利用python实现多功能计算器
利用python实现多功能计算器
————102101328林驰易
文章目录
- 利用python实现多功能计算器
-
- 作业基本信息
- 界面及功能演示
- Gitcode项目地址
- PSP表格
- 解题思路描述
-
- 问题一、界面设计
- 问题二、不同功能的切换
- 问题三、科学计算器运算的实现
- 问题四、标准计算器的实现
- 问题五、Back删除函数的实现
- 接口设计和实现过程
-
- 不同计算器间的跳转
- 界面设计
- 运算的实现
- 关键代码展示
- 性能改进
- 单元测试
- 异常处理
- 心得体会
作业基本信息
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/ssynkqtd-05 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617294583 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 完成一个具有可视化界面的科学计算器 |
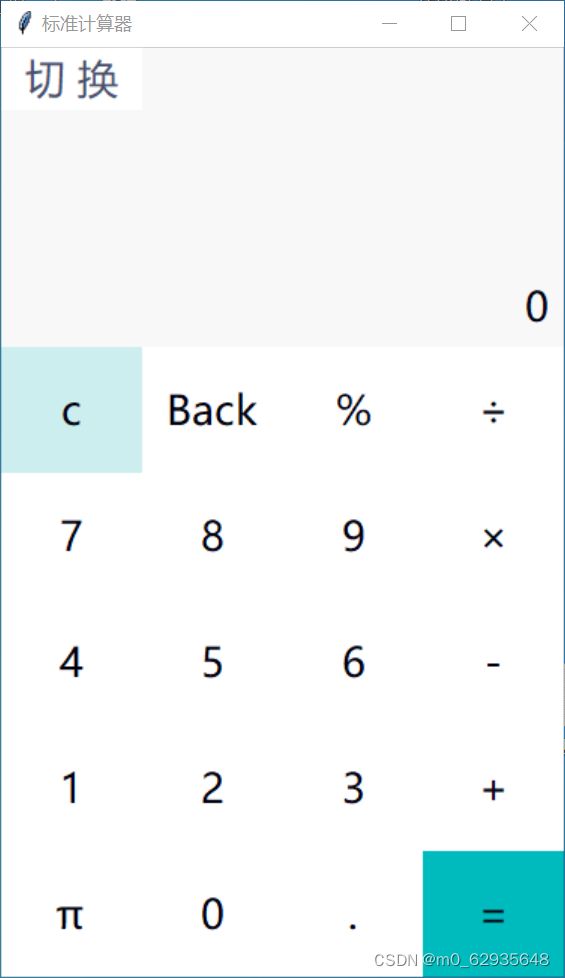
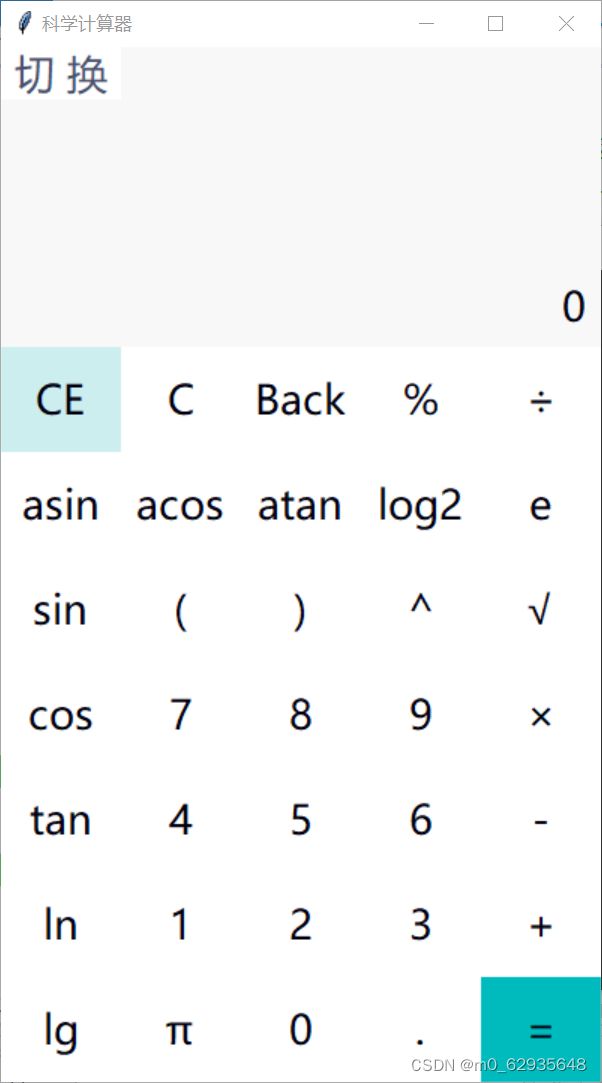
界面及功能演示
演示
Gitcode项目地址
GitHub项目地址
PSP表格
| PSP | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 15 | 10 |
| • Estimate | • 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 5 |
| Development | 开发 | 720 | 700 |
| • Analysis | • 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 80 |
| • Design Spec | • 生成设计文档 | 40 | 25 |
| • Design Review | • 设计复审 | 5 | 5 |
| • Coding Standard | • 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| • Design | • 具体设计 | 60 | 75 |
| • Coding | • 具体编码 | 360 | 420 |
| • Code Review | • 代码复审 | 120 | 120 |
| • Test | • 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 45 |
| • Test Repor | • 测试报告 | 20 | 20 |
| • Size Measurement | • 计算工作量 | 10 | 7 |
| • Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | • 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 12 | 10 |
| 合计 | 1572 | 1652 |
解题思路描述
本来想用html+css+js做一个微信小程序,但是发现微信小程序把eval函数给禁了,手搓运算的代码又来不及,于是改用python。
问题一、界面设计
借助python的tkinter库可实现GUI设计
问题二、不同功能的切换
在界面部分,每当按下"切换"键,便可以实现在标准计算器和科学计算器间来回切换。
问题三、科学计算器运算的实现
主要是利用python的eval()函数来进行各种运算。定义三个字符串,一个用于存放需要eval()运算的表达式,一个用来作为按下等号后显示出来的算式,还有一个用来当作运算的结果。每当按下按钮时,按钮会传递相应的参数给运算函数,并相应的放入对应的字符串中。需要注意的是当使用科学计算器时,对于三角函数、幂、开方、反三角函数、对数等这些特殊运算需要套一个if来进行特判,以保证放入eval()中的字符串正确。
def press_num(self, num):
if self.is_press_compute is True: # 如果判断等号按键被按下
self.record.set("")
self.result.set(0) # 清空self.result
self.is_press_compute = False
# 判断界面的数字是否为0
old_num = self.result.get()
new_num=[]
if old_num == '0' and num != '.':
new_num=num
else:
new_num = old_num+num
#判断特殊的符号
if num == '^':
num='**'
elif num == '√':
num='math.sqrt('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'sin':
num='math.sin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'cos':
num='math.cos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'tan':
num='math.tan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'lg':
num='math.log10('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'ln':
num='math.log('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'π':
num='math.pi'
elif num == 'asin':
num='math.asin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'acos':
num='math.acos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'atan':
num='math.atan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'e':
num='math.e'
elif num == 'log2':
num='math.log2('
new_num+='('
self.result.set(new_num)
temp=self.all_press_lists
temp+=num
self.all_press_lists=temp
def press_equal(self):
temp=self.result.get()
compute_str = ''.join(self.all_press_lists)
try:
calculate_result = eval(compute_str)
except:
calculate_result = 'error'
self.result.set(calculate_result) # 显示结果
self.record.set(temp + "=") # 显示运算过程
self.all_press_lists.clear() # 清空列表内容
self.is_press_compute = True
问题四、标准计算器的实现
科学计算器的函数能够完美适配标准计算器的运算函数,因此,当需要用标准计算器进行运算时,可以直接调用科学计算器的函数
问题五、Back删除函数的实现
在使用删除操作时,需要注意的是由于放入eval的字符串和展示给用户的字符串是不同的,可能出现显示给用户的是e而eval中的字符串是math.e,当用户删除e之后eval的字符串变为math.而导致计算出错。所以需要对特殊字符进行特判
#按下back
def press_back(self, sign):
num=self.result.get()
a = num[0:-1]
self.result.set(a)
num=self.all_press_lists
if len(num)>5 and num[-2] == '.' and num[-3] == 'h' and num[-4] == 't':
a = num[:-6]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>3 and num[-1] == 'i' and num[-2] == 'p':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>1 and num[-1] == '*' and num[-2] == '*':
a = num[:-2]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == 't' and num[-2] == 'r':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == '1' and num[-2] =='g' and num[-3] == 'o' and num[-4] == 'l':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>7 and num[-1] == 'g' and num[-2] =='o' and num[-3] == 'l' and num[-4] == '.':
a = num[:-8]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>6 and num[-1] == 'o' and num[-2] =='l' and num[-3] == '.' and num[-4] == 'h':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
else:
a = num[0:-1]
self.all_press_lists=a
接口设计和实现过程
定义了两个类
Calculator类用于实现标准计算器
scienceCalculator类用于实现科学计算器
不同计算器间的跳转
放一个按钮"切换",当按下这个按钮时,便触发函数press_change实现跳转。
跳转到Calculator:
def press_change(self):
self.root.destroy()
my_calculator = Calculator()
my_calculator.main()
跳转到scienceCalculator:
def press_change(self):
self.root.destroy()
my_calculator = scienceCalculator()
my_calculator.main()
界面设计
def main(self):
self.root.minsize(375, 620) # 显示框的最小长宽
self.root.title('标准计算器') # 标题
btn_w, btn_h = 93.75, 84 #按钮宽和高
my_font = tkinter.font.Font(family='微软雅黑', size=20) # 设置字体
self.result.set(0)
self.record.set('')
input_bg, btn_fg, btn_bg = "#f8f8f8", "#000011", "#ffffff" # 设定颜色
# displayscreen
label = tkinter.Label(self.root, font=my_font, bg=input_bg, bd='9', fg=btn_fg, anchor='se',
textvariable=self.record)
label.place(width=375, height=120)
label2 = tkinter.Label(self.root, font=my_font, bg=input_bg, bd='9', fg=btn_fg, anchor='se',
textvariable=self.result)
label2.place(y=120, width=375, height=80)
btn_change=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='切 换', font=tkinter.font.Font(family='微软雅黑', size=20), bg=btn_bg, fg="#49506c", bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_change())
btn_change.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h/2)
# 第一行
btn_ac = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='c', font=my_font, bg="#cdeeef", fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_ac('AC'))
btn_ac.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_back = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='Back', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_back('b'))
btn_back.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_per = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='%', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('%'))
btn_per.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_divi = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='÷', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('/'))
btn_divi.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第二行
btn7 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='7', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('7'))
btn7.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn8 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='8', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('8'))
btn8.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn9 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='9', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('9'))
btn9.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_mul = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='×', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('*'))
btn_mul.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第三行
btn4 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='4', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('4'))
btn4.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn5 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='5', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('5'))
btn5.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn6 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='6', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('6'))
btn6.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_sub = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='-', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('-'))
btn_sub.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第四行
btn1 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='1', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('1'))
btn1.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn2 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='2', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('2'))
btn2.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn3 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='3', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('3'))
btn3.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_add = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='+', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('+'))
btn_add.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第五行
btn_pai=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='π', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('π'))
btn_pai.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w , height=btn_h)
btn0 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='0', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('0'))
btn0.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w , height=btn_h)
btn_point = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='.', font=my_font, bg=btn_bg, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('.'))
btn_point.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_equ = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='=', bg='#00bbbe', font=my_font, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_equal())
btn_equ.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
self.root.mainloop()
def main(self):
self.root.minsize(400, 690) # 显示框的最小长宽
self.root.title('科学计算器') # 标题
#self.root.iconbitmap("./calc.ico") # 左上角图标
input_bg, num_fg, btn_fg, btn_background = "#f8f8f8", "#000011", "#000011", "#ffffff" # 各种颜色
btn_w, btn_h = 80, 70 # 按钮的长宽
my_font = tkinter.font.Font(family='微软雅黑', size=20) # 设置字体
self.result.set(0)
self.record.set('')
# 显示版
label = tkinter.Label(self.root, font=my_font, bg=input_bg, bd='9', fg=num_fg, anchor='se',
textvariable=self.record)
label.place(width=375, height=120)
label2 = tkinter.Label(self.root, font=my_font, bg=input_bg, bd='9', fg=num_fg, anchor='se',
textvariable=self.result)
label2.place(y=120, width=375, height=80)
btn_change=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='切 换', font=tkinter.font.Font(family='微软雅黑', size=20), bg=btn_background, fg="#49506c", bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_change())
btn_change.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h/2)
# 第一行
btn_ce = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='CE', font=my_font, bg='#cdeeef', fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_ac('CE'))
btn_ce.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_ac = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='C', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_ac('C'))
btn_ac.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_back = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='Back', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_back('b'))
btn_per = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='%', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('%'))
btn_back.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_divi = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='÷', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('/'))
btn_per.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_divi.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 0, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第二行
btn_asin=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='asin', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('asin'))
btn_acos= tkinter.Button(self.root, text='acos', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('acos'))
btn_atan= tkinter.Button(self.root, text='atan', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('atan'))
btn_log2=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='log2', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('log2'))
btn_e=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='e', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('e'))
btn_asin.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_acos.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_atan.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_log2.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_e.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 1, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
#第三行
btn_sin=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='sin', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('sin'))
btnl= tkinter.Button(self.root, text='(', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('('))
btnr= tkinter.Button(self.root, text=')', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num(')'))
btn_mi=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='^', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('^'))
btn_sqrt=tkinter.Button(self.root, text='√', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('√'))
btn_sin.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btnl.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btnr.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_mi.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_sqrt.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 2, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第三行
btn_cos= tkinter.Button(self.root, text='cos', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('cos'))
btn_cos.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn7 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='7', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('7'))
btn7.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn8 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='8', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('8'))
btn8.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn9 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='9', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('9'))
btn9.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_mul = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='×', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('*'))
btn_mul.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 3, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第四行
btn_tan = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='tan', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('tan'))
btn_tan.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn4 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='4', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('4'))
btn4.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn5 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='5', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('5'))
btn5.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn6 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='6', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('6'))
btn6.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_sub = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='-', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('-'))
btn_sub.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 4, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第五行
btn_log = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='ln', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('ln'))
btn_log.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 5, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn1 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='1', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('1'))
btn1.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 5, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn2 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='2', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('2'))
btn2.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 5, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn3 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='3', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('3'))
btn3.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 5, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_add = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='+', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=btn_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('+'))
btn_add.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 5, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
# 第六行
btn_ln = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='lg', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('lg'))
btn_ln.place(x=btn_w * 0, y=200 + btn_h * 6, width=btn_w , height=btn_h)
btn_pai = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='π', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('π'))
btn_pai.place(x=btn_w * 1, y=200 + btn_h * 6, width=btn_w , height=btn_h)
btn0 = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='0', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('0'))
btn0.place(x=btn_w * 2, y=200 + btn_h * 6, width=btn_w , height=btn_h)
btn_point = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='.', font=my_font, bg=btn_background, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_num('.'))
btn_point.place(x=btn_w * 3, y=200 + btn_h * 6, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
btn_equ = tkinter.Button(self.root, text='=', bg='#00bbbe', font=my_font, fg=num_fg, bd=0,
command=lambda: self.press_equal())
btn_equ.place(x=btn_w * 4, y=200 + btn_h * 6, width=btn_w, height=btn_h)
self.root.mainloop()
运算的实现
每次按下按钮,都会传递相应参数给运算函数,运算函数再将其加入对应的字符串中,最后按下等号后,再将需要运算的字符串放入eval中进行运算
def press_num(self, num):
if self.is_press_compute is True: # 如果判断等号按键被按下
self.record.set("")
self.result.set(0) # 清空self.result
self.is_press_compute = False
# 判断界面的数字是否为0
old_num = self.result.get()
new_num=[]
if old_num == '0' and num != '.':
new_num=num
else:
new_num = old_num+num
#判断特殊的符号
if num == '^':
num='**'
elif num == '√':
num='math.sqrt('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'sin':
num='math.sin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'cos':
num='math.cos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'tan':
num='math.tan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'lg':
num='math.log10('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'ln':
num='math.log('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'π':
num='math.pi'
elif num == 'asin':
num='math.asin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'acos':
num='math.acos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'atan':
num='math.atan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'e':
num='math.e'
elif num == 'log2':
num='math.log2('
new_num+='('
self.result.set(new_num)
temp=self.all_press_lists
temp+=num
self.all_press_lists=temp
def press_equal(self):
temp=self.result.get()
compute_str = ''.join(self.all_press_lists)
try:
calculate_result = eval(compute_str)
except:
calculate_result = 'error'
self.result.set(calculate_result) # 显示结果
self.record.set(temp + "=") # 显示运算过程
self.all_press_lists.clear() # 清空列表内容
self.is_press_compute = True
关键代码展示
#按下change
def press_change(self):
self.root.destroy()
my_calculator = Calculator()
my_calculator.main()
# 按下数字
def press_num(self, num):
if self.is_press_compute is True: # 如果判断等号按键被按下
self.record.set("")
self.result.set(0) # 清空self.result
self.is_press_compute = False
# 判断界面的数字是否为0
old_num = self.result.get()
new_num=[]
if old_num == '0' and num != '.':
new_num=num
else:
new_num = old_num+num
#判断特殊的符号
if num == '^':
num='**'
elif num == '√':
num='math.sqrt('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'sin':
num='math.sin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'cos':
num='math.cos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'tan':
num='math.tan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'lg':
num='math.log10('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'ln':
num='math.log('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'π':
num='math.pi'
elif num == 'asin':
num='math.asin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'acos':
num='math.acos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'atan':
num='math.atan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'e':
num='math.e'
elif num == 'log2':
num='math.log2('
new_num+='('
self.result.set(new_num)
temp=self.all_press_lists
temp+=num
self.all_press_lists=temp
#按下AC
def press_ac(self,sign):
self.all_press_lists.clear()
self.record.set("")
self.result.set(0)
#按下back
def press_back(self, sign):
num=self.result.get()
a = num[0:-1]
self.result.set(a)
num=self.all_press_lists
if len(num)>5 and num[-2] == '.' and num[-3] == 'h' and num[-4] == 't':
a = num[:-6]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>3 and num[-1] == 'i' and num[-2] == 'p':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>1 and num[-1] == '*' and num[-2] == '*':
a = num[:-2]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == 't' and num[-2] == 'r':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == '1' and num[-2] =='g' and num[-3] == 'o' and num[-4] == 'l':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>7 and num[-1] == 'g' and num[-2] =='o' and num[-3] == 'l' and num[-4] == '.':
a = num[:-8]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>6 and num[-1] == 'o' and num[-2] =='l' and num[-3] == '.' and num[-4] == 'h':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
else:
a = num[0:-1]
self.all_press_lists=a
# 获取运算结果
def press_equal(self):
temp=self.result.get()
compute_str = ''.join(self.all_press_lists)
try:
calculate_result = eval(compute_str)
except:
calculate_result = 'error'
self.result.set(calculate_result) # 显示结果
self.record.set(temp + "=") # 显示运算过程
self.all_press_lists.clear() # 清空列表内容
self.is_press_compute = True
性能改进
为了使科学运算器能够运算特殊符号,需要在运算函数中加入对特殊符号的特判:
#判断特殊的符号
if num == '^':
num='**'
elif num == '√':
num='math.sqrt('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'sin':
num='math.sin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'cos':
num='math.cos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'tan':
num='math.tan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'lg':
num='math.log10('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'ln':
num='math.log('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'π':
num='math.pi'
elif num == 'asin':
num='math.asin('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'acos':
num='math.acos('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'atan':
num='math.atan('
new_num+='('
elif num == 'e':
num='math.e'
elif num == 'log2':
num='math.log2('
new_num+='('
对应的删除操作Back也需要进行特判:
#按下back
def press_back(self, sign):
num=self.result.get()
a = num[0:-1]
self.result.set(a)
num=self.all_press_lists
if len(num)>5 and num[-2] == '.' and num[-3] == 'h' and num[-4] == 't':
a = num[:-6]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>3 and num[-1] == 'i' and num[-2] == 'p':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>1 and num[-1] == '*' and num[-2] == '*':
a = num[:-2]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == 't' and num[-2] == 'r':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>8 and num[-1] == '1' and num[-2] =='g' and num[-3] == 'o' and num[-4] == 'l':
a = num[:-9]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>7 and num[-1] == 'g' and num[-2] =='o' and num[-3] == 'l' and num[-4] == '.':
a = num[:-8]
self.all_press_lists=a
elif len(num)>6 and num[-1] == 'o' and num[-2] =='l' and num[-3] == '.' and num[-4] == 'h':
a = num[:-7]
self.all_press_lists=a
else:
a = num[0:-1]
self.all_press_lists=a
需要注意会有大聪明乱按计算器按钮,让计算器运算不合要求的式子,这时候需要对错误式子输出"error"
try:
calculate_result = eval(compute_str)
except:
calculate_result = 'error'
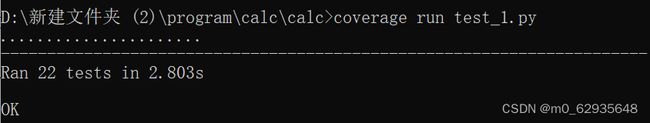
单元测试
测试代码:
import unittest
from tkinter import Tk
from calc import Calculator
from calc import scienceCalculator
import math
class Test_test_1(unittest.TestCase):
#__ , 启动!
def setUp(self):
self.root = Tk()
self.Calculator = Calculator()
self.sciCalculator=scienceCalculator()
#关闭
def tearDown(self):
self.root.destroy()
#测试加
def test_add(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_num( '+')
self.Calculator.press_num( '2')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '9')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '+')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '9')
#测试减
def test_sub(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_num( '-')
self.Calculator.press_num( '2')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '5')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '-')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '5')
#测试乘
def test_mul(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_num( '*')
self.Calculator.press_num( '2')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '14')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '*')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '14')
#测试除
def test_div(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_num( '/')
self.Calculator.press_num( '2')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '3.5')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '/')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '3.5')
#测试mod
def test_mod(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_num( '%')
self.Calculator.press_num( '2')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '1')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '%')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '1')
#测试AllClear
def test_ac(self):
self.Calculator.press_ac( 'C')
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '0')
self.sciCalculator.press_ac( 'C')
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '0')
#测试clear_entry
def test_ce(self):
self.Calculator.press_ac( 'CE')
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), '0')
self.sciCalculator.press_ac( 'CE')
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '0')
#测试back
def test_back(self):
self.Calculator.press_num( '7')
self.Calculator.press_back( 'b')
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.all_press_lists,[])
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(),'')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '7')
self.sciCalculator.press_back( 'b')
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.all_press_lists,[])
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(),'')
#测试根号
def test_genhao(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '√')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.sqrt(2)")))
#测试幂
def test_cf(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '^')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '3')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), '8')
#测试ln
def test_ln(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'ln')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.log(2)")))
#测试lg
def test_lg(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'lg')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.log10(2)")))
#测试log2
def test_log2(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'log2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.log2(2)")))
#测试pai
def test_pai(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num("π")
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.pi")))
#测试e
def test_e(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num("e")
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.e")))
#测试sin
def test_sin(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'sin')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.sin(2)")))
#测试cos
def test_cos(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'cos')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.cos(2)")))
#测试tan
def test_tan(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'tan')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.tan(2)")))
#测试asin
def test_asin(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'sin')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.sin(2)")))
#测试acos
def test_acos(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'cos')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.cos(2)")))
#测试atan
def test_atan(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( 'tan')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( '2')
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), str(eval("math.tan(2)")))
#测试错误判断
def test_error(self):
self.sciCalculator.press_num( ')')
self.sciCalculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.sciCalculator.result.get(), "error")
self.Calculator.press_num( ')')
self.Calculator.press_equal()
self.assertEqual(self.Calculator.result.get(), "error")
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
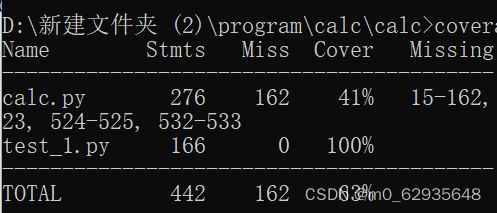
测试结果:
异常处理
对不符合规定的算式,直接输出error
def press_equal(self):
temp=self.result.get()
compute_str = ''.join(self.all_press_lists)
try:
calculate_result = eval(compute_str)
except:
calculate_result = 'error'
self.result.set(calculate_result) # 显示结果
self.record.set(temp + "=") # 显示运算过程
self.all_press_lists.clear() # 清空列表内容
self.is_press_compute = True
心得体会
在这次软工作业中,虽然因为是第一次所以很多地方磨了很多时间,但是总体还是收获颇丰。学到了python的很多语法,学到了python的tkinter库的使用,积累了前端界面的设计经验,并且加强了利用编程解决问题的能力。
同时,我也学会了python的诸多工具的使用,学会了如何利用coverage测试代码覆盖率,学会了单元测试,以及利用pyinstaller将python文件做成exe文件的方法。是一次愉快的编程体验!