【Java 数据结构】优先级队列(堆)
优先级队列(堆)
- 1. 优先级队列
-
- 1.1 概念
- 2. 优先级队列的模拟实现
-
- 2.1 堆的概念
- 2.2 堆的存储方式
- 2.3 堆的创建
-
- 2.3.1 堆向下调整
- 2.3.2 堆的创建
- 2.3.3 建堆的时间复杂度
- 2.4 堆的插入与删除
-
- 2.4.1 堆的插入
- 2.4.2 堆的删除
- 2.5 用堆模拟实现优先级队列
- 3.常用接口介绍
-
- 3.1 PriorityQueue的特性
- 3.2 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
- 4. 堆的应用
-
- 4.1 PriorityQueue的实现
- 4.2 堆排序
1. 优先级队列
1.1 概念
前面介绍过队列,队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,但有些情况下,操作的数据可能带有优先级,一般出队列时,可能需要优先级高的元素先出队列,
在这种情况下,数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)。
2. 优先级队列的模拟实现
JDK1.8中的PriorityQueue底层使用了堆这种数据结构,而堆实际就是在完全二叉树的基础上进行了一些调整。
2.1 堆的概念
如果有一个关键码的集合K = {k0,k1, k2,…,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足:Ki <= K2i+1 且 Ki<= K2i+2 (Ki >= K2i+1 且 Ki >= K2i+2) i = 0,1,2…,则称为 小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质:
2.2 堆的存储方式
从堆的概念可知,堆是一棵完全二叉树,因此可以层序的规则采用顺序的方式来高效存储
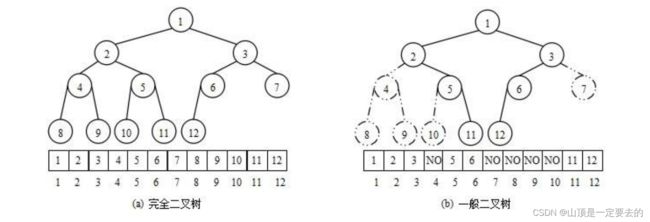
注意:对于非完全二叉树,则不适合使用顺序方式进行存储,因为为了能够还原二叉树,空间中必须要存储空节点,就会导致空间利用率比较低。
将元素存储到数组中后,可以根据二叉树章节的性质5对树进行还原。假设i为节点在数组中的下标,则有:
- 如果i为0,则i表示的节点为根节点,否则i节点的双亲节点为 (i - 1)/2
- 如果2 * i + 1 小于节点个数,则节点i的左孩子下标为2 * i + 1,否则没有左孩子
- 如果2 * i + 2 小于节点个数,则节点i的右孩子下标为2 * i + 2,否则没有右孩子
2.3 堆的创建
2.3.1 堆向下调整
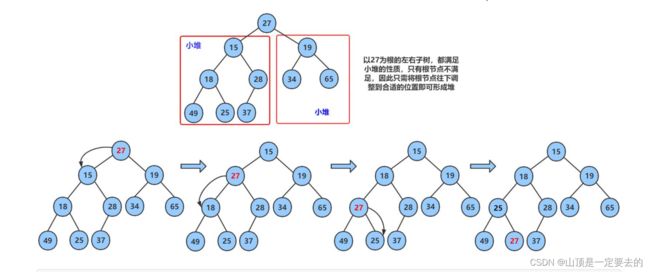
对于集合{ 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 }中的数据,如果将其创建成堆呢?
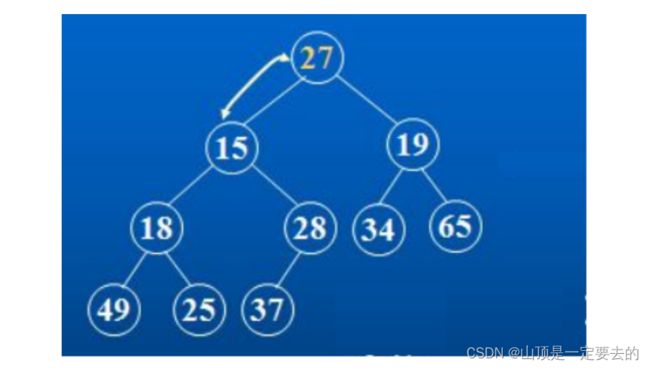
仔细观察上图后发现:根节点的左右子树已经完全满足堆的性质,因此只需将根节点向下调整好即可。
向下过程(以小堆为例):
- 让parent标记需要调整的节点,child标记parent的左孩子(注意:parent如果有孩子一定先是有左孩子)
- 如果parent的左孩子存在,即:child < size, 进行以下操作,直到parent的左孩子不存在
parent右孩子是否存在,存在找到左右孩子中最小的孩子,让child进行标将parent与较小的孩子child比较,如果:
public void shiftDown(int[] array, int parent) {
// child先标记parent的左孩子,因为parent可能右左没有右
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
int size = array.length;
while (child < size) {
// 如果右孩子存在,找到左右孩子中较小的孩子,用child进行标记
if(child+1 < size && array[child+1] < array[child]){
child += 1;
}
// 如果双亲比其最小的孩子还小,说明该结构已经满足堆的特性了
if (array[parent] <= array[child]) {
break;
}else{
// 将双亲与较小的孩子交换
int t = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = t;
// parent中大的元素往下移动,可能会造成子树不满足堆的性质,因此需要继续向下调整
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}
}
注意:在调整以parent为根的二叉树时,必须要满足parent的左子树和右子树已经是堆了才可以向下调整。
时间复杂度分析:
最坏的情况即图示的情况,从根一路比较到叶子,比较的次数为完全二叉树的高度,即时间复杂度为log2(n)
2.3.2 堆的创建
那对于普通的序列{ 1,5,3,8,7,6 },即根节点的左右子树不满足堆的特性,又该如何调整呢?

参考代码:
public static void createHeap(int[] array) {
// 找倒数第一个非叶子节点,从该节点位置开始往前一直到根节点,遇到一个节点,应用向下调整
int root = ((array.length-2)>>1);
for (; root >= 0; root--) {
shiftDown(array, root);
}
}
2.3.3 建堆的时间复杂度
因为堆是完全二叉树,而满二叉树也是完全二叉树,此处为了简化使用满二叉树来证明(时间复杂度本来看的就是
近似值,多几个节点不影响最终结果):
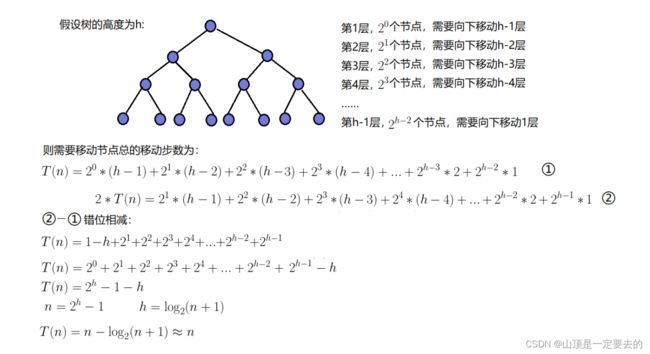
因此:建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)
2.4 堆的插入与删除
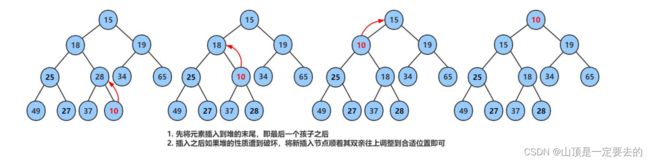
2.4.1 堆的插入
堆的插入总共需要两个步骤:
public void shiftUp(int child) {
// 找到child的双亲
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0) {
// 如果双亲比孩子大,parent满足堆的性质,调整结束
if (array[parent] > array[child]) {
break;
}
else{
// 将双亲与孩子节点进行交换
int t = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = t;
// 小的元素向下移动,可能到值子树不满足对的性质,因此需要继续向上调增
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 1;
}
}
}
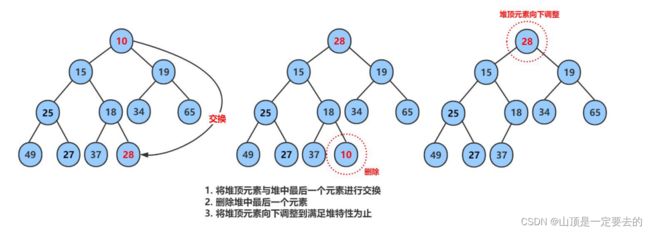
2.4.2 堆的删除
注意:堆的删除一定删除的是堆顶元素。具体如下:
2.5 用堆模拟实现优先级队列
public class MyPriorityQueue {
// 演示作用,不再考虑扩容部分的代码
private int[] array = new int[100];
private int size = 0;
public void offer(int e) {
array[size++] = e;
shiftUp(size - 1);
}
public int poll() {
int oldValue = array[0];
array[0] = array[--size];
shiftDown(0);
return oldValue;
}
public int peek() {
return array[0];
}
}
3.常用接口介绍
3.1 PriorityQueue的特性
Java集合框架中提供了PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue两种类型的优先级队列,PriorityQueue是线
程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的,本文主要介绍PriorityQueue。

关于PriorityQueue的使用要注意:
- 使用时必须导入PriorityQueue所在的包,即:
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
- PriorityQueue中放置的元素必须要能够比较大小,不能插入无法比较大小的对象,否则会抛出
ClassCastException异常 - 不能插入null对象,否则会抛出NullPointerException
- 没有容量限制,可以插入任意多个元素,其内部可以自动扩容
- 插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为O(log2(n))
- PriorityQueue底层使用了堆数据结构
- PriorityQueue默认情况下是小堆—即每次获取到的元素都是最小的元素
3.2 PriorityQueue常用接口介绍
static void TestPriorityQueue(){
// 创建一个空的优先级队列,底层默认容量是11
PriorityQueue<Integer> q1 = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 创建一个空的优先级队列,底层的容量为initialCapacity
PriorityQueue<Integer> q2 = new PriorityQueue<>(100);
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(4);
list.add(3);
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
// 用ArrayList对象来构造一个优先级队列的对象
// q3中已经包含了三个元素
PriorityQueue<Integer> q3 = new PriorityQueue<>(list);
System.out.println(q3.size());
System.out.println(q3.peek());
}
注意:默认情况下,PriorityQueue队列是小堆,如果需要大堆需要用户提供比较器
// 用户自己定义的比较器:直接实现Comparator接口,然后重写该接口中的compare方法即可
class IntCmp implements Comparator<Integer>{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
}
public class TestPriorityQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> p = new PriorityQueue<>(new IntCmp());
p.offer(4);
p.offer(3);
p.offer(2);
p.offer(1);
p.offer(5);
System.out.println(p.peek());
}
}
此时创建出来的就是一个大堆。
2. 插入/删除/获取优先级最高的元素
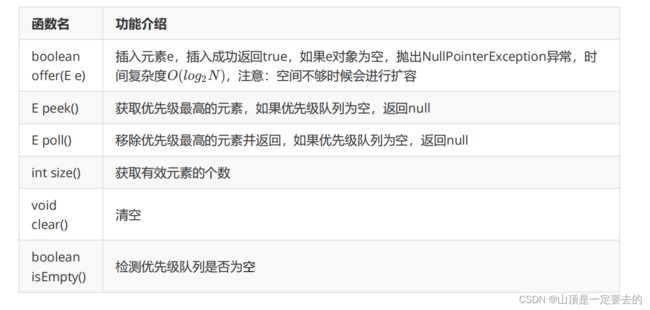
注意:以下是JDK 1.8中,PriorityQueue的扩容方式:
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
优先级队列的扩容说明:
- 如果容量小于64时,是按照oldCapacity的2倍方式扩容的
- 如果容量大于等于64,是按照oldCapacity的1.5倍方式扩容的
- 如果容量超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,按照MAX_ARRAY_SIZE来进行扩容
4. 堆的应用
4.1 PriorityQueue的实现
用堆作为底层结构封装优先级队列
4.2 堆排序
堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
- 建堆
- 升序:建大堆
- 降序:建小堆
- 利用堆删除思想来进行排序
建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序。