C# 多线程一: Thread 的简单理解与运用
目录
一:进程和线程的关系
二:线程的组成
三:多线程的实现
四:C#中的线程(Thread)
1.命名空间
2.构造函数
3.属性
(1).常用属性
Name:
Priority:
IsAlive:
IsBackground:
ThreadState:
(2).其他属性
4.方法
(1).常用方法:
public void Start()
public static void Sleep( int millisecondsTimeout )
public void Abort()
public static void ResetAbort()
public void Join()
public void Interrupt()
(2).其他方法
最后:
一:进程和线程的关系
了解线程之前首先了解下什么是进程
进程:
狭义定义:进程是正在运行的程序的实例。
广义定义:进程是一个具有一定独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合的一次运行活动。它是操作系统动态执行的基本单元,在传统的操作系统中,进程既是基本的分配单元,也是基本的执行单元。
进程的概念主要有两点:
第一,进程是一个实体。每一个进程都有它自己的地址空间,一般情况下,包括文本区域(text region)、数据区域(data region)和堆栈(stack region)。文本区域存储处理器执行的代码;数据区域存储变量和进程执行期间使用的动态分配的内存;堆栈区域存储着活动过程调用的指令和本地变量。
第二,进程是一个“执行中的程序”。程序是一个没有生命的实体,只有处理器赋予程序生命时(操作系统执行之),它才能成为一个活动的实体,我们称其为进程。
线程:
是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
二:线程的组成
线程主要是由cpu寄存器 调用栈 线程本地存储器(TLS) 组成
cpu寄存器:主要记录当前执行线程的状态
调用栈:主要用来维护线程所调用的内存和数据
TLS:用来存放线程的状态信息
三:多线程的实现
在单核处理器的电脑中
多线程的实现是通过cup在完成一个时间切片之后在活动的线程间进行切换执行来完成的,由于cup运行速度快,所以看上去是同一时刻执行了多个操作,实际同一时刻只有一个线程在处理。
在多核的电脑中
多线程被实现成混合时间片和真实的并发——不同的线程在不同的CPU上运行。由于操作系统的需要服务自己的线程,以及一些其他的应用程序。这几乎可以肯定仍然会出现一些时间切片。
四:C#中的线程(Thread)
1.命名空间
System.Threading
2.构造函数
Thread(ParameterizedThreadStart)
初始化 Thread 类的新实例,指定允许对象在线程启动时传递给线程的委托。要执行的方法是有参的。
实例:
static void Main(string[] args) {
object obj = "xxx";
//第一种写法
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Start(obj);
//第二种写法 delegate
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(LudwigThread));
thread1.Start(obj);
//第三种写法 lambda
Thread thread2 = new Thread((arg) => { LudwigThread(arg); });
thread2.Start(obj);
Console.WriteLine("mainThread");
Console.Read();
}
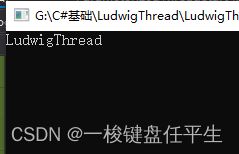
static void LudwigThread(object obj) {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread" + obj);
}注:可传参的写法 注意参数类型必须为object.
打印:
Thread(ParameterizedThreadStart, Int32)
初始化 Thread 类的新实例,指定允许对象在线程启动时传递给线程的委托,并指定线程的最大堆栈大小
实例:
static void Main(string[] args) {
object obj = "xxx";
//第一种写法
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread, 1024);
thread.Start(obj);
//第二种写法 delegate
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(LudwigThread), 1024);
thread1.Start(obj);
//第三种写法 lambda
Thread thread2 = new Thread((arg) => { LudwigThread(arg); }, 1024);
thread2.Start(obj);
Console.WriteLine("mainThread");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread(object obj) {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread" + obj);
}注: 根据.net api的解释 ,尽量不要使用这个重载
.Net API 地址:Thread 构造函数 (System.Threading) | Microsoft Learn
Thread(ThreadStart)
初始化 Thread 类的新实例。要执行的方法是无参的。
实例:
static void Main(string[] args) {
//第一种写法
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Start();
//第二种写法 delegate
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(LudwigThread));
thread1.Start();
//第三种写法 lambda
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => { LudwigThread(); });
thread2.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
}打印:
Thread(ThreadStart, Int32)
初始化 Thread 类的新实例,指定线程的最大堆栈大小。
实例:
static void Main(string[] args) {
//第一种写法
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread, 1024);
thread.Start();
//第二种写法 delegate
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(LudwigThread), 1024);
thread1.Start();
//第三种写法 lambda
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => { LudwigThread(); }, 1024);
thread2.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
}注: 根据.net api的解释 ,尽量不要使用这个重载
.Net API 地址:Thread 构造函数 (System.Threading) | Microsoft Learn
3.属性
(1).常用属性
Name:
获取或设置线程的名称。
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine(thread.Name);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
}打印:
Priority:
获取或设置一个值,该值指示线程的调度优先级。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(KobThread);
thread1.Name = "KobThread";
thread1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest;
thread1.Start();
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("Y");
}
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("X");
}
}
static void KobThread() {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("Z");
}
}打印:
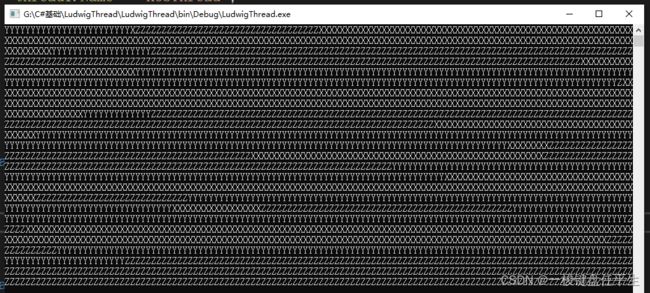 有打印可以看出所谓优先级并不是说优先级高的线程执行结束之后才执行优先级低的
有打印可以看出所谓优先级并不是说优先级高的线程执行结束之后才执行优先级低的
IsAlive:
获取一个值,该值指示当前线程的执行状态。
代码:
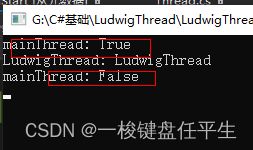
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.IsAlive);
thread.Suspend();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.IsAlive);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
IsBackground:
获取或设置一个值,该值指示某个线程是否为后台线程。
注:须在线程start之前设置
代码:
1.不设置
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
thread.Suspend();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.IsAlive);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
不设置IsBackground 后台线程 我们发现主线程结束后程序无法结束 会等待我们开的线程结束后整个程序才能结束
2.设置
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
thread.Suspend();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.IsAlive);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
一旦主线程结束后整个程序结束 不管后台线程是否完成
ThreadState:
获取一个值,该值包含当前线程的状态。
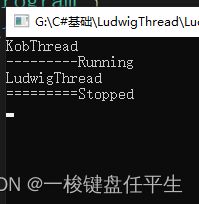
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(KobThread);
thread1.Name = "KobThread";
thread1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest;
thread1.Start();
Console.WriteLine("---------" + thread.ThreadState);
Console.WriteLine("=========" + thread1.ThreadState);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
}
static void KobThread() {
Console.WriteLine("KobThread");
}打印:
(2).其他属性
CurrentContext:
获取线程正在其中执行的当前上下文。
上下文这篇博客有介绍 有兴趣可以看一下
C#综合揭秘——细说进程、应用程序域与上下文之间的关系 - 风尘浪子 - 博客园
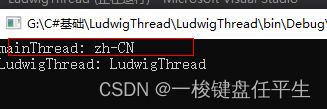
CurrentCulture:
获取或设置当前线程的区域性。
代码:
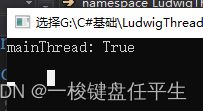
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.CurrentCulture);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
}打印:
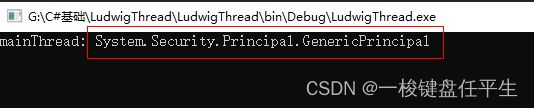
CurrentPrincipal:
获取或设置线程的当前负责人(对基于角色的安全性而言)。
解释:
CurrentPrincipal 是.NET应用程序表示运行该进程的用户或服务帐户的标识的方式.
它可以包含一个或多个标识,并允许应用程序通过该IsInRole方法检查主体是否在角色中.
.NET中的大多数身份验证库都将验证用户的凭据,并将Thread类上的此静态属性设置为新的主体对象.
不同的线程可以有不同的主体,因为它们可能正在处理来自不同用户的请求(在ASP.NET Web应用程序HttpContext.User中
Thread.CurrentPrincipal为每个新请求复制)
拓展:
- 主题 -在安全上下文中, 主题 是请求访问 对象的 任何实体。这些是通用术语,用于表示请求访问的事物和针对其进行请求的事物。当您登录到应用程序时,您就是主题,而应用程序就是对象。当有人敲门时,访客是请求访问的对象,而您的家是请求访问的对象。
- 主体 - 由帐户,角色或其他唯一标识符表示的 主题 子集。当我们达到实现细节的级别时,主体是我们在访问控制列表中使用的唯一键。它们可能代表人类用户,自动化,应用程序,连接等。
- 用户 - 主体的 一个子集,通常是指操作员。区别随着时间的流逝而变得模糊,因为单词“用户”或“用户ID”通常与“帐户”互换。但是,当您需要区分 主体 的大类事物和交互性运营商的子集(以不确定性方式驱动交易)时,“用户”是正确的词。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + Thread.CurrentPrincipal);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
}打印:
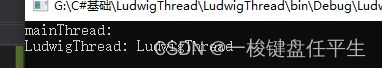
CurrentThread:
获取当前正在运行的线程。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
CurrentUICulture:
获取或设置资源管理器使用的当前区域性以便在运行时查找区域性特定的资源。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.CurrentUICulture);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
ExecutionContext:
获取一个 ExecutionContext 对象,该对象包含有关当前线程的各种上下文的信息。
IsThreadPoolThread:
获取一个值,该值指示线程是否属于托管线程池。
ManagedThreadId:
获取当前托管线程的唯一标识符。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("mainThread: " + thread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread: " + Thread.CurrentThread.Name);
}打印:
4.方法
(1).常用方法:
public void Start()
开始一个线程。
代码:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
}Thread初始化之后 调用Start表示开始执行线程
public static void Sleep( int millisecondsTimeout )
让线程暂停一段时间。
static void Main(string[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
Thread.Sleep(10000);
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread Wait");
}打印:
10s之后
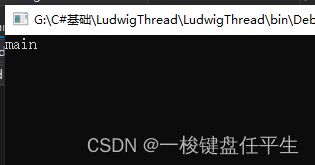
public void Abort()
在调用此方法的线程上引发 ThreadAbortException,以开始终止此线程的过程。调用此方法通常会终止线程。
1.在Start后调用
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
thread.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
Thread.Sleep(10000);
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread Wait");
}打印:
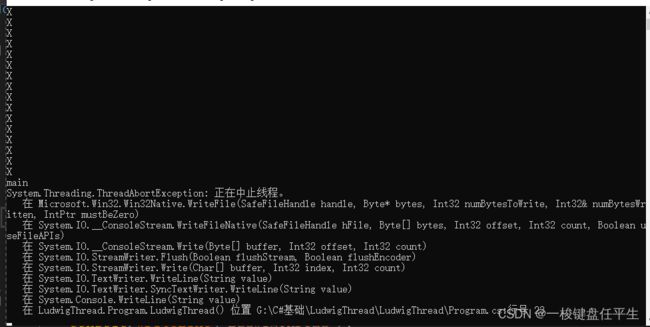
可以看到LudwigThread没有执行直接被中止
2.在线程WaitSleepJoin时调用
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
while(thread.ThreadState == ThreadState.WaitSleepJoin) {
thread.Abort();
}
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
Thread.Sleep(10000);
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread Wait");
}Abort调用 LudwigThread 线程尚未走完被终止
3.在线程挂起时调用
(1).
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
thread.Suspend();
thread.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(true) {
Console.WriteLine("X");
}
}结果:
(2).尝试捕获异常
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
thread.Suspend();
try {
thread.Abort();
} catch(Exception ex) {
//thread.Resume();
}
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(true) {
try {
Console.WriteLine("X");
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
}
}没有调用 Resume 线程被阻塞
(3).
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
thread.Suspend();
try {
thread.Abort();
} catch(Exception ex) {
thread.Resume();
}
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(true) {
try {
Console.WriteLine("X");
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
}
}直到调用 Resume 后,才在挂起的线程中引发 ThreadAbortException。
4.线程中捕获中止
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
//thread.Suspend();
thread.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(true) {
try {
Console.WriteLine("X");
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
}
}打印:
public static void ResetAbort()
取消为当前线程请求的 Abort。
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
thread.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static bool reset = true;
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(reset) {
try {
Console.WriteLine("X");
} catch(Exception ex) {
//Thread.ResetAbort();
reset = false;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("end");
}打印:
我们发现end没有被打印出来
尝试调用ResetAbort()
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(10);
thread.Abort();
Console.WriteLine("main");
Console.Read();
}
static bool reset = true;
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("LudwigThread");
while(reset) {
try {
Console.WriteLine("X");
} catch(Exception ex) {
Thread.ResetAbort();
reset = false;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("end");
}打印 :
end 被执行了
public void Join()
在继续执行标准的 COM 和 SendMessage 消息泵处理期间,阻塞调用线程,直到某个线程终止为止。此方法有不同的重载形式。
首先我们看下没有join的代码
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("Y");
}
Console.Read();
}
static bool reset = true;
static void LudwigThread() {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("X");
}
}打印:
XY无序打印
调用Join
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
thread.Join();
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("Y");
}
Console.Read();
}
static bool reset = true;
static void LudwigThread() {
for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Console.Write("X");
}
}打印 :
Join阻塞了其他线程,只有当前线程结束之后才允许调用其他线程
public void Interrupt()
中断处于 WaitSleepJoin 线程状态的线程。
首先还是先看不使用时的代码
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(100);
//thread.Interrupt();
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("Start");
try {
Thread.Sleep(10000);
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
Console.WriteLine("End");
}打印 :
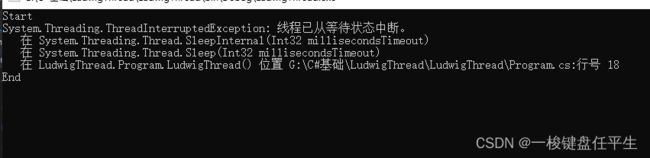
先打印Start 10s之后打印End
然后我们使用Interrupt()
代码:
static Thread thread;
static void Main(string[] args) {
thread = new Thread(LudwigThread);
thread.Name = "LudwigThread";
thread.Start();
Thread.Sleep(100);
thread.Interrupt();
Console.Read();
}
static void LudwigThread() {
Console.WriteLine("Start");
Thread.Sleep(10000);
Console.WriteLine("End");
}打印:
抛出异常并且直接打印出了End
(2).其他方法
public static LocalDataStoreSlot AllocateDataSlot()
在所有的线程上分配未命名的数据槽。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static LocalDataStoreSlot AllocateNamedDataSlot( string name)
在所有线程上分配已命名的数据槽。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static void BeginCriticalRegion()
通知主机执行将要进入一个代码区域,在该代码区域内线程中止或未经处理的异常的影响可能会危害应用程序域中的其他任务。
public static void BeginThreadAffinity()
通知主机托管代码将要执行依赖于当前物理操作系统线程的标识的指令。
public static void EndCriticalRegion()
通知主机执行将要进入一个代码区域,在该代码区域内线程中止或未经处理的异常仅影响当前任务。
public static void EndThreadAffinity()
通知主机托管代码已执行完依赖于当前物理操作系统线程的标识的指令。
public static void FreeNamedDataSlot(string name)
为进程中的所有线程消除名称与槽之间的关联。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static Object GetData( LocalDataStoreSlot slot )
在当前线程的当前域中从当前线程上指定的槽中检索值。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static AppDomain GetDomain()
返回当前线程正在其中运行的当前域。
public static AppDomain GetDomainID()
返回唯一的应用程序域标识符。
public static LocalDataStoreSlot GetNamedDataSlot( string name )
查找已命名的数据槽。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static void MemoryBarrier()
按如下方式同步内存存取:执行当前线程的处理器在对指令重新排序时,不能采用先执行 MemoryBarrier 调用之后的内存存取,再执行 MemoryBarrier 调用之前的内存存取的方式。
public static void SetData( LocalDataStoreSlot slot, Object data )
在当前正在运行的线程上为此线程的当前域在指定槽中设置数据。为了获得更好的性能,请改用以 ThreadStaticAttribute 属性标记的字段。
public static void SpinWait( int iterations )
导致线程等待由 iterations 参数定义的时间量。
public static byte VolatileRead( ref byte address )
public static double VolatileRead( ref double address )
public static int VolatileRead( ref int address )
public static Object VolatileRead( ref Object address )
读取字段值。无论处理器的数目或处理器缓存的状态如何,该值都是由计算机的任何处理器写入的最新值。此方法有不同的重载形式。这里只给出了一些形式。
public static void VolatileWrite( ref byte address, byte value )
public static void VolatileWrite( ref double address, double value )
public static void VolatileWrite( ref int address, int value )
public static void VolatileWrite( ref Object address, Object value )
立即向字段写入一个值,以使该值对计算机中的所有处理器都可见。此方法有不同的重载形式。这里只给出了一些形式。
public static bool Yield()
导致调用线程执行准备好在当前处理器上运行的另一个线程。由操作系统选择要执行的线程。
最后:
有些属性和方法没有添加代码和运行结果 有些引用了一些大佬的博客,想要完全理解Thread的同学一定要耐下性子仔细阅读,有些需要使用不求甚解的同学也要把几个主要的属性和方法看一遍,不管是怎样 一定是先理解了什么是线程 他的工作原理是什么,然后再学习其方法和属性,最后最后一定要自己写一遍几个常用的方法和属性,才能真的记得住。