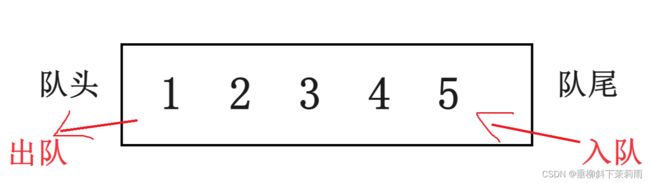队列的实现
学习就像一段长跑,比的不是谁跑得快,而是谁更能坚持!!
1 队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
2 队列的实现
分析
有两种实现队列的方式:数组和链表。链表可以用单链表也可以用双链表。
使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率很低!
数组实现:效率低!!
链表实现:单链表更合适!!
思考一个问题,需要带哨兵位的头节点吗?
- 其实都可以,不带也可以,可以不用判断直接尾插,但是如果带了哨兵位的头节点,要malloc,最后也要free释放空间。
因为队列我们只需要入队(尾插)和出队(头删),单链表都可以实现,不需要使用双链表。但是我们要想,我们要怎么分清队头和队尾呢?所以我们在尾插头删的时候:
- 需要ptail指针维护队列最后一个元素
- 需要phead指针维护队列第一个元素
那么这个时候实现起来就需要用到二级指针了。很不方便。
那么我们怎么解决这个问题呢?(不用二级指针的等效替换方法)
①带哨兵位的头节点。②返回值。③可以考虑用一个结构体封装起来。
这里我们用结构体。
代码实现
Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return 0;
}函数声明Queue.h
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef int QDataType;
//创建队列节点
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
//创建维护队列的指针
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;//原本是需要遍历的,写在结构体里可以很好的是时间复杂度由O(N)变为O(1)
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//空间释放
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
//尾插
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//头删
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//取队头的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//取队尾的数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//队列元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq); 函数实现Queue.c
初始化QueueInit
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}空间释放QueueDestroy
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}入队列QueuePush
这里需要创建一个节点
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}出队列QueuePop
要注意两种情况
- 空链表
- 只有一个元素(ptail野指针的情况,要进行判断置空)
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//链表不为空
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
//链表中只有一个元素,删完以后为空
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}队头元素QueueFront
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}队尾元素QueueBack
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}判断队列是否为空QueueEmpty
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}队列元素个数QueueSize
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}Queue.c总代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}以上就是用单链表实现队列的代码实现。