51单片机入门代码(上篇)
前言
必读
因为一些图片不显示,可以点击以下链接
个人博客文章地址:51单片机入门教程(上篇)(代码+个人理解) – Echo (liveout.cn)
GitHub仓库链接:https://github.com/PGwind/51code
这篇文章是记录我粗略学习51单片机的一些代码,我会加些个人理解以及注释在里面。
因为是囫囵吞枣式学习,所以质量不是很好,后期我会慢慢优化
如果你想要学习单片机,可以观看下面的B站教程并配合本文档学习
本文章使用的51单片机是 普中STC89C52RC
教程
推荐B站视频: 【51单片机入门教程-2020版 程序全程纯手打 从零开始入门】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Mb411e7re/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=55024add0415795a359bd7b29ca21142(应该都知道吧)。
资源
B站江科大资源 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dLED_1VqL66qYItLl5ic4A?pwd=1111 提取码:1111
普中 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dNCHm9lLMP8pe3rZu3ktZQ?pwd=1111 提取码:1111
1. 入门
原理: 单片机核心
cpu通过配置寄存器来控制驱动器,来控制硬件电路
寄存器:连接软硬件的媒介
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oEYash0v-1670833987844)(https://yy.liveout.cn/article/Learn/cmicrocpu/22_12/%E5%8D%95%E7%89%87%E6%9C%BA%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83.png)]
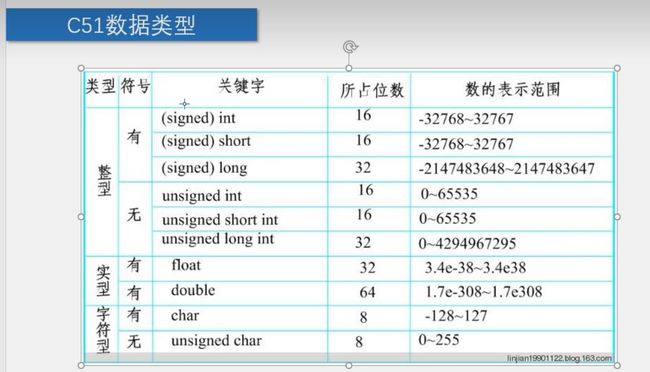
数据类型
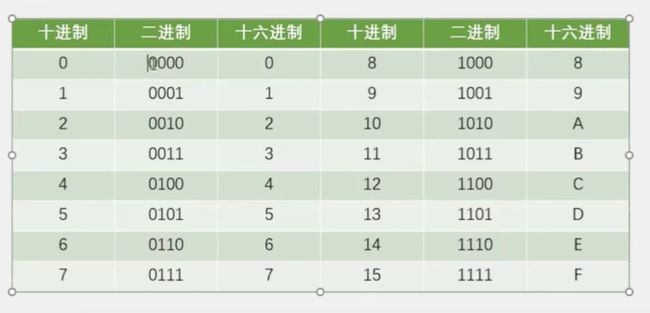
2进制----16进制转换
2. 点灯
原理
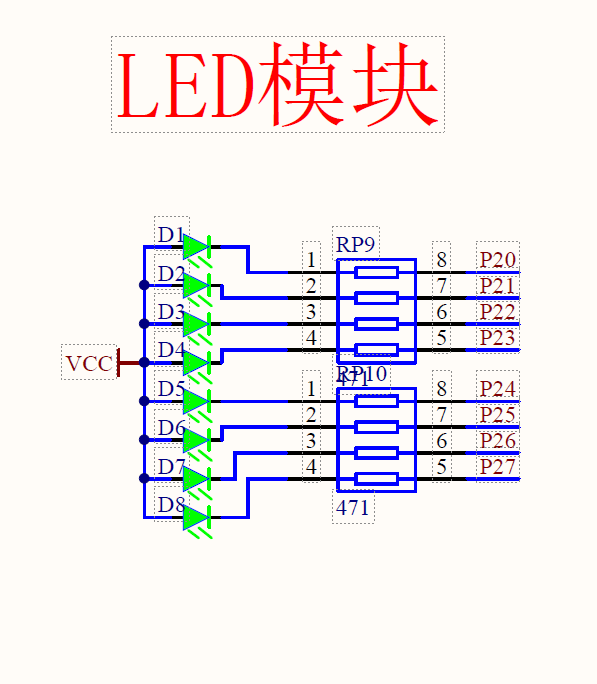
2.1 点亮第一个LED
#include //右键添加头文件
void main()
{ //2进制转16进制,前缀为 0x 87654321 8个灯序号对应进制
// 8个1分别为8个led,0则是负极点亮。最后一个0是D1,第一个是D8
P2 = 0xFE; //1111 1110 点亮第1个led
P2 = 0x7F; //0111 1111 点亮第8个led
P2 = 0x5F; //0101 1111 led 6,8亮
P2 = 0xAA; //1010 1010 led 1,3,5,7亮
P2 = 0x55; //0101 0101 led 2,4,6,8亮
while (1) //程序一直运行
{
}
}
2.2 LED闪烁
#include
#include
void Delay500ms() //@11.0592MHz 500ms延迟函数
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
_nop_(); //去掉nop不用加头文件#include
i = 4;
j = 129;
k = 119;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
P2 = 0xFE;
Delay500ms(); //延迟500ms
P2 = 0xFF;
Delay500ms();
}
}
2.3 LED流水灯
#include
void Delay500ms() //@11.0592MHz 延迟500ms
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
i = 4;
j = 129;
k = 119;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
P2 = 0xFE; //1111 1110
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xFD; //1111 1101
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xFB; //1111 1011
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xF7; //1111 0111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xEF; //1110 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xDF; //1101 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xBF; //1011 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0x7F; //0111 1111
Delay500ms();
}
}
2.4 LED流水灯Plus
#include
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{ //xms 为延迟秒数
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
P2 = 0xFE; //1111 1110
Delay1ms(500); //延迟500ms
P2 = 0xFD; //1111 1101
Delay1ms(100); //100ms
P2 = 0xFB; //1111 1011
Delay1ms(1000); //1000ms
P2 = 0xF7; //1111 0111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xEF; //1110 1111
Delay1ms(200);
P2 = 0xDF; //1101 1111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xBF; //1011 1111
Delay1ms(900);
P2 = 0x7F; //0111 1111
Delay1ms(500);
}
Delay1ms(500);
}
3.独立按键控制LED
原理(高电平、低电平)
电平和电压是有差别的,高电平指的是与低电平相对的高电压,是电工程上的一种说法。
在逻辑电平中,保证逻辑门的输入为高电平时所允许的最小输入高电平,当输入电平高于输入高电压(Vih)时,则认为输入电平为高电平。
在电子和自动化控制中,分为模拟信号和数字信号,在数字逻辑电子电路中,数字信号是二进制的,即只有0信号和1信号。
高电平表示电压高的状态,记为1,一般规定高电平为3.5~5V
低电平表示电压低的状态, 记为0,一般规定低电平为0~0.25V
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-o21HlK7Z-1670833987845)(https://yy.liveout.cn/article/Learn/cmicrocpu/22_12/%E7%8B%AC%E7%AB%8B%E6%8C%89%E9%94%AE%E6%A8%A1%E5%9D%97.png)]
按键松开 高电平 1
按键按下 低电平 0
3.1 独立按键控制LED灯灭
#include
//P2_0就是单片机上面的一个端口,这个端口就是链接右边第一个led灯的
//等于左边七个LED直接不给信号了,只给右边第一个一个亮的信号
void main()
{
//P2 = 0xFE;
P2_0 = 1;
while(1)
{ // 按下亮,松开灭
if(P3_1==0) //P3_1控制第一个按键,即P31
{
P2_0 = 0; //P2_0是第一个LED,0则亮
}
else
{
P2_0=1;
}
if (P3_0==0)
{
P2_1 = 0;
}
else
{
P2_1 = 1;
}
}
}
3.2 独立按键控制LED状态
#include
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{ //按一次亮,再按一次灭
while(1)
{
if(P3_1==0)
{
Delay1ms(20); //按下时消抖
while(P3_1==0); //松开跳出while循环,不松开一直循环,所以灯不会有反应
Delay1ms(20); //松开时消抖
P2_0=~P2_0; //取反,灭变亮,亮变灭
}
}
}
3.3 独立按键控制LED显示二进制
#include
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{
unsigned char LEDNum = 0;
while(1)
{
if(P3_1==0)
{
Delay1ms(20);
while(P3_1==0)
Delay1ms(20);
LEDNum++; //0000 0001
P2 = ~LEDNum; //取反, 1111 1110,第一个LED灯亮
}
}
}
3.4 独立按键控制LED移位
0000 0001 -> 0000 0010 -> 0000 0100 …
0x01<<0 0x01<<1 0x01<<2 …
#include
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main()
{
unsigned char LEDNum = 0;
P2 = ~0x01; //LED初始化,不然第一次led1不亮
while(1)
{
//按键1右移
if(P3_1==0) //按键1按下
{
Delay1ms(20);
while(P3_1==0);
Delay1ms(20);
LEDNum++; //右移
if (LEDNum>=8)
LEDNum=0; //重置
P2=~(0x01< 4.数码管
LED数码管:由多个发光二极管封装在一起组成“8”字型
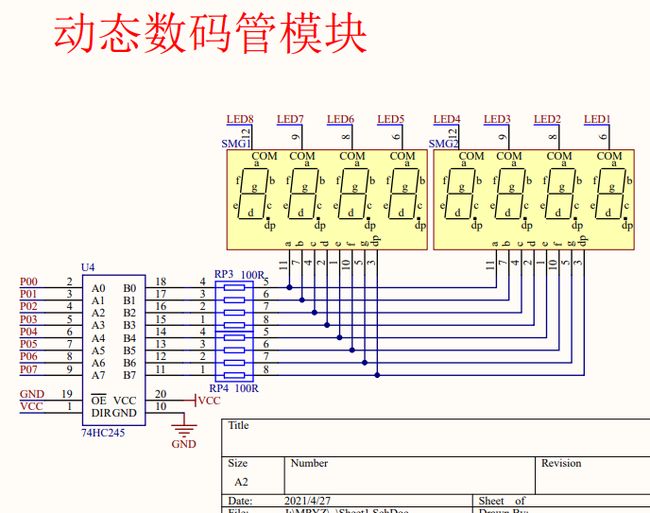
输出扫描:显示第一位->显示第二位->显示第三位…,然后快速循环这个过程,最终实现所有数码管同时显示的效果
原理
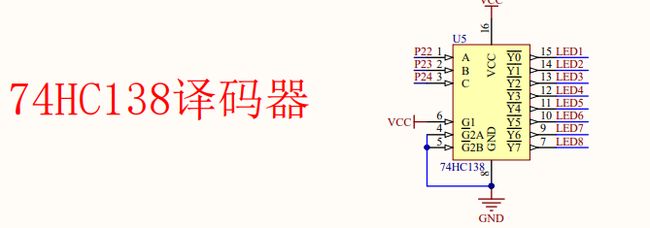
//这里灯的顺序排列我的理解有错误,还没仔细研究。我的单片机111时是Y0,即LED1亮
C(P24) B(P23) A(P22) Y LED 8 -> 1
0(4) 0(2) 0(1) Y7 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 LED8
0 0 1 Y6 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 LED7
1 0 1 Y2 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 LED3
1 1 1 Y0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 LED1
上面是共阴极,公共端为0则亮。如LED7(引脚9)为0,其他为1。即 1011 1111,则LED7亮,其他不亮。
下面是阴码。LED显示7,则b、c为1,其他0。即 0110 0000
4.1 静态数码管显示
点亮一个
#include
void main()
{
//100,即4,LED4亮
P2_4 = 1;
P2_3 = 0;
P2_2 = 0;
//P07->P00 0000 0111 ,即0x07,
//a、b、c为1,即a、b、c亮,显示为7
P0 = 0x07;
while(1)
{
}
}
模块化
#include
//显示数字的段码存储在数组中
//0~9 -> 0~9
unsigned char NixieTable[]={0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,
0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7C,0x39,0x5E,0x79,0x71,0x00};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{ //Location为LED灯序号,Number为显示数字
switch(Location)
{
case 1:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 2:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 3:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 4:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
case 5:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 6:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 7:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 8:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number];
}
void main()
{
Nixie(6,2); //第6个LED显示2
while(1)
{
}
}
4.2 动态数码管显示
个人理解:就像早期电影一样,通过视觉残留动态显示。实际上只能有一个LED灯亮
消影:位选 段选 清零 位选 段选 清零
利用延时来抵消人的视觉暂留现象达到消影
#include
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
unsigned char NixieTable[]={0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,
0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7C,0x39,0x5E,0x79,0x71,0x00};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
switch(Location)
{
case 1:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 2:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 3:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 4:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
case 5:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 6:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 7:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 8:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number]; //段选
Delay1ms(1);
P0=0x00; //清零
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
Nixie(1,1);
//Delay1ms(500); //此延迟用于从第一个led1依次显示数字
Nixie(2,2);
//Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(3,3);
//Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(4,4);
// Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(5,5);
// Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(6,6);
// Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(7,7);
// Delay1ms(500);
Nixie(8,8);
// Delay1ms(500);
}
}
5 .1模块化编程
视频
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Mb411e7re?p=13&vd_source=a1234589a3616351986bc6d13bcbd8f8
代码
头文件
//Delay.h
#ifndef __DELAY_H_
#define __DELAY_H_
void Delay(unsigned int xms) ;
#endif
//Nixie.h
#ifndef __NIXIE_H___
#define __NIXIE_H__
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number);
#endif
函数
//main.c
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "Nixie.h"
void main()
{
while(1)
{
Nixie(1,1);
Nixie(2,2);
Nixie(3,3);
}
}
其他函数
//Delay.c
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
//Nixe.c
#include
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char NixieTable[]={0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,
0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7C,0x39,0x5E,0x79,0x71,0x00};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number)
{
switch(Location)
{
case 1:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 2:P2_4=1;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 3:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 4:P2_4=1;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
case 5:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=1;break;
case 6:P2_4=0;P2_3=1;P2_2=0;break;
case 7:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=1;break;
case 8:P2_4=0;P2_3=0;P2_2=0;break;
}
P0=NixieTable[Number];
Delay(1);
P0=0x00;
}
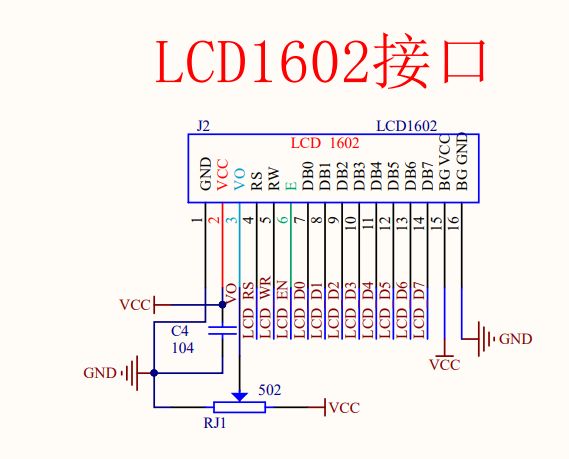
5.2 LCD1602调试工具
LCD与数码管引脚冲突
原理
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2stC76sm-1670833987845)(https://yy.liveout.cn/article/Learn/cmicrocpu/22_12/LCD%E8%B0%83%E8%AF%95.png)]
代码
记得添加之前定义过的函数和头文件
//LCD1602.h 分别为显示各种进制数组以及字符
#ifndef __LCD1602_H__
#define __LCD1602_H__
void LCD_Init();
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char);
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String);
void LCD_ShowNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
#endif
#include
//引脚配置:
sbit LCD_RS=P2^6;
sbit LCD_RW=P2^5;
sbit LCD_EN=P2^7;
#define LCD_DataPort P0
//函数定义:
/**
* @brief LCD1602延时函数,12MHz调用可延时1ms
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Delay()
{
unsigned char i, j;
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写命令
* @param Command 要写入的命令
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteCommand(unsigned char Command)
{
LCD_RS=0;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Command;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写数据
* @param Data 要写入的数据
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteData(unsigned char Data)
{
LCD_RS=1;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Data;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602设置光标位置
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_SetCursor(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column)
{
if(Line==1)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1));
}
else if(Line==2)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1+0x40));
}
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602初始化函数
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Init()
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x38);//八位数据接口,两行显示,5*7点阵
LCD_WriteCommand(0x0c);//显示开,光标关,闪烁关
LCD_WriteCommand(0x06);//数据读写操作后,光标自动加一,画面不动
LCD_WriteCommand(0x01);//光标复位,清屏
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置上显示一个字符
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Char 要显示的字符
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char)
{
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
LCD_WriteData(Char);
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始显示所给字符串
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param String 要显示的字符串
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=0;String[i]!='\0';i++)
{
LCD_WriteData(String[i]);
}
}
/**
* @brief 返回值=X的Y次方
*/
int LCD_Pow(int X,int Y)
{
unsigned char i;
int Result=1;
for(i=0;i0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以有符号十进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:-32768~32767
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~5
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned int Number1;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
if(Number>=0)
{
LCD_WriteData('+');
Number1=Number;
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData('-');
Number1=-Number;
}
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number1/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以十六进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~0xFFFF
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~4
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i,SingleNumber;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
SingleNumber=Number/LCD_Pow(16,i-1)%16;
if(SingleNumber<10)
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber+'0');
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber-10+'A');
}
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以二进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~1111 1111 1111 1111
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(2,i-1)%2+'0');
}
}
//输出固定值
#include
#include "LCD1602.h"
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowChar(1,1,'A');
LCD_ShowString(1,3,"Hello");
LCD_ShowNum(1,9,123,3);
LCD_ShowSignedNum(1,13,-66,2);
LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,0xA8,2);
LCD_ShowBinNum(2,4,0xAA,8);
while(1)
{
}
}
//输出变量值
#include
#include "LCD1602.h"
int Result;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
Result = 1+1;
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Result,3);
while(1)
{
}
}
//输出变量值Plus 从0开始显示秒数
#include
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
int Result=0;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
while(1)
{
Result++;
Delay(1000); //1000ms == 1s
LCD_ShowNum(1,1,Result,3);
}
}
6. 矩阵键盘
输入扫描:读取第一行(列)->读取第二(列)->读取第三行(列)…,然后快速循环这个过程,最终实现所有按键同时检测的效果
原理
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LhsevxtI-1670833987846)(https://yy.liveout.cn/article/Learn/cmicrocpu/22_12/%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5%E6%8C%89%E9%94%AE.png)]
6.1矩阵键盘
记得添加之前定义过的函数和头文件
头文件
//MatrixKey.h
#ifndef __MATRIXKEY_H_
#define __MATRIXKEY_H_
unsigned char MatrixKey();
#endif
函数
//main.c
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"Hello Echo"); //第一行显示字符串
while(1)
{
KeyNum=MatrixKey();
if (KeyNum) //如何没有if,按下一瞬间显示数字,但是松手会重置为0
{
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,KeyNum,2);//第2行显示KeyNum,即按下按键键码值
}
}
}
//MatrixKey.c
#include
#include "Delay.h"
//Function Definition:
/**
* @brief 矩阵键盘读取按键码
* @param 无
* @retval KeyNumber 按下按键的键码值
如果按键按下不放,程序会停留在此函数,松手一瞬间,返回按键键码。没有按键按下时返回0
*/
unsigned char MatrixKey()
{
unsigned char KeyNumber=0;
P1 = 0xFF; //初始化
P1_3=0; //第1列
if(P1_7==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_7==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=1;}//第1行
if(P1_6==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_6==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=5;}//第2行
if(P1_5==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_5==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=9;}//第3行
if(P1_4==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_4==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=13;}//第4行
P1 = 0xFF;
P1_2=0; //第2列
if(P1_7==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_7==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=2;}
if(P1_6==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_6==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=6;}
if(P1_5==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_5==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=10;}
if(P1_4==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_4==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=14;}
P1 = 0xFF;
P1_1=0; //第3列
if(P1_7==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_7==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=3;}
if(P1_6==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_6==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=7;}
if(P1_5==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_5==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=11;}
if(P1_4==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_4==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=15;}
P1 = 0xFF;
P1_0=0; //第4列
if(P1_7==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_7==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=4;}
if(P1_6==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_6==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=8;}
if(P1_5==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_5==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=12;}
if(P1_4==0) {Delay(20);while(P1_4==0);Delay(20);KeyNumber=16;}
return KeyNumber; //返回按下按键键码值
}
6.2 密码锁
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
//unsigned char没有符号位,因此能表示0~255,但是密码肯定不能这么短。
//B站视频教程是unsigned char类型,但是我输入时只能到256,改为int类型就行了
int KeyNum;
int Password,Count;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"PassWord");
while(1)
{
KeyNum=MatrixKey();
if (KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum<=10) //如果S1~S2按键按下,输入密码
{
if(Count<4)
Password*=10; //密码左移一位
Password+=KeyNum%10; //获取一位密码
}
Count++; 。//计次加一
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4); //更新显示
}
if(KeyNum==11) //按下S11按键确认
{
if (Password==2345) //密码正确
{
LCD_ShowString(1,12,"OK"); //显示OK
Password=0; //密码清理
Count=0; //计数清理
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4); //更新显示
}
else
{
LCD_ShowString(1,12,"ERROR");
//Delay(2000); //延时2s,然后空格替代,不然OK后面会显示ROR
Password=0;
Count=0;
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);
//LCD_ShowString(1,12," "); //空格替代
}
}
if (KeyNum==12) //按键S12手动清零
{
Password=0; //密码清零
Count=0; //计次清零
LCD_ShowString(1,12," "); //空格替代
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4); //更新显示
}
}
}
7. 定时器
原理
这章比较难,得多看几遍视频
视频教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Mb411e7re/?p=17&spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=a1234589a3616351986bc6d13bcbd8f8
定时器个数:3个(T0、T1、T2),T0和T1与传统的51单片机兼容,T2是此型号单片机增加的资源
SySclk:系统时钟,即晶振周期,本开发板上的晶振为11.0592MHz
时钟:给0定时器,给1计数器
基础理解代码:实现led1灯每1s闪烁一次
0~65535 每隔1us计数加一 总共定时时间65535us
给初值6435 离计数器65535 差1000us 所以计数时间为1ms
#include
//定时器0初始化
void Timer0_Init() //这个函数可以通过软件直接生成的!!!,但是没有中断,即最后三个
{
//定时器
//TMOD=0x01; //0000 0001 高四位 低四位
TMOD=TMOD&0xF0; //把TMOD的低四位清0,高四位保持不变
TMOD=TMOD|0x01; //把TMOD的最低位 置为1,高四位保持不变
TF0=0; //TF0是进入中断程序后,硬件自动清零
TR0=1; //定时器从0开始计时
//TH0,TL0为二进制8位,单独可计256次 低8位计满256后高8位进1
//设置定时初值
TH0=64535/256; //高8位次数
TL0=64535%256; //低8位次数
//中断
ET0=1;
EA=1;
PT0=0; //设置优先级
}
//主程序
void main()
{
Timer0_Init();
while(1)
{
}
}
//中断服务程序B
unsigned int T0Count;
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
TH0=64535/256;
TL0=64535%256; //重新赋值
T0Count++; //每次加1us,1000次就是1s
if (T0Count>=1000)
{
T0Count=0; //重新赋值
P2_0=~P2_0; //每1s闪烁一次
}
}
7.1 按键控制LED流水灯模式
头文件
//Delay.h
#ifndef __DELAY_H_
#define __DELAY_H_
void Delay(unsigned int xms);
#endif
//Key.h
#ifndef __KEY_H_
#define __KEY_H_
usigned char Key();
#endif
//Timer0.h
#ifndef __TIMER0_H_
#define __TIMER0_H_
void Timer0_Init();
#endif
函数
//Delay.c
//Function Definition
/**
* @brief 延迟函数
* @param 无
* @retval 1ms
*/
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@11.0592MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms)
{
i = 2;
j = 199;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
//Key.c
#include
#include "Delay.h"
//Function Definition
/**
* @brief 获取独立按键键码
* @param 无
* @retval 按下按键的键码,范围0~4,无按键按下的返回值为0
*/
unsigned char Key()
{
unsigned char KeyNum=0;
if(P2_1==0) {Delay(20);while(P2_1==0);Delay(20);KeyNum=1;}
if(P2_0==0) {Delay(20);while(P2_0==0);Delay(20);KeyNum=2;}
if(P2_3==0) {Delay(20);while(P2_3==0);Delay(20);KeyNum=3;}
if(P2_4==0) {Delay(20);while(P2_4==0);Delay(20);KeyNum=4;}
return KeyNum;
}
//Timer0.c
#include
//Function Definition
/**
* @brief 定时器0初始化
* @param 无
* @retval 1ms
*/
void Timer0_Init() //1毫秒@12.000MHz
{
TMOD &= 0xF0; //设置定时器模式
TMOD |= 0x01; //设置定时器模式
TL0 = 0x66; //设置定时初值
TH0 = 0xFC; //设置定时初值
TF0 = 0; //清除TF0标志
TR0 = 1; //定时器0开始计时
ET0=1;
EA=1;
PT0=0;
}
//mian.c (测试) 按键控制灯亮
#include
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Key.h"
unsigned char KeyNum;
void main()
{
Timer0_Init(); //定时器0初始化
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if (KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum==1) P2_0=~P2_0; //按K1,led1亮,再按一次则熄灭
if(KeyNum==2) P2_1=~P2_1;
if(KeyNum==3) P2_2=~P2_2;
if(KeyNum==4) P2_3=~P2_3;
}
}
}
//main.c 流水灯,按下K1改变方向
#include
#include "Timer0.h"
#include "Key.h"
#include "INTRINS.H"
unsigned char KeyNum,LEDMode;
void main()
{
P2=0xFE;
Timer0_Init(); //定时器0初始化
while(1)
{
KeyNum=Key();
if (KeyNum)
{
if(KeyNum==1) //按下K1,改变方向
{
LEDMode++;
if(LEDMode>=2) LEDMode=0;
}
}
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count;
TL0 = 0x18; //重新赋值1us
TH0 = 0xFC;
T0Count++;
if (T0Count>=500) //0.5s
{
T0Count=0;
if(LEDMode==0)
P2=_crol_(P2,1); //向左移位,并且循环
if(LEDMode==1)
P2=_cror_(P2,1); //向右移位,并且循环
}
}
7.2 定时器时钟
头文件之前都定义过了
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Timer0.h"
unsigned char Sec,Min,Hou;
void main()
{
LCD_Init();
Timer0_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"Clock:");
LCD_ShowString(2,1," : :");
while(1)
{
//LCD显示
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Hour,2);
LCD_ShowNum(2,4,Min,2);
LCD_ShowNum(2,7,Sec,2);
}
}
void Timer0_Routine() interrupt 1
{
static unsigned int T0Count;
TL0 = 0x18; //重新赋值1us
TH0 = 0xFC;
T0Count++;
if (T0Count>=1000) //1s
{
T0Count=0;
Sec++; //每秒递增
if(Sec>=60)
{
Sec=0;
Min++;
if(Min>=60)
{
Min=0;
Hour++;
if(Hour>=24)
{
Hour=0;
}
}
}
}
}
8. 串口
串口是一种应用十分广泛的通讯接口,成本低,容易使用,通讯线路简单,可以实现两个设备的互通性。
51单片机内部自带UART(通用异步收发器),可实现单片机的串口通信。串口接口是DB9接口
STC89C52有一个UART,STC89C52URAT有四种工作模式
原理
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-A8nbd6de-1670833987846)(https://yy.liveout.cn/article/Learn/cmicrocpu/22_12/%E4%B8%B2%E5%8F%A3%E5%AF%84%E5%AD%98%E5%99%A8.png)]
数据显示模式
HEX模式/十六进制模式/二进制模式:以原始数据的形式显示
文本模式/字符模式:以原始数据编码后的形式显示
8.1 串口向电脑发送数据
头文件
//UART.h
#ifndef __UART_H_
#define __UART_H_
void UART_Init(); //初始化
void UART_SendByte(unsigned char Byte);//只发送,不接收
#endif
函数
//UART.c
#include
//Function Definition
/**
* @brief 串口初始化 [email protected]
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void UART_Init() //初始化 [email protected]
{
SCON = 0x40; //0100 0000
PCON |= 0x80;
TMOD &= 0x0F; //设置定时器1模式 0000 1111
TMOD |= 0x20; //设置定时器1模式 0010 0000
TL1 = 0xF4; //设定定时初值
TH1 = 0xF4; //设定定时器重装值
ET1 = 0; //禁止定时器1中断
TR1 = 1; //启动定时器1
}
//Function Definition
/**
* @brief 串口发送一个字节数据
* @param Byte 要发送一个字节数字
* @retval 无
*/
void UART_SendByte(unsigned char Byte) //只发送,不接收
{
SBUF = Byte;
while(TI==0); //发送成功跳出循环,TI变为1
TI = 0; //重置为0
}
//串口中断函数模板(用在下一个例子中)
//void UART_Routine() interrupt 4 //串口中断号为4
//{ //RI:接收中断请求标志位
// if(RI==1) //RI=1向主机请求中断响
// {
// RI=0;//应中断后必须用软件复位,即RI=0
// }
//}
//main.c
//每一秒发送一个字节
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "UART.h"
unsigned char Sec;
void main()
{
UART_Init(); //初始化
while(1)
{
UART_SendByte(Sec); //发送 16进制格式
Sec++;
Delay(1000);
}
}
8.2 电脑通过串口控制LED
#include
#include "Delay.h"
#include "UART.h"
void main()
{
UART_Init();
while(1)
{
}
}
void UART_Routine() interrupt 4 //串口中断号为4
{ //RI:接收中断请求标志位
if(RI==1) //RI=1向主机请求中断响
{
P2=~SBUF;
UART_SendByte(SBUF);
RI=0;//应中断后必须用软件复位,即RI=0
}
}