基于二值化图像转GCode的单向扫描实现
- 基于二值化图像转GCode的单向扫描实现
- 什么是单向扫描
- 单向扫描代码示例
基于二值化图像转GCode的单向扫描实现
什么是单向扫描
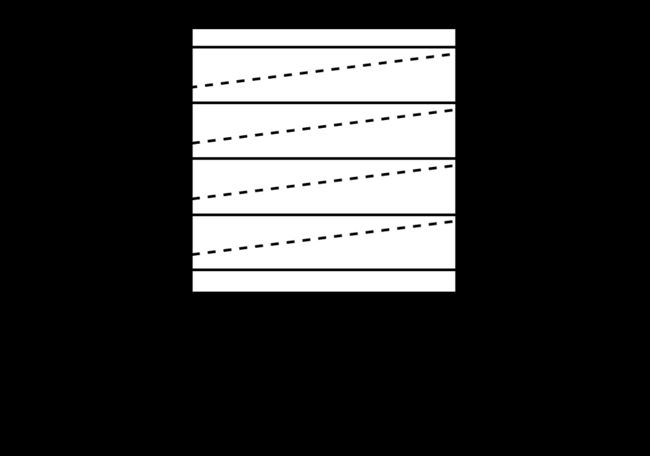
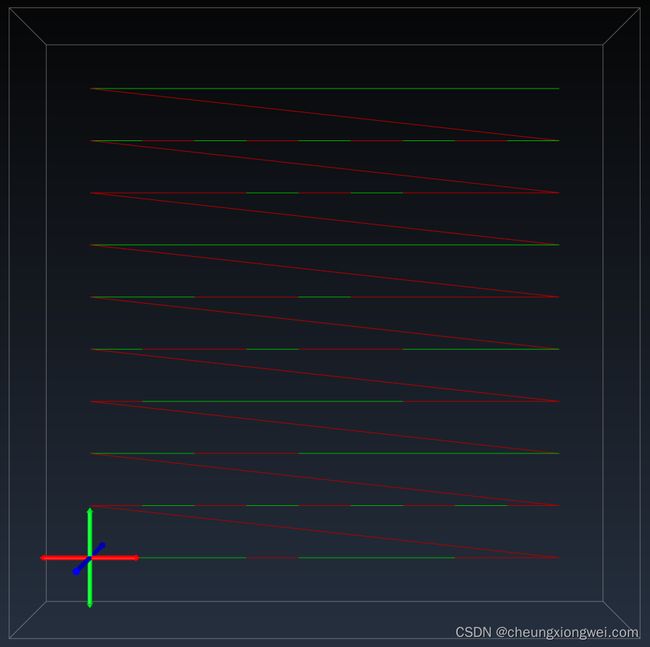
在激光雕刻中,单向扫描(Unidirectional Scanning)是一种雕刻技术,其中激光头只在一个方向上移动,而不是来回移动。这种移动方式主要应用于通过激光逐行扫描图像表面的过程。
具体而言,单向扫描的过程通常包括以下步骤:
-
横向移动(X轴): 激光头沿X轴方向移动到图像的一侧。
-
纵向移动(Y轴): 激光头沿Y轴方向开始逐行移动,刻蚀图像表面。这一过程是单向的,即在每一行上激光头只在一个方向上移动。
-
返回横向移动: 一旦一行完成,激光头返回到图像的一侧,准备进行下一行的刻蚀。
-
循环重复: 重复以上步骤,直到整个图像都被刻蚀完成。
相比于双向扫描,单向扫描通常更加简单,因为它只需沿一个方向移动。然而,它的缺点是激光头在返回时的空闲时间较多,可能导致整体雕刻速度较慢。选择使用单向或双向扫描通常取决于具体的激光雕刻机型和雕刻需求。
总体而言,单向扫描是一种常见的激光雕刻方式,特别适用于需要简单操作且对雕刻速度要求不是很高的场景。
单向扫描代码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct G0 {
std::optional x, y;
std::optional s;
std::string toString() {
std::string command = "G0";
if(x.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" X{:.3f}", x.value());
}
if(y.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" Y{:.3f}", y.value());
}
if(s.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" S{:d}", s.value());
}
return command;
}
explicit operator std::string() const {
std::string command = "G0";
if(x.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" X{:.3f}", x.value());
}
if(y.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" Y{:.3f}", y.value());
}
if(s.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" S{:d}", s.value());
}
return command;
}
};
struct G1 {
std::optional x, y;
std::optional s;
std::string toString() {
std::string command = "G1";
if(x.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" X{:.3f}", x.value());
}
if(y.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" Y{:.3f}", y.value());
}
if(s.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" S{:d}", s.value());
}
return command;
}
explicit operator std::string() const {
std::string command = "G1";
if(x.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" X{:.3f}", x.value());
}
if(y.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" Y{:.3f}", y.value());
}
if(s.has_value()) {
command += std::format(" S{:d}", s.value());
}
return command;
}
};
inline bool ExportGCode(const std::string &fileName, std::vector &&gcode) {
std::fstream file;
file.open(fileName, std::ios_base::out | std::ios_base::trunc);
if(!file.is_open()) {
return false;
}
for(auto &&v: gcode | std::views::transform([](auto item) { return item += "\n"; })) {
file.write(v.c_str(), v.length());
}
return true;
}
int main() {
constexpr int imageWidth = 10;
constexpr int imageHeight = 10;
// clang-format off
// 假设图像数据,0表示非激光刻蚀部分,1表示进行激光刻蚀的区域
constexpr int image[imageWidth][imageHeight] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0}, // G0 G1 G1 G1 G0 G1 G1 G1 G0 G0
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
};
// clang-format on
std::vector command;
for(int y = 0; y < imageHeight; ++y) {
command.emplace_back(G0 {0, y, 0});
for(int x = 0; x < imageWidth; ++x) {
if(auto const value = image[y][x];value) {
command.emplace_back(G1 {x, std::nullopt, 1000}); // 最大激光功率 S=1000
} else {
command.emplace_back(G0 {x, std::nullopt, 0});
}
}
}
// 导出GCode
ExportGCode("gcode.nc",std::move(command));
std::println("Export data to gcode.nc");
return 0;
}
上述示例展示了一个10x10的二维图像数据,其中0表示非激光刻蚀部分,1表示进行激光刻蚀的区域。通过遍历图像数据,代码生成了相应的G代码指令序列,用于描述激光头在工件表面的运动路径。