springboot整合Redis哨兵
1.1SpringBoot整合Redis哨兵
1.1.1入门案例
/**
* 哨兵测试
* 1.配置redis的节点数据集合
* 2.利用哨兵机制连接redis节点.
* 3.用户通过哨兵 实现缓存操作.
*
* 参数1: masterName
*/
@Test
public void testSentinel() {
//配置哨兵的信息
Set sentinels = new HashSet<>();
sentinels.add("192.168.226.128:26379");
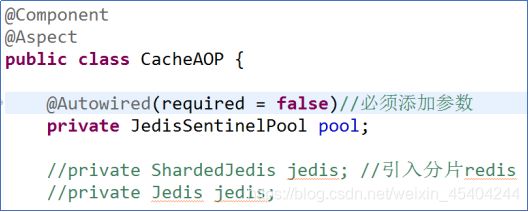
JedisSentinelPool pool =
new JedisSentinelPool("mymaster", sentinels);
Jedis jedis = pool.getResource();
jedis.set("1909","哨兵搭建成功!!!!");
System.out.println(jedis.get("1909"));
jedis.close();
}
1.1.2编辑properties文件
redis.sentinel=192.168.226.128:26379
//标识配置类信息
@Configuration
1.1.3编辑RedisConfig配置类
@PropertySource("classpath:/properties/redis.properties")
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.sentinel}")
private String sentinel;
/**
* 使用redis哨兵机制.实现redis缓存操作
*
*/
@Bean
public JedisSentinelPool sentinelPool() {
Set sentinels = new HashSet<>();
sentinels.add(sentinel);
return new JedisSentinelPool("mymaster", sentinels);
}}
1.1Redis集群
1.1.1为什么要搭建集群
通常,为了提高网站响应速度,总是把热点数据保存在内存中而不是直接从后端数据库中读取。
Redis是一个很好的Cache工具。大型网站应用,热点数据量往往巨大,几十G上百G是很正常的事儿。
由于内存大小的限制,使用一台 Redis 实例显然无法满足需求,这时就需要使用多台 Redis作为缓存数据库。但是如何保证数据存储的一致性呢,这时就需要搭建redis集群.采用合理的机制,保证用户的正常的访问需求.
采用redis集群,可以保证数据分散存储,同时保证数据存储的一致性.并且在内部实现高可用的机制.实现了服务故障的自动迁移.
1.1.2集群搭建计划
主从划分:
3台主机 3台从机共6台 端口划分7000-7005
1.2集群搭建
1.2.1准备集群文件夹
1.准备集群文件夹
Mkdir cluster
2.在cluster文件夹中分别创建7000-7005文件夹
1.2.2复制配置文件
说明:
将redis根目录中的redis.conf文件复制到cluster/7000/ 并以原名保存
cp redis.conf cluster/7000/
1.2.3编辑配置文件
1.注释本地绑定IP地址

2.关闭保护模式

3.修改端口号

4.启动后台启动

5.修改pid文件

6.修改持久化文件路径
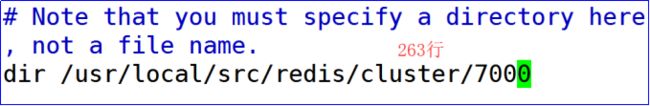
7.设定内存优化策略

8.关闭AOF模式

9.开启集群配置

10.开启集群配置文件

11.修改集群超时时间

1.2.4复制修改后的配置文件
说明:将7000文件夹下的redis.conf文件分别复制到7001-7005中
[root@localhost cluster]# cp 7000/redis.conf 7001/
[root@localhost cluster]# cp 7000/redis.conf 7002/
[root@localhost cluster]# cp 7000/redis.conf 7003/
[root@localhost cluster]# cp 7000/redis.conf 7004/
[root@localhost cluster]# cp 7000/redis.conf 7005/
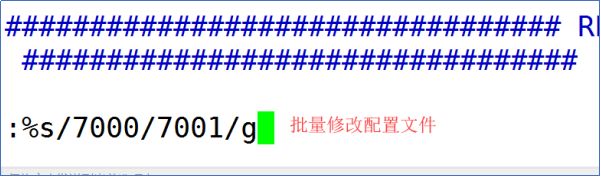
1.2.5批量修改
说明:分别将7001-7005文件中的7000改为对应的端口号的名称,
修改时注意方向键的使用
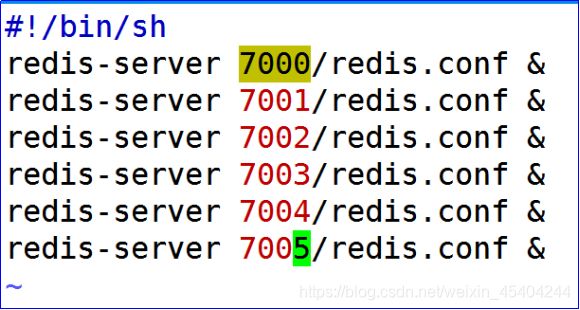
1.2.6通过脚本编辑启动/关闭指令
1.创建启动脚本 vim start.sh
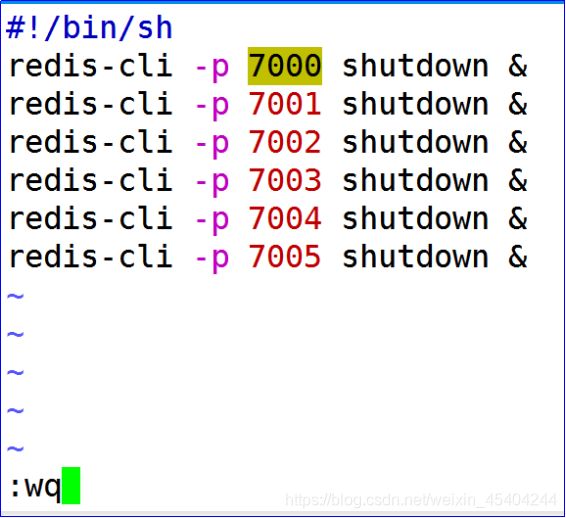
2.编辑关闭的脚本 vim shutdown.sh
3.启动redis节点
sh start.sh
4.检查redis节点启动是否正常
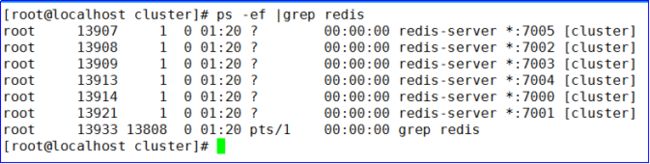
1.2.7创建redis集群
#5.0版本执行 使用C语言内部管理集群
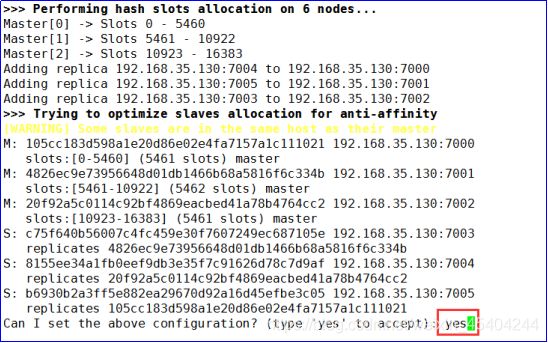
redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 192.168.35.130:7000 192.168.35.130:7001 192.168.35.130:7002 192.168.35.130:7003 192.168.35.130:7004 192.168.35.130:7005
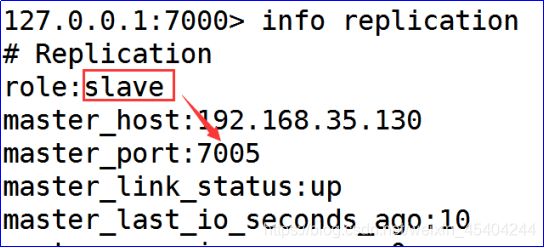
1.关闭redis主机.检查是否自动实现故障迁移.
2.再次启动关闭的主机.检查是否能够实现自动的挂载.
一般情况下 能够实现主从挂载
个别情况: 宕机后的节点重启,可能挂载到其他主节点中(7001-7002) 正确的
1.3Redis集群原理
1.3.1Redis集群高可用推选原理
如图-24所示
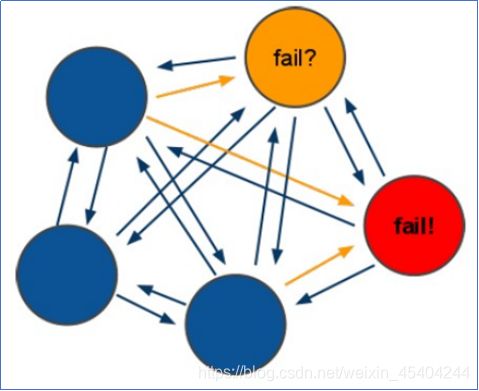
原理说明:
Redis的所有节点都会保存当前redis集群中的全部主从状态信息.并且每个节点都能够相互通信.当一个节点发生宕机现象.则集群中的其他节点通过PING-PONG检测机制检查Redis节点是否宕机.当有半数以上的节点认为宕机.则认为主节点宕机.同时由Redis剩余的主节点进入选举机制.投票选举链接宕机的主节点的从机.实现故障迁移.
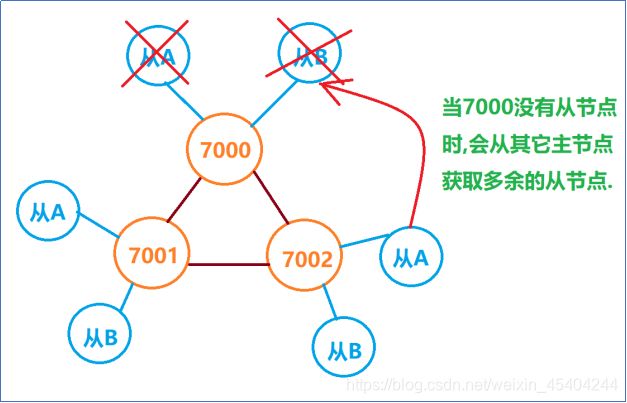
1.3.2Redis集群宕机条件
特点:集群中如果主机宕机,那么从机可以继续提供服务,
当主机中没有从机时,则向其它主机借用多余的从机.继续提供服务.如果主机宕机时没有从机可用,则集群崩溃.
答案:9个redis节点,节点宕机5-7次时集群才崩溃.
如图-25所示:
1.3.3Redis hash槽存储数据原理
说明: RedisCluster采用此分区,所有的键根据哈希函数(CRC16[key]&16383)映射到0-16383槽内,共16384个槽位,每个节点维护部分槽及槽所映射的键值数据.根据主节点的个数,均衡划分区间.
算法:哈希函数: Hash()=CRC16[key]%16383按位与
如图-26所示

当向redis集群中插入数据时,首先将key进行计算.之后将计算结果匹配到具体的某一个槽的区间内,之后再将数据set到管理该槽的节点中.
如图-27所示

Redis7000~~~0-5460
crc16(aaa)%16383 = 2000 redis7000.set("aaa","valuexxx");
crc16(bbb)%16383 = 2000 redis7000.set("bbb","valuexxx");
2.1SpringBoot整合redis集群
2.1.1入门案例
/**
* redis集群测试案例
*/
@Test
public void testCluster() {
Set nodes = new HashSet<>();
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7000));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7001));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7002));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7003));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7004));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.226.128",7005));
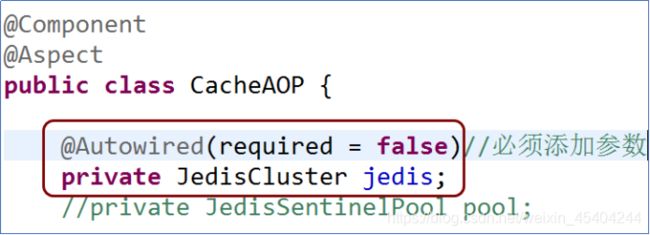
JedisCluster cluster = new JedisCluster(nodes);
cluster.set("key", "redis集群搭建成功!!!!");
System.out.println(cluster.get("key"));
}
2.1.2编辑Properties文件
#配置redis集群
redis.nodes=192.168.226.128:7000,192.168.226.128:7001,192.168.226.128:7002,192.168.226.128:7003,192.168.226.128:7004,192.168.226.128:7005
2.1.3编辑RedisConfig
//标识配置类信息
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:/properties/redis.properties")
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.nodes}")
private String nodes; //node,node,node
/**
* 实现集群整合
*/
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public JedisCluster jedisCluster() {
Set setNodes = new HashSet<>();
String[] arrayNodes = nodes.split(",");
for (String node : arrayNodes) { //host:port
String host = node.split(":")[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(node.split(":")[1]);
HostAndPort hostAndPort =
new HostAndPort(host, port);
setNodes.add(hostAndPort);
}
return new JedisCluster(setNodes);
}
}