Binary Insertion Sort-折半插入排序,介绍,伪代码,复杂度计算,在java上的案例应用
目录
- 伪代码
- 复杂度分析(最坏情况)
- 源代码(有详细注释)
- 演示
Binary Insertion Sort是在搜索位置时使用binary search二分查找法的insertion sort插入排序,其最好情况是O(n),最坏情况O(nlogn),属于in-place,空间复杂度O(1),稳定。
直接上本人的小小homework:(本来是英文的,就机翻一下吧)
伪代码
BinaryInsertionSort(A[0,...,n-1])
//Implement insertion sort with binary search which find the position
//Input: An unsorted array A[0...n-1]
//Output:A sorted increasing array A[0...n-1]
//带有二进制搜索的插值插入排序,以找到位置
//输入:一个未排序的数组A[0.n-1]
//输出:排序递增数组A[0.n-1]
for keyIndex←1 to n-1 do
insertIndex←binarySearch(A, keyIndex) //返回的是应该插入的位置
//对插入位置~当前key在的位置进行移位
temp←A[keyIndex]
j←keyIndex
while j>insertIndex do
A[j]←A[j-1]
j←j-1
A[insertIndex]←temp
return A
BinarySearch(A[0...n], keyIndex)
//Find the position to insert the key, indicated by keyIndex of the array, in the sorted part of array, which is index from 0 to keyIndex - 1
//Input:An array A[0...n], the part to the left of key is sorted
an index of key, the key is in A
//Output:An index that indicate the position to insert that key
/在数组的排序部分(从0到键索引-1)中找到插入按数组键索引指示的键的位置
//输入:数组A[0.n],键左边的部分被排序
键的索引,键在A中
//输出:指示插入该键的位置的索引
key←A[keyIndex]
low←0; high←keyIndex - 1
while low<=high do
mid←⌊(low+high)/2⌋
if key复杂度分析(最坏情况)
key comparison: comparison in “if key
if the sorted part is j, which increase along with we sort the array, from 1 to n-1
in binary search, it is a worst case that we have to compare ⌈logj⌉ times every loop
so the number of total times is
关键比较:comparison计数的基准是:if key
如果排序的部分是j,随着我们对数组的排序而增加,从1到n-1
在二进制搜索中,这是一个最坏的情况,我们必须比较每个循环的logj
所以总次数是
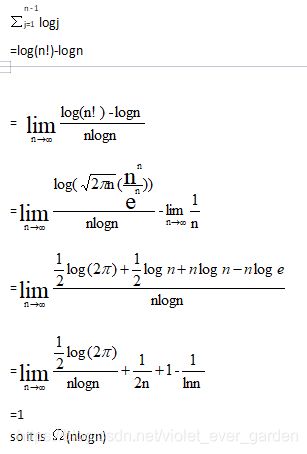
源代码(有详细注释)
Java实现
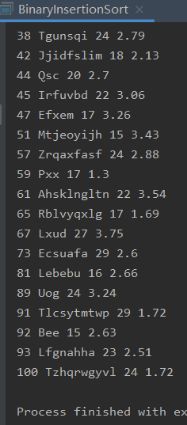
解释:这是对一坨学生的ID name age GPA的记录进行排序
使用generateRandomRecordsTxt可以自动生成一系列随机的数据,可以定义存放,条数,随机ID范围以及是否允许重复ID,其中GPA默认1-4,等等可以在代码直接看出;生成后可以手动注释掉跳过这步。
在排序过程中是建立了一个以对象为元素的数组,然后对比部分使用对象里面的属性,换位置直接交换对象本身。用二维数组也类似·。
代码中包含未演示的对于普通数字序列进行排序的实现。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author YJY
* 2020/11/20,14:50
* 奇怪的程序增加了
*/
public class BinaryInsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
generateRandomRecordsTxt("./record.txt", 30, 1, 100, true);
Student[] stuArr = readTxtFile("./record.txt");
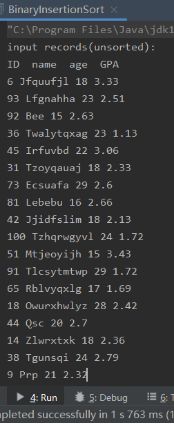
System.out.println("input records(unsorted):");
System.out.println("ID name age GPA");
printStuArr(stuArr);
Student[] sortedStuArr = binaryInsertionSortStudent(stuArr);
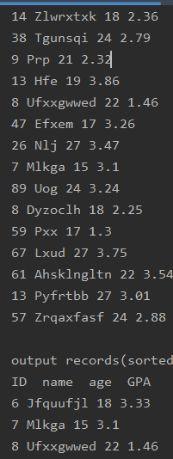
System.out.println("\noutput records(sorted):");
System.out.println("ID name age GPA");
printStuArr(sortedStuArr);
writeRecordsToTxt(sortedStuArr,"./record(sorted).txt");
// basic sort
// int[] A =new int[]{24,67,7,7,80,25,90,69,90,5,36,80,39,66,9,58,36,44,77,41};
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(binaryInsertionSort(A)));
}
//数组写入txt文档
private static void writeRecordsToTxt(Student[] StuArr, String filePath) {
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.print("");
for (int i = 0; i < StuArr.length; i++) {
//in a line: student's ID, name, age, and GPA
ps.append(StuArr[i].id + " " +
StuArr[i].name + " " +
StuArr[i].age + " " +
StuArr[i].GPA);
ps.append("\n");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//打印
public static void printStuArr(Student[] stuArr){
for (int i = 0; i < stuArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(stuArr[i].toString());
}
}
//insertionSort and binarySort are implementation of basic binary insertion sort
//with special Student[], use binaryInsertionSortStudent and binarySearchStudent
//insertionSort() 和 binarySort() 是基本二进制插入排序的实现
//对于本例中数据结构special Student[]实现,是binaryInsertionSortStudent() 和 binarySearchStudent()
//过程与伪代码一致
public static int[] binaryInsertionSort(int[] A) {
for (int keyIndex = 1, len = A.length; keyIndex < len; keyIndex++) {
int insertIndex = binarySearch(A,keyIndex);
int temp = A[keyIndex];
for (int j = keyIndex; j > insertIndex; j--) {
A[j] = A[j-1];
}
A[insertIndex] = temp;
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(A));//test
}
return A;
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] array,int keyIndex){
//find the insert position of key,
// if contains positions with same value of key, return (the rightest position of those in sorted part +1)
int key = array[keyIndex];
int low = 0;
int high = keyIndex - 1;
while(low <= high) {
int mid = (low+high)/2;
// System.out.println(low+" "+mid+" "+high);//test
if (array[mid] > key) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
// System.out.println(low);
return low;
}
//with Student[] case
//对于村有别的信息的结构,比较其中用于比较的那个数,然后插入改变位置时改变这个结构本身,
//比如这里是用数组存的一坨student对象,比较id属性,改变整实例在这坨实例中的位置上
public static Student[] binaryInsertionSortStudent(Student[] A) {
for (int keyIndex = 1, len = A.length; keyIndex < len; keyIndex++) {
int insertIndex = binarySearchStudent(A,keyIndex);
Student temp = A[keyIndex];
for (int j = keyIndex; j > insertIndex; j--) {
A[j] = A[j-1];
}
A[insertIndex] = temp;
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(A));//test
}
return A;
}
public static int binarySearchStudent(Student[] array,int keyIndex){
//find the insert position of key,
// if contains positions with same value of key, return (the rightest position of those in sorted part +1)
int key = array[keyIndex].id;
int low = 0;
int high = keyIndex - 1;
while(low <= high) {
int mid = (low+high)/2;
// System.out.println(low+" "+mid+" "+high);//test
if (array[mid].id > key) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
// System.out.println(low);
return low;
}
//our algorithm can deal with duplicated numbers
//we can also generate records with duplication by setting ifAllowRepeatID true
//random number include idRangeLowBound and idRangeHighBound
//我们的算法可以处理重复的数字
//,我们也可以通过设置如果允许重复ID为真来生成具有重复的记录
//随机数包括id范围低绑定和id范围高绑定
public static void generateRandomRecordsTxt(String filePath, int number, int idRangeLowBound, int idRangeHighBound, boolean ifAllowRepeatID) {
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.print("");
int[] ids = new int[number];//store generated ids and check to make sure no repetition
int id = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
//in a line: student's ID, name, age, and GPA
if(ifAllowRepeatID){
id = (int) (Math.random() * (idRangeHighBound-idRangeLowBound+1)+idRangeLowBound);//round down from [idRangeLowBound,idRangeHighBound+1)
}
//make sure new id not repeated
boolean ifRepeaated = false;
do {
ifRepeaated = false;
id = (int) (Math.random() * (idRangeHighBound-idRangeLowBound+1)+idRangeLowBound);
for (int j = 0; j < i+1; j++) {
if(ids[j]==id){
ifRepeaated = true;
}
}
}while (ifRepeaated);
ps.append(id + " " +
randomName(3, 10) + " " +
(int) (Math.random() * 15 + 15) + " " +
String.format("%.2f", (Math.random() * 3 + 1)) + " ");
ps.append("\n");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String randomName(int min,int max) {
String name;
char[] nameChar;
//min<=length<=max
int nameLength=(int)(Math.random()*(max-min+1))+min;
nameChar=new char[nameLength];
//first letter up
nameChar[0]=(char) (Math.random()*26+65);
for(int i=1;i<nameLength;i++) {
nameChar[i]=(char)(Math.random()*26+97);
}
name=new String(nameChar);
return name;
}
//用于存储的类
private static class Student {
public int id;
public String name;
public int age;
public float GPA;
private Student(int id, String name, int age, float GPA){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.GPA = GPA;
}
public String toString(){
return id+" "+name+" "+age+" "+GPA;
}
}
//读取
public static Student[] readTxtFile(String filePath){
Student[] stuArr = null;//this array stores student objects
try {
String encoding="GBK";
File file=new File(filePath);
if(file.isFile() && file.exists()){
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file),encoding);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read);
//count lines(number of records)
int count = 0;
String lineTxt = null;
//we can slao use arraylist to dynamically read records to array
while((lineTxt = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
if(!lineTxt.trim().equals("")){
String[] strArr = lineTxt.split(" ");
count++;
}
}
//read objects
read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file),encoding);
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read);
stuArr = new Student[count];
count = 0;
while((lineTxt = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
String[] strArr = lineTxt.split(" ");
stuArr[count] = new Student(Integer.parseInt(strArr[0]),strArr[1],Integer.parseInt(strArr[2]),Float.parseFloat(strArr[3]));
count++;
}
read.close();
}else{
System.out.println("no such file");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("wrong in reading");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stuArr;
}
}