Qt Concurrent框架详解(QFuture、QFutureWatcher)
1.概述
Qt Concurrent是Qt提供的一个并发编程框架,用于简化多线程和并行计算的开发。它提供了一组易于使用的函数和类,可以方便地在多线程环境下处理并发任务。
有以下特点:
简单易用:Qt Concurrent提供了一组高级函数和类,使多线程和并行计算变得简单易用。开发者无需显式地创建和管理线程,而是通过调用Qt Concurrent提供的函数实现并发任务。
自动任务分割:Qt Concurrent能够根据可用的线程数自动将大的问题拆分成更小的任务,并分配给不同的线程并行执行。这样能够最大程度地利用系统资源,提高并发执行效率。
异步计算:Qt Concurrent提供了异步执行任务的机制,可以在后台执行任务,同时不会阻塞主线程,从而提高用户界面的响应性。 主要的类和函数:
- QFuture:表示一个异步任务的未来结果。可以通过调用QFuture的result()方法来获取结果。还可以使用QFutureWatcher类来监视并处理异步任务的结果。
- QFutureIterator:用于遍历QFuture所代表的异步任务的结果集合。
- QThread:Qt Concurrent内部会自动管理线程,不需要手动创建和管理线程。但如果需要更细粒度的控制线程的操作,可以使用QThread类。
- QtConcurrent::run():用于在后台线程执行函数。它会自动创建一个新的线程,并在该线程中执行指定的函数。
- QtConcurrent::map():用于并行计算,将一个函数应用于一个容器中的每个元素,并返回结果集。它会根据可用的线程数自动进行任务分割和分配。
- QtConcurrent::filter():根据指定的谓词函数,在容器中筛选符合条件的元素。也会进行任务分割和分配。
- QtConcurrent::blockingMapped():与map类似,但是会阻塞当前线程直到所有任务完成。
2.常用方法
在 pro 文件添加“Qt += concurrent”并且在我们的 h 文件添加“#include
- run 相关:执行函数用;
- map 相关:处理容器中的每一项;
- filter 相关:筛选容器中的每一项。
run方法:创建一个新的线程,并在该线程中执行指定的函数。
- QFuture
run(Function function, ...) - QFuture
run(QThreadPool *pool, Function function, ...)
map方法:在单独的线程里对容器中的每一项进行操作,并返回结果集。
- QtConcurrent::map():直接操作容器中的每一项。
- QtConcurrent::mapped():操作容器中的每一项,将处理结果返回一个新的容器,原容器不变。
- QtConcurrent::mappedReduced():在 mapped() 的基础上将处理结果进一步传递给一个函数继续处理。
filter方法:filter 相关函数和 map 相关函数类似,也是对容器中的元素进行处理,但 filter 更多侧重筛选元素。
- QtConcurrent::filter()
- QtConcurrent::filtered()
- QtConcurrent::filteredReduced()
3.示例
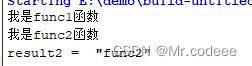
示例1:将普通函数运行在两个不同的线程中,使用QFuture的result()方法来获取返回结果。
#include
#include
#include
QString func1()
{
qDebug()<<"我是func1函数";
}
QString func2(QString name)
{
qDebug()<<"我是func2函数";
return name;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
//用QFuture获取该函数的运行结果
QFuture fut1 = QtConcurrent::run(func1);
//参数2:向func函数传递的参数
QFuture fut2 = QtConcurrent::run(func2, QString("func2"));
QString result2 = fut2.result();
fut1.waitForFinished();
fut2.waitForFinished();
qDebug()<<"result2 = "< 运行结果:
示例2: 使用QtConcurrent::map(),QtConcurrent::mapped() ,QtConcurrent::mappedReduced()
map:直接操作容器中的每一项,不返回。
mapped:操作容器中的每一项,将处理结果返回一个新容器,原容器不变。
mappedReduced:mapped() 的基础上将处理结果进一步传递给下一个函数继续处理。
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include
#include
#include
void processString1(QString& str) {
str = str.toUpper(); //转大写
}
QString processString2(const QString& str) {
// 模拟一些复杂的处理逻辑
QThread::msleep(1000); // 延迟1秒
return str.toUpper(); //转大写
}
void processString3(QString &result, const QString &intermedia)
{
result += " ";
result += intermedia;
}
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
QStringList strings1 = {"hello", "world", "qt", "concurrent"};
QFuture fut1 = QtConcurrent::map(strings1, processString1);
fut1.waitForFinished();
qDebug()<<"==========result1=========";
for(const QString& result : strings1) {
qDebug() << result;
}
qDebug()<<"==========result1=========";
qDebug()<<"==========result2=========";
QStringList strings2 = {"hello", "world", "qt", "concurrent"};
QFuture future = QtConcurrent::mapped(strings2, processString2);
future.waitForFinished();
QList results = future.results();
for(const QString& result : results) {
qDebug() << result;
}
qDebug()<<"==========result2=========";
qDebug()<<"==========result3=========";
QStringList strings3 = {"hello", "world", "qt", "concurrent"};
QFuture future2 = QtConcurrent::mappedReduced(strings3, processString2,processString3);
future2.waitForFinished();
QList results2 = future2.results();
for(const QString& results : results2) {
qDebug() << results;
}
qDebug()<<"==========result3=========";
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
运行结果:
示例3:使用QFutureWatcher来监视并处理异步任务的结果。
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
QFutureWatcher watcher;
QStringList processString(const QStringList& str) {
// 模拟一些复杂的处理逻辑
QThread::msleep(1000); // 延迟1秒
QStringList ret;
for(int i=0;isetupUi(this);
QStringList strings = {"hello", "world", "qt", "concurrent"};
QFuture future = QtConcurrent::run(processString, strings);
watcher.setFuture(future);
QObject::connect(&watcher, &QFutureWatcher::finished, this, [&]() {
qDebug() << "All tasks finished!";
for(const QString& result2 : watcher.result()) {
qDebug() << result2;
}
});
QObject::connect(&watcher, &QFutureWatcher::progressValueChanged, [](int value) {
qDebug() << "Progress: " << value << "%";
});
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
运行结果: