SharePoint 2010 Localization with Visual Studio 2010
In this walkthrough, I’ll show you how to create a SharePoint 2010 localized feature using Visual Studio 2010. The basic mechanics of localizing a SharePoint 2010 feature are the same as localizing a SharePoint 2007 feature, and is well documented. If you are unfamiliar with localization in SharePoint, please see Additional Resources at the end of this article. In a nutshell, localized resources are stored in Resources (.resx) files, and in SharePoint exist in one of the following locations:
- \14\Template\Features\<Feature Name>\Resources\
- \14\Resources\
- \14\Config\Resources\
- <Virtual Directory>\App_GlobalResources\ (note: resources files from \14\Config\Resources are copied here when provisioned)
Resources files follow a naming convention that consists of a base name such as “HelloLocalization.resx” and culture-specific resources such as “HelloLocalization.es-ES.resx.” In SharePoint, these files must be in a particular location depending on usage. In this walkthrough, I’ll show you how to create a “centralized” resources files that will be stored in 14\Resources. My preference is to store custom files in as few locations as possible within the SharePoint hive. I have also found that certain resources cannot be accessed from certain locations. So with that in mind, let’s get started:
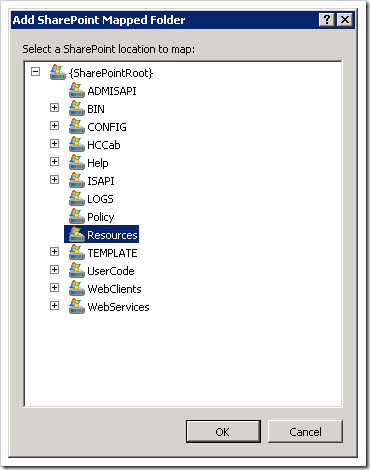
Since we are deploying to 14\Resources, we need to add a mapped folder. Select Add > SharePoint Mapped Folder…
Select the Resources folder:
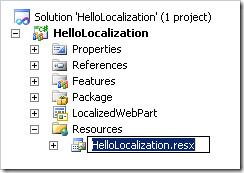
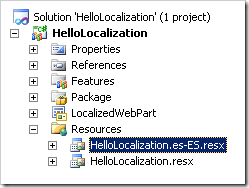
In the solution, delete the subfolder that was created in the Resources folder. Next, right-click on the mapped folder and select Add New Item. In the Search Installed Templates search box, type Resources to select the Resources file template. Rename the resources file to something unique to your feature:
Set the Build Action to Content for the resources file:
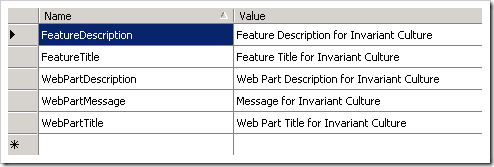
Add your localized strings to the resource file:
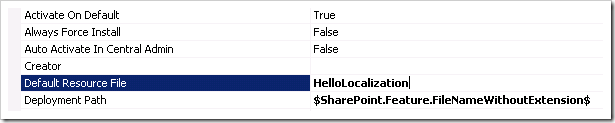
For each feature, set the Default Resource File to the resource file name. This enables you to reference a resource without fully qualifying it:
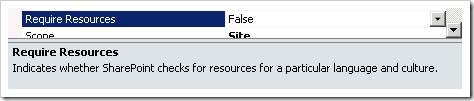
Optional: you can hide a feature when localized resources are not available for it by setting the Require Resources setting to True:
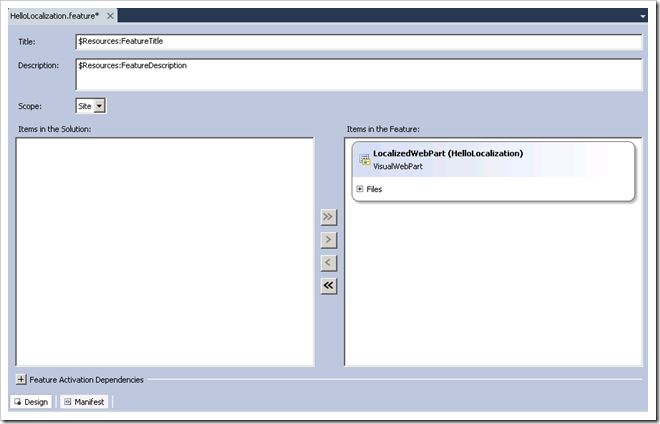
Now you can use the localized strings throughout your feature such as in the feature title and description:
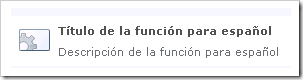
When deployed, the feature appears like this in Site Collection Features:
The resources can also be used in the .webpart file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<webParts>
<webPart xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WebPart/v3">
<metaData>
<type name="HelloLocalization.LocalizedWebPart.LocalizedWebPart, $SharePoint.Project.AssemblyFullName$" />
<importErrorMessage>$Resources:core,ImportErrorMessage;</importErrorMessage>
</metaData>
<data>
<properties>
<property name="Title" type="string">$Resources:HelloLocalization,WebPartTitle</property>
<property name="Description" type="string">$Resources:HelloLocalization,WebPartDescription</property>
</properties>
</data>
</webPart>
</webParts>
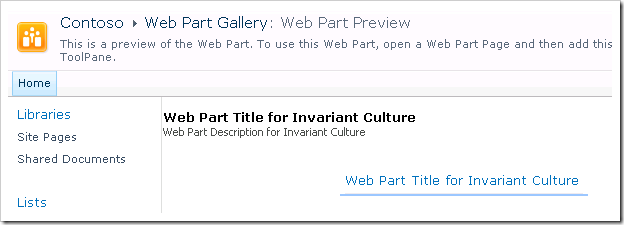
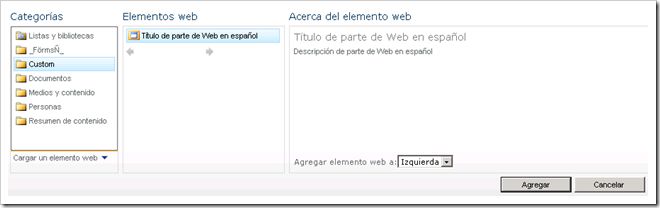
Which appears like this in the Web Part Gallery:
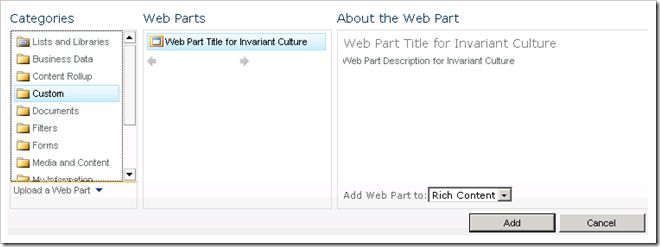
When you add the web part to a page, it appears like this:
The localized resources can also be used in the web part:
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { var lang = SPContext.Current.Web != null ? SPContext.Current.Web.Language : 1033; webPartMessage.Text = SPUtility.GetLocalizedString( "$Resources:WebPartMessage", "HelloLocalization", lang); }
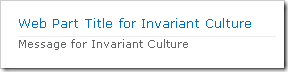
Which appears like this when added to a page:
To support a different culture, copy the resources file, and rename it to [ResourcesFileName].[Culture].resx. For example, to create a Spanish (Spain) resources file:
Make the culture-specific changes to the resources strings:
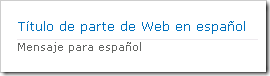
If the language pack is installed on the SharePoint server, and the site has been created using that language, the resources file will be used:
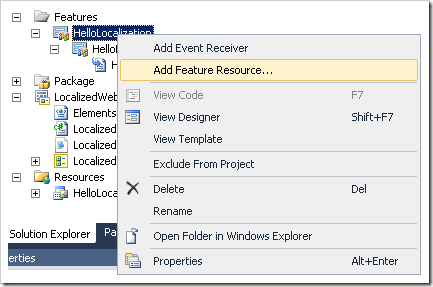
For completeness, you should also be aware of the Visual Studio 2010 Feature Resources feature. When you select Add Feature Resource...:
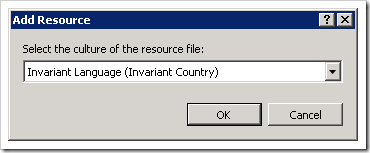
you are prompted for the culture, and the appropriately named resource file is created automatically:
Conclusion
In this walkthrough, I showed you how to localize a SharePoint 2010 feature. Even if you aren’t targeting multiple languages, in my opinion it’s good practice to store resources outside of your compiled code. I hope you found this useful, and your feedback is welcomed!