力扣刷题记录(Java)(一)
-
- 两数之和
-
- 遍历解法(个人版本一)
- Map映射解法(其他解法)
- 两数相加
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本
- 个人版本二
- 无重复字符的最长子串
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本
- 其他版本一
- 串联所有单词的子串
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本
- 其他版本一
- 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
-
- 个人版本一
- 个人版本二
- 官方版本一
- 官方版本二
- 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本一(二分查找)
- 官方版本二(划分数组)
- 最长回文子串
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本一(动态规划)
- 官方版本二(中心扩散算法)
- Z 字形变换
-
- 个人版本一(规律推导)
- 个人版本二(模拟矩阵)
- 官方版本一(压缩矩阵空间(个人版本二优化))
- 官方版本二(直接构造)
- 整数反转
-
- 个人版本一(暴力拆解)
- 官方版本一(自动机)
- 其他版本一
- 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本一
- 回文数
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本一
- 正则表达式匹配
-
- 官方版本一
- 其他版本一
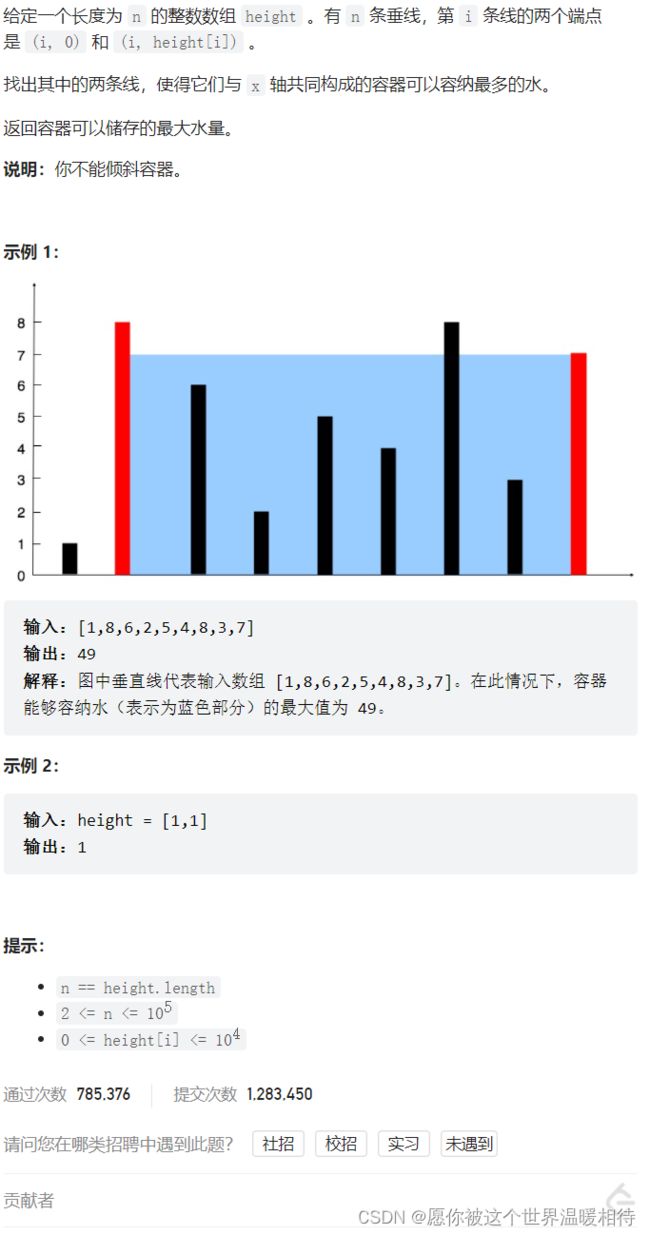
- 盛最多水的容器
-
- 个人版本一
- 官方版本一
- 个人版本二
- 整数转罗马数字
-
- 官方解法一(模拟)
- 官方解法二
- 罗马数字转整数
-
- 其他版本一
- 最长公共前缀
-
- 官方版本一(横向扫描)
- 官方版本二(纵向扫描)
两数之和
知识点:哈希表的键值查找为O(1)
题目链接:两数之和
遍历解法(个人版本一)
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] returnSize = {-1,-1};
for(int i=0 ; i<nums.length-1 ; i++){
int first = nums[i];
int ling = target-first;
for (int j=i+1 ; j<nums.length ; j++){
if(nums[j] == ling){
returnSize[0] = i;
returnSize[1] = j;
break;
}
}
if (returnSize[0] != -1){
break;
}
}
return returnSize;
}
Map映射解法(其他解法)
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i< nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[] {map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
两数相加
知识点:链表
题目链接:两数相加
个人版本一
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
boolean flag = false;
ListNode headNode = new ListNode();
headNode.val = l1.val + l2.val;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
ListNode tail = headNode;
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
ListNode tmp = new ListNode();
tmp.val = l1.val + l2.val;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tmp;
if(flag){
tail.val += 1;
flag = false;
}
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
while (l1 != null){
tail.next = l1;
tail = l1;
if(flag){
tail.val += 1;
flag = false;
}
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
l1= l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null){
tail.next = l2;
tail = l2;
if(flag){
tail.val += 1;
flag = false;
}
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
l2= l2.next;
}
if(flag){
tail.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return headNode;
}
}
官方版本
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = null, tail = null;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int n1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int n2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
if (head == null) {
head = tail = new ListNode(sum % 10);
} else {
tail.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = tail.next;
}
carry = sum / 10;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head;
}
}
个人版本二
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int carry = 0;
int sum = 0;
ListNode headNode = new ListNode();
sum = l1.val + l2.val;
headNode.val = sum%10;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
ListNode tail = headNode;
carry = sum/10;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
ListNode tmp = new ListNode();
sum = l1.val + l2.val + carry;
tmp.val = sum%10;
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tmp;
carry = sum/10;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
boolean flag = carry > 0?true:false;
while (l1 != null){
tail.next = l1;
tail = l1;
if(flag){
tail.val += 1;
flag = false;
}
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
l1= l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null){
tail.next = l2;
tail = l2;
if(flag){
tail.val += 1;
flag = false;
}
if(tail.val >= 10){
tail.val = tail.val%10;
flag = true;
}
l2= l2.next;
}
if(flag){
tail.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return headNode;
}
}
无重复字符的最长子串
知识点:滑动窗口
题目链接:无重复字符的最长子串
个人版本一
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int len = 0,tmpLen,
sLen = s.length();
String tmpStr;
if(s.length() == 0){
return 0;
}
for(int i=0 ; i<sLen-len; i++){
tmpStr = s.substring(i, i+1);
for (int j=i+1 ; j<sLen ; j++){
String nChar = s.substring(j, j+1);
if(!tmpStr.contains(nChar)){
tmpStr += nChar;
continue;
}
break;
}
tmpLen = tmpStr.length();
if(tmpLen > len){
len = tmpLen;
}
}
return len;
}
}
官方版本
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
// 哈希集合,记录每个字符是否出现过
Set<Character> occ = new HashSet<Character>();
int n = s.length();
// 右指针,初始值为 -1,相当于我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动
int rk = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
// 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符
occ.remove(s.charAt(i - 1));
}
while (rk < n && !occ.contains(s.charAt(rk))) {
// 不断地移动右指针
occ.add(s.charAt(rk));
++rk;
}
// 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串
ans = Math.max(ans, rk - i);
}
return ans;
}
}
其他版本一
if (s.length()==0) return 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
int max = 0;
int left = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){
left = Math.max(left,map.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
max = Math.max(max,i-left+1);
}
return max;
串联所有单词的子串
知识点:滑动窗口
题目链接:串联所有单词的子串
个人版本一
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(), tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
int wordLen, wordNum, startFlag=0, start, end, count;
wordLen = words[0].length();
wordNum = words.length;
count = wordNum;
if(s.length() < wordLen*wordNum) return resultList;
for (int i=0 ; i<wordNum ; i++){
if(map.containsKey(words[i])){
map.put(words[i], map.get(words[i])+1);
}else{
map.put(words[i], new Integer(1));
}
}
tmpMap.putAll(map);
start=0;end=start+wordLen;
while (end <= s.length()){
String tmpStr = s.substring(start, end);
boolean isContain = map.containsKey(tmpStr);
if(isContain&&tmpMap.get(tmpStr)>0){
int num = tmpMap.get(tmpStr);
tmpMap.put(tmpStr, num-1);
count--;
if(count == wordNum-1){
startFlag = start;
}
if(count == 0){
resultList.add(startFlag);
count = wordNum;
start = startFlag+1;
end = start+wordLen;
tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
tmpMap.putAll(map);
}else{
start = end;
end = end+wordLen;
}
}else{
if(!isContain){
if(count == wordNum){
start++;
}else{
start = startFlag+1;
}
// start++;
tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
tmpMap.putAll(map);
end = start+wordLen;
count = wordNum;
}else{
count = wordNum;
tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
tmpMap.putAll(map);
start = startFlag+1;
end = start+wordLen;
}
}
}
return resultList;
}
}
官方版本
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 所有单词的个数
int num = words.length;
// 每个单词的长度(是相同的)
int wordLen = words[0].length();
// 字符串长度
int stringLen = s.length();
/**
* 切割方式有wordlen种,wordlen是words中的每个单词的长度
* 此处类似希尔排序,定一个基点然后在这个基点上向后划分单词(单词是以words中单个单词的长度),也就是滑动窗口比较
* 所以划分为wordlen种,也就是一个words中一个单词的长度的个数,超过该次数已经包含中该次数中,例如从0开始的,其中wordlen下标开始就包含在
* 从0开始的滑动窗口中(0~wordlen-1是一个单词)
*/
for (int i = 0; i < wordLen; i++) {
// 遍历的长度超过了整个字符串的长度,退出循环
if (i + num * wordLen > stringLen) {
break;
}
// differ表示窗口中的单词频次和words中的单词频次之差
Map<String, Integer> differ = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 初始化滑动窗口,先将字符串中划分出一个完整的单词串(也就是由words中单词组成的串)
* +1表示添加到窗口中
*/
for (int j = 0; j < num; j++) {
String word = s.substring(i + j * wordLen, i + (j + 1) * wordLen);
differ.put(word, differ.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
/**
* 遍历words中的word,如果开始几个单词都包含words中全部,那么最终differ为空
* 如果某个单词不属于words中,那么他的值就是-1
* -1的作用就是例如,开始的单词中都不包括words中的单词,那么经过以下步骤words中单词对应的次数就是-1
* 如果遇到下一个符合要求的单词串,也就是滑动窗口滑动到该串,那么进入窗口的时候就会+1,综合得0,differ为空,表示符合要求
*/
for (String word : words) {
differ.put(word, differ.getOrDefault(word, 0) - 1);
// 差值为0时,移除掉这个word
if (differ.get(word) == 0) {
differ.remove(word);
}
}
/**
* 以wordlen个基准开始滑动窗口
* start < stringlen - num*wordlen +1 保证start移动到最后剩下的单词足够一个单词串
* 每次start跨域一个单词的距离
*/
for (int start = i; start < stringLen - num * wordLen + 1; start += wordLen) {
if (start != i) {
/**
* 右边的单词滑进来
* start + (num - 1) * wordLen, start + num * wordLen:当进入该段逻辑的时候start已经移动一个单词了
* 但是窗口还在原来的位置,这个时候以start为起点,单词串的最右边的单词就是将要进入到窗口的单词
*/
String word = s.substring(start + (num - 1) * wordLen, start + num * wordLen);
differ.put(word, differ.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
if (differ.get(word) == 0) {
differ.remove(word);
}
// 左边的单词滑出去
word = s.substring(start - wordLen, start);
differ.put(word, differ.getOrDefault(word, 0) - 1);
if (differ.get(word) == 0) {
differ.remove(word);
}
}
// 窗口匹配的单词数等于words中对应的单词数
if (differ.isEmpty()) {
res.add(start);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
其他版本一
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || words == null || words.length == 0) return res;
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int one_word = words[0].length();
int word_num = words.length;
int all_len = one_word * word_num;
for (String word : words) {
map.put(word, map.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < one_word; i++) {
int left = i, right = i, count = 0;
HashMap<String, Integer> tmp_map = new HashMap<>();
while (right + one_word <= s.length()) {
String w = s.substring(right, right + one_word);
right += one_word;
if (!map.containsKey(w)) {
count = 0;
left = right;
tmp_map.clear();
} else {
tmp_map.put(w, tmp_map.getOrDefault(w, 0) + 1);
count++;
while (tmp_map.getOrDefault(w, 0) > map.getOrDefault(w, 0)) {
String t_w = s.substring(left, left + one_word);
count--;
tmp_map.put(t_w, tmp_map.getOrDefault(t_w, 0) - 1);
left += one_word;
}
if (count == word_num) res.add(left);
}
}
}
return res;
找到字符串中所有字母异位词
知识点:滑动窗口
题目链接:找到字符串中所有字母异位词
个人版本一
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(), tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
int start = 0, end = start, pLen = p.length(), count = 0;
for(int i=0; i<pLen; i++){
map.put(p.charAt(i), map.getOrDefault(p.charAt(i), 0)+1);
}
if(pLen > s.length()) return resultList;
while(end < s.length()){
char c = s.charAt(end);
tmpMap.put(c, tmpMap.getOrDefault(c, 0)+1);
end++;
if(map.containsKey(c)){
count++;
while (tmpMap.get(c) > map.get(c)){
count--;
char tmpC = s.charAt(start);
tmpMap.put(tmpC, tmpMap.get(tmpC)-1);
start++;
}
if(count == pLen){
resultList.add(start);
char tmpC = s.charAt(start);
tmpMap.put(tmpC, tmpMap.get(tmpC)-1);
start++;
count--;
}
}else{
count = 0;
tmpMap.clear();
start = end;
}
}
return resultList;
}
}
个人版本二
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int start = 0, pLen = p.length();
if(pLen > s.length()) return resultList;
// 初始化窗口
for(int i=0; i<pLen; i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
map.put(c, map.getOrDefault(c, 0)+1);
}
for(int i=0; i<pLen; i++){
char c = p.charAt(i);
map.put(c, map.getOrDefault(c, 0)-1);
if(map.get(c) == 0){
map.remove(c);
}
}
for(int i=start; i<=s.length()-pLen; i++){
if(i != start){
char addChar = s.charAt(i+pLen-1);
map.put(addChar, map.getOrDefault(addChar, 0)+1);
if(map.get(addChar) == 0){
map.remove(addChar);
}
char removeChar = s.charAt(i-1);
map.put(removeChar, map.getOrDefault(removeChar, 0)-1);
if(map.get(removeChar) == 0){
map.remove(removeChar);
}
}
if(map.isEmpty()){
resultList.add(i);
}
}
return resultList;
}
}
官方版本一
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
int sLen = s.length(), pLen = p.length();
if (sLen < pLen) {
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int[] sCount = new int[26];
int[] pCount = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < pLen; ++i) {
++sCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
++pCount[p.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
if (Arrays.equals(sCount, pCount)) {
ans.add(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < sLen - pLen; ++i) {
--sCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
++sCount[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a'];
if (Arrays.equals(sCount, pCount)) {
ans.add(i + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
官方版本二
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
int sLen = s.length(), pLen = p.length();
if (sLen < pLen) {
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
/**
* count用来统计窗口在s中与p相同或者不同的情况
* differ用来统计窗口在s中相同或不同的个数,当count中
* 值不为0那么就是不同
**/
int[] count = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < pLen; ++i) {
++count[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
--count[p.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
int differ = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) {
if (count[j] != 0) {
++differ;
}
}
if (differ == 0) {
ans.add(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < sLen - pLen; ++i) {
/**
* 窗口需要左移,按照数据结构,左移操作相当于减少当前的数量,即--count[s.charAt(i) - 'a']
* 该处逻辑中 ==1 表示之前该位置是不同的与p的元素(包括重复的), ==0 表示之前是相同的元素
* 因为最后需要窗口左移,需要进行--count[s.charAt(i) - 'a']操作,因而,之前==1,进行该操作后
* 就是0,那么就相当于跟原来相同,differ自减,表示不同p中的字母的数量减少,其他逻辑大概如此
*
*/
if (count[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] == 1) {
--differ;
} else if (count[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] == 0) {
++differ;
}
--count[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
/**
* 类似上述,窗口需要向右进行新添加元素,因而进行 ++count[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a']操作
* ==-1表示原来是不同的,后边进行了该操作后 ==0 就是会变成相同了,所以differ自减,表示窗口在s内与p中不同
* 的字母的个数减少
*/
if (count[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a'] == -1) { // 窗口中字母 s[i+pLen] 的数量与字符串 p 中的数量从不同变得相同
--differ;
} else if (count[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a'] == 0) { // 窗口中字母 s[i+pLen] 的数量与字符串 p 中的数量从相同变得不同
++differ;
}
++count[s.charAt(i + pLen) - 'a'];
if (differ == 0) {
ans.add(i + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
寻找两个正序数组的中位数
知识点:分治
题目链接:寻找两个正序数组的中位数
个人版本一
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
double middle = 0, tmpMiddleIndex = -1, middleIndex;
int nums1Len = nums1.length;
int nums2Len = nums2.length;
int i = 0,j = 0;
int isOu = (nums1Len+nums2Len)%2==0?2:1, tmpOu = 0;
middleIndex = (nums1Len+nums2Len-1)/2;
while (i<nums1Len&&j<nums2Len&&tmpOu != isOu){
int min;
if(nums1[i]<=nums2[j]){
min = nums1[i++];
}else{
min = nums2[j++];
}
tmpMiddleIndex++;
if(tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex||tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex+1){
if(tmpOu == 1){
middle = (middle+min)/2;
}else{
middle = min;
}
tmpOu++;
}
}
while (i < nums1Len&&tmpOu != isOu){
tmpMiddleIndex++;
if(tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex||tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex+1){
if(tmpOu == 1){
middle = (middle+nums1[i])/2;
}else{
middle = nums1[i];
}
tmpOu++;
}
i++;
}
while (j < nums2Len&&tmpOu != isOu){
tmpMiddleIndex++;
if(tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex||tmpMiddleIndex == middleIndex+1){
if(tmpOu == 1){
middle = (middle+nums2[j])/2;
}else{
middle = nums2[j];
}
tmpOu++;
}
j++;
}
return middle;
}
}
官方版本一(二分查找)
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
/* 主要思路:要找到第 k (k>1) 小的元素,那么就取 pivot1 = nums1[k/2-1] 和 pivot2 = nums2[k/2-1] 进行比较
* 这里的 "/" 表示整除
* nums1 中小于等于 pivot1 的元素有 nums1[0 .. k/2-2] 共计 k/2-1 个
* nums2 中小于等于 pivot2 的元素有 nums2[0 .. k/2-2] 共计 k/2-1 个
* 取 pivot = min(pivot1, pivot2),两个数组中小于等于 pivot 的元素共计不会超过 (k/2-1) + (k/2-1) <= k-2 个
* 这样 pivot 本身最大也只能是第 k-1 小的元素
* 如果 pivot = pivot1,那么 nums1[0 .. k/2-1] 都不可能是第 k 小的元素。把这些元素全部 "删除",剩下的作为新的 nums1 数组
* 如果 pivot = pivot2,那么 nums2[0 .. k/2-1] 都不可能是第 k 小的元素。把这些元素全部 "删除",剩下的作为新的 nums2 数组
* 由于我们 "删除" 了一些元素(这些元素都比第 k 小的元素要小),因此需要修改 k 的值,减去删除的数的个数
*/
int length1 = nums1.length, length2 = nums2.length;
int index1 = 0, index2 = 0;
int kthElement = 0;
while (true) {
/**
* 边界情况
* 当一边结束后,k就只要在另一个数组去找就可以了
*
*/
if (index1 == length1) {
return nums2[index2 + k - 1];
}
if (index2 == length2) {
return nums1[index1 + k - 1];
}
// 当k等于1的时候最小的元素就是第k小的元素
if (k == 1) {
return Math.min(nums1[index1], nums2[index2]);
}
// 正常情况
int half = k / 2;
/**
* Math.min处理到达边界的情况
*/
int newIndex1 = Math.min(index1 + half, length1) - 1;
int newIndex2 = Math.min(index2 + half, length2) - 1;
int pivot1 = nums1[newIndex1], pivot2 = nums2[newIndex2];
if (pivot1 <= pivot2) {
/**
* 当pivot1比较小,那么说明在num1数组中,newIndex1以前不可能存在地k小的数
* 对于原来第k小的元素是要的答案,现在就排除了newIndex1 - index1 + 1个元素,并且这些元素
* 都肯定是在第k小元素的前边,所以使用k直接减去该数字
* index1更新为下一个
*/
k -= (newIndex1 - index1 + 1);
index1 = newIndex1 + 1;
} else {
k -= (newIndex2 - index2 + 1);
index2 = newIndex2 + 1;
}
}
}
}
官方版本二(划分数组)
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
if (nums1.length > nums2.length) {
return findMedianSortedArrays(nums2, nums1);
}
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
int left = 0, right = m;
// median1:前一部分的最大值
// median2:后一部分的最小值
int median1 = 0, median2 = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// 前一部分包含 nums1[0 .. i-1] 和 nums2[0 .. j-1]
// 后一部分包含 nums1[i .. m-1] 和 nums2[j .. n-1]
int i = (left + right) / 2;
int j = (m + n + 1) / 2 - i;
// nums_im1, nums_i, nums_jm1, nums_j 分别表示 nums1[i-1], nums1[i], nums2[j-1], nums2[j]
int nums_im1 = (i == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums1[i - 1]);
int nums_i = (i == m ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums1[i]);
int nums_jm1 = (j == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums2[j - 1]);
int nums_j = (j == n ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums2[j]);
if (nums_im1 <= nums_j) {
median1 = Math.max(nums_im1, nums_jm1);
median2 = Math.min(nums_i, nums_j);
left = i + 1;
} else {
right = i - 1;
}
}
return (m + n) % 2 == 0 ? (median1 + median2) / 2.0 : median1;
}
}
最长回文子串
知识点:动态规划
题目链接:最长回文子串
个人版本一
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
String returnStr = "";
int start=0, end=s.length()-1, maxLen = -1;
if(s.length() == 1) return s;
while (start<end&&end-start+1>maxLen){
int tmpStart = start, i, j;
while (tmpStart<end&&end-tmpStart+1>maxLen){
if(s.charAt(tmpStart) == s.charAt(end)){
i = tmpStart;j = end;
while (s.charAt(++i) == s.charAt(--j)&&i<=j);
if(i>j){
String str = s.substring(tmpStart, end+1);
if(str.length() > maxLen){
returnStr = str;
maxLen = str.length();
break;
}
}
}
tmpStart++;
}
end--;
}
return maxLen == -1?s.charAt(0)+"":returnStr;
}
}
官方版本一(动态规划)
public static String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if (len < 2) {
return s;
}
int maxLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i..j] 是否是回文串
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
// 初始化:所有长度为 1 的子串都是回文串
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
// 递推开始
// 先枚举子串长度
for (int L = 2; L <= len; L++) {
// 枚举左边界,左边界的上限设置可以宽松一些
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 由 L 和 i 可以确定右边界,即 j - i + 1 = L 得
int j = L + i - 1;
// 如果右边界越界,就可以退出当前循环
if (j >= len) {
break;
}
if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) {
dp[i][j] = false;
} else {
/**
* 长度为2,3的时候,两端的元素相等,那么就是回环字符串
*/
if (j - i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
/**
* 当两端相等时,回文字符串的结果取决于内层字符串
*/
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
// 只要 dp[i][L] == true 成立,就表示子串 s[i..L] 是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置
if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen);
}
官方版本二(中心扩散算法)
class Solution {
public static String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) {
return "";
}
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 两种边界条件进行扩散
// 单个字母扩散,代表奇数的回文字符串
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
// 两个字母扩散,代表偶数的回文字符串
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if (len > end - start) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
public static int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
--left;
++right;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
}
Z 字形变换
知识点:
题目链接:Z 字形变换
个人版本一(规律推导)
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
String resturnStr = "";
int sLen = s.length();
if(numRows == 1){
return s;
}
// LinkedList[]链表数组,表示每一行的元素和顺序
LinkedList[] linkedLists = new LinkedList[numRows];
for(int i=0 ; i<numRows ; i++){
LinkedList<Character> list = new LinkedList<>();
linkedLists[i] = list;
}
// start和end分别是z中完整一竖的顶端元素和低端元素
int start = 0, end = numRows-1, index;
for(int i=0 ; i<sLen ; i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(i>=start&&i<=end){
index = i-start;
linkedLists[index].add(c);
if(i == end){
/**
*当i==end的时候,表示下一步遍历将会轮到z的斜线上边
*将start变成下一个z的顶端,end变成低端
*这样就可以在非完整一竖上的元素,通过start-i拿到他所在的行
**/
start = start+2*numRows-2;
end = start+numRows-1;
}
}else{
index = start - i;
linkedLists[index].add(c);
}
}
for(int i=0 ; i<numRows ; i++){
Iterator<Character> iterator = linkedLists[i].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// appending using "+" operator
resturnStr = resturnStr + iterator.next();
} }
return resturnStr;
}
}
个人版本二(模拟矩阵)
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
int n = s.length(), r = numRows;
if (r == 1 || r >= n) {
return s;
}
// 2r-2是一个周期内包括的字符串的长度,一个周期是z的其中一横加上斜的那一段
int t = r * 2 - 2;
/**
* r-1是一个周期的列数(字符串是从上到下开始排列的,也就是z的一横和斜的一段占用的列数)
* c是要创建的矩阵的列数
* (n + t - 1) / t保证容纳所有的元素:t-1是加上一个周期数减1,是因为,一个周期是一横加一竖,如果n刚好就是
* 多个完整周期少1的情况,n/t是最终得到的是不足以容纳整个数组的矩阵,所以加上t-1最大程度容纳所有的自付出
*/
int c = (n + t - 1) / t * (r - 1);
char[][] mat = new char[r][c];
for (int i = 0, x = 0, y = 0; i < n; ++i) {
mat[x][y] = s.charAt(i);
if (i % t < r - 1) {
++x; // 向下移动
} else {
--x;
++y; // 向右上移动
}
}
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for (char[] row : mat) {
for (char ch : row) {
if (ch != 0) {
ans.append(ch);
}
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
官方版本一(压缩矩阵空间(个人版本二优化))
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
int n = s.length(), r = numRows;
if (r == 1 || r >= n) {
return s;
}
StringBuffer[] mat = new StringBuffer[r];
for (int i = 0; i < r; ++i) {
mat[i] = new StringBuffer();
}
for (int i = 0, x = 0, t = r * 2 - 2; i < n; ++i) {
mat[x].append(s.charAt(i));
if (i % t < r - 1) {
++x;
} else {
--x;
}
}
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for (StringBuffer row : mat) {
ans.append(row);
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
官方版本二(直接构造)
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
int n = s.length(), r = numRows;
if (r == 1 || r >= n) {
return s;
}
// 一个周期字符串的长度
int t = r * 2 - 2;
/**
* 由于 Z 字形变换的周期为 t=2r-2t=2r−2,因此对于矩阵第一行的非空字符,其对应的idx 均为 t 的倍数,即 idx≡0(mod t);同理,
* 对于矩阵最后一行的非空字符,应满足 idx≡r−1(mod t)。
* 对于矩阵的其余行(行号设为 i),每个周期内有两个字符,第一个字符满足 idx≡i(mod t),第二个字符满足idx≡t−i(mod t)
*/
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) { // 枚举矩阵的行
for (int j = 0; j < n - i; j += t) {
/**
* 当i=0时直接添加第一行所有元素
* 0 < i && i < r - 1:表示除第一行和最后一行
* 除第一行和最后一行时,每行中每个周期只有两个元素:ans.append(s.charAt(j + i))是添加
* z字形中一横的位置。s.charAt(j + t - i):表示添加斜线上另个元素
*/
ans.append(s.charAt(j + i));
if (0 < i && i < r - 1 && j + t - i < n) {
ans.append(s.charAt(j + t - i));
}
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
整数反转
题目链接:整数反转
个人版本一(暴力拆解)
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
double returnInt = 0;
boolean flag = false;
if(x == 0){
return x;
}
if(x<0){
x *= -1;
flag = true;
}
String str = Integer.valueOf(x).toString();
int len = str.length();
int i = len-1;
while (str.charAt(i) == '0'){
len--;
i--;
}
str = str.substring(0, len);
for(i = len-1; i>=0; i--){
String cc = str.charAt(i)+"";
int j = Integer.valueOf(cc);
returnInt = returnInt+j*Math.pow(10, len-1);
len--;
if(returnInt < Integer.MIN_VALUE || returnInt > Integer.MAX_VALUE){
return 0;
}
}
int returnNum = (int) returnInt;
return flag?returnNum*-1:returnNum;
}
}
官方版本一(自动机)
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int rev = 0;
while (x != 0) {
// rev * 10 + digit时,如果rev符合下方条件,经过该表达式就会大于32位整型最大值或者是下雨最小值
if (rev < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || rev > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10) {
return 0;
}
int digit = x % 10;
x /= 10;
rev = rev * 10 + digit;
}
return rev;
}
}
其他版本一
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int res = 0;
while(x!=0) {
//每次取末尾数字
int tmp = x%10;
//判断是否 大于 最大32位整数
if (res>214748364 || (res==214748364 && tmp>7)) {
return 0;
}
//判断是否 小于 最小32位整数
if (res<-214748364 || (res==-214748364 && tmp<-8)) {
return 0;
}
res = res*10 + tmp;
x /= 10;
}
return res;
}
}
字符串转换整数 (atoi)
题目链接:字符串转换整数 (atoi)
个人版本一
class Solution {
public int myAtoi(String s) {
int returnInt = 0;
int isZheng = 1;
// 去除前后空格
s = s.trim();
if(s.length() == 0){
return returnInt;
}
// 正负判断
int index = -1;
char startChar = s.charAt(0);
if(startChar == '-'){
isZheng = -1;
index++;
}else if(startChar == '+'){
isZheng = 1;
index++;
}
// 去除前导0
index++;
while (index < s.length()&&s.charAt(index) == '0'){
index++;
}
while (index < s.length()){
char tmpChar = s.charAt(index);
int tail = 0;
if(isDigit(tmpChar)){
tail = tmpChar-'0';
// 下一步要进行returnInt*10+tail,2^31是2147483648,末尾为8,如果前边都大了,那么接下来不需要继续进行
if (returnInt > 214748364) {
if(isZheng ==1){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}else if(returnInt == 214748364){
if(isZheng == 1 && tail >= 7){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if(isZheng == -1 && tail >= 8){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
returnInt = returnInt*10+tail;
}else{
break;
}
index++;
}
return isZheng*returnInt;
}
public boolean isDigit(char c){
if(c >= '0'&&c <= '9'){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
官方版本一
class Solution {
public int myAtoi(String str) {
Automaton automaton = new Automaton();
int length = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
automaton.get(str.charAt(i));
}
return (int) (automaton.sign * automaton.ans);
}
}
class Automaton {
public int sign = 1;
public long ans = 0;
private String state = "start";
private Map<String, String[]> table = new HashMap<String, String[]>() {{
put("start", new String[]{"start", "signed", "in_number", "end"});
put("signed", new String[]{"end", "end", "in_number", "end"});
put("in_number", new String[]{"end", "end", "in_number", "end"});
put("end", new String[]{"end", "end", "end", "end"});
}};
public void get(char c) {
state = table.get(state)[get_col(c)];
if ("in_number".equals(state)) {
ans = ans * 10 + c - '0';
ans = sign == 1 ? Math.min(ans, (long) Integer.MAX_VALUE) : Math.min(ans, -(long) Integer.MIN_VALUE);
} else if ("signed".equals(state)) {
sign = c == '+' ? 1 : -1;
}
}
private int get_col(char c) {
if (c == ' ') {
return 0;
}
if (c == '+' || c == '-') {
return 1;
}
if (Character.isDigit(c)) {
return 2;
}
return 3;
}
}
回文数
题目链接:回文数
个人版本一
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
boolean isH = false;
if(x < 0) return false;
String s = x + "";
int len = s.length();
int i = -1, j = len;
while (i<j&&s.charAt(++i) == s.charAt(--j));
if(i>=j) isH = true;
return isH;
}
}
官方版本一
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
// 特殊情况:
// 如上所述,当 x < 0 时,x 不是回文数。
// 同样地,如果数字的最后一位是 0,为了使该数字为回文,
// 则其第一位数字也应该是 0
// 只有 0 满足这一属性
if (x < 0 || (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)) {
return false;
}
int revertedNumber = 0;
while (x > revertedNumber) {
revertedNumber = revertedNumber * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
// 当数字长度为奇数时,我们可以通过 revertedNumber/10 去除处于中位的数字。
// 例如,当输入为 12321 时,在 while 循环的末尾我们可以得到 x = 12,revertedNumber = 123,
// 由于处于中位的数字不影响回文(它总是与自己相等),所以我们可以简单地将其去除。
return x == revertedNumber || x == revertedNumber / 10;
}
}
正则表达式匹配
知识点:动态规划
题目链接:正则表达式匹配
官方版本一
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int m = s.length();
int n = p.length();
boolean[][] f = new boolean[m + 1][n + 1];
f[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (p.charAt(j - 1) == '*') {
f[i][j] = f[i][j - 2];
if (matches(s, p, i, j - 1)) {
f[i][j] = f[i][j] || f[i - 1][j];
}
} else {
if (matches(s, p, i, j)) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
public boolean matches(String s, String p, int i, int j) {
if (i == 0) {
return false;
}
if (p.charAt(j - 1) == '.') {
return true;
}
return s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 1);
}
}
其他版本一
class Solution {
public static boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
char[] cp = p.toCharArray();
// dp[i][j]:表示s的前i个字符,p的前j个字符是否能够匹配
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[cs.length + 1][cp.length + 1];
// 初期值
// s为空,p为空,能匹配上
dp[0][0] = true;
// p为空,s不为空,必为false(boolean数组默认值为false,无需处理)
// s为空,p不为空,由于*可以匹配0个字符,所以有可能为true
for (int j = 1; j <= cp.length; j++) {
if (cp[j - 1] == '*') {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2];
}
}
// 填格子
for (int i = 1; i <= cs.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= cp.length; j++) {
// 文本串和模式串末位字符能匹配上
if (cs[i - 1] == cp[j - 1] || cp[j - 1] == '.') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else if (cp[j - 1] == '*') { // 模式串末位是*
// 模式串*的前一个字符能够跟文本串的末位匹配上
if (cs[i - 1] == cp[j - 2] || cp[j - 2] == '.') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] // *匹配0次的情况
|| dp[i - 1][j]; // *匹配1次或多次的情况
} else { // 模式串*的前一个字符不能够跟文本串的末位匹配
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2]; // *只能匹配0次
}
}
}
}
return dp[cs.length][cp.length];
}
}
盛最多水的容器
知识点:贪心算法
题目链接:盛最多水的容器个人版本一
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int result = 0;
if(height.length == 2){
result = Math.min(height[0], height[1]);
return result;
}
int i = 0, j = height.length-1;
while (i < j){
int tmp = (j-i)*Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
if(tmp > result){
result = tmp;
}
if(height[i] > height[j]){
// 右边为短边
tmp = j-1;
while (tmp > i && height[tmp] <= height[j]){
tmp--;
}
j = tmp;
}else if(height[i] < height[j]){
// 左边为短边
tmp = i+1;
while (tmp < j && height[tmp] <= height[i]){
tmp++;
}
i = tmp;
}else{
// 二者相等
int tmpI = i+1, tmpJ = j-1;
if(tmpI < tmpJ){
if(height[tmpI] > height[i]&&height[tmpJ] > height[i]){
i = tmpI;j = tmpJ;
}else if(height[tmpI] > height[i]&&height[tmpJ] <= height[i]){
i = tmpI;
}else if(height[tmpI] <= height[i]&&height[tmpJ] > height[i]){
j = tmpJ;
}else{
// 内部都小于两边
int r1 = maxArea(Arrays.copyOfRange(height, tmpI+1, j+1));
int r2 = maxArea(Arrays.copyOfRange(height, i, tmpJ));
result = r1 > r2? r1 > result?r1:result:r2 > result?r2:result;
break;
}
}else if(tmpI == tmpJ){
tmp = Math.min(height[tmpI], height[i]);
if(tmp > result){
result = tmp;
}
i = tmpI; j = tmpJ;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
官方版本一
public class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
int ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
int area = Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = Math.max(ans, area);
if (height[l] <= height[r]) {
++l;
}
else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
个人版本二
public class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int result = 0;
if(height.length == 2){
result = Math.min(height[0], height[1]);
return result;
}
int i = 0, j = height.length-1;
while (i < j){
int tmp = (j-i)*Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
if(tmp > result){
result = tmp;
}
if(height[i] > height[j]){
// 右边为短边
tmp = j-1;
while (tmp > i && height[tmp] <= height[j]){
tmp--;
}
j = tmp;
}else if(height[i] < height[j]){
// 左边为短边
tmp = i+1;
while (tmp < j && height[tmp] <= height[i]){
tmp++;
}
i = tmp;
}else{
// 二者相等
int tmpI = i+1, tmpJ = j-1;
if(tmpI < tmpJ){
if(height[tmpI] > height[i]&&height[tmpJ] > height[i]){
i = tmpI;j = tmpJ;
}else if(height[tmpI] > height[i]&&height[tmpJ] <= height[i]){
i = tmpI;
}else if(height[tmpI] <= height[i]&&height[tmpJ] > height[i]){
j = tmpJ;
}else{
i = tmpI;
}
}else if(tmpI == tmpJ){
tmp = Math.min(height[tmpI], height[i]);
if(tmp > result){
result = tmp;
}
i = tmpI; j = tmpJ;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
整数转罗马数字
class Solution {
public String intToRoman(int num) {
String roman = "", key, tmpStr;
Map<String, String> table = new HashMap<String, String>(){{
put("1:1", "I");
put("1:2", "II");
put("1:3", "III");
put("1:4", "IV");
put("1:5", "V");
put("1:6", "VI");
put("1:7", "VII");
put("1:8", "VIII");
put("1:9", "IX");
put("2:1", "X");
put("2:4", "XL");
put("2:5", "L");
put("2:9", "XC");
put("3:1", "C");
put("3:4", "CD");
put("3:5", "D");
put("3:9", "CM");
put("4:1", "M");
}};
int flag = 0;
while (num > 0){
int yu = num%10;
num = num/10;
flag++;
if(yu != 0){
if(flag == 1){
key = String.format("%d:%d", flag, yu);
roman = table.get(key) + roman;
}else{
key = String.format("%d:%d", flag, yu);
tmpStr = table.get(key);
if(tmpStr == null){
key = String.format("%d:1", flag, yu);
tmpStr = table.get(key);
// 小于5的
if(yu < 5){
while (yu-- > 0){
roman = tmpStr + roman;
}
}else{
String key2 = String.format("%d:5", flag, yu);
String tmpStr2 = table.get(key2);
yu = yu-5;
while (yu-- > 0){
tmpStr2 = tmpStr2 + tmpStr;
}
roman = tmpStr2 + roman;
}
}else{
roman = tmpStr + roman;
}
}
}
}
return roman;
}
}
官方解法一(模拟)
class Solution {
int[] values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};
String[] symbols = {"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"};
public String intToRoman(int num) {
StringBuffer roman = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; ++i) {
int value = values[i];
String symbol = symbols[i];
while (num >= value) {
num -= value;
roman.append(symbol);
}
if (num == 0) {
break;
}
}
return roman.toString();
}
}
官方解法二
public static String intToRoman(int num) {
// 硬编码表,表示千、百、十、个位上0到9的表现,如下thousands数组中,0表现为“”,而1表现为M
// 题目要求num《=3999,所以thousands只到MMM
String[] thousands = {"", "M", "MM", "MMM"};
String[] hundreds = {"", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"};
String[] tens = {"", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"};
String[] ones = {"", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX"};
StringBuffer roman = new StringBuffer();
// 分割每个位置
roman.append(thousands[num / 1000]);
roman.append(hundreds[num % 1000 / 100]);
roman.append(tens[num % 100 / 10]);
roman.append(ones[num % 10]);
return roman.toString();
}
罗马数字转整数
![]()
题目链接:罗马数字转整数
class Solution {
public int romanToInt(String s) {
int result = 0;
Map<Character, Integer> table = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(){{
put('I', 1);
put('V', 5);
put('X', 10);
put('L', 50);
put('C', 100);
put('D', 500);
put('M', 1000);
}};
int j = s.length()-1, max = 0;
while (j >= 0){
char c = s.charAt(j);
int tmpNum = table.get(c);
if(tmpNum >= max){
max = tmpNum;
result = result+tmpNum;
}else{
result = result-tmpNum;
}
j--;
}
return result;
}
}
其他版本一
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int romanToInt(String s) {
int sum = 0;
int preNum = getValue(s.charAt(0));
for(int i = 1;i < s.length(); i ++) {
int num = getValue(s.charAt(i));
if(preNum < num) {
sum -= preNum;
} else {
sum += preNum;
}
preNum = num;
}
sum += preNum;
return sum;
}
private int getValue(char ch) {
switch(ch) {
case 'I': return 1;
case 'V': return 5;
case 'X': return 10;
case 'L': return 50;
case 'C': return 100;
case 'D': return 500;
case 'M': return 1000;
default: return 0;
}
}
}
最长公共前缀
题目链接:最长公共前缀
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
String resultStr = "";
int i = -1;
boolean flag = true;
char nowChar = ' ';
if(strs.length == 1){
return strs[0];
}
// 查看有无混杂的情况的
for(int j=0 ; j<strs.length ; j++){
if(strs[j].equals("")){
return resultStr;
}
}
while (flag){
i++;
for(int j=0 ; j<strs.length ; j++){
if(i < strs[j].length()){
nowChar = strs[0].charAt(i);
if (strs[j].charAt(i) != nowChar) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}else{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
resultStr = resultStr+nowChar;
}
}
return resultStr;
}
}
官方版本一(横向扫描)
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
String prefix = strs[0];
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
prefix = longestCommonPrefix(prefix, strs[i]);
if (prefix.length() == 0) {
break;
}
}
return prefix;
}
public String longestCommonPrefix(String str1, String str2) {
int length = Math.min(str1.length(), str2.length());
int index = 0;
while (index < length && str1.charAt(index) == str2.charAt(index)) {
index++;
}
return str1.substring(0, index);
}
}
官方版本二(纵向扫描)
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return "";
}
int length = strs[0].length();
int count = strs.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = strs[0].charAt(i);
for (int j = 1; j < count; j++) {
if (i == strs[j].length() || strs[j].charAt(i) != c) {
return strs[0].substring(0, i);
}
}
}
return strs[0];
}
}