C#利用接口实现选择不同的语种
目录
一、涉及到的知识点
1.接口定义
2.接口具有的特征
3.接口通过类继承来实现
4.有效使用接口进行组件编程
5.Encoding.GetBytes(String)方法
(1)检查给定字符串中是否包含中文字符
(2)编码和还原前后
6.Encoding.GetString(Byte[])方法
(1)示例
二、实例
1. 源码
2.生成效果
一、涉及到的知识点
1.接口定义
接口是一种用来定义程序的协议,它描述可属于任何类或结构的一组相关行为,可以把它看成是实现一组类的模板。接口可由方法、属性、事件和索引器或这4种成员类型的任何组合构成,但不能包含字段。类和结构可以像类继承基类一样从接口继承,但是可以继承多个接口。当类或结构继承接口时,它继承成员定义但不继承实现。若要实现接口成员,类或结构中的对应成员必须是公共的、非静态的,并且与接口成员具有相同的名称和签名。类或结构的属性和索引器可以为接口中定义的属性或索引器定义额外的访问器。例如,接口可以声明一个带有get访问器的属性,而实现该接口的类可以声明同时带有get和set访问器的同一属性。但是,如果属性或索引器使用显式实现,则访问器必须匹配。
另外,接口也可以继承其他接口,类可以通过其继承的基类或接口多次继承某个接口,在这种情况下,如果将该接口声明为新类的一部分,则类只能实现该接口一次。如果没有将继承的接口声明为新类的一部分,其实现将由声明它的基类提供。基类可以使用虚拟成员实现接口成员。在这种情况下,继承接口的类可通过重写虚拟成员来更改接口行为。
C#中使用interface关键字声明接口,语法格式如下:
修饰符 interface接口名称:继承的接口列表
{
//接口内容;
}
说明:
声明接口时,通常以大写字母“I”开头。
声明接口时,除interface关键字和接口名称外,其他的都是可选项。
可以使用new、public、protected、internal和private等修饰符声明接口,但接口成员必须是公共的。2.接口具有的特征
- 接口类似于抽象基类,继承接口的任何非抽象类型都必须实现接口的所有成员。
- 不能直接实例化接口。
- 接口可以包含事件、索引器、方法和属性。口 接口不包含方法的实现。
- 类和结构可从多个接口继承。
- 接口自身可从多个接口继承。
3.接口通过类继承来实现
一个类虽然只能继承一个基类,但可以继承任意多个接口。声明实现接口的类时,需要在基类列表中包含类所实现的接口的名称。
C#中实现继承的语法格式如下:
class DerivedClass:BaseClass {}
说明:
继承接口时,必须在子类和接口之间用冒号(:)。
另外,如果继承多个接口,那么在继承的每个接口之间用逗号(,)分隔。4.有效使用接口进行组件编程
接口使得服务的协议与实现相分离,它是组件编程的基础,在组件编程中,接口是组件向外公布其功能的唯一方法。
5.Encoding.GetBytes(String)方法
C# 中的 Encoding.GetBytes(String) 方法用于将指定的字符串转换为字节数组。该方法属于 System.Text.Encoding 类,它提供了用于将字符转换为字节以及将字节转换为字符的静态方法。
public static byte[] GetBytes(string str);
参数
str String
包含要编码的字符的字符串。
返回
Byte[]
一个字节数组,包含对指定的字符集进行编码的结果。在本例中,使用该方法把字符串编码为UnicodeEncoding序列。
(1)检查给定字符串中是否包含中文字符
- 在循环中,每次迭代都会检查当前字节的下一个字节(索引 i+1 处的字节)是否不等于 0。因为在 Unicode 编码中,一个中文字符通常由两个字节表示,所以如果下一个字节不等于 0,则表示当前字节表示的是一个中文字符的一部分。
- 如果发现中文字符,将
flag设置为true。否则,将flag保持为false。 - 循环结束后,返回
flag的值,表示是否在字符串中找到了中文字符。
///
/// 检查给定字符串中是否包含中文字符
///
public static bool IsChineseChecked(string str)
{
bool flag = false;
UnicodeEncoding a = new();
byte[] bt = a.GetBytes(str);//在派生类中重写时,将指定字符数组中的所有字符编码为一个字节序列。
for (int i = 0; i < bt.Length; i++)
{
i++;
if (bt[i] != 0)
{
flag = true;
}
else
{
flag = false;
}
}
return flag;
}(2)编码和还原的前后
编码的结果是获得一序列数字表达的字节数组。
还原的结果就是把编码还原到源字符串。
// 使用 Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(String) 方法编码为字节数组
// 使用 Encoding.UTF8.GetString(byte[]) 方法还原为字符串
using System.Text;
namespace _117_1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(args);
string str = "Hello, World!";
byte[] bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str);
Console.WriteLine("Original string: " + str);
Console.WriteLine("Byte array length: " + bytes.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Byte array: " + string.Join(", ", bytes));
// 转换回字符串
string backToString = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes);
Console.WriteLine("Back to string: " + backToString);
Console.WriteLine("********************************");
string str1 = "万里长城";
byte[] bytes1 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str1);
Console.WriteLine("源字符串:" + str1);
Console.WriteLine("Byte array length: " + bytes1.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Byte array: " + string.Join(", ", bytes1));
// 转换回字符串
string backToString1 = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes1);
Console.WriteLine("还原到源字符串:" + backToString1);
}
}
}
//运行结果:
/*
Original string: Hello, World!
Byte array length: 13
Byte array: 72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 44, 32, 87, 111, 114, 108, 100, 33
Back to string: Hello, World!
********************************
源字符串:万里长城
Byte array length: 12
Byte array: 228, 184, 135, 233, 135, 140, 233, 149, 191, 229, 159, 142
还原到源字符串:万里长城
*/6.Encoding.GetString(Byte[])方法
C# 中的Encoding.GetString(byte[])方法用于将字节数组解码为字符串。它属于System.Text.Encoding类,该类提供了用于将字符转换为字节以及将字节转换为字符的静态方法和属性。
public virtual string GetString (byte[] bytes);
参数
bytes Byte[]
包含要解码的字节序列的字节数组。
返回
String
包含指定字节序列解码结果的字符串。(1)示例
// 使用 Encoding.GetString(byte[]) 方法
using System.Text;
namespace _117_2
{
internal class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(args);
// 创建一个 Unicode 编码实例
Encoding unicodeEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
// 定义一个字节数组,包含一些 Unicode 字符的字节表示
byte[] bytes = [0x04, 0x41, 0x04, 0x42, 0x04, 0x43];
// 使用 Unicode 编码将字节数组解码为字符串
string decodedString = unicodeEncoding.GetString(bytes);
// 输出解码后的字符串
Console.WriteLine(decodedString);
}
}
}
//运行结果:
/*
ABC
*/二、实例
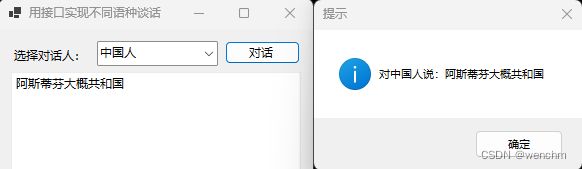
在程序中可以建立一个接口,该接口定义一个方法用于对话,而对话这个方法是在类中实现的。分别创建一个中国人的类和一个美国人的类,这两个类都继承自接口,在中国人的类中说汉语,在美国人的类中说英语,当和不同国家的人交流时,实例化接口,并调用相应类中的方法即可。
1. 源码
//
using System.Text;
namespace _117
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Label? label1;
private Button? button1;
private ComboBox? comboBox1;
private TextBox? textBox1;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
Load += Form1_Load;
}
private void Form1_Load(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
//
// label1
//
label1 = new Label
{
AutoSize = true,
Location = new Point(12, 18),
Name = "label1",
Size = new Size(80, 17),
TabIndex = 0,
Text = "选择对话人:"
};
//
// button1
//
button1 = new Button
{
Location = new Point(226, 12),
Name = "button1",
Size = new Size(75, 23),
TabIndex = 2,
Text = "对话",
UseVisualStyleBackColor = true
};
button1.Click += Button1_Click;
//
// comboBox1
//
comboBox1 = new ComboBox
{
FormattingEnabled = true,
Location = new Point(98, 12),
Name = "comboBox1",
Size = new Size(121, 25),
TabIndex = 3,
//SelectedIndex = 0
};
comboBox1.Items.AddRange([
"中国人",
"美国狗"]);
//
// textBox1
//
textBox1 = new TextBox
{
Location = new Point(12, 43),
Multiline = true,
Name = "textBox1",
Size = new Size(290, 161),
TabIndex = 4
};
//
// Form1
//
AutoScaleDimensions = new SizeF(7F, 17F);
AutoScaleMode = AutoScaleMode.Font;
ClientSize = new Size(314, 216);
Controls.Add(textBox1);
Controls.Add(comboBox1);
Controls.Add(button1);
Controls.Add(label1);
Name = "Form1";
Text = "用接口实现不同语种谈话";
}
///
/// 按钮事件
/// 选择通话对象的语种,并输入该语种的通话内容
///
private void Button1_Click(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1!.Text == "")
{
MessageBox.Show("不想说点什么吗?", "警告", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return;
}
else
{
if (comboBox1!.SelectedIndex == 0)//与中国人对话
{
if (IsChineseChecked(textBox1.Text))
{
ISelectLanguage Interface1 = new C_SpeakChinese();
Interface1.Speak(textBox1.Text);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("和中国人说汉语 ", "警告", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return;
}
}
else//与美国人对话
{
if (IsChineseChecked(textBox1.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("和米国狗说英语! ", "警告", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
return;
}
else
{
ISelectLanguage Interface1 = new C_SpeakEnglish();
Interface1.Speak(textBox1.Text);
}
}
}
}
///
/// 声明一个接口,用于定义Seak方法,而具体Speak方法功能的实现是在类中进行的
///
interface ISelectLanguage
{
void Speak(string str);
}
///
/// 如果跟中国人对话,则说汉语
///
class C_SpeakChinese : ISelectLanguage
{
public void Speak(string str)
{
MessageBox.Show("对中国人说:" + str, "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
///
/// 如果跟美国人对话,则说英语
///
class C_SpeakEnglish : ISelectLanguage
{
public void Speak(string str)
{
MessageBox.Show("对美国狗说:" + str, "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
public static bool IsChineseChecked(string str)
{
bool flag = false;
UnicodeEncoding a = new();
byte[] bt = a.GetBytes(str);//在派生类中重写时,将指定字符数组中的所有字符编码为一个字节序列。
for (int i = 0; i < bt.Length; i++)
{
i++;
if (bt[i] != 0)
{
flag = true;
}
else
{
flag = false;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
}