【转】MongoDB 中“$“操作符表达式汇总
转自:
https://www.cnblogs.com/fengting0913/p/14616629.html
比较操作
$eq
释义: 匹配等于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age = 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$eq: 20
}
})
$gt
释义: 匹配大于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age > 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$gt: 20
}
})
$gte
释义: 匹配大于等于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age >= 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$gte: 20
}
})
$lt
释义: 匹配小于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age < 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$lt: 20
}
})
$lte
释义: 匹配小于等于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age <= 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$lte: 20
}
})
$ne
释义: 匹配不等于指定值的文档
示例: 查询 age != 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$ne: 20
}
})
$in
释义: 匹配数组中的任一值
示例: 查询该集合中字段 qty 的值与数组中的任意值相等的文档
db.inventory.find({
qty: {
$in: [ 5, 15 ]
}
})
$nin
释义: 不匹配数组中的值
逻辑操作
$or
释义: 或条件查询
示例: 查询 age < 20 或者 address = "beijing"的文档
db.person.find({
$or: [
{
age: {
$lt: 20
}
},
{
address: "beijing"
}
]
})
$and
释义: 与条件查询
$not
释义: 查询与表达式不匹配的文档
示例: 查询 age 不大于 20 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$not: {
$gt: 20
}
}
})
$nor
释义: 查询与任一表达式都不匹配的文档
示例: 查询 age 既不等于 20, sex 也不是"男"的文档
db.person.find({
$nor: [
{
age: 20
},
{
sex: "男"
}
]
})
集合字段操作 —— “存在”、“类型”
$exists
释义: 查询存在指定字段的文档
示例: 查询存在 phone 字段的文档
db.person.find({
phone: {
$exists: true
}
})
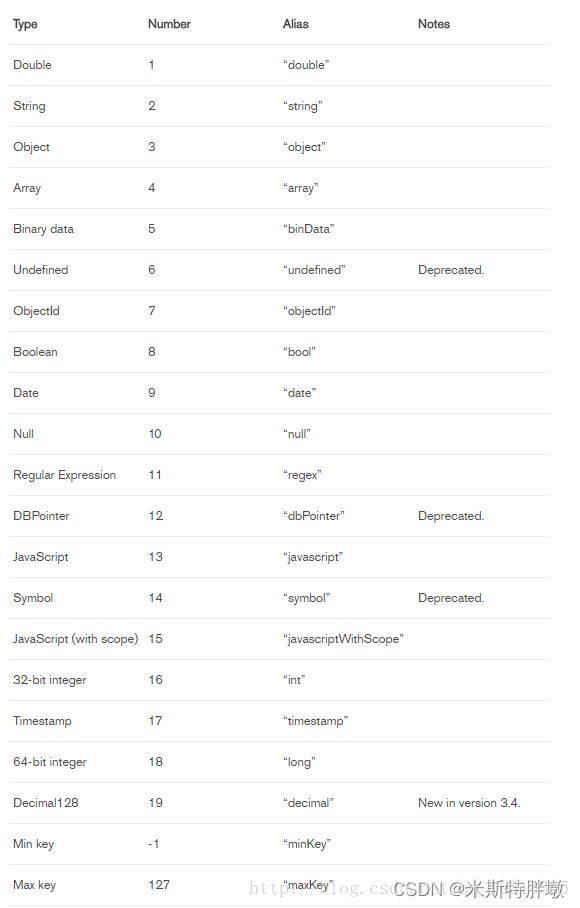
$type
释义: 查询类型为指定类型的文档(v3.2 版本添加了 alias 别名, 各种类型的 Number 及 Alias 见文末所示)
示例: 假设存在如下集合, 查询该集合中 zipCode 字段的数据类型为 String 类型的文档
{ "_id": 1, address: "2030 Martian Way", zipCode: "90698345" },
{ "_id": 2, address: "156 Lunar Place", zipCode: 43339374 },
{ "_id": 3, address: "2324 Pluto Place", zipCode: NumberLong(3921412) },
{ "_id": 4, address: "55 Saturn Ring", zipCode: NumberInt(88602117) }
db.addressBook.find({
"zipCode" : {
$type : 2
}
})
db.addressBook.find({
"zipCode" : {
$type : "string"
}
})
运算操作
$mod
释义: 取余条件查询
示例: 查询 age 字段的值除以 2 余 0 的文档
db.person.find({
age: {
$mod: [ 2, 0 ]
}
})
$regex
语法:
{ key: { $regex: /pattern/, $options: '' } }
{ key: { $regex: 'pattern', $options: '' } }
{ key: { $regex: /pattern/ } }
释义: 正则表达式查询
示例:
db.products.find({
sku: {
$regex: /^ABC/i
}
})
$text
语法:
{
$text: {
# 关键词
$search: <string>,
# 语言, 不支持中文
# https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/text-search-languages/#text-search-languages
$language: <string>,
# 是否区分大小写, 默认false
$caseSensitive: <boolean>,
# 是否区分读音, 默认false
$diacriticSensitive: <boolean>
}
}
释义: 文本索引查询
示例: 较为复杂, 请参考官网
$where
释义: 把一个含有 JavaScript 表达式的字符串或者是整个 JavaScript 函数转换到查询系统中, 对内嵌文档不起作用
示例:
db.myCollection.find({
$where: "this.credits == this.debits"
})
db.myCollection.find({
$where: function() {
return obj.credits == obj.debits
}
})
数组操作
$all
释义: 匹配文档的数组字段中包含所有指定元素的文档
示例: 查询 articles 集合中 tags 数组字段中包含"ssl"和"security"的文档(包含, 但并不是全部等于)
db.articles.find({
tags: {
$all: [
[ "ssl", "security" ]
]
}
})
$elemMatch
释义: 匹配内嵌文档或数组中的部分 field
示例: 假设有如下集合, 查询 results 数组中含有区间 [80, 85) 元素的文档(结果为第一条)
{ _id: 1, results: [ 82, 85, 88 ] }
{ _id: 2, results: [ 75, 88, 89 ] }
db.scores.find({
results: {
$elemMatch: {
$gte: 80,
$lt: 85
}
}
})
$size
释义: 匹配数组长度为指定大小的文档
示例: 查询已经集齐了 5 张福卡的文档
db.person.find({
card: {
$size: 5
}
})
查询相似 document 操作
$(projection)
释义:查询数组中首个匹配条件的元素
示例: 假设有如下集合 students, 查询 semester = 1, 并且 grades 符合大于等于 85 的 document 中 "grades" 中字段的第一个元素
{ "_id" : 1, "semester" : 1, "grades" : [ 70, 87, 90 ] }
{ "_id" : 2, "semester" : 1, "grades" : [ 90, 88, 92 ] }
{ "_id" : 3, "semester" : 1, "grades" : [ 85, 100, 90 ] }
{ "_id" : 4, "semester" : 2, "grades" : [ 79, 85, 80 ] }
{ "_id" : 5, "semester" : 2, "grades" : [ 88, 88, 92 ] }
{ "_id" : 6, "semester" : 2, "grades" : [ 95, 90, 96 ] }
db.students.find({
semester: 1,
grades: {
$gte: 85
}
}, {
"grades.$": 1
})
返回如下结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "grades" : [ 87 ] }, { "_id" : 2, "grades" : [ 90 ] }, { "_id" : 3, "grades" : [ 85 ] }
$elemMatch(projection)
释义: 用于数组或内嵌文档中的元素匹配(子元素匹配), 只会返回匹配的第一个元素
示例: 假设有如下集合, 查询 zipcode 为 63109 并且 students 数组中 school = 102 的文档
{
_id: 1,
zipcode: "63109",
students: [
{ name: "john", school: 102, age: 10 },
{ name: "jess", school: 102, age: 11 },
{ name: "jeff", school: 108, age: 15 }
]
}
{
_id: 2,
zipcode: "63110",
students: [
{ name: "ajax", school: 100, age: 7 },
{ name: "achilles", school: 100, age: 8 },
]
}
{
_id: 3,
zipcode: "63109",
students: [
{ name: "ajax", school: 100, age: 7 },
{ name: "achilles", school: 100, age: 8 },
]
}
db.schools.find({
zipcode: "63109"
}, {
students: {
$elemMatch: {
school: 102
}
}
})
返回如下结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "students" : [ { "name" : "john", "school" : 102, "age" : 10 } ] }, { "_id" : 3 }
$slice(projection)
释义: 在查询中将数组进行切片(类似于分页)
示例:
1. 查询结果中, 对于 comments 数组的元素只显示前5个
db.posts.find({}, {
comments: {
$slice: 5
}
})
2. 查询结果中, 对于 comments 数组的元素只显示后 5 个
db.posts.find({}, {
comments: {
$slice: -5
}
})
3. 查询结果中, 对于 comments 数组的元素跳过(skip)前 20 个, 并只显示(limit) 10 个元素(即 21 - 30)
db.posts.find({}, {
comments: {
$slice: [ 20, 10 ]
}
})
4. 同理, 跳过后 20 个, 并只显示 10 个
db.posts.find({}, {
comments: {
$slice: [ -20, 10 ]
}
})
字段更新
$inc
释义: 将文档中的某个 field 对应的 value 自增或自减某个数字 amount
示例: 将 _id 为 1 的文档的 age 字段在原来的基础上 +1
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$inc: {
age: 1
}
})
$mul
释义: 将文档中的某个 field 对应的 value 做乘法操作
示例: 将 _id 为 1 的文档的 price 值乘以 1.25 并更新
db.products.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$mul: {
price: 1.25
}
})
$rename
释义: 重命名文档中的指定字段的名
示例: 将 _id 为 1 的文档的 nickname 字段重命名为 alias, cell 字段重命名为 mobile
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$rename: {
'nickname': 'alias',
'cell': 'mobile'
}
})
$setOnInsert
释义: 配合 upsert 操作, 作为 insert 时可以为新文档扩展更多的 field
示例: 将 _id 为 1 的文档的 item 字段更改为 apple, 并插入新字段 defaultQty(值为 100)
db.products.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$set: {
item: "apple"
},
$setOnInsert: {
defaultQty: 100
}
}, {
upsert: true
})
详解:
setOnInsert 指令往往同 upsert、$set 指令配合使用
MongoDB 官网说明:
If an update operation with upsert: true results in an insert of a document, then $setOnInsert assigns the specified values to the fields in the document. If the update operation does not result in an insert, $setOnInsert does nothing.
如果 upsert 设为 true, 当满足查询条件的记录存在时则不执行 setOnInsert 中的操作, 当满足条件的记录不存在时则执行 setOnInsert 中的操作
与 set 指令配合使用, 可以作为 set 指令的补充, 当满足查询条件的记录存在时则执行 set 操作, 当满足查询条件的记录不存在时则新增一条记录, 其中包含 set 指令设置的属性以及 $setOnInsert 指令设置的属性
示例:
db.getCollection('tt').update({
_id: ObjectId("5dc2cd255ee0a3a2c2c4c384")
}, {
setOnInsert: {
pon: "a"
},
set: {
a: "e"
}
}, {
upsert: true
})
当满足查询条件 { _id: ObjectId("5dc2cd255ee0a3a2c2c4c384") } 的记录存在时, 则只更新或新增其 { a: "e" } 属性, 如果不存在则创建一条包含自动生成主键的记录 { _id: ObjectId("5dc2cd255ee0a3a2c2c4c384"), a: "e", pon: "a" }
注意:
- setOnInsert 和 set 中的属性记录不能相同
- MongoDB 更新语句时, 使用 setOnInsert、upsert 和 set、upsert 的区别
对于查询到的记录, 使用 set、upsert 时存在则更新, 不存在则新增, 使用 setOnInsert、upsert 时存在则不操作, 不存在则新增
$set
释义: 更新文档中的某一个字段, 而不是全部替换
示例:
假设有如下文档
{ _id: 1, name: "zhangsan", sex: "男" }
如果这样写:
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
sex: "女"
})
则更改之后的结果为:
{ _id: 1, sex: "女" }
若只想更改 sex 字段, 可以这样写:
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$set: {
sex: "女"
}
})
$unset
释义: 删除文档中的指定字段, 若字段不存在则不操作
示例: 删除 _id 为 1 的文档中的 name 字段
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$unset: {
name: ""
}
})
$min
释义: 将文档中的某字段与指定值作比较, 如果原值小于指定值则不更新, 若大于指定值则更新
示例:
假设有如下文档:
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 200 }
执行:
db.scores.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$min: {
lowScore: 150
}
})
执行结果:
{ _id: 1, highScore: 800, lowScore: 150 }
$max
释义: 与 $min 功能相反
$currentDate
释义: 设置指定字段为当前时间
示例:
db.person.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$currentDate: {
"lastLogin": {
$type: "timestamp"
}
}
})
数组更新
$(update)
语法:
{
".$": value
}
释义: 请参考官网
$addToSet
释义: 用于添加一个元素到 array 中, 一般用于 update
示例:
假设有如下文档:
{ _id: 1, letters: ["a", "b"] }
执行:
db.test.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$addToSet: {
letters: "c"
}
})
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "letters" : [ "a", "b", "c" ] }
执行:
db.test.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$addToSet: {
letters: [ "d", "e" ]
}
})
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "letters" : [ "a", "b", "c", [ "d", "e" ] ] }
注意:
若想让添加的多个元素分开成单个元素的效果, 请参考 $each 的使用方法
$pop
释义: 删除数组中的第一个或最后一个元素, -1 表示第一个, 1 表示最后一个
示例:
db.test.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$pop: {
letters: -1
}
})
$pullAll
释义: 删除数组或内嵌文档字段中所有指定的元素
示例:
假设有如下文档:
{ _id: 1, scores: [ 0, 2, 5, 5, 1, 0 ] }
执行:
db.test.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$pullAll: {
scores: [ 0, 5 ]
}
})
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "scores" : [ 2, 1 ] }
$pull
释义: 删除满足条件的元素
示例:
假设有如下文档:
{ _id: 1, votes: [ 3, 5, 6, 7, 7, 8 ] }
执行:
db.test.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$pull: {
votes: {
$gte: 6
}
}
})
结果:
{ _id: 1, votes: [ 3, 5 ] }
$push
释义: 往数组中追加指定的元素, 若在该文档中数组不存在, 则创建并添加指定元素(自 v2.4 起添加了对 $.each 的支持)
示例:
db.students.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$push: {
scores: 89
}
})
$each
语法:
{
$addToSet: {
<field>: {
$each: [ <value1>, <value2> ... ]
}
}
}
{
$push: {
<field>: {
$each: [ <value1>, <value2> ... ]
}
}
}
释义: 需要搭配 addToSet 或 push 方可使用
$sort
语法:
{
$push: {
<field>: {
$each: [ <value1>, <value2>, ... ],
$sort: <sort specification>
}
}
}
释义: 自 v2.4 起配合 $push 使用, 表示给文档中的指定数组元素排序, 1 是升序, -1 是降序
示例:
db.students.update({
_id: 1
}, {
$push: {
quizzes: {
$each: [ { id: 3, score: 8 }, { id: 4, score: 7 }, { id: 5, score: 6 } ],
$sort: { score: 1 }
}
}
})
$position
语法:
{
$push: {
<field>: {
$each: [ <value1>, <value2>, ... ],
$position: <num>
}
}
}
释义: 自 v2.6 起配合 $push 使用, 表示往数组元素中的指定位置插入元素
问题小结
使用 $size 获取文档中某个数组的长度, 数组不存在时语法报错, 可结合 $ifNull 进行判断:
... ...
{
$project: {
people: 1,
count: {
$size: {
$ifNull: [ '$myFieldArray', [] ]
}
}
}
}
... ...
给数组头部添加元素(实现unshift), 如果想在数组头部添加数据, 好像没有 $unshift 方法, 但可以利用 $each、$postition 把数据插入到指定的数组位置。
以下示例是将新元素插入到 activity_detail.continuous_times 数组字段的头部, 而不是默认的尾部, 即指定 position 为 0。
... ...
db.activity_users.update({
"_id": ObjectId("6375f4612e5827005c18938e"),
}, {
$push: {
'activity_detail.continuous_times': {
$each: [
{
"date": "20221117",
"times": NumberInt("1")
},
{
"date": "20221118",
"times": NumberInt("1")
},
{
"date": "20221119",
"times": NumberInt("1")
}
],
$position: 0
}
},
})
... ...
$merge 合并管道操作可以将一个文档添加到指定的集合或更新现有文档, 在更新文档时可以指定更新的规则。
$merge 操作的语法如下:
db.collection.aggregate( [ { $merge: { into: <collection to merge into>, whenMatched: <update conditions>, whenNotMatched: <insert document> } } ] )
其中:
into: 指定合并的集合名;
whenMatched: 指定在文档匹配时的更新规则;
whenNotMatched: 指定在文档不匹配时的插入规则;
示例:
db.students.aggregate([
{
$merge:
{
into: "students",
whenMatched: "replace",
whenNotMatched: "insert"
}
}
])
// 合并数据
... ...
const matchIds = tableDatas.map(o => o._id);
const tableNameAggregate: any[] = [
{ $match: { _id: { $in: matchIds } } },
{
$merge: {
into: intoTableName,
on: '_id',
whenMatched: 'merge',
whenNotMatched: 'insert',
},
},
];
await mongoConnection.db.collection(tableName).aggregate(tableNameAggregate).toArray()
... ...
有文档规格数据格式如下:
{
"specification": [
{
"specification_no": "7009086716208218112",
"specification_name": "款式",
"specification_value": "随机一款 J赏 文件夹套组"
},
{
"specification_no": "7009086716208218112",
"specification_name": "款式",
"specification_value": "随机一款 J赏 文件夹套组 大号"
}
]
}
摘取规格值字段并以空格拼接:
... ...
{
$project: {
"商品规格": {
$reduce: {
input: "$specification",
initialValue: "",
in: {
$concat: ["$$value", " ", "$$this.specification_value"],
},
},
},
},
}
... ...
有 orders 表如下:
db.orders.insertMany( [
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "almonds", "price" : 12, "ordered" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "cookies", "price" : 10, "ordered" : 60 }
] )
有 warehouses 表如下:
db.warehouses.insertMany( [
{ "_id" : 1, "stock_item" : "almonds", warehouse: "A", "instock" : 120 },
{ "_id" : 3, "stock_item" : "almonds", warehouse: "B", "instock" : 60 },
{ "_id" : 5, "stock_item" : "cookies", warehouse: "A", "instock" : 80 }
] )
联表查询时减少被驱动表的联表字段:
// 从 orders 表入手
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
// 聚合查询 warehouse 表
from: "warehouses",
// 用 $$order_item 指代 order 表的 .item 字段, $$ 可以理解成 lookup 中的变量前缀, $ 表示当前层级
let: {
order_item: "$item",
},
pipeline: [
{
// 在 warehouse 中匹配
$match: {
// 表达式
$expr: {
// eq 即等于, 注意这里的变量名, $stock_item 是 warehouse 表的, $$order_item 是来自 order 表 lookup 的变量
$eq: [ "$stock_item", "$$order_item" ],
},
},
},
{
// 各种对 warehouse 表查询的限定都放在这里
$project: {
stock_item: 0,
_id: 0,
},
},
{
$limit: 10,
},
{
$skip: 0,
},
],
// 输出字段名, 就是会把 warehouse 中查到的信息放到结果对象的 .stockdata 中
as: "stockdata",
},
},
]);
参考资料:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5d6f801fa231
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/operator/aggregation/lookup/#std-label-lookup-multiple-joins