【C++】C++基础知识(四)---程序流程结构
C++基础知识(四)
- 1. 顺序结构
- 2. 选择结构
-
- 2.1 if语句
- 2.2 switch语句
- 2.3 选择结构案例
- 3. 循环结构
-
- 3.1 循环语句
- 3.2 循环结构案例
- 4. 跳转语句
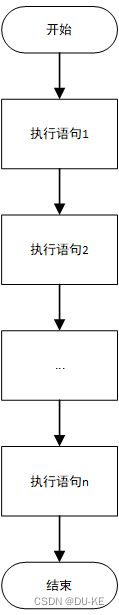
C++中支持的三种流程结构:顺序结构、选择结构、循环结构
- 顺序结构:程序按照顺序执行,不会发生跳转
- 选择结构:根据条件是否满足,有选择的执行相应的功能
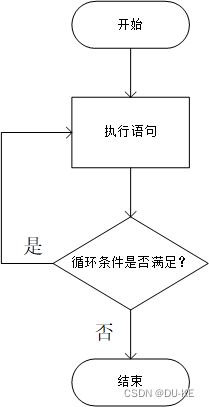
- 循环结构:根据条件是否满足,循环多次执行某代码块
1. 顺序结构
2. 选择结构
2.1 if语句
1. 单行if语句
- 语法:
if (条件) {执行语句}
#include 2. 多行if语句
- 语法
if (条件) {执行语句1}
else {执行语句2}
#include 3. 多条件if语句
- 语法
if (条件1) {执行语句1}
else if (条件2) {执行语句2}
else if (条件3) {执行语句3}
else {执行语句4}
#include 4. 嵌套if语句
- 语法
if (条件1)
{
执行语句1;
if (条件2) {执行语句2}
else if (条件3) {执行语句3}
else {执行语句4}
}
else if (条件4) {执行语句5}
else if (条件5) {执行语句6}
else {执行语句7}
- 流程图:
流程图与多条件if语句流程图类似
- 实例
#include 2.2 switch语句
- 语法
switch(表达式)
{
case 结果1 : 执行语句;
break;
case 结果2 : 执行语句;
break;
…
case 结果n : 执行语句;
break;
default : 执行语句;
break;
}
- 实例
#include 1、case中如果没有break,语句将会一直往下执行。
2、if与switch的区别:
switch语句中表达式类型只能是整型和字符型,不可以是一个区间;但是其结构清晰,执行效率比较高。
2.3 选择结构案例
1. 三目运算符
通过三目运算符可以实现简单的判断。
- 语法
表达式1(a > b) ? 表达式2(a) :表达式3(b)
返回的是一个变量
if a > b为真 则返回a;
if a > b为假 则返回b;
- 实例
#include 2. 求三个数中的最大值
- 案例描述
A、B、C三个数比较大小(三个数互不相等时),求其中的最大值
- 实现思路
—>if A>B
----------->if A>C,则A最大
----------->else,则C最大
—>else
----------->if B>C,则B最大
----------->else,则C最大
- 实例
#include 3. 循环结构
3.1 循环语句
1. while语句
满足循环条件,执行循环语句
- 语法
while (表达式)
{循环语句}
#include 注意:在执行循环语句的时候,必须设置跳出循环的出口,否则会出现死循环。
2. do while语句
- 语法
do {循环语句}
while (循环条件)
#include while与do while的区别:
while是先判断条件如果条件满足则执行语句;
do while是先执行一次语句再进行判断条件是否满足,若满足继续执行语句。
3. for语句
- 语法
for(起始表达式(0);条件表达式(1);末尾循环(3))
{循环语句(2);}
在使用for循环语句时,程序执行的顺序如编号0-3所示
for循环结构比较清晰,比较常用
- 实例
#include 4. 循环嵌套
- 任务描述
通过循环语句在屏幕上输出:
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * * * *
- 代码实现
#include 3.2 循环结构案例
1. 猜数字while
- 案例描述
基本功能:
随机生成一个1~100之间的数字,用户去猜测这个数字是多少,猜测不对时会对玩家进行提醒:猜测过大!猜测过小!恭喜你猜对了!猜错了会继续让你猜测,猜对了游戏则会退出!
附加功能:
玩家猜测的机会不是无限的,仅仅只有6次机会,如果6次也还未猜对,也会退出游戏,并提醒玩家,很遗憾,您未能通关!
- 代码实现
#include 2. 水仙花数do while
- 案例描述
水仙花数:
一个三位数,如果(个位)^3 + (十位)^3 + (百位)^3 = 三位数本身,这个三位数则为一个水仙花数。请在屏幕中输出所有的水仙花数。
- 代码实现
#include 其中:
x / 100 = 百位数
x / 10 % 10 = 十位数
x % 10 = 个位数
3. 敲桌子for
- 案例描述
参加聚会时,玩敲桌子游戏,从1开始数数,最大数到100结束,如果数到的数中有7或者是7的倍数时,就要敲一下桌子,不能说出来,否则将会受到惩罚。
- 代码实现
#include 4. 实现乘法口诀表的打印循环嵌套案例
- 案例描述
- 思路
—>打印所有的行数和列数
—>打印范围(列数<=行数)
—>打印列数 * 行数 = 计算结果
- 代码实现
#include 4. 跳转语句
1. break语句
- 作用
用于跳出选择结构或循环结构
- 使用场合
1、出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case跳出switch语句
2、出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句
3、出现在嵌套循环语句中,作用是跳出最近的内层循环语句
- 实例
1、break出现在switch语句中
#include 2、break出现在switch语句中
#include 3、break出现在嵌套循环语句中
#include - 输出结果
2. goto语句
- 作用
若标记的名称存在,执行到goto语句时,会跳转到标记的位置
goto语句不提倡在代码中频繁使用
- 实例
#include 3. continue语句
- 作用
在循环语句中,跳出本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,进入下一次循环
- 实例
#include