数据结构之链式栈
栈的链式存储结构简称为链栈
链式栈是通过单链表来实现的。每次入栈一个元素,向链表中添加一个节点(相当于头插法),出栈一个元素,释放一个节点。
栈顶应该放在链首还是链尾?
因为栈具有“后进先出”的特点,如果每次在链表的尾部进行插入和删除,就要遍历整个链表来找到尾节点。而在头部进行插入和删除时,只需根据头指针即可找到链表的首元素结点。而无需遍历链表。所以链式栈的出,入栈通过对链表进行头删和头插来实现。单链表中常用的的头结点也就失去了意义,因为通常对于链栈来说,是不需要头结点的。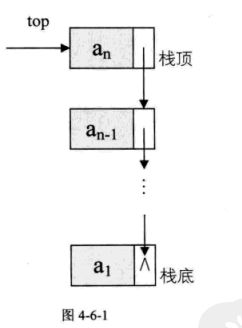
对于链栈来说,基本不存在栈满的情况,除非内存已经没有可以使用的空间。但对于空栈来说,链表原定义是头指针指向空,那么链栈的空其实就是top == NULL.
结构定义:
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}Node,*Pstack;
基本操作
void InitStack(Pstack ps); // 初始化链栈
bool Push(Pstack ps,int val); // 入栈
bool Pop(Pstack ps,int *rtv); // 出栈
bool GetTop(Pstack ps,int *rtv); // 得到栈顶元素
bool IsEmpty(Pstack ps); // 判空
void Destroy(Pstack ps); // 销毁栈
int GetLengthStack(Pstack ps); // 得到栈长
void Show(Pstack ps); // 打印
入栈操作
链式栈的入栈是由单链表的头插来实现的.对于链栈的进栈push操作,假设元素值为e的新节点是s,top为栈顶指针,如下图所示
bool Push(Pstack ps,int val)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
Node *pGet = GetNode(val);
pGet->next = ps->next;
ps->next = pGet;
return true;
}出栈操作
假设变量p用来存储要删除的栈顶节点,将栈顶指针下移一位,最后释放p即可。
bool Pop(Pstack ps,int *rtv)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(ps)) // 判空
{
return false;
}
if (rtv != NULL)
{
*rtv = ps->next->data; // 保存要删除的数据元素
}
Node *p = ps->next;
ps->next = p->next;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return true;
}对于链栈而言,如果再栈的使用过程中元素变化不可预料,有时很小有时有非常大,那么最好使用链栈。
#pragma once
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}Node,*Pstack;
void InitStack(Pstack ps); // 初始化链栈
bool Push(Pstack ps,int val); // 入栈
bool Pop(Pstack ps,int *rtv); // 出栈
bool GetTop(Pstack ps,int *rtv); // 得到栈顶元素
bool IsEmpty(Pstack ps); // 判空
void Destroy(Pstack ps); // 销毁
int GetLengthStack(Pstack ps); //得到栈长度
void Show(Pstack ps); // 打印
#include"LStack.h"
#include
#include
#include
void InitStack(Pstack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
ps->next = NULL;
}
Node *GetNode(int val)
{
Node *pGet = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(pGet != NULL);
pGet->next = NULL;
pGet->data = val;
return pGet;
}
bool Push(Pstack ps,int val)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
Node *pGet = GetNode(val);
pGet->next = ps->next;
ps->next = pGet;
return true;
}
bool Pop(Pstack ps,int *rtv)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(ps))
{
return false;
}
if (rtv != NULL)
{
*rtv = ps->next->data;
}
Node *p = ps->next;
ps->next = p->next;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return true;
}
bool GetTop(Pstack ps,int *rtv)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(ps))
{
return false;
}
if (rtv != NULL)
{
*rtv = ps->next->data;
}
return true;
}
bool IsEmpty(Pstack ps)
{
return ps->next == NULL;
}
void Destroy(Pstack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
Node *p = NULL;
while (ps->next != NULL)
{
p = ps->next;
ps->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
p = NULL;
}
int GetLengthStack(Pstack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
Node *p = ps->next;
int len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
len++;
p = p->next;
}
return len;
}
void Show(Pstack ps)
{
Node *p = ps->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
} 
