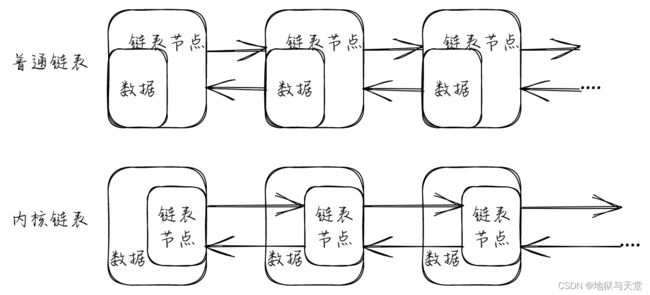
内核链表list_head
内核链表
普通链表与内核链表的区别
普通链表:把数据结构放入链表
struct list_element {
void *data;
struct list_element *next;
struct list_element *prev;
}
内核链表:把链表放入数据结构
struct fox {
unsigned long tail_length;
unsigned long weight;
struct list_head list;
}
list_head
简介
内核中已经实现了链表的结构体,直接拿来用即可。
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next,*prev;
}
使用例程:
struct fox {
unsigned long tail_length;
unsigned long weight;
struct list_head list_node;
}
如何找到父结构呢
因为一个给定的结构,在编译的时候,其大小和内部成员的便宜地址就被确定下来了,所以,通过计算偏移量即可获得父结构体的地址。
链表头
链表头:
创建一个链表后,需要一个头节点来索引这个链表,这个头节点一般不存储数据(链表的遍历方法中,是没有获取head的这个结构体的,不会取出head,所以也无法取出这个数据,所以一般不在这个head的节点这存储数据。),只用来索引其他的数据。
示意图:
创建链表头有两个方法,两个方法是一样的:
-
LIST_HEAD(); -
struct list_head head; LIST_HEAD_INIT(head);
他们的宏定义如下:
INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list->prev = list;
}
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
提示
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }这个的作用是将list_head的next、prev都指向自己。
例如:
struct fox red_fox {
.tail_length = 40,
.weight = 6,
.list = LIST_HEAD_INIT(red_fox.list),
}
//宏展开后就变成了
struct fox red_fox {
.tail_length = 40,
.weight = 6,
.list = {&red_fox.list,red_fox.list},
}
list_head相关的操作方法
list_add
给链表增加一个节点
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, \
struct list_head *head);
list_del
删除一个节点
void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
提示
这个函数只将entry元素从链表中移除,但并不释放这个元素所占用的内存空间。通常还需要用其他函数(例如:kfree(const void *objp))删除这个结构体。
list_del删除原理
源码:
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del_entry(entry);//从链表中中移除
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
//将删除的entry的list_head指向内核内存之外的地方,只要使用就会报错。
}
在使用了list_del后,被删除的entry指向的地址在内核内存地址之外,所以要么释放掉内存,要么使用list_del_init。
list_del_init
list_del和list_del_init的区别就是被删除的entry会被重新指向自己就相当于自己成为了链表头
list_del和list_del_init的区别图示:
list_empty
检查链表是否为空,为空则返回1(真),不为空则返回0(假)。
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
list_for_each_entry
遍历所有的节点
list_for_each_entry(struct list_head *pos, \
struct list_head *head, \
<member.list_head's name>)
-
pos:list_head结构体,需要新建一个,以作为遍历的成员。 -
head:链表头 -
提示
如果链表头的list_head的父结构体也有数据,那这个数据是无法遍历出来的,具体看完整例程,这里可以看到
list_entry
通过list_head成员获取父结构体(通过链表节点获取数据)
struct <struct_type> *list_entry(struct list_head *pos, \
struct <struct_type>, \
<member.list_head's name>)
示例:
//前面省略,详细代码可以查看完整例程
struct fox *fp;
printk("get letter_head data\n");
fp = list_entry(&fox_let_head.list_node,struct fox,list_node);
printk("fox id: %s\n",fp->fox_name);
printk("get letter_head data done\n");
printk("\n");
//结果
/*
[ 92.619530] get letter_head data
[ 92.619540] fox id: let_head
[ 92.619550] get letter_head data done
[ 92.619562]
*/
list_splice
将两个链表拼接起来
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
-
*list是要被放到后面的链表,这个链表的链表头会被丢弃 -
*head这个链表是主链表,最后拼接的链表的链表头就是这个
例子:
//前面省略,详细代码可以查看完整例程
//遍历letter链表
printk("all letter_fox:\n");
list_for_each_entry(fp,&fox_let_head.list_node,list_node){
printk("fox id: %s\n",fp->fox_name);
}
printk("\n");
//遍历number链表
printk("all num_fox:\n");
list_for_each_entry(fp,&fox_num_head.list_node,list_node){
printk("fox id: %s\n",fp->fox_name);
}
printk("\n");
//链表拼接
printk("splice number_fox_list to letter_fox_list \n");
list_splice_init(&fox_num_head.list_node,&fox_let_head.list_node);
printk("splice number_fox_list to letter_fox_list done\n");
printk("\n");
//检查拼接结果,letter_fox链表的状态
printk("all letter_fox:\n");
list_for_each_entry(fp,&fox_let_head.list_node,list_node){
printk("fox id: %s\n",fp->fox_name);
}
printk("\n");
//检查number_fox链表的状态
printk("all num_fox:\n");
list_for_each_entry(fp,&fox_num_head.list_node,list_node){
printk("fox id: %s\n",fp->fox_name);
}
printk("\n");
retun 0;
}
//结果
/*
[ 36.954121] all letter_fox:
[ 36.954131] fox id: b
[ 36.954141] fox id: c
[ 36.954152] fox id: a
[ 36.954160]
[ 36.954168] all num_fox:
[ 36.954176] fox id: 3
[ 36.954184] fox id: 2
[ 36.954192] fox id: 1
[ 36.954199]
[ 36.954208] splice number_fox_list to letter_fox_list
[ 36.954218] splice number_fox_list to letter_fox_list done
[ 36.954228]
[ 36.954238] all letter_fox:
[ 36.954249] fox id: 3
[ 36.954257] fox id: 2
[ 36.954267] fox id: 1
[ 36.954276] fox id: b
[ 36.954287] fox id: c
[ 36.954295] fox id: a
[ 36.954305]
[ 36.954315] all num_fox:
[ 36.954325] fox id: 3
[ 36.954334] fox id: 2
[ 36.954344] fox id: 1
[ 36.954353] fox id: b
[ 36.954364] fox id: c
[ 36.954373] fox id: a
[ 36.954380] fox id: let_head
[ 36.954389] fox id: 3
[ 36.954400] fox id: 2
[ 36.954410] fox id: 1
[ 36.954420] fox id: b
[ 36.954430] fox id: c
[ 36.954439] fox id: a
[ 36.954449] fox id: let_head
[ 36.954459] fox id: 3
[ 36.954468] fox id: 2
[ 36.954479] fox id: 1
[ 36.954488] fox id: b
[ 36.954499] fox id: c
[ 36.954508] fox id: a
[ 36.954518] fox id: let_head
......无限循环
*/
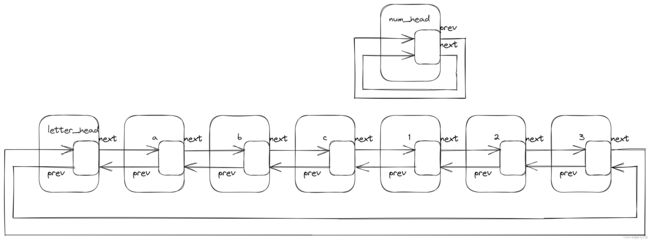
为什么会产生无线循环?
拼接后链表的示意图:
根据list_for_each_entry原理可知,当遍历num_list时,无法返回num_head,所以会一直循环遍历。解决这个问题,看list_splice_init
list_splice_init
将两个链表拼接起来,并且初始化*list的链表头。
功能和list_splice一样,增加了初始化*list链表头的功能。
static inline void list_splice_init(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
对比list_splice例程的示意图:
list_for_each_entry_safe
如果想在使用list_for_each_entry遍历的时候删除该项时,会因为把next的指针也删除掉而找不到下一个节点。所以,linux内核提供list_for_each_entry_safe,这个函数的作用是,把当前遍历项的next或者prev指针保存在一个临时的变量当中,当要删除该项的时候,就不会出现找不到下一个(或者上一个)的情况。
list_for_each_entry_safe(){
list_del();
}
为什么不删除遍历当前项的上一项呢?
如果删除遍历的上一项,当删除第一项的时候,会将链表头也删除,到遍历到最后一项的时候,因为回不到链表头了,就会报错。
提示
这个函数仍然需要加锁!这个函数只能保证在函数内部进行删除不会出问题,如果在其他地方有并发删除,这仍然会出问题。
完整例程
#include