postgresql源码学习(51)—— 提交日志CLOG 原理 用途 管理函数
一、 CLOG是什么
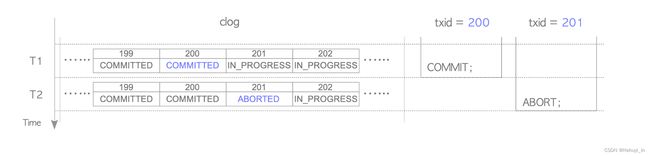
CLOG(commit log)记录事务的最终状态。
- 物理上,是$PGDATA/pg_xact目录下的一些文件
- 逻辑上,是一个数组,下标为事务id,值为事务最终状态
1. 事务最终状态
clog.h中定义了4种事务状态
/*
* Possible transaction statuses --- note that all-zeroes is the initial
* state. 全0为初始状态
*
* subcommitted状态表示子事务已提交,但父事务尚未提交或回滚
*/
typedef int XidStatus;
#define TRANSACTION_STATUS_IN_PROGRESS 0x00
#define TRANSACTION_STATUS_COMMITTED 0x01
#define TRANSACTION_STATUS_ABORTED 0x02
#define TRANSACTION_STATUS_SUB_COMMITTED 0x032. CLOG空间占用
由于只有4种状态,因此只需要2个bit即可表示它们,一个字节则可以存4个事务的状态,在clog.c中也可以看到这些定义。
/* We need two bits per xact, so four xacts fit in a byte */
#define CLOG_BITS_PER_XACT 2
#define CLOG_XACTS_PER_BYTE 4
#define CLOG_XACTS_PER_PAGE (BLCKSZ * CLOG_XACTS_PER_BYTE)
#define CLOG_XACT_BITMASK ((1 << CLOG_BITS_PER_XACT) - 1)- CLOG_BITS_PER_XACT:每个事务占用几个 bit(默认2)
- CLOG_XACTS_PER_BYTE :每个字节可以存几个事务的状态(默认4,8 bit/2)
- CLOG_XACTS_PER_PAGE:每个页可以存几个事务的状态(默认8KB*4=32K=2^15个)
- CLOG_XACT_BITMASK:位掩码(没查到是干啥的),计算方式是CLOG_BITS_PER_XACT左移1位然后减1。例如默认值为2,二进制为0010,左移一位0100,再减1则为0011
另外在slru.h中还定义了SLRU段大小(CLOG日志缓冲池是基于SLRU缓冲池实现的)。
32代表每个CLOG文件(段)由32个页组成,每个段可记录32*2^15=2^20个事务的状态。
#define SLRU_PAGES_PER_SEGMENT 32目前事务id为32位,最多有2^32个事务,因此最多需要2^32/2^20=2^12个日志段。
CLOG以段号命名,因此只需要12位,不过实际上,pg是使用4位16进制数来表示段号,并作为日志名,也就是我们前面看到的0000,0001这种名字。
3. CLOG四元组
前面提到,CLOG在逻辑上是一个数组,下标为事务id,值为事务最终状态。那么怎么通过事务id定位它在CLOG中的具体位置并获取事务最终状态?答案就是下面这个四元组:
#define TransactionIdToPage(xid) ((xid) / (TransactionId) CLOG_XACTS_PER_PAGE)
#define TransactionIdToPgIndex(xid) ((xid) % (TransactionId) CLOG_XACTS_PER_PAGE)
#define TransactionIdToByte(xid) (TransactionIdToPgIndex(xid) / CLOG_XACTS_PER_BYTE)
#define TransactionIdToBIndex(xid) ((xid) % (TransactionId) CLOG_XACTS_PER_BYTE)- TransactionIdToPage:事务id对应在哪个CLOG页
- TransactionIdToPgIndex:事务id对应在上面页中的偏移量
- TransactionIdToByte:事务id对应在上面页中第几个的字节
- TransactionIdToBIndex:事务id对应在上面字节中的哪个bit
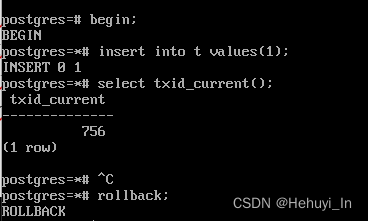
例如事务id 756,最终状态是已回滚
- TransactionIdToPage = 756/(2^15)=0 -> 第0号page
- TransactionIdToPgIndex = 756%(2^15)=0 -> 第0号page的756偏移位
- TransactionIdToByte = 756/4=189 -> 第0号page的189个byte
- TransactionIdToBIndex = 756%4=0 -> 该byte的首2位bit
查看clog
hexdump -C ./0000 -s 189 -n 1
# -C 定义导出的格式;-s 指定了从文件头跳过多少字节,默认十进制,0x开头则是十六进制;-n 指定导出多少字节长度#define TRANSACTION_STATUS_ABORTED 0x02二、 主要用途
CLOG中保存的事务最终状态用来干什么?答案是用来在可见性判断中确定事务的运行状态。
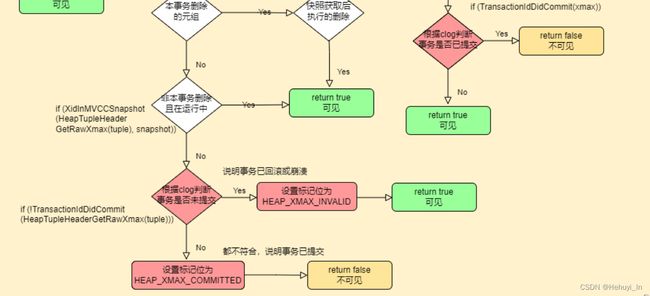
postgresql源码学习(十九)—— MVCC④-可见性判断 HeapTupleSatisfiesMVCC函数_Hehuyi_In的博客-CSDN博客 再回来看看这个复杂的流程图
可以看到在t_infomask未设置时,会根据clog来判断事务是否提交。之前的文章也有提到过,这样做是为了加速判断,避免每行都需要读取clog文件(或者缓冲区)数据。
流程图中可以看到,clog主要判断函数为 TransactionIdDidCommit,其实还有一个函数TransactionIdDidAbort也会查询pg_xact目录。另一个TransactionIdIsInProgress函数查的是PGPROC数组,这个函数过于复杂,这里就跳过了。
除去子事务相关部分,其实这两个函数非常简单
/*
* TransactionIdDidCommit
* True if transaction associated with the identifier did commit.
* Note:
* Assumes transaction identifier is valid and exists in clog.
*/
bool /* true if given transaction committed */
TransactionIdDidCommit(TransactionId transactionId)
{
XidStatus xidstatus;
xidstatus = TransactionLogFetch(transactionId);
/*
* If it's marked committed, it's committed.
*/
if (xidstatus == TRANSACTION_STATUS_COMMITTED)
return true;
…
/*
* It's not committed.
*/
return false;
}/*
* TransactionIdDidAbort
* True iff transaction associated with the identifier did abort.
* Note:
* Assumes transaction identifier is valid and exists in clog.
*/
bool /* true if given transaction aborted */
TransactionIdDidAbort(TransactionId transactionId)
{
XidStatus xidstatus;
xidstatus = TransactionLogFetch(transactionId);
/*
* If it's marked aborted, it's aborted.
*/
if (xidstatus == TRANSACTION_STATUS_ABORTED)
return true;
…
/*
* It's not aborted.
*/
return false;
}三、 CLOG主要管理函数
以下函数都在clog.c文件中,按照函数名和注释可以看出主要用途。下面按照pg 14版本简单记录,详情可以查看具体定义。
1. CLOG日志管理器启动
StartupCLOG函数:在pg启动后会调用,以启动CLOG日志管理器
2. CLOG日志管理器初始化
CLOGShmemInit函数:用于在共享内存中初始化CLOG缓冲池。
3. CLOG段创建
BootStrapCLOG函数:在PG安装及CLOGShmemInit函数执行后,会调用本函数创建第一个CLOG文件(0000),本函数会调用ZeroCLOGPage函数
4. CLOG页面初始化
ZeroCLOGPage函数:初始化指定页面为全0
5. CLOG读操作
TransactionIdGetStatus函数:从CLOG文件(缓冲池)中读取日志记录,获取事务状态位
6. CLOG写操作
TransactionIdSetStatusBit函数:设置事务状态位,实际就是在CLOG文件中写该事务对应的CLOG日志记录。
7. CLOG的扩展
ExtendCLOG函数:为新分配的事务id创建CLOG一个新页,以供日志记录写入
8. 构建CLOG页时创建XLOG记录
WriteZeroPageXlogRec函数:当创建新CLOG页时,调用本函数创建一条” CLOG_ZEROPAGE”类型的XLOG记录,保存所创建的CLOG页号,用于在系统崩溃或恢复时重建CLOG
9. CLOG的REDO操作
clog_redo函数:前面提到在创建新CLOG页时会记XLOG日志,在REDO执行过程中,当遇到CLOG_ZEROPAGE和CLOG_TRUNCATE类型的XLOG记录时,则由该函数处理
10. 创建检查点时CLOG的操作
CheckPointCLOG函数:创建检查点时,调用该函数将脏CLOG页写入磁盘
11. CLOG删除
TruncateCLOG函数:以CLOG段为单位,删除已经过时的事务id(由AdvanceOldestClogXid函数确定哪些已经过时)对应的事务状态记录文件
12. CLOG关闭
旧版本在ShutdownCLOG函数,pg 14中没有该函数了
参考
《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》第7章
https://www.interdb.jp/pg/pgsql05.html#_5.4.
[2021-06-17]PostgreSQL事物提交日志信息clog解析_qxy0503的博客-CSDN博客
hexdump的用法_lijun5635的博客-CSDN博客_hexdump 大小端
PostgreSQL DBA(22) - MVCC#2(commit log)_ITPUB博客
https://www.slideshare.net/pgday_seoul/pgdayseoul-2017-3-postgresql-wal-buffers-clog-buffers-deep-dive