详细解读Java中的ArrayList集合类 以及 用Java简单模拟实现顺序表
文章目录
- 模拟顺序表
-
- 1.线性表
- 2.顺序表
- ArrayList 类
-
- 1.ArrayList介绍
- 2.实例化
- 3.ArrayList的方法
- 4.ArrayList的扩容机制
模拟顺序表
1.线性表
啥是线性表?线性表是数据结构里众多结构中的一种,是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储,常见的线性表有:顺序表、链表、栈、队列……
本篇文章就来介绍一下顺序表的内容。
2.顺序表
顺序表: 是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改,这个数组的大小还必须是可以动态变化的。
开始模拟:
(1)顺序表的底层是一个数组,换言之就是用数组来存储数据。还得有一个变量来存数组的有效数据大小,为了看到里面的内容,这里写一个打印方法。
public class MyArrayList {
//加上 private 是为了封装,不能让外面直接访问数组。
private int[] array;//用来装数据
private int usedSize;//用来记录有效数据,因为我们的顺序表的大小是动态变化的。
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;//初始容量
public MyArrayList(){
this.array = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];//初始化
this.usedSize = 0;//此时有效数据为0
}
//打印顺序表
public void print(){
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
(2)我们还需要判断顺序表是否为空或满的方法,方便后面的编码。
//判断顺序表是否满了
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize >= this.array.length;
}
//判断顺序表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
(3)开始编写“增”这一逻辑的代码,插入数据这一板块可以实现两个方法,一个是在末尾插入,一个是在index下标位置插入,必须注意的是要考虑顺序表装满扩容的问题。
//在数组的尾部添加数据
public void add(int data){
if(isFull()){
//扩容:当顺序表满的时候,容量扩大原来的1.5倍。
this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,(int)(this.array.length * 1.5));
}
this.array[usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//在 index 位置插入元素(支持尾插)
public void add(int index,int data) throws IndexWrongException{
if(isFull()){
//扩容:当顺序表满的时候,容量扩大原来的1.5倍。
this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,(int)(this.array.length * 1.5));
}
//要判断 index 是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > this.usedSize) {
//这里也可以自己写一个异常
throw new IndexWrongException("index不合法!");
}
//往后移动元素
for (int i = this.usedSize;i > index;i--) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i - 1];
}
this.array[index] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
在编码过程中可能需要的异常:
//顺序表为空
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException() {
}
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
//index 非法
public class IndexWrongException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexWrongException() {
}
public IndexWrongException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
(4)查找板块:查找某个元素对应的位置、判定是否包含某个元素、获取 pos 位置的元素、获取顺序表的长度。
//返回顺序表的长度
public int size(){
return this.usedSize;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置,如果找到了返回下标,没有找到返回-1
public int indexOf(int data){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.array[i] == data){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//判断是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int data){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.array[i] == data){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//获取 index 位置的元素
public int get(int index) throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= this.usedSize){
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
return this.array[index];
}
(5)删除板块:删除指定位置的元素、删除第一次出现的关键字key、尾删。
//尾删
public void remove() throws EmptyException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
this.usedSize--;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int key) throws EmptyException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
int index = this.indexOf(key);
if(index == -1){
System.out.println("没有找到该数据");
return;
}
//左移动
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i + 1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
//删除指定位置 index 的数据
public void removeIndex(int index)throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= this.usedSize){
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
//左移动
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i + 1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
(6)修改板块:将index下标改为 传入的值。
public void set(int index,int value) throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isFull()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index > this.usedSize || index < 0) {
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
this.array[index] = value;
}
(7)再提供一个清除顺序表所有数据的方法。
//清除顺序表里的所有数据。
public void clear(){
this.usedSize = 0;
}
完整代码:
//顺序表为空
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException() {
}
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
//index 非法
public class IndexWrongException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexWrongException() {
}
public IndexWrongException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList {
//加上 private 是为了封装,不能让外面直接访问数组。
private int[] array;//用来装数据
private int usedSize;//用来记录有效数据,因为我们的顺序表的大小是动态变化的。
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;//初始容量
public MyArrayList(){
this.array = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];//初始化
this.usedSize = 0;
}
//打印顺序表,
public void print(){
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//判断顺序表是否满了
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize >= this.array.length;
}
//判断顺序表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
//在数组的尾部添加数据
public void add(int data){
if(isFull()){
//扩容:当顺序表满的时候,容量扩大原来的1.5倍。
this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,(int)(this.array.length * 1.5));
}
this.array[usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//在 index 位置插入元素(支持尾插)
public void add(int index,int data) throws IndexWrongException{
if(isFull()){
//扩容:当顺序表满的时候,容量扩大原来的1.5倍。
this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array,(int)(this.array.length * 1.5));
}
//要判断 index 是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > this.usedSize) {
//这里也可以自己写一个异常
throw new IndexWrongException("index不合法!");
}
//往后移动元素
for (int i = this.usedSize;i > index;i--) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i - 1];
}
this.array[index] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//返回顺序表的长度
public int size(){
return this.usedSize;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置,如果找到了返回下标,没有找到返回-1
public int indexOf(int data){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.array[i] == data){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//判断是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int data){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.array[i] == data){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//获取 index 位置的元素
public int get(int index) throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= this.usedSize){
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
return this.array[index];
}
//尾删
public void remove() throws EmptyException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
this.usedSize--;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int key) throws EmptyException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
int index = this.indexOf(key);
if(index == -1){
System.out.println("没有找到该数据");
return;
}
//左移动
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i + 1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
//删除指定位置 index 的数据
public void removeIndex(int index)throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= this.usedSize){
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
//左移动
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.array[i] = this.array[i + 1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
//把 index 位置改为value
public void set(int index,int value) throws EmptyException,IndexWrongException{
if(isFull()){
throw new EmptyException("顺序表为空!!!");
}
if(index > this.usedSize || index < 0) {
throw new IndexWrongException("index 非法!!!");
}
this.array[index] = value;
}
//清除顺序表里的所有数据
public void clear(){
this.usedSize = 0;
}
}
ArrayList 类
ArrayList就是一个顺序表,它的底层是一个数组,原理与我们上面模拟的相似,但是源码肯定更复杂的多,我们只需要掌握它的用法就够了。
1.ArrayList介绍
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:
1.ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问,也就是通过下标来访问。
2.ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的。
3.ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的。
4.ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表。
5.实现Iterable接口表示可以用 for-each 来遍历。
2.实例化
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.源码里说初始容量为10,但是在没有add之前容量为0,详细的后文介绍。
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2.构造具有指定初始容量的空列表,这里的容量为100
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(100);
//3.相当于拷贝
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
tmp.add(1);
tmp.add(2);
tmp.add(3);
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(tmp);//直接传入一个ArrayList。
System.out.println(list2);//输出[1, 2, 3]
}
}
3.ArrayList的方法
ArrayList里的方法很多,这里只罗列了常用的,大家自己可以扩展。
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
这里面要注意的是subList这个方法:
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(10);
list.add(11);
list.add(12);
list.add(13);
list.add(14);
System.out.println("list没有被截取的时候:"+list);
//左闭右开[0,3)
List<Integer> tmp = list.subList(0,3);
System.out.println("tmp截取的部分:" + tmp);
//修改 tmp
tmp.set(0,999);
tmp.set(1,999);
tmp.set(2,999);
System.out.println("修改tmp后的list:" + list);
}
}
subList截取的内容没有重新创建一个空间,而是原来的空间,所以修改截取部分tmp时候,原来的list也会跟着被修改。
4.ArrayList的扩容机制
当我们实例化一个 ArrayList 的时候:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
我们看看它的构造方法:
可以看到,这里的elementData数组指向了DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA这个空数组。也就是说,当我们new ArrayList<>()的时候,顺序表的实际容量为0。(elementData数组就是用来装数据的)
什么时候才开始扩容呢?扩多大呢?
当我们放入第一个数据的时候才开始扩容:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(10);
}
}
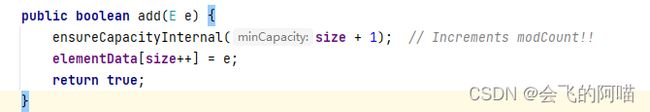
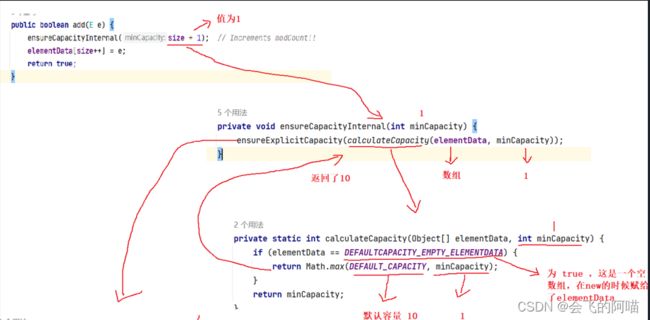
点进add的源码:
很显然ensureCapacityInternal方法是扩容的,当我们第一次调用add的时候,size的值为0,所以传入的值为1。
总结:当我们调用不带参数的构造方法的时候,只有调用第一次add的时候才会分配大小为10的内存。
如果超过10的时候又怎么扩容呢?
上面grow方法中:
当我们调用不带参数的构造方法的时候,只有调用第一次add的时候才会分配大小为10的内存;新增数据时,如果超过容量大小,就按原来的1.5倍扩容。