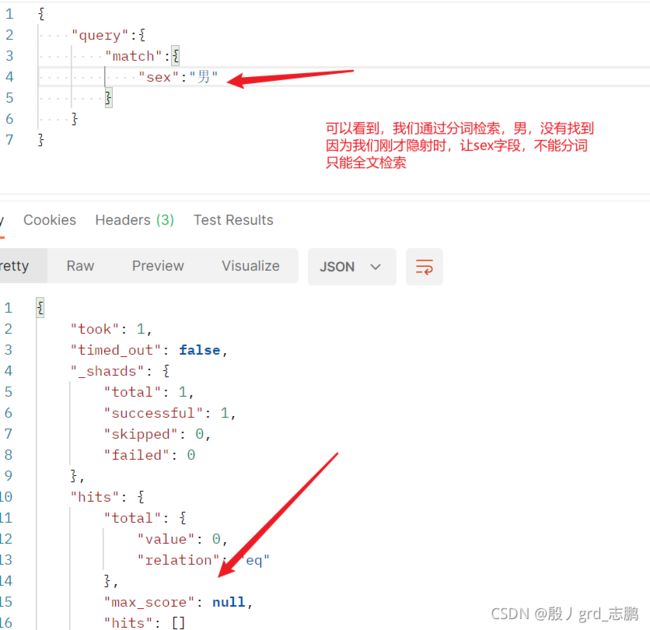


二、javaAPI 操作Elasticsearch
1. 环境搭建
- 创建maven工程,引入依赖

<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- elasticsearch 依赖 2.x 的 log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 创建实体类
package com.yzpnb.es.entity;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
2. 测试类
- 测试类,代码量比较大,我们日后使用一些框架提供的工具,不使用这些代码,但是工具就是封装了这些代码,所以要理解这些代码,代码量虽然多,但是基本所有操作都写了,为了方便大家理解,我将每一个用法,都单独写成一个方法,所以,重复的代码很多
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.yzpnb.es.entity.User;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.support.master.AcknowledgedResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.Fuzziness;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.BoolQueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.RangeQueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.AggregationBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.highlight.HighlightBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.highlight.HighlightField;
import org.elasticsearch.search.sort.SortOrder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
public class Elasticsearch01_Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http"))
);
createDocList(client,"user1");
client.close();
}
private static void delIndex(RestHighLevelClient client, String indexName) {
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest(indexName);
AcknowledgedResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("操作结果 : " + response.isAcknowledged());
}
public static void creteIndex(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName){
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest(indexName);
CreateIndexResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean acknowledged = response.isAcknowledged();
System.out.println("操作状态 = " + acknowledged);
}
public static void getIndex(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName){
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest(indexName);
GetIndexResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.indices().get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("aliases:"+response.getAliases());
System.out.println("mappings:"+response.getMappings());
System.out.println("settings:"+response.getSettings());
}
public static void createDoc(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName,String docId){
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest();
request.index(indexName).id(docId);
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(30);
user.setSex("男");
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
String productJson = null;
try {
productJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
request.source(productJson, XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("_index:" + response.getIndex());
System.out.println("_id:" + response.getId());
System.out.println("_result:" + response.getResult());
}
public static void getDocbyId(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName,String docId){
GetRequest request = new GetRequest().index(indexName).id(docId);
GetResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("_index:" + response.getIndex());
System.out.println("_type:" + response.getType());
System.out.println("_id:" + response.getId());
System.out.println("source:" + response.getSourceAsString());
}
public static void updateDoc(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName,String docId){
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest();
request.index(indexName).id(docId);
request.doc(XContentType.JSON, "sex", "女");
UpdateResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("_index:" + response.getIndex());
System.out.println("_id:" + response.getId());
System.out.println("_result:" + response.getResult());
}
public static void delDoc(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName,String docId){
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest().index(indexName).id(docId);
DeleteResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(response.toString());
}
public static void createDocList(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName){
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
request.add(new IndexRequest().index(indexName).id("1001").source(XContentType.JSON, "name", "zhangsan"));
request.add(new IndexRequest().index(indexName).id("1002").source(XContentType.JSON, "name", "lisi"));
request.add(new IndexRequest().index(indexName).id("1003").source(XContentType.JSON, "name", "wangwu"));
BulkResponse responses = null;
try {
responses = client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("took:" + responses.getTook());
System.out.println("items:" + responses.getItems());
}
public static void delDocList(RestHighLevelClient client,String indexName){
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
request.add(new DeleteRequest().index(indexName).id("1001"));
request.add(new DeleteRequest().index(indexName).id("1002"));
request.add(new DeleteRequest().index(indexName).id("1003"));
BulkResponse responses = null;
try {
responses = client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("took:" + responses.getTook());
System.out.println("items:" + responses.getItems());
}
public static void queryBodyDocAll(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocTerm(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("age", "30"));
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDoclimit(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.from(0);
sourceBuilder.size(2);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocSort(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
sourceBuilder.sort("age", SortOrder.ASC);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); }
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocFilter(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
String[] excludes = {};
String[] includes = {"name", "age"};
sourceBuilder.fetchSource(includes, excludes);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocBool(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
boolQueryBuilder.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("age", "30"));
boolQueryBuilder.mustNot(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("name", "zhangsan"));
boolQueryBuilder.should(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("sex", "男"));
sourceBuilder.query(boolQueryBuilder);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocRange(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
RangeQueryBuilder rangeQuery = QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("age");
rangeQuery.gte("30");
rangeQuery.lte("40");
sourceBuilder.query(rangeQuery);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocFuzzy(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.fuzzyQuery("name","zhangsan").fuzziness(Fuzziness.ONE));
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took:" + response.getTook());
System.out.println("timeout:" + response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total:" + hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("MaxScore:" + hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits========>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
System.out.println("<<========");
}
public static void queryBodyDocHighlight(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest();
request.indices("student");
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
highlightBuilder.preTags("");
highlightBuilder.postTags("");
highlightBuilder.field("name");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println("took::"+response.getTook());
System.out.println("time_out::"+response.isTimedOut());
System.out.println("total::"+hits.getTotalHits());
System.out.println("max_score::"+hits.getMaxScore());
System.out.println("hits::::>>");
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
String sourceAsString = hit.getSourceAsString();
System.out.println(sourceAsString);
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
System.out.println(highlightFields);
}
System.out.println("<<::::");
}
public static void queryBodyDocAggregation(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest().indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.max("maxAge").field("age"));
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println(response);
}
public static void queryBodyDocGroup(RestHighLevelClient client){
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest().indices("student");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.aggregation(AggregationBuilders.terms("age_groupby").field("age"));
request.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse response = null;
try {
response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
System.out.println(response);
}
}
三、Linux集群搭建
1. 单机环境
- 将tar包上传到linux系统,然后解压缩

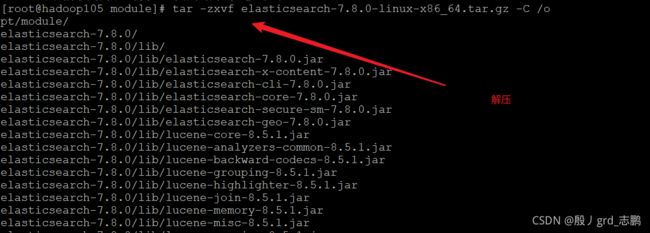
- 修改配置文件
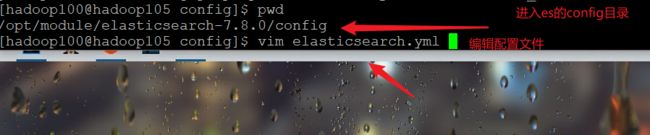
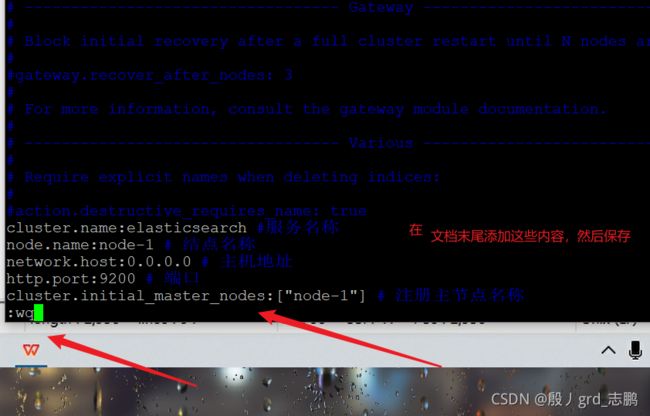
cluster.name: elasticsearch
node.name: node-1
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
- 更改系统配置
- 修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件(
里面配置的es是文件目录,你根据自己文件目录更改,或者直接复制我的代码块,用*直接对所有文件配置)


vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 65536
- 编辑文件 /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf

vim /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf
- 修改/etc/sysctl.conf文件VMA(虚拟内存区域)的数量,为655360

vim /etc/sysctl.conf
# 一个进程可以拥有的VMA(虚拟内存区域)的数量,默认65536
vm.max_map_count=655360
- 重新加载

sysctl -p
- 因为es为了安全起见,不允许root用户访问,所以我们需要切换成非root用户操作es
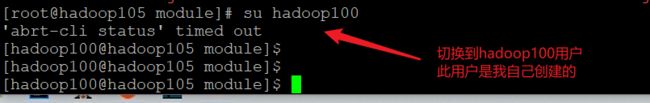
- 使用root用户,给非root用户操作权限

chown -R hadoop100:hadoop100 /opt/module/elasticsearch-7.8.0
- 进入es安装目录,执行bin/elasticsearch
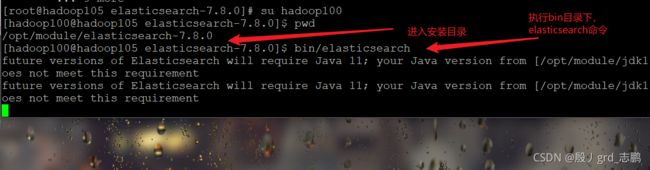
- 测试

2. 集群TODO
四、重点
1. 核心概念
- 索引就类似新华字典的目录,可以通过偏旁部首等快速找到汉字
- Elasticsearch的精髓,一切设计都是为了提高搜索效率
- 文档就是一条数据,可以被索引的基础信息单元
- 一个索引中,可以存储多个文档
- 对文档数据的不同数据,进行分类标识
- mapping 是处理数据的方式和规则方面做一些限制,如:某个字段的数据类型、默认值、分析器、是否被索引等等
- Elasticsearch 提供了将索引划分成多份的能力,每一份就称之为分片
- 创建一个索引的时候,可以指定你想要的分片的数量,可以被放置到集群中的任何节点
上
- 允许你水平分割 / 扩展你的内容容量
- 允许你在分片之上进行分布式的、并行的操作,进而提高性能/吞吐量
- 被混淆的概念是,一个 Lucene 索引 我们在 Elasticsearch 称作 分片 。 一个Elasticsearch 索引 是分片的集合。 当 Elasticsearch 在索引中搜索的时候, 他发送查询到每一个属于索引的分片(Lucene 索引),然后合并每个分片的结果到一个全局的结果集。
- Elasticsearch 允许你创建分片的一份或多份拷贝,这些拷贝叫做复制分片(副本)
- 在分片/节点失败的情况下,提供了高可用性。因为这个原因,注意到复制分片从不与原/主要(original/primary)分片置于同一节点上是非常重要的
- 扩展你的搜索量/吞吐量,因为搜索可以在所有的副本上并行运行
- 将分片分配给某个节点的过程,包括分配主分片或者副本。如果是副本,还包含从主分片复制数据的过程。这个过程是由 master 节点完成的
2. 单节点集群的不足,和多节点故障转移
| 我们创建users索引,并传递json,分配3个主分片和一个副本,就是每个主分片都有一个福本 |
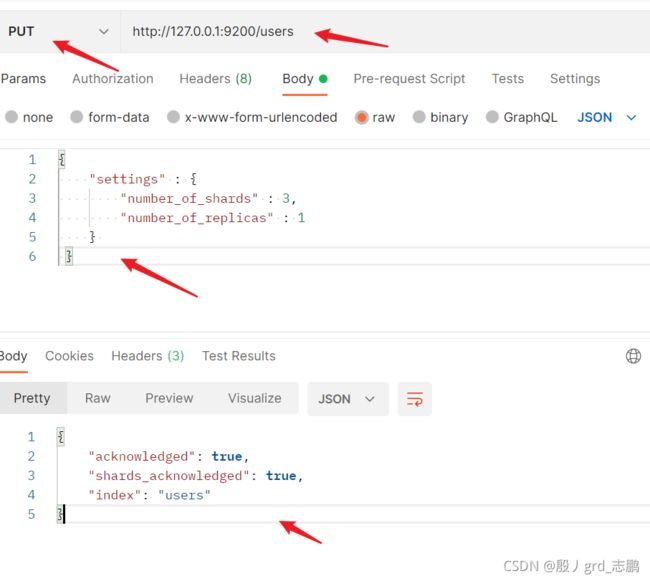
{
"settings" : {
"number_of_shards" : 3,
"number_of_replicas" : 1
}
}

百度Elasticsearch-head插件,安装到浏览器即可
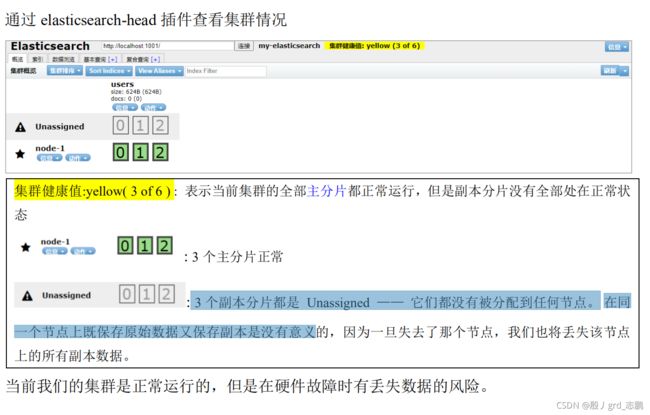
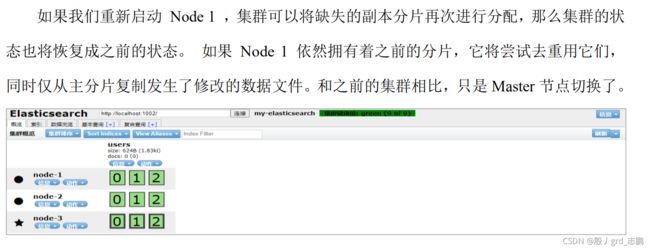
- 当集群中只有一个节点在运行时,意味着会有一个单点故障问题——没有冗余。 幸运的是,我们只需再启动一个节点即可防止数据丢失。当你在同一台机器上启动了第二个节点时,只要它和第一个节点有同样的 cluster.name 配置,它就会自动发现集群并加入到其中。但是在不同机器上启动节点的时候,为了加入到同一集群,你需要配置一个可连接到的单播主机列表。之所以配置为使用单播发现,以防止节点无意中加入集群。只有在同一台机器上运行的节点才会自动组成集群

- 怎样为我们的正在增长中的应用程序按需扩容呢?当启动了第三个节点,我们的集群将会拥有三个节点的集群 : 为了分散负载而对分片进行重新分配


- 主分片的数目在索引创建时就已经确定了下来。实际上,这个数目定义了这个索引能够存储 的最大数据量。(实际大小取决于你的数据、硬件和使用场景。) 但是,读操作——搜索和返回数据——可以同时被主分片 或 副本分片所处理,所以当你拥有越多的副本分片时,也将拥有越高的吞吐量
- 在运行中的集群上是可以动态调整副本分片数目的,我们可以按需伸缩集群。让我们把副本数从默认的 1 增加到 2
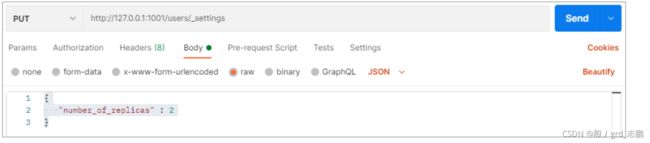
{
"number_of_replicas" : 2
}

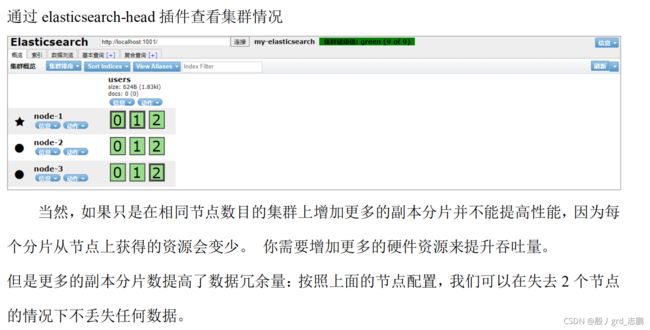

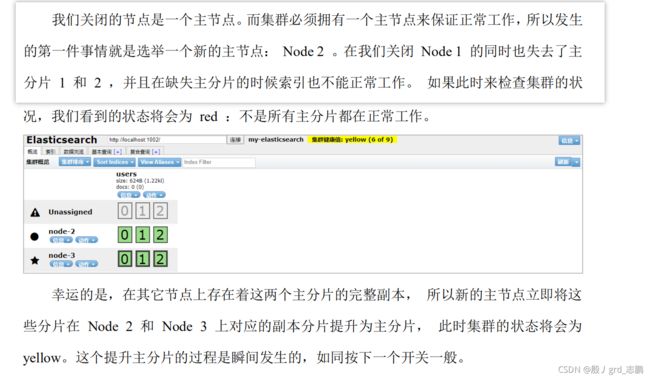
| 为什么我们集群状态是 yellow 而不是 green 呢 |
- 虽然我们拥有所有的三个主分片,但是同时设置了每个主分片需要对应 2 份副本分片,而此时只存在一份副本分片。 所以集群不能为 green 的状态,不过我们不必过于担心:如果我们同样关闭了 Node 2 ,我们的程序 依然 可以保持在不丢任何数据的情况下运行,因为Node 3 为每一个分片都保留着一份副本。
3. 路由计算和分片控制
- 当索引一个文档的时候,文档会被存储到一个主分片中。 Elasticsearch 如何知道一个文档应该存放到哪个分片中呢?当我们创建文档时,它如何决定这个文档应当被存储在分片1 还是分片 2 中呢?首先这肯定不会是随机的,否则将来要获取文档的时候我们就不知道从何处寻找了。
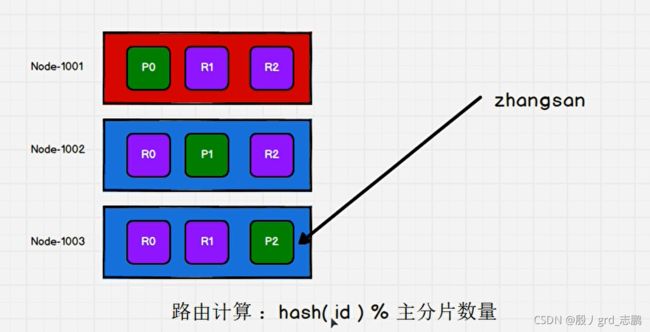
实际上,这个过程是根据下面这个公式决定的:

- 所有的文档 API( get 、 index 、 delete 、 bulk 、 update 以及 mget )都接受一个叫做 routing 的路由参数 ,通过这个参数我们可以自定义文档到分片的映射。一个自定义的路由参数可以用来确保所有相关的文档——例如所有属于同一个用户的文档——都被存储到同一个分片中。
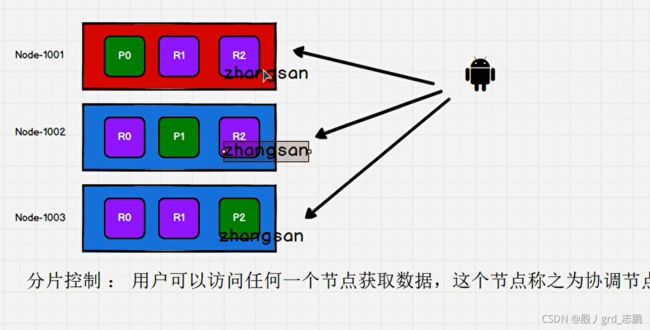
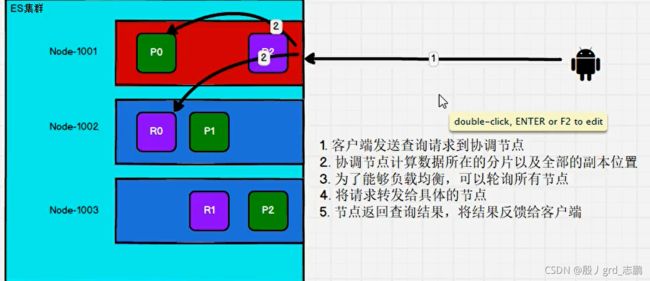
- 我们可以发送请求到集群中的任一节点。 每个节点都有能力处理任意请求。 每个节点都知道集群中任一文档位置,所以可以直接将请求转发到需要的节点上。 在下面的例子中,将所有的请求发送到 Node 1,我们将其称为 协调节点(coordinating node)
- 当发送请求的时候, 为了扩展负载,更好的做法是轮询集群中所有的节点
4. 写流程和读流程,以及更新流程

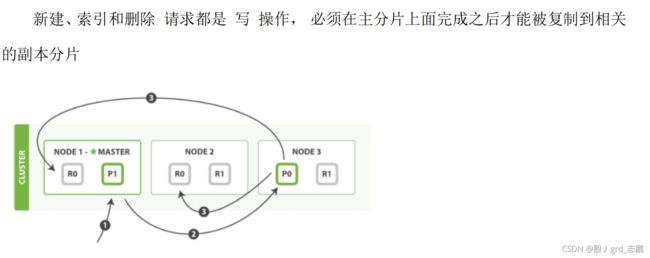
- 新建,索引和删除文档所需要的步骤顺序:
- 客户端向 Node 1 发送新建、索引或者删除请求。
- 节点使用文档的 _id 确定文档属于分片 0 。请求会被转发到 Node 3,因为分片 0 的主分片目前被分配在 Node 3 上。
- Node 3 在主分片上面执行请求。如果成功了,它将请求并行转发到 Node 1 和 Node 2 的副本分片上。一旦所有的副本分片都报告成功, Node 3 将向协调节点报告成功,协调节点向客户端报告成功
- 在客户端收到成功响应时,文档变更已经在主分片和所有副本分片执行完成,变更是安全的。
- 有一些可选的请求参数允许您影响这个过程,可能以数据安全为代价提升性能。这些选项很少使用,因为 Elasticsearch 已经很快,但是为了完整起见,请参考下面图片:
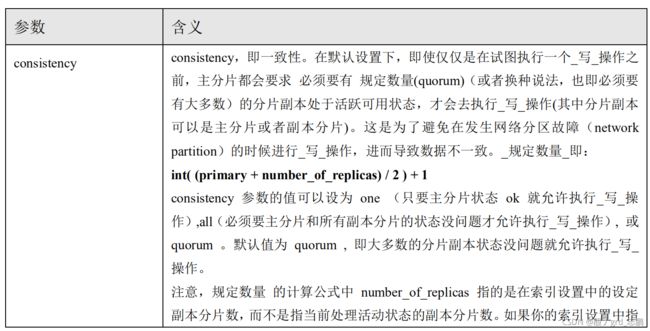

- 新索引默认有 1 个副本分片,这意味着为满足规定数量应该需要两个活动的分片副本。 但是,这些默认的设置会阻止我们在单一节点上做任何事情。为了避免这个问题,要求只有当 number_of_replicas 大 于 1 的时候,规定数量才会执行
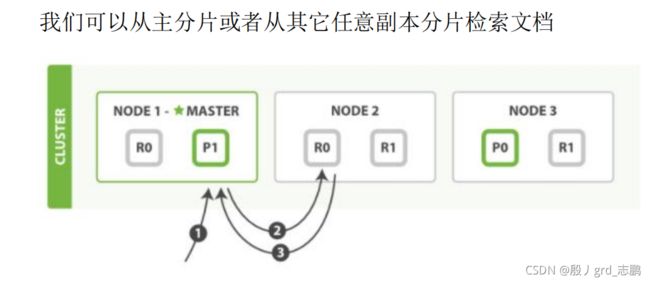
- 从主分片或者副本分片检索文档的步骤顺序
- 客户端向 Node 1 发送获取请求。
- 节点使用文档的 _id 来确定文档属于分片 0 。分片 0 的副本分片存在于所有的三个节点上。 在这种情况下,它将请求转发到 Node 2 。
- Node 2 将文档返回给 Node 1 ,然后将文档返回给客户端。
- 在处理读取请求时,协调结点在每次请求的时候都会通过轮询所有的副本分片来达到负载均衡。在文档被检索时,已经被索引的文档可能已经存在于主分片上但是还没有复制到副本分片。 在这种情况下,副本分片可能会报告文档不存在,但是主分片可能成功返回文档。 一旦索引请求成功返回给用户,文档在主分片和副本分片都是可用的

- 部分更新一个文档的步骤如下
- 客户端向 Node 1 发送更新请求。
- 它将请求转发到主分片所在的 Node 3 。
- Node 3 从主分片检索文档,修改 _source 字段中的 JSON ,并且尝试重新索引主分片的文档。如果文档已经被另一个进程修改,它会重试步骤 3 ,超过 retry_on_conflict 次后放弃。
- 如果 Node 3 成功地更新文档,它将新版本的文档并行转发到 Node 1 和 Node 2 上的副本分片,重新建立索引。一旦所有副本分片都返回成功, Node 3 向协调节点也返回成功,协调节点向客户端返回成功
- 当主分片把更改,转发到副本分片时, 它不会转发更新请求。 相反,它转发完整文档的新版本。请记住,这些更改将会异步转发到副本分片,并且不能保证它们以发送它们相同的顺序到达。 如果 Elasticsearch 仅转发更改请求,则可能以错误的顺序应用更改,导致得到损坏的文档。
5. 多文档的操作流程
- mget 和 bulk API 的模式类似于单文档模式。区别在于协调节点知道每个文档存在于哪个分片中。它将整个多文档请求分解成 每个分片 的多文档请求,并且将这些请求并行转发到每个参与节点。
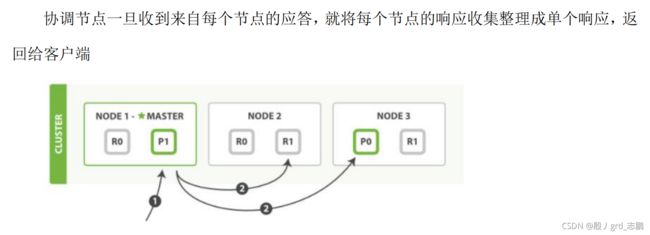
- 用单个 mget 请求取回多个文档所需的步骤顺序(可以对 docs 数组中每个文档设置 routing 参数)
- 客户端向 Node 1 发送 mget 请求
- Node 1 为每个分片构建多文档获取请求,然后并行转发这些请求到托管在每个所需的主分片或者副本分片的节点上。一旦收到所有答复, Node 1 构建响应并将其返回给客户端
- bulk API, 允许在单个批量请求中执行多个创建、索引、删除和更新请求,按如下步骤顺序执行
- 客户端向 Node 1 发送 bulk 请求。
- Node 1 为每个节点创建一个批量请求,并将这些请求并行转发到每个包含主分片的节点主机。
- 主分片一个接一个按顺序执行每个操作。当每个操作成功时,主分片并行转发新文档(或删除)到副本分片,然后执行下一个操作。 一旦所有的副本分片报告所有操作成功,该节点将向协调节点报告成功,协调节点将这些响应收集整理并返回给客户端
6. 分片原理和倒排索引
- 分片是 Elasticsearch 最小的工作单元。但是究竟什么是一个分片,它是如何工作的?传统的数据库每个字段存储单个值,但这对全文检索并不够。文本字段中的每个单词需要被搜索,对数据库意味着需要单个字段有索引多值的能力。最好的支持是一个字段多个值需求的数据结构是
倒排索引
- Elasticsearch 使用一种称为倒排索引的结构,它适用于快速的全文搜索
- 先说所谓的正向索引,就是搜索引擎会将待搜索的文件都对应一个文件 ID,搜索时将这个ID 和搜索关键字进行对应,形成 K-V 对,然后对关键字进行统计计数

- 但是互联网上收录在搜索引擎中的文档的数目是个天文数字,这样的索引结构根本无法满足实时返回排名结果的要求
- 所以,搜索引擎会将正向索引重新构建为倒排索引,即把文件ID对应到关键词的映射转换为关键词到文件ID的映射,每个关键词都对应着一系列的文件,这些文件中都出现这个关键词
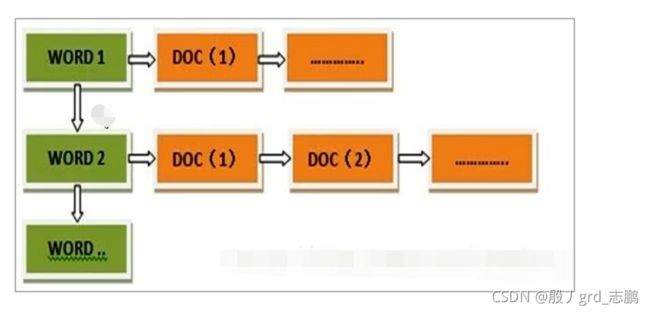
- 一个倒排索引由文档中所有不重复词的列表构成,对于其中每个词,有一个包含它的文档列表。例如,假设我们有两个文档,每个文档的 content 域包含如下内容:
- The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog
- Quick brown foxes leap over lazy dogs in summer
- 为了创建倒排索引,我们首先将每个文档的 content 域拆分成单独的 词(我们称它为 词条或 tokens ),创建一个包含所有不重复词条的排序列表,然后列出每个词条出现在哪个文档。结果如下所示

- 现在,如果我们想搜索 quick brown ,我们只需要查找包含每个词条的文档


- 为了解决搜索+Quick和+fox 这样的索引查找不到文档的问题(Quick和quick是我们都希望检索到的,但Q和q不同,会检索不到),我们需要将词条规范为标准模式,就是找到与用户搜索的词条不完全一致,但具有足够相关性的文档

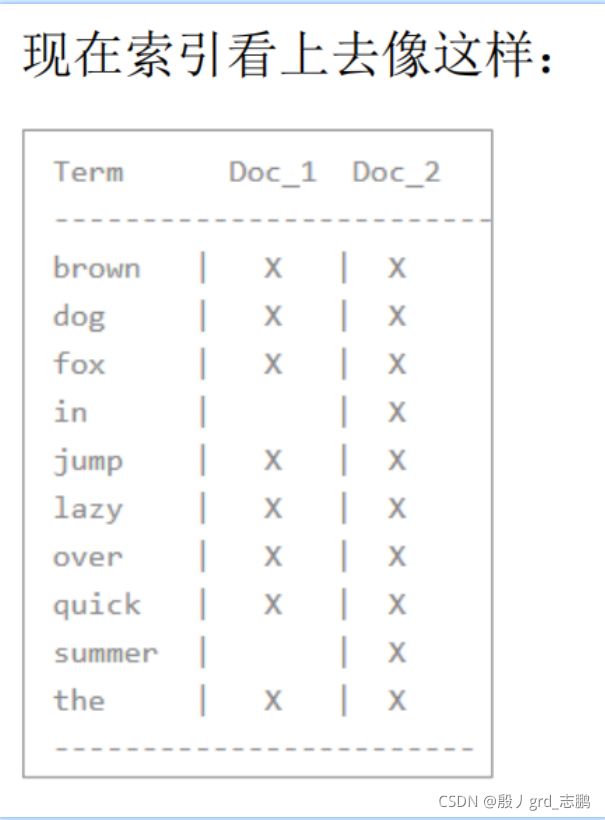
- 此时我们索引的Quick就不复存在了(因为标准化成quick了),那么如果我们还索引+Quick,就找不到了,所有此时我们对搜索的字符串使用与 content 域相同的标准化规则,会变成查询+quick +fox,这样两个文档都会匹配!分词和标准化的过程称为
分析
- 你只能搜索在索引中出现的词条,所以索引文本和查询字符串必须标准化为相
同的格式
7. 文档搜索
- 早期的全文检索会为整个文档集合建立一个很大的倒排索引并将其写入到磁盘。 一旦新的索引就绪,旧的就会被其替换,这样最近的变化便可以被检索到。
- 倒排索引被写入磁盘后是 不可改变的:它永远不会修改
- 不变性有重要的价值
- 不需要锁。如果你从来不更新索引,你就不需要担心多进程同时修改数据的问题。
- 一旦索引被读入内核的文件系统缓存,便会留在哪里,由于其不变性。只要文件系统缓存中还有足够的空间,那么大部分读请求会直接请求内存,而不会命中磁盘。这提供了很大的性能提升。
- 其它缓存(像 filter 缓存),在索引的生命周期内始终有效。它们不需要在每次数据改变时被重建,因为数据不会变化。
- 写入单个大的倒排索引允许数据被压缩,减少磁盘 I/O 和 需要被缓存到内存的索引的使用量。
- 当然,一个不变的索引也有不好的地方。主要事实是它是不可变的! 你不能修改它。如果你需要让一个新的文档 可被搜索,你需要重建整个索引。这要么对一个索引所能包含的数据量造成了很大的限制,要么对索引可被更新的频率造成了很大的限制
8.文档刷写和文档合并
- 如何在保留不变性的前提下实现倒排索引的更新?
- 用更多的索引。通过增加新的补充索引来反映新近的修改,而不是直接重写整个倒排索引。每一个倒排索引都会被轮流查询到,从最早的开始查询完后再对结果进行合并
- Elasticsearch 基于 Lucene, 这个 java 库引入了按段搜索的概念.每一 段本身都是一个倒排索引, 但索引在 Lucene 中除表示所有段的集合外,还增加了提交点的概念 — 一个列出了所有已知段的文件
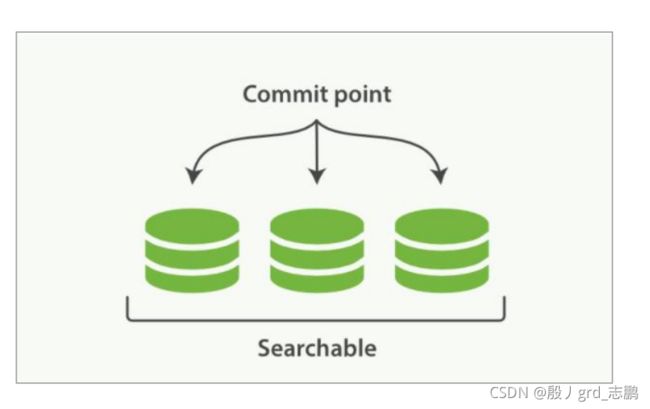
- 按段搜索会以如下流程执行
- 新文档被收集到内存索引缓存

- 不时地, 缓存被提交
- 一个新的段—一个追加的倒排索引—被写入磁盘。
- 一个新的包含新段名字的 提交点 被写入磁盘
- 磁盘进行同步 — 所有在文件系统缓存中等待的写入都刷新到磁盘,以确保它们被写入物理文件
- 新的段被开启,让它包含的文档可见以被搜索
- 内存缓存被清空,等待接收新的文档

- 当一个查询被触发,所有已知的段按顺序被查询。词项统计会对所有段的结果进行聚合,以保证每个词和每个文档的关联都被准确计算。 这种方式可以用相对较低的成本将新文档添加到索引。
- 段是不可改变的,所以既不能从把文档从旧的段中移除,也不能修改旧的段来进行反映文档的更新。 取而代之的是,每个提交点会包含一个 .del 文件,文件中会列出这些被删除文档的段信息。当一个文档被 “删除” 时,它实际上只是在 .del 文件中被 标记 删除。一个被标记删除的文档仍然可以被查询匹配到, 但它会在最终结果被返回前从结果集中移除
- 文档更新也是类似的操作方式:当一个文档被更新时,旧版本文档被标记删除,文档的新版本被索引到一个新的段中。 可能两个版本的文档都会被一个查询匹配到,但被删除的那个旧版本文档在结果集返回前就已经被移除
- 随着按段(per-segment)搜索的发展,一个新的文档从索引到可被搜索的延迟显著降低了,新文档在几分钟之内即可被检索,但这样还是不够快。磁盘在这里成为了瓶颈
- 每提交一次新段,都要刷写到磁盘,虽然保证数据安全性,但是性能问题很大
- Lucene 允许新段被写入和打开—使其包含的文档在未进行一次完整提交时便对搜索可见。这种方式比进行一次提交代价要小得多,并且在不影响性能的前提下可以被频繁地执行。在ES中写入和打开一个新段的轻量的过程叫做 refresh,它的刷新时间可以配置,当然也可以请求api/users/_refresh手动刷新
refresh_interval 可以在既存索引上进行动态更新。 在生产环境中,当你正在建立一个大的
新索引时,可以先关闭自动刷新,待开始使用该索引时,再把它们调回来
# 关闭自动刷新
PUT /users/_settings
{ "refresh_interval": -1 }
# 每一秒刷新
PUT /users/_settings
{ "refresh_interval": "1s" }
- 有了近实时搜索,我们就不能保证数据在断电甚至是程序正常退出之后依然存在,
- 即使通过每秒刷新(refresh)实现了近实时搜索,我们仍然需要经常进行完整提交来确保能从失败中恢复。但在两次提交之间发生变化的文档怎么办?我们也不希望丢失掉这些数据。Elasticsearch 增加了一个 translog ,或者叫事务日志,在每一次对Elasticsearch 进行操作时均进行了日志记录


- 首先我们要写入段落,此时将其提交Segment,近实时搜索
- 同时Translog记录日志
- 然后先刷到系统缓存区,refresh代表此过程,可以调整每次刷新时长
- 系统缓存区将内容刷入磁盘
- 日志也会刷入磁盘,但不经过缓冲区
9. 文档分析和IK分词器
- 将一块文本分成适合于倒排索引的独立的 词条
- 将这些词条统一化为标准格式以提高它们的“可搜索性”,或者 recall
- 分析器执行上面的工作。分析器实际上是将三个功能封装到了一个包里
- 字符过滤器:首先,字符串按顺序通过每个 字符过滤器 。他们的任务是在分词前整理字符串。一个字符过滤器可以用来去掉 HTML,或者将 & 转化成 and
- 分词器:其次,字符串被 分词器 分为单个的词条。一个简单的分词器遇到空格和标点的时候,可能会将文本拆分成词条
- Token 过滤器:最后,词条按顺序通过每个 token 过滤器 。这个过程可能会改变词条(例如,小写化Quick ),删除词条(例如, 像 a, and, the 等无用词),或者增加词条(例如,像 jump 和 leap 这种同义词)
- 下面列出最重要的分析器我,我们看看每个分析器会从"Set the shape to semi-transparent by calling set_trans(5)"这个字符串得到哪些词条
- 标准分析器
- 标准分析器是 Elasticsearch 默认使用的分析器。它是分析各种语言文本最常用的选择。它根据 Unicode 联盟 定义的 单词边界 划分文本。删除绝大部分标点。最后,将词条小写。
- 它会产生:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set_trans, 5
- 简单分析器
- 简单分析器在任何不是字母的地方分隔文本,将词条小写。
- 它会产生:set, the, shape, to, semi, transparent, by, calling, set, trans
- 空格分析器
- 空格分析器在空格的地方划分文本。
- 它会产生:Set, the, shape, to, semi-transparent, by, calling, set_trans(5)
- 语言分析器
- 特定语言分析器可用于 很多语言。它们可以考虑指定语言的特点。例如, 英语 分析器附带了一组英语无用词(常用单词,例如 and 或者 the ,它们对相关性没有多少影响),它们会被删除。 由于理解英语语法的规则,这个分词器可以提取英语单词的 词干 。
- 会产生下面的词条:set, shape, semi, transpar, call, set_tran, 5
- 注意看 transparent、 calling 和 set_trans 已经变为词根格式
- 因为默认分词器对中文支持不好,所以我们需要使用IK分词器,这个分词器对中文分词支持很好
- 下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/tag/v7.8.0
- 将解压后的后的文件夹放入 ES 根目录下的 plugins 目录下,重启 ES 即可使用
# GET http://localhost:9200/_analyze
{
"text":"测试单词",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
ik_max_word:会将文本做最细粒度的拆分
ik_smart:会将文本做最粗粒度的拆分
- 扩展词汇(自定义一些搜索单词,比如弗雷尔卓德)
- 首先进入 ES 根目录中的 plugins 文件夹下的 ik 文件夹,进入 config 目录,创建 custom.dic文件,写入弗雷尔卓德。同时打开 IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml 文件,将新建的custom.dic 配置其中,重启 ES 服务器

# PUT http://localhost:9200/my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"char_filter": {
"&_to_and": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [ "&=> and "]
}},
"filter": {
"my_stopwords": {
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": [ "the", "a" ]
}},
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": [ "html_strip", "&_to_and" ],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [ "lowercase", "my_stopwords" ]
}}
}}}
10 客户端管理工具
| Kibana 是一个免费且开放的用户界面,能够让你对 Elasticsearch 数据进行可视化,并让你在 Elastic Stack 中进行导航。你可以进行各种操作,从跟踪查询负载,到理解请求如何流经你的整个应用,都能轻松完成。 |
1.下载:
https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/kibana
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-7.8.0-windows-x86_64.zip
2. 修改 config/kibana.yml 文件
server.port: 5601
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
kibana.index: ".kibana"
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
- Windows 环境下执行 bin/kibana.bat 文件
- 通过浏览器访问 : http://localhost:5601

五、使用集成框架操作Elasticsearch
| Spring Data 是一个用于简化数据库、非关系型数据库、索引库访问,并支持云服务的开源框架。其主要目标是使得对数据的访问变得方便快捷,并支持 map-reduce 框架和云计算数据服务。 Spring Data 可以极大的简化 JPA(Elasticsearch„)的写法,可以在几乎不用写实现的情况下,实现对数据的访问和操作。除了 CRUD 外,还包括如分页、排序等一些常用的功能 |
- spring data常用模块
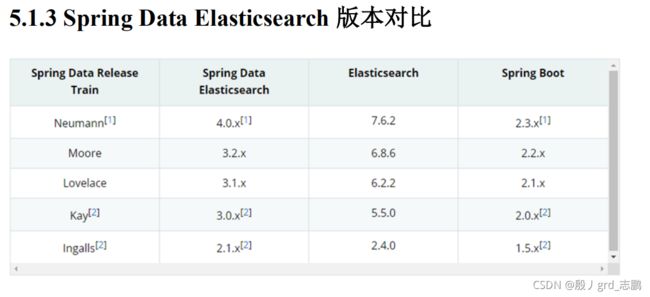
- 官网查找版本对应
- 创建项目,引入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- junit 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 配置文件
elasticsearch:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 9200
logging:
level:
com:
yzpnb:
es: debug
- 配置类

import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.config.AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration;
@Configuration
@Data
public class ElasticsearchConfig extends AbstractElasticsearchConfiguration {
@Value("${elasticsearch.host}")
private String host ;
@Value("${elasticsearch.port}")
private Integer port ;
@Override
public RestHighLevelClient elasticsearchClient() {
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost(host, port));
RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
return restHighLevelClient;
}
}
- 实体类,映射索引和文档

package com.yzpnb.es.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Document(indexName = "product", shards = 3, replicas = 1)
public class Product {
@Id
private Long id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String category;
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private Double price;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword, index = false)
private String images;
}
- dao层
import com.yzpnb.es.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface ProductDao extends ElasticsearchRepository<Product,Long> {
}
- 启动类
- 测试类
import com.yzpnb.es.Application;
import com.yzpnb.es.dao.ProductDao;
import com.yzpnb.es.entity.Product;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.TermQueryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class SpringDataESIndexTest {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate elasticsearchRestTemplate;
@Test
public void createIndex(){
System.out.println("创建索引");
}
@Test
public void deleteIndex(){
boolean flg = elasticsearchRestTemplate.deleteIndex(Product.class);
System.out.println("删除索引 = " + flg);
}
@Autowired
private ProductDao productDao;
@Test
public void save(){
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(2L);
product.setTitle("华为手机");
product.setCategory("手机");
product.setPrice(2999.0);
product.setImages("http://www.atguigu/hw.jpg");
productDao.save(product);
}
@Test
public void update(){
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1L);
product.setTitle("小米 2 手机");
product.setCategory("手机");
product.setPrice(9999.0);
product.setImages("http://www.atguigu/xm.jpg");
productDao.save(product);
}
@Test
public void findById(){
Product product = productDao.findById(1L).get();
System.out.println(product);
}
@Test
public void findAll(){
Iterable<Product> products = productDao.findAll();
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
@Test
public void delete(){
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(1L);
productDao.delete(product);
}
@Test
public void saveAll(){
List<Product> productList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(Long.valueOf(i));
product.setTitle("["+i+"]小米手机");
product.setCategory("手机");
product.setPrice(1999.0+i);
product.setImages("http://www.atguigu/xm.jpg");
productList.add(product);
}
productDao.saveAll(productList);
}
@Test
public void findByPageable(){
Sort sort = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
int currentPage=0;
int pageSize = 5;
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(currentPage, pageSize,sort);
Page<Product> productPage = productDao.findAll(pageRequest);
for (Product Product : productPage.getContent()) {
System.out.println(Product);
}
}
@Test
public void termQuery(){
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("title", "机");
Iterable<Product> products = productDao.search(termQueryBuilder);
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
@Test
public void termQueryByPage(){
int currentPage= 0 ;
int pageSize = 5;
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(currentPage, pageSize);
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("title", "小");
Iterable<Product> products = productDao.search(termQueryBuilder,pageRequest);
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
}

































































































