双非本科准备秋招(13.1)—— 力扣 栈、队列与堆
1、103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
昨天做的二叉树的层序遍历,把代码直接拿过来。
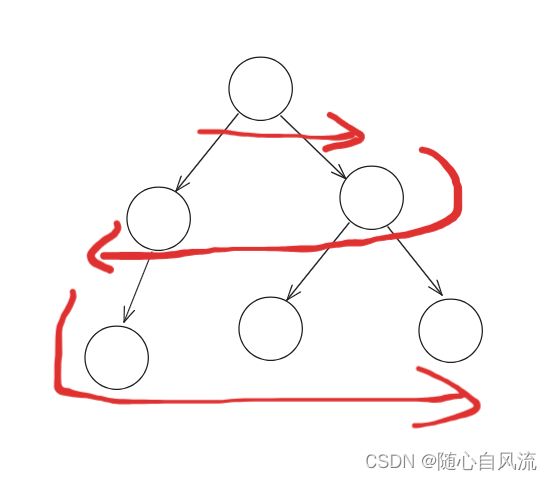
这个题要求的是一个Z型遍历,如下图。
用一个变量f记录正反顺序,然后使用LinkedList记录答案,下图可以看到LinkedList继承了Deque,所以可以当作双端队列来用。
每次记录答案时,根据f的值选择调用offerLast和offerFirst方法。
class Solution {
public List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
LinkedBlockingQueue q = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
q.offer(root);
int cnt = 1;
boolean f = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
LinkedList L = new LinkedList<>();
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
TreeNode t = q.poll();
if(f) L.offerLast(t.val);
else L.offerFirst(t.val);
if(t.left != null){
q.offer(t.left);
temp++;
}
if(t.right != null){
q.offer(t.right);
temp++;
}
}
cnt = temp;
list.add(L);
f = !f;
}
return list;
}
} 2、23. 合并 K 个升序链表
用优先队列来做,默认排序即可(小顶堆),最后处理一下答案,把队列q中的元素转移到新的链表上。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
PriorityQueue q = new PriorityQueue<>();
ListNode head = new ListNode();
ListNode p = head;
for(int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++){
while(lists[i] != null){
q.offer(lists[i].val);
lists[i] = lists[i].next;
}
}
while(!q.isEmpty()){
ListNode t = new ListNode(q.poll());
p.next = t;
p = p.next;
}
return head.next;
}
} 3、215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
堆这种数据结构就适合求前几个具有xx特性的元素问题,包括下一个题目和最后一个题目。
这个题用小顶堆做,我们可以手写一个堆的结构class MinHeap。
我们只需要把前k个元素加入堆(offer()方法),然后后面的元素只需要判断是否大于堆中的第一个元素即可,如果大于,就替换第一个元素(replace()方法)。
因为堆中第一个元素是k个中最小的,我们不断加入大的元素,那么最后是不是堆中只剩下最大的k个元素了,k个最大元素中最小的不就是堆的第一个元素嘛。
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
MinHeap heap = new MinHeap(k);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
heap.offer(nums[i]);
}
for(int i = k; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] > heap.array[0]){
heap.replace(nums[i]);
}
}
return heap.array[0];
}
}
public class MinHeap {
int[] array;
int size;
public MinHeap(int capacity) {
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
public void offer(int offerd){
up(offerd);
size++;
}
public void up(int offerd){
int child = size;
while(child > 0){
int parent = (child-1)/2;
if(array[parent] > offerd){
array[child] = array[parent];
}
else{
break;
}
child = parent;
}
array[child] = offerd;
}
public void replace(int replaced){
array[0] = replaced;
down(0);
}
private void down(int parent) {
int lc = parent*2+1;
int rc = lc+1;
int min = parent;
if(lc < size && array[lc] < array[min]){
min = lc;
}
if(rc < size && array[rc] < array[min]){
min = rc;
}
if(min != parent){
swap(min, parent);
down(min);
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
}
4、703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
与上个题不能说一模一样,只能说完全一致。
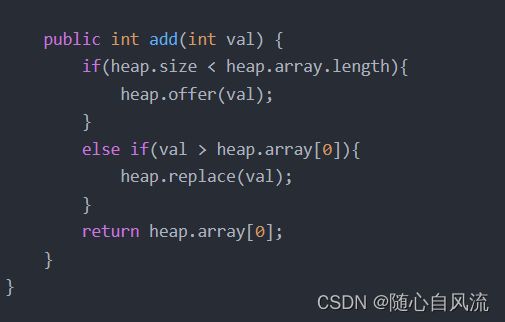
需要注意add方法要判断一下堆是不是满了,因为初始化堆的时候有可能提供的元素个数小于k个,如果没满直接加入堆就好。
class KthLargest {
MinHeap heap = null;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
heap = new MinHeap(k);
int len = Math.min(k, nums.length);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
heap.offer(nums[i]);
}
for(int i = k; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] > heap.array[0]){
heap.replace(nums[i]);
}
}
}
public int add(int val) {
if(heap.size < heap.array.length){
heap.offer(val);
}
else if(val > heap.array[0]){
heap.replace(val);
}
return heap.array[0];
}
}
public class MinHeap {
int[] array;
int size;
public MinHeap(int capacity) {
this.array = new int[capacity];
Arrays.fill(this.array, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
public void offer(int offerd){
up(offerd);
size++;
}
public void up(int offerd){
int child = size;
while(child > 0){
int parent = (child-1)/2;
if(array[parent] > offerd){
array[child] = array[parent];
}
else{
break;
}
child = parent;
}
array[child] = offerd;
}
public void replace(int replaced){
array[0] = replaced;
down(0);
}
private void down(int parent) {
int lc = parent*2+1;
int rc = lc+1;
int min = parent;
if(lc < size && array[lc] < array[min]){
min = lc;
}
if(rc < size && array[rc] < array[min]){
min = rc;
}
if(min != parent){
swap(min, parent);
down(min);
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}
}5、1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
解释: 例如,在 "abbaca" 中,我们可以删除 "bb" 由于两字母相邻且相同,这是此时唯一可以执行删除操作的重复项。之后我们得到字符串 "aaca",其中又只有 "aa" 可以执行重复项删除操作,所以最后的字符串为 "ca"。
读完解释后,感觉就是明示了栈的数据结构。
我们把a入栈,b入栈,b入栈,b和栈顶重复,b不入了并且弹出栈顶元素,这时候栈只剩下a,然后a入栈,a和栈顶重复,a不入了并且弹出栈顶元素,栈空了,然后c入栈,a入栈。
这时候我们依次弹出,得到ac,那么我们可以倒着遍历字符串,倒着入栈,结果都是一样的,不影响删除相邻重复的字母。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = s.length()-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == s.charAt(i)){
stack.pop();
}
else{
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
}
String ans = "";
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
ans += stack.pop();
}
return ans;
}
} 6、347. 前 K 个高频元素
元素与元素的次数,让人联想到哈希表。存到哈希表后,对出现的次数进行排序,这应该是第一思路。
前k个高频元素,有出现了前几个具有xx特性的这种要求,我们就会想到堆,在堆中只存放前k个高频元素,使用小顶堆,我们最后得到的就是前k个最高频的元素了。
java中的ProrityQueue的底层就是堆,我就不用自己写的了。因为我们的堆中要存储数据和出现的次数,因此可以存个数组,下标0代表是什么数据,下标1代表出现的次数。
我们先加入到map中,然后遍历map集合,把cnt大于堆顶的元素替换掉原来的元素,也就是队列出队,这样就得到了前k个高频的元素了。
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
PriorityQueue q = new PriorityQueue<>(k, (o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]);
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int v = 0;
if(map.containsKey(nums[i])){
v = map.get(nums[i]);
}
map.put(nums[i], v+1);
}
for(Integer n : map.keySet()){
int cnt = map.get(n);
if(q.size() < k){
q.offer(new int[]{n, cnt});
}
else if(cnt > q.peek()[1]){
q.poll();
q.offer(new int[]{n, cnt});
}
}
int[] ans = new int[k];
int j = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
ans[j++] = q.poll()[0];
}
return ans;
}
}