苍穹外卖(四)
查漏补缺
Stream流
Stream流的常见生成方式
- Stream流的三类方法
- 获取Stream流
- 创建一条流水线,并把数据放到流水线上准备进行操作
- 中间方法
- 流水线上的操作
- 一次操作完毕之后,还可以继续进行其他操作
- 终结方法
- 一个Stream流只能有一个终结方法
- 是流水线上的最后一个操作- 生成Stream流的方式
- Collection体系集合
使用默认方法stream()生成流, default Stream
stream() - Map体系集合
把Map转成Set集合,间接的生成流
- 数组
通过Arrays中的静态方法stream生成流
- 同种数据类型的多个数据
通过Stream接口的静态方法of(T... values)生成流
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection体系的集合可以使用默认方法stream()生成流
List list = new ArrayList();
Stream listStream = list.stream();
Set set = new HashSet();
Stream setStream = set.stream();
//Map体系的集合间接的生成流
Map map = new HashMap();
Stream keyStream = map.keySet().stream();
Stream valueStream = map.values().stream();
Stream> entryStream = map.entrySet().stream();
//数组可以通过Arrays中的静态方法stream生成流
String[] strArray = {"hello","world","java"};
Stream strArrayStream = Arrays.stream(strArray);
//同种数据类型的多个数据可以通过Stream接口的静态方法of(T... values)生成流
Stream strArrayStream2 = Stream.of("hello", "world", "java");
Stream intStream = Stream.of(10, 20, 30);
}
} Stream流中间操作方法
- 概念
中间操作的意思是,执行完此方法之后,Stream流依然可以继续执行其他操作
- 常见方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Stream |
用于对流中的数据进行过滤 |
| Stream |
返回此流中的元素组成的流,截取前指定参数个数的数据 |
| Stream |
跳过指定参数个数的数据,返回由该流的剩余元素组成的流 |
| static |
合并a和b两个流为一个流 |
| Stream |
返回由该流的不同元素(根据Object.equals(Object) )组成的流 |
filter代码演示
List list=new ArrayList<>(List.of("张三丰","张无忌","张翠山","王二麻子","张良","谢广坤"));
list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s)); limit&skip代码演示
List list=new ArrayList<>(List.of("张三丰","张无忌","张翠山","王二麻子","张良","谢广坤"));
//list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
list.stream().skip(2).limit(2).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s)); concat&distinct代码演示
public class StreamDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个集合,存储多个字符串元素
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("林青霞");
list.add("张曼玉");
list.add("王祖贤");
list.add("柳岩");
list.add("张敏");
list.add("张无忌");
//需求1:取前4个数据组成一个流
Stream s1 = list.stream().limit(4);
//需求2:跳过2个数据组成一个流
Stream s2 = list.stream().skip(2);
//需求3:合并需求1和需求2得到的流,并把结果在控制台输出
// Stream.concat(s1,s2).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
//需求4:合并需求1和需求2得到的流,并把结果在控制台输出,要求字符串元素不能重复
Stream.concat(s1,s2).distinct().forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
}
} Stream流终结操作方法
-
概念
终结操作的意思是,执行完此方法之后,Stream流将不能再执行其他操作
常见方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void forEach(Consumer action) | 对此流的每个元素执行操作 |
| long count() | 返回此流中的元素数 |
public class MyStream5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("张三丰");
list.add("张无忌");
list.add("张翠山");
list.add("王二麻子");
list.add("张良");
list.add("谢广坤");
//method1(list);
// long count():返回此流中的元素数
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
}
private static void method1(ArrayList list) {
// void forEach(Consumer action):对此流的每个元素执行操作
// Consumer接口中的方法void accept(T t):对给定的参数执行此操作
//在forEach方法的底层,会循环获取到流中的每一个数据.
//并循环调用accept方法,并把每一个数据传递给accept方法
//s就依次表示了流中的每一个数据.
//所以,我们只要在accept方法中,写上处理的业务逻辑就可以了.
list.stream().forEach(
new Consumer() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
);
System.out.println("====================");
//lambda表达式的简化格式
//是因为Consumer接口中,只有一个accept方法
list.stream().forEach(
(String s)->{
System.out.println(s);
}
);
System.out.println("====================");
//lambda表达式还是可以进一步简化的.
list.stream().forEach(s->System.out.println(s));
}
} map
package com.sky.test;/*
*
* @author pengjx
*
* */
import io.swagger.models.auth.In;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class DemoTest {
@Test
public void streamTest(){
List list=new ArrayList<>(List.of("张三丰","张无忌","张翠山","王二麻子","张良","谢广坤","谢广坤","谢广坤"));
//list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
//list.stream().skip(2).limit(2).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// long count = list.stream().distinct().count();
//
// System.out.println(count);
List list1=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list1.add(i);
}
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
// List collect = list1.stream().filter(s -> s % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());
// System.out.println(collect);
// Set collect = list1.stream().filter(s -> s % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// System.out.println(collect);
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("zhangsan,23");
list2.add("lisi,24");
list2.add("wangwu,25");
// Map collect = list2.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(s -> s.split(",")[0], s -> s.split(",")[1]));
// System.out.println(collect);
list2.stream().map(new Function() {
@Override
public Integer apply(String s) {
String[] split = s.split(",");
Integer i = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
return i;
}
}).forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
}
}
Stream流的收集操作
- 概念
对数据使用Stream流的方式操作完毕后,可以把流中的数据收集到集合中
- 常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| R collect(Collector collector) | 把结果收集到集合中 |
工具类Collectors提供了具体的收集方式
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static |
把元素收集到List集合中 |
| public static |
把元素收集到Set集合中 |
| public static Collector toMap(Function keyMapper,Function valueMapper) | 把元素收集到Map集合中 |
// toList和toSet方法演示
public class MyStream7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list1.add(i);
}
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
list1.add(10);
//filter负责过滤数据的.
//collect负责收集数据.
//获取流中剩余的数据,但是他不负责创建容器,也不负责把数据添加到容器中.
//Collectors.toList() : 在底层会创建一个List集合.并把所有的数据添加到List集合中.
List list = list1.stream().filter(number -> number % 2 == 0)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
Set set = list1.stream().filter(number -> number % 2 == 0)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
}
}
/**
Stream流的收集方法 toMap方法演示
创建一个ArrayList集合,并添加以下字符串。字符串中前面是姓名,后面是年龄
"zhangsan,23"
"lisi,24"
"wangwu,25"
保留年龄大于等于24岁的人,并将结果收集到Map集合中,姓名为键,年龄为值
*/
public class MyStream8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("zhangsan,23");
list.add("lisi,24");
list.add("wangwu,25");
Map map = list.stream().filter(
s -> {
String[] split = s.split(",");
int age = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
return age >= 24;
}
// collect方法只能获取到流中剩余的每一个数据.
//在底层不能创建容器,也不能把数据添加到容器当中
//Collectors.toMap 创建一个map集合并将数据添加到集合当中
// s 依次表示流中的每一个数据
//第一个lambda表达式就是如何获取到Map中的键
//第二个lambda表达式就是如何获取Map中的值
).collect(Collectors.toMap(
s -> s.split(",")[0],
s -> Integer.parseInt(s.split(",")[1]) ));
System.out.println(map);
}
} 方法引用
体验方法引用
方法引用的出现原因
在使用Lambda表达式的时候,我们实际上传递进去的代码就是一种解决方案:拿参数做操作
那么考虑一种情况:如果我们在Lambda中所指定的操作方案,已经有地方存在相同方案,那是否还有必要再写重复逻辑呢?答案肯定是没有必要
那我们又是如何使用已经存在的方案的呢?
这就是我们要讲解的方法引用,我们是通过方法引用来使用已经存在的方案
方法引用符
方法引用符
:: 该符号为引用运算符,而它所在的表达式被称为方法引用
引用类方法
引用类方法,其实就是引用类的静态方法
格式
类名::静态方法
范例
Integer::parseInt
Integer类的方法:public static int parseInt(String s) 将此String转换为int类型数据
练习描述
定义一个接口(Converter),里面定义一个抽象方法 int convert(String s);
定义一个测试类(ConverterDemo),在测试类中提供两个方法
一个方法是:useConverter(Converter c)
一个方法是主方法,在主方法中调用useConverter方法
public interface Converter {
int convert(String s);
}
public class ConverterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda写法
useConverter(s -> Integer.parseInt(s));
//引用类方法
useConverter(Integer::parseInt);
}
private static void useConverter(Converter c) {
int number = c.convert("666");
System.out.println(number);
}
}
使用说明
Lambda表达式被类方法替代的时候,它的形式参数全部传递给静态方法作为参数
引用对象的实例方法
引用对象的实例方法,其实就引用类中的成员方法
格式
对象::成员方法
范例
"HelloWorld"::toUpperCase
String类中的方法:public String toUpperCase() 将此String所有字符转换为大写
练习描述
定义一个类(PrintString),里面定义一个方法
public void printUpper(String s):把字符串参数变成大写的数据,然后在控制台输出
定义一个接口(Printer),里面定义一个抽象方法
void printUpperCase(String s)
定义一个测试类(PrinterDemo),在测试类中提供两个方法
一个方法是:usePrinter(Printer p)
一个方法是主方法,在主方法中调用usePrinter方法
public class PrintString {
//把字符串参数变成大写的数据,然后在控制台输出
public void printUpper(String s) {
String result = s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
public interface Printer {
void printUpperCase(String s);
}
public class PrinterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda简化写法
usePrinter(s -> System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()));
//引用对象的实例方法
PrintString ps = new PrintString();
usePrinter(ps::printUpper);
}
private static void usePrinter(Printer p) {
p.printUpperCase("HelloWorld");
}
}
使用说明
Lambda表达式被对象的实例方法替代的时候,它的形式参数全部传递给该方法作为参数
引用类的实例方法
引用类的实例方法,其实就是引用类中的成员方法
格式
类名::成员方法
范例
String::substring
public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
从beginIndex开始到endIndex结束,截取字符串。返回一个子串,子串的长度为endIndex-beginIndex
练习描述
定义一个接口(MyString),里面定义一个抽象方法:
String mySubString(String s,int x,int y);
定义一个测试类(MyStringDemo),在测试类中提供两个方法
一个方法是:useMyString(MyString my)
一个方法是主方法,在主方法中调用useMyString方法
public interface MyString {
String mySubString(String s,int x,int y);
}
public class MyStringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda简化写法
useMyString((s,x,y) -> s.substring(x,y));
//引用类的实例方法
useMyString(String::substring);
}
private static void useMyString(MyString my) {
String s = my.mySubString("HelloWorld", 2, 5);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
使用说明
Lambda表达式被类的实例方法替代的时候 第一个参数作为调用者 后面的参数全部传递给该方法作为参数
引用构造器
引用构造器,其实就是引用构造方法
l格式
类名::new
范例
Student::new
练习描述
定义一个类(Student),里面有两个成员变量(name,age)
并提供无参构造方法和带参构造方法,以及成员变量对应的get和set方法
定义一个接口(StudentBuilder),里面定义一个抽象方法
Student build(String name,int age);
定义一个测试类(StudentDemo),在测试类中提供两个方法
一个方法是:useStudentBuilder(StudentBuilder s)
一个方法是主方法,在主方法中调用useStudentBuilder方法
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public interface StudentBuilder {
Student build(String name,int age);
}
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda简化写法
useStudentBuilder((name,age) -> new Student(name,age));
//引用构造器
useStudentBuilder(Student::new);
}
private static void useStudentBuilder(StudentBuilder sb) {
Student s = sb.build("林青霞", 30);
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
使用说明
Lambda表达式被构造器替代的时候,它的形式参数全部传递给构造器作为参数
@ConfigurationProperties
用来注入外部配置的属性的,可以批量的将外部的属性配置注入到bean对象的属性中
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
第三方bean
如果要管理的 bean 对象来自于第三方(不是自定义的),是无法用 @Component 及衍生注解声明 bean 的,就需要用到 @Bean 注解。若 要管理的第三方 bean 对象,建议对这些 bean 进行集中分类配置,可以通过 @Configuration 注解声明一个配置类。
通过 @Bean 注解的 name 或 value 属性可以声明 bean 的名称,如果不指定,默认 bean 的名称就是方法名。如果第三方 bean 需要依赖其它 bean 对象,直接在 bean 定义方法中设置形参即可,容器会根据类型自动装配。
1. Spring Task
1.1 介绍
Spring Task 是Spring框架提供的任务调度工具,可以按照约定的时间自动执行某个代码逻辑。
应用场景:
• 信用卡每月还款提醒• 银行贷款每月还款提醒• 火车票售票系统处理未支付订单• 入职纪念日为用户发送通知只要是需要定时处理的场景都可以使用Spring Task
1.2 cron表达式
cron表达式其实就是一个字符串,通过cron表达式可以定义任务触发的时间
构成规则:分为6或7个域,由空格分隔开,每个域代表一个含义
每个域的含义分别为:秒、分钟、小时、日、月、周、年(可选)
1.3 入门案例
Spring Task使用步骤:
① 导入 maven 坐标 spring-context (已存在)② 启动类添加注解 @EnableScheduling 开启任务调度③ 自定义定时任务类
package com.sky.task;/*
*
* @author pengjx
*
* */
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void task(){
log.info("{}",new Date());
}
}
2 订单状态定时处理
2.1 需求分析
用户下单后可能存在的情况:
• 下单后未支付,订单一直处于“ 待支付 ”状态• 用户收货后管理端未点击完成按钮,订单一直处于“ 派送中 ”状态对于上面两种情况需要通过定时任务来修改订单状态,具体逻辑为:
• 通过定时任务 每分钟检查一次 是否存在支付超时订单(下单后超过 15 分钟仍未支付则判定为支付超时订单),如果存在则修改订单状态为“已取消”• 通过定时任务 每天凌晨 1 点检查一次 是否存在“派送中”的订单,如果存在则修改订单状态为“已完成”
2.2 代码开发
在OrderMapper接口中扩展方法
@Select("select * from orders where status=#{status} and order_time < #{time}")
List getByStatusAndTimeLT(Integer status, LocalDateTime time); 完善定时任务类的processTimeoutOrder方法:
/**
* @description:支付超时
* @date: 2023/12/26 19:36
**/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * ?")
public void processTimeOutOrder(){
log.info("开始进行支付超时订单查询:{}", LocalDateTime.now());
LocalDateTime time = LocalDateTime.now();
time = time.plusMinutes(-15);
List ordersList=orderMapper.getByStatusAndTimeLT(Orders.PENDING_PAYMENT,time);
if(ordersList !=null && ordersList.size()>0){
for (Orders orders : ordersList) {
orders.setStatus(Orders.CANCELLED);
orders.setCancelTime(LocalDateTime.now());
orders.setCancelReason("支付超时");
orderMapper.update(orders);
}
}
} 完善定时任务类的processDeliveryOrder方法:
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 1 * * ?")
public void processDeliveryOrder(){
log.info("开始进行未完成订单状态处理:{}",LocalDateTime.now());
LocalDateTime time = LocalDateTime.now().plusMinutes(-60);
List ordersList=orderMapper.getByStatusAndTimeLT(Orders.DELIVERY_IN_PROGRESS,time);
if(ordersList !=null && ordersList.size()>0){
for (Orders orders : ordersList) {
orders.setStatus(Orders.COMPLETED);
orderMapper.update(orders);
}
} 3 WebSocket
3.1 介绍
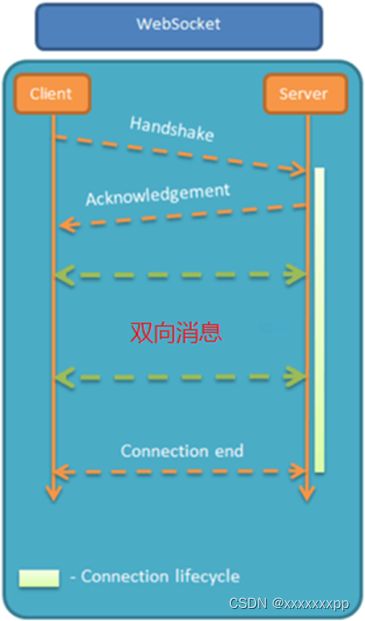
WebSocket 是基于 TCP 的一种新的网络协议。它实现了浏览器与服务器全双工通信——浏览器和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就可以创建持久性的连接, 并进行双向数据传输。
HTTP协议和WebSocket协议对比:
• HTTP 是 短连接• WebSocket 是 长连接• HTTP 通信是 单向 的,基于请求响应模式• WebSocket 支持 双向 通信• HTTP 和 WebSocket 底层都是 TCP 连接
应用场景:
• 视频弹幕• 网页聊天• 体育实况更新• 股票基金报价实时更新
3.2 入门案例
实现步骤:
① 直接使用 websocket.html 页面作为 WebSocket 客户端② 导入 WebSocket 的 maven 坐标③ 导入 WebSocket 服务端组件 WebSocketServer ,用于和客户端通信④ 导入配置类 WebSocketConfiguration ,注册 WebSocket 的服务端组件⑤ 导入定时任务类 WebSocketTask ,定时向客户端推送数据
既然WebSocket支持双向通信,功能看似比HTTP强大,那么我们是不是可以基于WebSocket开发所有的业务功能?
WebSocket缺点:
• 服务器长期维护长连接需要一定的成本• 各个浏览器支持程度不一• W eb S ocket 是长连接,受网络限制比较大,需要处理好重连结论:WebSocket并不能完全取代HTTP,它只适合在特定的场景下使用
4 来单提醒
4.1 需求分析和设计
用户下单并且支付成功后,需要第一时间通知外卖商家。通知的形式有如下两种:
• 语音播报• 弹出提示框
设计:
• 通过 WebSocket 实现管理端页面和服务端保持长连接状态• 当客户支付后,调用 WebSocket 的相关 API 实现服务端向客户端推送消息• 客户端浏览器解析服务端推送的消息,判断是来单提醒还是客户催单,进行相应的消息提示和语音播报• 约定服务端发送给客户端浏览器的数据格式为 JSON ,字段包括: type , orderId , content- type 为消息类型,1为来单提醒 2为客户催单
- orderId 为订单id
- content 为消息内容
4.2 代码开发
在OrderServiceImpl中注入WebSocketServer对象,修改paySuccess方法,加入如下代码:
Map map=new HashMap();
map.put("type",1);//1表示来单提醒,2表示用户存单
map.put("orderId",ordersDB.getId());
map.put("content","订单号:"+outTradeNo);
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(map);
webSocketServer.sendToAllClient(jsonString);5 客户催单
5.1 需求分析和设计
5.2 代码开发
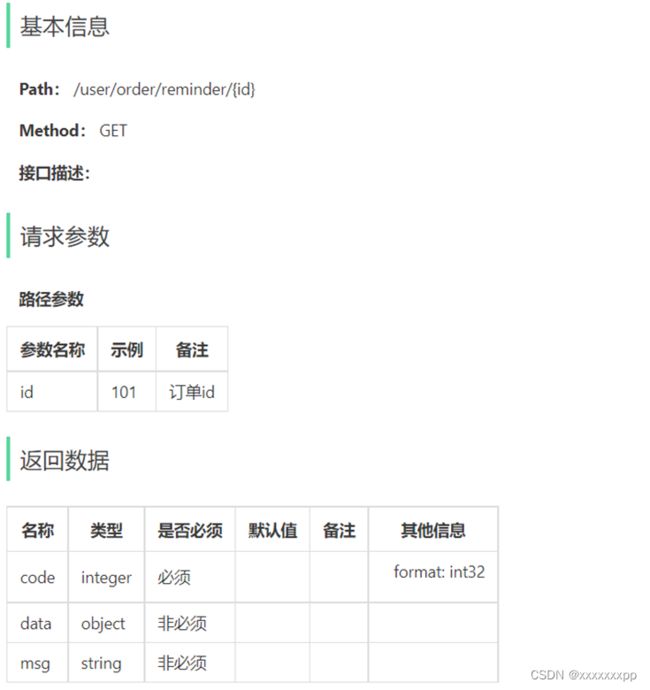
根据用户催单的接口定义,在user/OrderController中创建催单方法:
/**
* @description:客户存单
* @date: 2023/12/27 20:10
* @param: id
* @return: com.sky.result.Result
**/
@GetMapping("/reminder/{id}")
@ApiOperation("客户存单")
public Result reminder(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
log.info("客户催单:{}",id);
orderService.reminder(id);
return Result.success();
}
在OrderService接口中声明reminder方法:
/**
* @description:客户存单
* @date: 2023/12/27 20:10
* @param: id
**/
void reminder(Long id);在OrderServiceImpl中实现reminder方法:
/**
* @description:客户存单
* @date: 2023/12/27 20:10
* @param: id
**/
@Override
public void reminder(Long id) {
Orders orders = orderMapper.getById(id);
if(orders==null){
throw new OrderBusinessException(MessageConstant.ORDER_NOT_FOUND);
}
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("type",2);
map.put("orderId",orders.getId());
map.put("content","订单号:"+orders.getNumber());
webSocketServer.sendToAllClient(JSON.toJSONString(map));
}6. 营业额统计
6.1 需求分析和设计
业务规则:
• 营业额指订单状态为已完成的订单金额合计• 基于可视化报表的折线图展示营业额数据, X 轴为日期, Y 轴为营业额• 根据时间选择区间,展示每天的营业额数据
接口设计:
6.2 代码开发
根据接口定义创建ReportController:
/**
* @description:营业额统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 8:24
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.result.Result
**/
@GetMapping("turnoverStatistics")
@ApiOperation("营业额统计")
public Result turnoverStatistics(
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end
){
log.info("营业额统计:{},{}",begin,end);
TurnoverReportVO turnoverReportVO=reportService.getTurnoverStatistics(begin,end);
return Result.success(turnoverReportVO);
} 创建ReportService接口,声明getTurnover方法:
/**
* @description:营业额统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 8:24
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.TurnoverReportVO
**/
TurnoverReportVO getTurnoverStatistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);创建ReportServiceImpl实现类,实现getTurnover方法:
/**
* @description:营业额统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 8:24
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.TurnoverReportVO
**/
@Override
public TurnoverReportVO getTurnoverStatistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) {
List localDateList=new ArrayList<>();
localDateList.add(begin);
while (!begin.equals(end)){
begin = begin.plusDays(1);
localDateList.add(begin);
}
List turnoverList=new ArrayList<>();
for (LocalDate date : localDateList) {
LocalDateTime beginTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MAX);
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", Orders.COMPLETED);
map.put("begin", beginTime);
map.put("end", endTime);
Double turnover=orderMapper.sumByMap(map);
turnover = turnover == null ? 0.0 : turnover;
turnoverList.add(turnover);
}
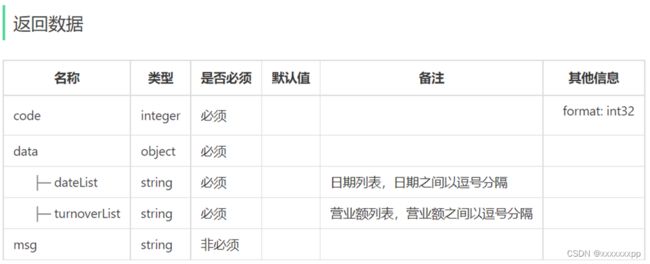
TurnoverReportVO turnoverReportVO = TurnoverReportVO.builder()
.dateList(StringUtils.join(localDateList, ","))
.turnoverList(StringUtils.join(turnoverList, ","))
.build();
return turnoverReportVO;
} 在OrderMapper接口声明sumByMap方法:
Double sumByMap(Map map);在OrderMapper.xml文件中编写动态SQL:
7 用户统计
7.1 需求分析和设计
业务规则:
• 基于可视化报表的折线图展示用户数据, X 轴为日期, Y 轴为用户数• 根据时间选择区间,展示每天的用户总量和新增用户量数据
接口设计:
7.2 代码开发
根据接口定义,在ReportController中创建userStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:用户统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 9:50
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.result.Result
**/
@GetMapping("/userStatistics")
@ApiOperation("用户统计")
public Result userStatistic(
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end
){
log.info("用户统计:{},{}",begin,end);
UserReportVO userReportVO=reportService.getUserStatistic(begin,end);
return Result.success(userReportVO);
} 在ReportService接口中声明getUserStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:用户统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 9:51
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.UserReportVO
**/
UserReportVO getUserStatistic(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
在ReportServiceImpl实现类中实现getUserStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:用户统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 9:51
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.UserReportVO
**/
@Override
public UserReportVO getUserStatistic(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) {
List localDateList=new ArrayList<>();
localDateList.add(begin);
while (!begin.equals(end)){
begin=begin.plusDays(1);
localDateList.add(begin);
}
List totalUserList=new ArrayList<>();
List newUserList=new ArrayList<>();
for (LocalDate date : localDateList) {
LocalDateTime beginTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MAX);
Map map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("end",endTime);
Integer totalUser=userMapper.countByMap(map);
totalUser=totalUser==null?0:totalUser;
totalUserList.add(totalUser);
map.put("begin",beginTime);
Integer newUser=userMapper.countByMap(map);
newUser=newUser==null?0:newUser;
newUserList.add(newUser);
}
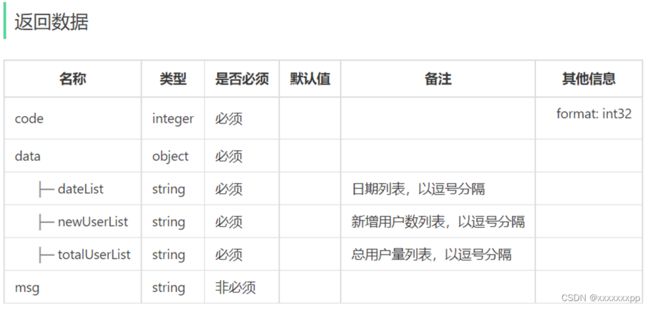
UserReportVO userReportVO = UserReportVO.builder()
.dateList(StringUtils.join(localDateList, ","))
.newUserList(StringUtils.join(newUserList, ","))
.totalUserList(StringUtils.join(totalUserList, ","))
.build();
return userReportVO;
} 在ReportServiceImpl实现类中创建私有方法getUserCount:
private Integer getOrderCount(LocalDateTime begin,LocalDateTime end,Integer status){
Map map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("begin",begin);
map.put("end",end);
map.put("status",status);
return orderMapper.countByMap(map);
}
在UserMapper接口中声明countByMap方法:
Integer countByMap(Map map);在UserMapper.xml文件中编写动态SQL:
8 订单统计
8.1 需求分析和设计
业务规则:
• 有效订单指状态为 “ 已完成 ” 的订单• 基于可视化报表的折线图展示订单数据, X 轴为日期, Y 轴为订单数量• 根据时间选择区间,展示每天的订单总数和有效订单数• 展示所选时间区间内的有效订单数、总订单数、订单完成率,订单完成率 = 有效订单数 / 总订单数 * 100%
接口设计:
8.2 代码开发
在ReportController中根据订单统计接口创建orderStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:订单统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 14:26
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.result.Result
**/
@GetMapping("/ordersStatistics")
@ApiOperation("订单统计")
public Result ordersStatistics(
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end
){
log.info("订单统计:{},{}",begin,end);
OrderReportVO orderReportVO=reportService.getOrdersStatistics(begin,end);
return Result.success(orderReportVO);
} 在ReportService接口中声明getOrderStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:订单统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 14:27
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.OrderReportVO
**/
OrderReportVO getOrdersStatistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);在ReportServiceImpl实现类中实现getOrderStatistics方法:
/**
* @description:订单统计
* @date: 2023/12/28 14:27
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.OrderReportVO
**/
@Override
public OrderReportVO getOrdersStatistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) {
List localDateList=new ArrayList<>();
localDateList.add(begin);
while (!begin.equals(end)){
begin=begin.plusDays(1);
localDateList.add(begin);
}
List orderCountList=new ArrayList<>();
List validOrderCountList=new ArrayList<>();
for (LocalDate date : localDateList) {
LocalDateTime beginTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MAX);
Integer orderCount = getOrderCount(beginTime, endTime, null);
orderCount=orderCount==null?0:orderCount;
orderCountList.add(orderCount);
Integer validOrderCount = getOrderCount(beginTime, endTime, Orders.COMPLETED);
validOrderCount=validOrderCount==null?0:validOrderCount;
validOrderCountList.add(validOrderCount);
}
Integer totalOrderCount = orderCountList.stream().reduce(Integer::sum).get();
Integer validOrderCount = validOrderCountList.stream().reduce(Integer::sum).get();
Double orderCompletionRate=0.0;
if(totalOrderCount!=0){
orderCompletionRate=validOrderCount.doubleValue()/totalOrderCount;
}
return OrderReportVO.builder()
.dateList(StringUtils.join(localDateList,","))
.orderCountList(StringUtils.join(orderCountList,","))
.validOrderCountList(StringUtils.join(validOrderCountList,","))
.totalOrderCount(totalOrderCount)
.validOrderCount(validOrderCount)
.orderCompletionRate(orderCompletionRate)
.build();
} 在OrderMapper接口中声明countByMap方法:
Integer countByMap(Map map);在OrderMapper.xml文件中编写动态SQL:
9 销量排名Top10
9.1 需求分析和设计
业务规则:
• 根据时间选择区间,展示销量前 10 的商品(包括菜品和套餐)• 基于可视化报表的柱状图降序展示商品销量• 此处的销量为商品销售的份数
接口设计:
9.3 代码开发
在ReportController中根据销量排名接口创建top10方法:
/**
* @description:销售排名Top10
* @date: 2023/12/28 15:15
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.result.Result
**/
@GetMapping("/top10")
@ApiOperation("销售排名Top10")
public Result salesTop10Statistics(
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end
){
log.info("销售排名Top10:{},{}",begin,end);
SalesTop10ReportVO salesTop10ReportVO=reportService.getSalesTop10Statistics(begin,end);
return Result.success(salesTop10ReportVO);
}
在ReportService接口中声明getSalesTop10方法:
/**
* @description:销售排名Top10
* @date: 2023/12/28 15:15
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.SalesTop10ReportVO
**/
SalesTop10ReportVO getSalesTop10Statistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);在ReportServiceImpl实现类中实现getSalesTop10方法:
/**
* @description:销售排名Top10
* @date: 2023/12/28 15:15
* @param: begin
* @param: end
* @return: com.sky.vo.SalesTop10ReportVO
**/
@Override
public SalesTop10ReportVO getSalesTop10Statistics(LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) {
LocalDateTime beginTime = LocalDateTime.of(begin, LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.of(end, LocalTime.MAX);
List goodsSalesDTOList = orderMapper.getSalesTop10(beginTime,endTime);
List name = goodsSalesDTOList.stream().map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
String nameList = StringUtils.join(name, ",");
List number = goodsSalesDTOList.stream().map(s -> s.getNumber()).collect(Collectors.toList());
String numberList = StringUtils.join(number, ",");
return SalesTop10ReportVO.builder()
.nameList(nameList)
.numberList(numberList)
.build();
} 在OrderMapper接口中声明getSalesTop10方法:
List getSalesTop10(LocalDateTime beginTime, LocalDateTime endTime); 在OrderMapper.xml文件中编写动态SQL:
10 Apache POI
10.1 介绍
Apache POI 是一个处理Miscrosoft Office各种文件格式的开源项目。简单来说就是,我们可以使用 POI 在 Java 程序中对Miscrosoft Office各种文件进行读写操作。
一般情况下,POI 都是用于操作 Excel 文件。
Apache POI 的应用场景:
• 银行网银系统导出交易明细• 各种业务系统导出 Excel 报表• 批量导入业务数据
10.2 入门案例
Apache POI的maven坐标:
org.apache.poi
poi
org.apache.poi
poi-ooxml
将数据写入Excel文件:
//通过POI创建Excel文件并写入文件内容
public static void write() throws Exception {
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.createSheet("info");
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(1);
row.createCell(1).setCellValue("姓名");
row.createCell(2).setCellValue("城市");
XSSFRow row1 = sheet.createRow(2);
row1.createCell(1).setCellValue("小明");
row1.createCell(2).setCellValue("赣州");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\pengjixuan\\Documents\\excel\\POITest.xlsx"));
excel.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
excel.close();
}读取Excel文件中的数据:
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\itcast.xlsx"));
//通过输入流读取指定的Excel文件
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook(in);
//获取Excel文件的第1个Sheet页
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.getSheetAt(0);
//获取Sheet页中的最后一行的行号
int lastRowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
for (int i = 0; i <= lastRowNum; i++) {
//获取Sheet页中的行
XSSFRow titleRow = sheet.getRow(i);
//获取行的第2个单元格
XSSFCell cell1 = titleRow.getCell(1);
//获取单元格中的文本内容
String cellValue1 = cell1.getStringCellValue();
//获取行的第3个单元格
XSSFCell cell2 = titleRow.getCell(2);
//获取单元格中的文本内容
String cellValue2 = cell2.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println(cellValue1 + " " +cellValue2);
}
//关闭资源
in.close();
excel.close();
11 导出运营数据Excel报表
11.1 •需求分析和设计
业务规则:
• 导出 Excel 形式的报表文件• 导出最近 30 天的运营数据
接口设计:
注意:当前接口没有返回数据,因为报表导出功能本质上是文件下载,
服务端会通过输出流将Excel文件下载到客户端浏览器
11.2 代码开发
实现步骤:
① 设计 Excel 模板文件② 查询近 30 天的运营数据③ 将查询到的运营数据写入模板文件④ 通过输出流将 Excel 文件下载到客户端浏览器
根据接口定义,在ReportController中创建export方法:
/**
* @description:导出运营数据Excel报表
* @date: 2023/12/28 20:18
* @param: httpServletResponse
**/
@GetMapping("/export")
@ApiOperation("导出运营数据Excel报表")
public void export(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse){
log.info("导出运营数据Excel报表");
reportService.exportBusinessData(httpServletResponse);
}
在ReportService接口中声明导出运营数据报表的方法:
/**
* @description:导出运营数据Excel报表
* @date: 2023/12/28 20:18
* @param: httpServletResponse
**/
void exportBusinessData(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse);在ReportServiceImpl实现类中实现导出运营数据报表的方法:
/**
* @description:导出运营数据Excel报表
* @date: 2023/12/28 20:18
* @param: httpServletResponse
**/
@Override
public void exportBusinessData(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) {
LocalDate time = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate beginTime = time.minusDays(30);
LocalDateTime begin=LocalDateTime.of(beginTime,LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDate endTime = time.minusDays(1);
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.of(endTime, LocalTime.MAX);
BusinessDataVO businessData = workspaceService.getBusinessData(begin, end);
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("template/运营数据报表模板.xlsx");
try {
XSSFWorkbook excel = new XSSFWorkbook(in);
XSSFSheet sheet = excel.getSheetAt(0);
sheet.getRow(1).getCell(1).setCellValue(beginTime+" 至 "+endTime);
XSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(3);
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getTurnover());
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getOrderCompletionRate());
row.getCell(6).setCellValue(businessData.getNewUsers());
row=sheet.getRow(4);
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getValidOrderCount());
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getUnitPrice());
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LocalDate date = beginTime.plusDays(i);
LocalDateTime beginDate = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MIN);
LocalDateTime endDate = LocalDateTime.of(date, LocalTime.MAX);
businessData = workspaceService.getBusinessData(beginDate, endDate);
row = sheet.getRow(i + 7);
row.getCell(1).setCellValue(date.toString());
row.getCell(2).setCellValue(businessData.getTurnover());
row.getCell(3).setCellValue(businessData.getValidOrderCount());
row.getCell(4).setCellValue(businessData.getOrderCompletionRate());
row.getCell(5).setCellValue(businessData.getUnitPrice());
row.getCell(6).setCellValue(businessData.getNewUsers());
}
ServletOutputStream outputStream = httpServletResponse.getOutputStream();
excel.write(outputStream);
outputStream.close();
in.close();
excel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}