Mybatis学习笔记--延迟加载与缓存
Mybatis学习笔记:
- Mybatis的概念与入门案例
- 自定义Mybatis
- Mybatis实现CRUD
- 动态SQL语句
- 多表查询
- 延迟加载与缓存
- 注解开发
Mybatis中的延迟加载
什么是延迟加载
在一对多的表的操作中,存在着多个用户与账户,那么在查询用户时,需不需要我们将其所有关联的账户同时查询出来?当我们查询账户时,需不需要我们把其关联的用户查询出来?
这时我们会发现,当查询一个用户时,其账户信息应该是,什么时候用什么时候查询,这种在真正使用数据时才发起查询,不使用时不查询,按需要进行加载的方式就是延迟加载。而我们在查询账户时,账户的所属用户信息应该随着账户的查询一起查出来。这种不管用不用,只要一调用方法,马上发起查询的方式称为立即加载。
在对应的四种表关系中:一对多,多对多通常情况下我们采用延时加载,多对一、一对一通常情况下我们都是采用立即加载。
关于延迟加载的参数配置:
| 设置参数 | 概述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 | true /false | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | 开启时,任一方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有延迟加载属性。 否则,每个延迟加载属性会按需加载(参考 lazyLoadTriggerMethods)。 | true /false | false (在 3.4.1 及之前的版本中默认为 true) |
在SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件中配置mybatis延迟加载的相关参数:
<configuration>
<properties>
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="123456">property>
properties>
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.ly.domain"/>
typeAliases>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}">property>
<property name="url" value="${url}">property>
<property name="username" value="${username}">property>
<property name="password" value="${password}">property>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/IUserDao.xml"/>
<mapper resource="com/IAccountDao.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
一对一延迟加载:
以之前的用户账户案例为例:删除IAccountDao接口中的findAllAccount方法,以及IAccountDao.xml配置文件中的相关映射配置,对IAccountDao.xml配置文件进行修改:
<mapper namespace="com.ly.dao.IAccountDao">
<resultMap id="accountUserMap" type="account">
<id property="id" column="id">id>
<result property="uid" column="uid">result>
<result property="money" column="money">result>
<association property="user" column="uid" javaType="User" select="com.ly.dao.IUserDao.findById">association>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="accountUserMap">
select * from account
select>
<select id="findAccountByUid" resultType="account">
select * from account where uid = #{uid}
select>
mapper>
代码测试:
/**
* 测试查询所有
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<Account> accounts=accountDao.findAll();
for (Account account : accounts){
System.out.println("每个account信息");
System.out.println(account);
System.out.println(account.getUser());
}
}
一对多延迟加载:
以之前的用户账户案例为例:在IAccountDao接口中添加List方法,以及修改IUserDao.xml配置文件中的相关映射配置:
<mapper namespace="com.ly.dao.IUserDao">
<resultMap id="userAccountMap" type="user">
<id property="id" column="id">id>
<result property="username" column="username">result>
<result property="address" column="address">result>
<result property="sex" column="sex">result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday">result>
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account" column="id" select="com.ly.dao.IAccountDao.findAccountByUid">collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userAccountMap">
select * from user
select>
<select id="findById" parameterType="INT" resultType="User">
select * from user where id=#{id}
select>
mapper>
代码测试:
/**
* 测试查询所有
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users=userDao.findAll();
for (User user : users){
System.out.println("-----------每个用户的信息----------");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user.getAccounts());
}
}
Mybatis中的缓存
缓存:存在于内存中的临时数据
为了减少和数据库的交互次数,提高执行效率引入了缓存机制,当一些数据满足:经常查询、不经常改变、并且其正确与否对最终结果影响不大等特点时,可以对数据进行缓存以提高效率。而当数据经常改变,并且对数据的准确性要求很高时,不适合使用缓存。
前期准备
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String address;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
IUserDao接口:
public interface IUserDao{
/**
* 查询所有用户
* @return
*/
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 根据id查询一个用户id
* @param userId
*/
User findById(Integer userId);
/**
* 更新用户信息
* @param user
*/
void updateUser(User user);
}
IUserDao.xml配置文件:
<mapper namespace="com.ly.dao.IUserDao">
<cache/>
<select id="findAll" resultType="user">
select * from user
select>
<select id="findById" parameterType="INT" resultType="User" useCache="true">
select * from user where id=#{id}
select>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update user set username=#{username},address=#{address} where id=#{id}
update>
mapper>
Mybatis中的一级缓存和二级缓存
一级缓存:指的是mybatis中SqlSession对象的缓存。当我们执行查询之后,查询的结果会同时存在到SqlSession为我们提供的一块区域中。该区域的结构就是一个Map。当我们再次查询同样的数据,mybatis会先去sqlsession中查询是否有,有的话直接拿出来用。当SqlSession对象消失时,mybatis的一级缓存就会消失。
测试代码:
public class UserTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
private IUserDao userDao;
@Before//再测试方法执行之前执行
public void init() throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件,生成字节输入流
in= Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂,获取SqlSessionFactory对象
factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
//3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象
sqlSession=factory.openSession();
//4.使用SqlSession创建Dao接口的代理对象
userDao=sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
@After//用于在测试方法执行之后执行
public void destroy() throws Exception{
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//6.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
in.close();
}
/**
* 测试一级缓存
*/
@Test
public void testFirstLevelCache(){
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
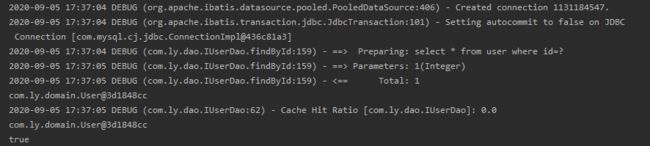
User user1=userDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
/*
通过测试我们会发现两个对象是同一个,返回的值是true,并且只进行了一次查询,第二次是从缓存中取,而当我们关闭sqlSession后再次创建时,会发现两个对象已经不一样了。
sqlSession.close();
//再次开启SqlSession对象
sqlSession =factory.openSession();
userDao =sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//sqlSession.clearCache(); //和上面三行代码效果一样,可以清空缓存
*/
User user2=userDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println(user1==user2);
}
/**
* 测试缓存的同步
*/
@Test
public void testClearCache(){
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
//根据id查询用户
User user1=userDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
//更新用户
user1.setUsername("update");
user1.setAddress("北京");
userDao.updateUser(user1);
User user2=userDao.findById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
/*
*一级缓存时SqlSession范围的缓存,当调用SqlSession的修改、添加、删除、commit()、close()等方法时会清空缓存。
*从测试结果中我们可以看出,对象已经改变,在使用user2进行查询时,又执行了一次查询语句
*/
System.out.println(user1==user2);
}
}
二级缓存:它指的是Mybatis中SqlSessionFactory对象的缓存。由同一个SqlSessionFactory对象创建的SqlSession共享其缓存。
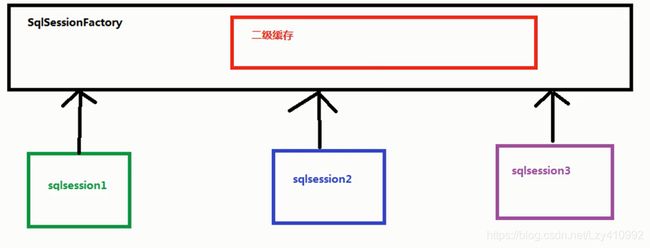
二级缓存的使用步骤:
第一步:让Mybatis框架支持二级缓存(在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置)
第二步:让当前的映射文件支持二级缓存(在IUserDao.xml中配置)
第三步:让当前的操作支持二级缓存(在select标签中配置)
配置SqlMapConfig.xml: 在SqlMapConfig.xml的中添加配置
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
配置IUserDao.xml:
在IUserDao.xml的中添加配置
<cache/>
在IUserDao.xml中修改根据id查询语句:
<!-- 根据id查询用户-->
<select id="findById" parameterType="INT" resultType="User" useCache="true">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
测试代码:
public class SeconLevelCacheTest {
private InputStream in;
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
@Before//再测试方法执行之前执行
public void init() throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件,生成字节输入流
in= Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂,获取SqlSessionFactory对象
factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
}
@After//用于在测试方法执行之后执行
public void destroy() throws Exception{
in.close();
}
/**
* 测试一级缓存
*/
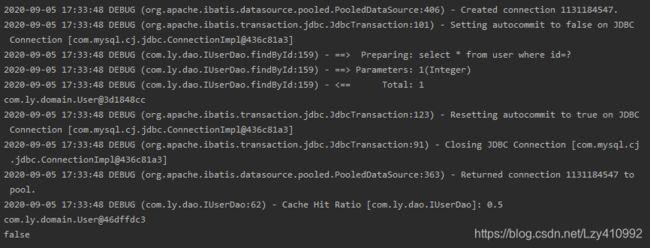
@Test
public void testFirstLevelCache(){
SqlSession sqlSession1=factory.openSession();
IUserDao dao1 =sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user1=dao1.findById(1);
System.out.println(user1);
sqlSession1.close();
SqlSession sqlSession2=factory.openSession();
IUserDao dao2 =sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user2=dao2.findById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession2.close();
/*
* 我们会发现结果中查询语句只执行了一次(实现了二次缓存),但是打印的结果为false,说明二级缓存存放的内容时数据而不是对象。
*/
System.out.println(user1==user2);
}
}