SpringBoot+flowable快速实现工作流
文章目录
1.使用flowable-ui绘制流程图
1.1 网关
2.SpringBoot集成flowable
2.1 添加Maven依赖
2.2 添加配置
2.3 添加代理类
2.4 流程开发
2.5 测试
1.创建流程
2.查询待办列表
3.同意
4.生成流程图
最近在一个开源项目里见到有使用另一个工做流框架:flowable 。
在简单了解flowable后与activiti框架相比的第一感觉就是开发方便快速,易与springBoot等各种框架快速整合。如果项目中需要快速实现一些工作流的相关功能那么用此框架是一个不错的选择。我先给大家简单的对flowable做个介绍吧。
Flowable提供了一个组高效的核心开源业务流程引擎,为开发人员,系统管理员和业务用户提供工作流和业务流程管理(BPM)平台。全部用Java编写,并且基于Apache 2.0许可的开源,代码在社区维护。其核心是一个快速,经过试验和测试的动态BPMN流程引擎,附带DMN决策表和CMMN Case管理引擎。
通俗来讲,Flowable是BPMN的一个基于java的软件实现,不过Flowable不仅仅包括BPMN,还有DMN决策表和CMMN Case管理引擎,并且有自己的用户管理、微服务API等一系列功能,是一个服务平台。
对于flowable是什么以及关于此框架的具体信息可以参看此项目的官方文档:https://www.flowable.org/docs/userguide/index.html
我们下面的操作需要用到flowable-ui,所以大家安装一下,此处给出docker下的安装方案:
《Docker部署Flowable-UI》
我们下面实现一个报销的审批流程,流程图如下所示:
下面我就开始带着大家从绘制流程到导出流程数据,到和Spring Boot整合来实现一个流程的控制。
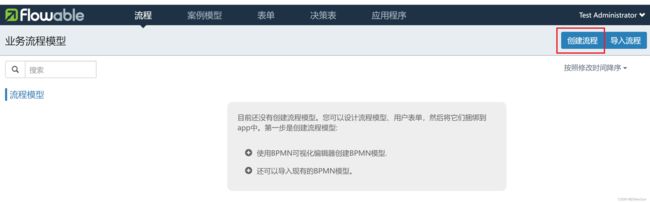
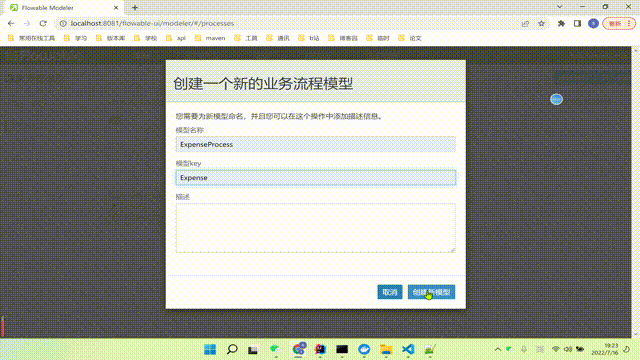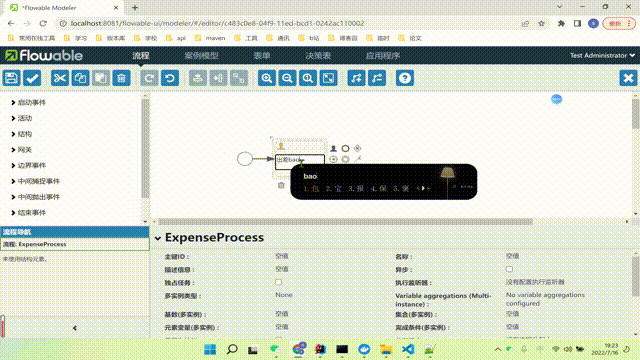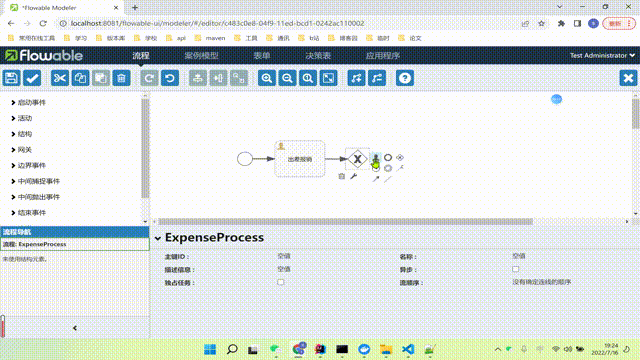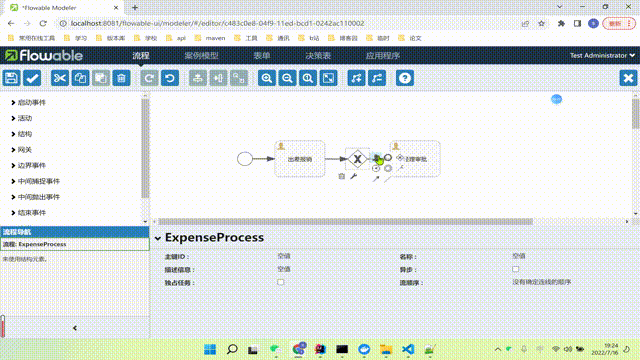
使用flowable-ui绘制流程图
首先要确保你已经安装并且能够正常使用flowable,然后进到以下页面:
我们可以先创建一个用户任务,我们依次类推继续创建出差报销、经理审批、老板审批。
由于不太好截图,我把操作放在视频里,视频不长,只有三四分钟,大家可以看一下。
flowable-operation
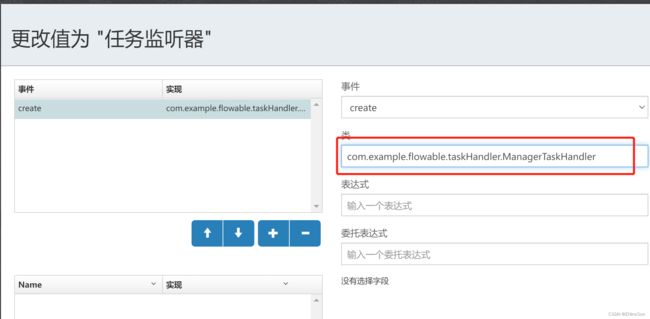
同时,我们需要给我们的用户任务添加监听器
里面有个类路径,它来源于哪里呢?这个值来源于后面我们创建的两个handler,读到这儿大家可以先跳过去,等到看到新增ManagerTaskHandler,BoosTaskHandler的时候在回来把这个监听器加上也来得及。
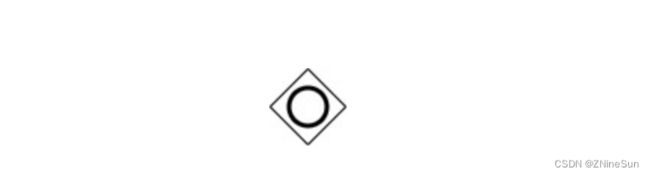
下面我给大家说一下网关。
这个符号的含义,这个符号被称为网关
我么可以看到我们这里的流程图使用的是排他网关,下面还有三种网关,我大致给大家简单介绍一下。
1.1 网关
互斥网关(Exclusive Gateway),又称排他网关,他有且仅有一个有效出口,可以理解为if…else if… else if…else,就和我们平时写代码的一样。
并行网关(Parallel Gateway),他的所有出口都会被执行,可以理解为开多线程同时执行多个任务。
包容性网关(Inclusive Gateway),只要满足条件的出口都会执行,可以理解为 if(…) do, if (…) do, if (…) do,所有的条件判断都是同级别的。
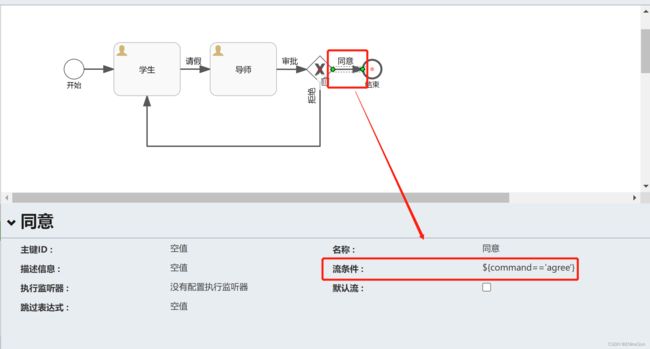
有了网关,我们就需要有判断的执行条件
同理,同意的连线也要设置流条件,条件为:
最后保存我们的流程图,就可以在我们的流程模型里看到。
我们需要导出该流程模型:点击进入之后点击下载按钮即可。
如果你不想自己画,想直接开始流程相关的操作,可以把我下面的内容复制下来,文件名建议命名为:ExpenseProcess.bpmn20.xml,然后在flowable-ui上直接导入便可以看到流程图了。
报销流程
500}]]>
尽管上面的BPMN文件很长,但放心,毕竟那是通过相关的工具生成出来的,对于核心的逻辑部分也很少(主要在process 标签内) ,如需要详细了解的可自行学习下BPMN的标签即可!当然,在flowable的使用文档中也有相关的描述,详见:《Creating a ProcessEngine》
SpringBoot集成flowable
2.1 添加Maven依赖
org.flowable
flowable-spring-boot-starter
6.7.2
由于我们的流程需要数据库的支持,所以还需添加数据库连接依赖
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.projectlombok
lombok
PS:
我的数据库版本8.0+;
SpringBoot版本:2.4.0
2.2 添加配置
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=flowable
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8080
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/flowable_demo?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&&zeroDateTimeBehavior=CONVERT_TO_NULL&&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&&nullCatalogMeansCurrent=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 关闭异步,不关闭历史数据的插入就是异步的,会在同一个事物里面,无法回滚
# 开发可开启会提高些效率,上线需要关闭
flowable.async-executor-activate=true
注意:你需要新建一个数据库,我把数据库命名为:flowable_demo,大家自己随意
2.3 添加代理类
import org.flowable.engine.delegate.TaskListener;
import org.flowable.task.service.delegate.DelegateTask;
public class BossTaskHandler implements TaskListener {
@Override
public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) {
delegateTask.setAssignee("老板");
}
}
import org.flowable.engine.delegate.TaskListener;
import org.flowable.task.service.delegate.DelegateTask;
public class ManagerTaskHandler implements TaskListener {
@Override
public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) {
delegateTask.setAssignee("经理");
}
}
我们需要把这两个handler的相对路径添加到你流程图里所对应的监听器里。
接下来我们需要在resource目录新建目录processes,并将 我们导出的ExpenseProcess.bpmn20.xml放入其中。
如果,你是复制我的流程文件没有自己创建的话,则需要将我们上面的两个handler的下相对路径进行修改,改成你自己项目地址下的相对路径。
这样当此框架启动的时候它会默认加载resource目录下的processes时就可以将此流程配置加载到数据库进行持久化了(注意:项目启动之后系统会自动建表)
注意:监听的相对路径未修改之前,请务必不要启动项目,否则项目启动之后会将该路径持久化到数据库中
2.4 流程开发
通过传入流程ID生成当前流程的流程图给前端,如果流程中使用到中文且生成的图片是乱码的,则需要进配置下字体:
import org.flowable.spring.SpringProcessEngineConfiguration;
import org.flowable.spring.boot.EngineConfigurationConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author ninesun
* date: 2022/07/16
* desc: flowable配置----为放置生成的流程图中中文乱码
*/
@Configuration
public class FlowableConfig implements EngineConfigurationConfigurer {
@Override
public void configure(SpringProcessEngineConfiguration engineConfiguration) {
engineConfiguration.setActivityFontName("宋体");
engineConfiguration.setLabelFontName("宋体");
engineConfiguration.setAnnotationFontName("宋体");
}
}
编写Controller
import org.flowable.bpmn.model.BpmnModel;
import org.flowable.engine.*;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.Execution;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.ProcessInstance;
import org.flowable.image.ProcessDiagramGenerator;
import org.flowable.task.api.Task;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "expense")
public class ExpenseController {
@Autowired
private RuntimeService runtimeService;
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@Autowired
private RepositoryService repositoryService;
@Autowired
private ProcessEngine processEngine;
/**
* 添加报销
*
* @param userId 用户Id
* @param money 报销金额
* @param descption 描述
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "add", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String addExpense(@RequestParam(value = "userId") String userId,
@RequestParam(value = "money") String money,
@RequestParam(value = "descption") String descption) {
//启动流程
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("taskUser", userId);
map.put("money", money);
map.put("descption", descption);
//Expense是我们绘制流程图时自己所填写的key
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("Expense", map);
return "提交成功.流程Id为:" + processInstance.getId();
}
/**
* 获取审批管理列表
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/list")
public Object list(String userId) {
List tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee(userId).orderByTaskCreateTime().desc().list();
for (Task task : tasks) {
System.out.println(task.toString());
}
return tasks.toArray().toString();
}
/**
* 批准
*
* @param taskId 任务ID
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "apply")
public String apply(String taskId) {
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
if (task == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("流程不存在");
}
//通过审核
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("outcome", "通过");
taskService.complete(taskId, map);
return "processed ok!";
}
/**
* 拒绝
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "reject")
public String reject(String taskId) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("outcome", "驳回");
taskService.complete(taskId, map);
return "reject";
}
/**
* 生成流程图
*
* @param processId 任务ID
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "processDiagram")
public void genProcessDiagram(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, String processId) throws Exception {
ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processId).singleResult();
//流程走完的不显示图
if (pi == null) {
return;
}
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(pi.getId()).singleResult();
//使用流程实例ID,查询正在执行的执行对象表,返回流程实例对象
String InstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
List executions = runtimeService
.createExecutionQuery()
.processInstanceId(InstanceId)
.list();
//得到正在执行的Activity的Id
List activityIds = new ArrayList<>();
List flows = new ArrayList<>();
for (Execution exe : executions) {
List ids = runtimeService.getActiveActivityIds(exe.getId());
activityIds.addAll(ids);
}
//获取流程图
BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(pi.getProcessDefinitionId());
ProcessEngineConfiguration engconf = processEngine.getProcessEngineConfiguration();
ProcessDiagramGenerator diagramGenerator = engconf.getProcessDiagramGenerator();
InputStream in = diagramGenerator.generateDiagram(bpmnModel, "png", activityIds, flows,
engconf.getActivityFontName(), engconf.getLabelFontName(),
engconf.getAnnotationFontName(), engconf.getClassLoader(), 1.0, true);
OutputStream out = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int legth = 0;
try {
out = httpServletResponse.getOutputStream();
while ((legth = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, legth);
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}
大家复制的自己的idea中认真读一下,上面基本包含流程的所有内容
启动项目,下面开始测试
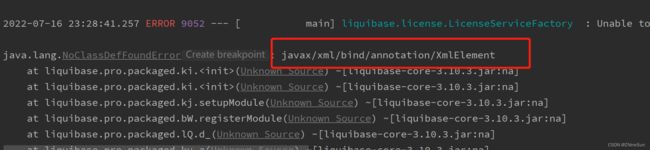
注意:如果大家遇到下面这种问题,也不要担心,这是因为jdk版本导致的。
解决办法:
方式1:将jdk的版本退回到jdk8,因为jdk8还支持自带javax.xml.bind.annotation包。
方式2:新增依赖
javax.xml.bind
jaxb-api
2.3.0
com.sun.xml.bind
jaxb-core
2.3.0
com.sun.xml.bind
jaxb-impl
2.3.0
javax.activation
activation
1.1.1
2.5 测试
创建流程
访问接口:http://localhost:8080/expense/add?userId=ninesun&money=300&descption=500元以下的流程测试
返回结果:
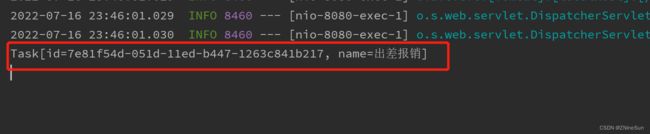
查询待办列表
访问接口:http://localhost:8080/expense/list?userId=ninesun
返回结果: (PS:此处的返回结果为控制台返回结果,页面返回值,我没做处理,所以返回内容为地址)
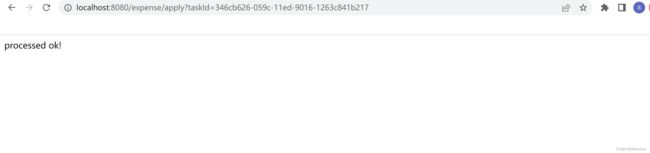
同意
访问接口:http://localhost:8080/expense/apply?taskId=7e81f54d-051d-11ed-b447-1263c841b217
返回结果:
生成流程图
由于我们到第三步的时候流程已经走完了,所以我们在重新新增一个任务,你直接调用第一步创建流程即可
然后访问接口:http://localhost:8080/expense/processDiagram?processId=50fe234f-059d-11ed-9016-1263c841b217
返回结果:
至此,一个完整的流程就走完了
项目开源地址:https://gitee.com/ninesuntec/flowable
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「ZNineSun」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zhiyikeji/article/details/125832031