【集训笔记】【大数模板】特殊的数 【Catalan数】【HDOJ1133【HDOJ1134【HDOJ1130
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3324
http://blog.csdn.net/xymscau/article/details/6776182

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<queue> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 using namespace std; 8 const int INF=1000100000; 9 struct node{ 10 int x,y; 11 }n[1010]; 12 bool cmp(node a,node b){ 13 return a.x<b.x; 14 } 15 int main(){ 16 int p,r,xmax,xmin,ymax,ymin,y[1010]; 17 while(scanf("%d%d",&p,&r)!=EOF){ 18 ymax=xmax=-INF;ymin=xmin=INF; 19 for(int i=0;i<p;i++){ 20 scanf("%d%d",&n[i].x,&n[i].y); 21 if(ymax<n[i].y)ymax=n[i].y; 22 if(ymin>n[i].y)ymin=n[i].y; 23 if(xmax<n[i].x)xmax=n[i].x; 24 if(xmin>n[i].x)xmin=n[i].x; 25 } 26 if((ymax-ymin <= r)&&(xmax-xmin <= r)){ 27 printf("%d\n",p); 28 continue; 29 } 30 else{ 31 sort(n,n+p,cmp); 32 int ans=0; 33 for(int i=0;i<p;i++){ 34 int k=0; 35 for(int j=i;n[j].x <= n[i].x + r && j < p;j++) 36 y[k++]=n[j].y; 37 sort(y,y+k); 38 int count=0,tem=0; 39 for(int j=0;j < k && tem < k;j++){ 40 while(y[tem]-y[j] <= r && tem<k) 41 tem++; 42 if(count < tem-j) 43 count=tem-j; 44 } 45 if(ans < count) 46 ans=count; 47 } 48 printf("%d\n",ans); 49 } 50 } 51 return 0; 52 }
http://blog.csdn.net/jxy859/article/details/6746254
http://blog.csdn.net/wwwzys/article/details/6746829
http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/09/03/2165771.html
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1134
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1130
HDOJ 1133
是道经典的50元100元排队求组合的问题
一种看不太懂的方法:

1 //F(a,b)=F(a-1,b)+F(a,b-1) 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 int a[101][101][101]={0}; 5 int b[101][101]={0}; //b数组里面保存的是a数组里面的元素个数 6 void qiuhe(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int n)//大数相加这种方法可以先学习下,否则看起来比较吃力 7 { 8 int i,j,k=0; 9 j=b[x0][y0]; 10 if(j<b[x1][y1]) 11 j=b[x1][y1]; 12 for(i=0;i<j;i++){ 13 a[x0][y0][i]+=a[x1][y1][i]*n+k; 14 k=a[x0][y0][i]/10000;//每个元素四位 15 a[x0][y0][i]%=10000; 16 } 17 if(k){ 18 a[x0][y0][j]=k; 19 b[x0][y0]=j+1; 20 } 21 else 22 b[x0][y0]=j; 23 } 24 void jiecheng(int n)//求大数阶乘 25 { 26 int i,j,k=0; 27 for(i=0;i<b[n-1][0];i++){ 28 a[n][0][i]=1; 29 a[n][0][i]=a[n-1][0][i]*n+k; 30 k=a[n][0][i]/10000; 31 a[n][0][i]=a[n][0][i]%10000; 32 } 33 if(k){ 34 a[n][0][i]=k; 35 b[n][0]=i+1; 36 } 37 else 38 b[n][0]=b[n-1][0]; 39 } 40 int main(){ 41 int T=0,i,j,m,n; 42 a[1][0][0]=1;b[1][0]=1; 43 for(i=2;i<=100;i++) 44 jiecheng(i);//当m=0时的排列数 45 for(i=1;i<=100;i++) 46 for(j=i;j<=100;j++){ 47 qiuhe(j,i,j-1,i,j); 48 qiuhe(j,i,j,i-1,i); 49 } 50 while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF&&(m||n)){ 51 T++; 52 printf("Test #%d:\n",T); 53 printf("%d",a[m][n][b[m][n]-1]); 54 for(i=b[m][n]-2;i>=0;i--) 55 printf("%4.4d",a[m][n][i]); 56 printf("\n"); 57 } 58 return 0; 59 }
利用大数模板AC:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<iomanip> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 #define MAXN 9999 8 #define MAXSIZE 10 9 #define DLEN 4 10 11 class BigNum 12 { 13 private: 14 int a[500]; //可以控制大数的位数 15 int len; //大数长度 16 public: 17 BigNum(){ len = 1;memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); } //构造函数 18 BigNum(const int); //将一个int类型的变量转化为大数 19 BigNum(const char*); //将一个字符串类型的变量转化为大数 20 BigNum(const BigNum &); //拷贝构造函数 21 BigNum &operator=(const BigNum &); //重载赋值运算符,大数之间进行赋值运算 22 23 friend istream& operator>>(istream&, BigNum&); //重载输入运算符 24 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&, BigNum&); //重载输出运算符 25 26 BigNum operator+(const BigNum &) const; //重载加法运算符,两个大数之间的相加运算 27 BigNum operator-(const BigNum &) const; //重载减法运算符,两个大数之间的相减运算 28 BigNum operator*(const BigNum &) const; //重载乘法运算符,两个大数之间的相乘运算 29 BigNum operator/(const int &) const; //重载除法运算符,大数对一个整数进行相除运算 30 31 BigNum operator^(const int &) const; //大数的n次方运算 32 int operator%(const int &) const; //大数对一个int类型的变量进行取模运算 33 bool operator>(const BigNum & T)const; //大数和另一个大数的大小比较 34 bool operator>(const int & t)const; //大数和一个int类型的变量的大小比较 35 36 void print(); //输出大数 37 }; 38 BigNum::BigNum(const int b) //将一个int类型的变量转化为大数 39 { 40 int c,d = b; 41 len = 0; 42 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 43 while(d > MAXN) 44 { 45 c = d - (d / (MAXN + 1)) * (MAXN + 1); 46 d = d / (MAXN + 1); 47 a[len++] = c; 48 } 49 a[len++] = d; 50 } 51 BigNum::BigNum(const char*s) //将一个字符串类型的变量转化为大数 52 { 53 int t,k,index,l,i; 54 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 55 l=strlen(s); 56 len=l/DLEN; 57 if(l%DLEN) 58 len++; 59 index=0; 60 for(i=l-1;i>=0;i-=DLEN) 61 { 62 t=0; 63 k=i-DLEN+1; 64 if(k<0) 65 k=0; 66 for(int j=k;j<=i;j++) 67 t=t*10+s[j]-'0'; 68 a[index++]=t; 69 } 70 } 71 BigNum::BigNum(const BigNum & T) : len(T.len) //拷贝构造函数 72 { 73 int i; 74 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 75 for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) 76 a[i] = T.a[i]; 77 } 78 BigNum & BigNum::operator=(const BigNum & n) //重载赋值运算符,大数之间进行赋值运算 79 { 80 int i; 81 len = n.len; 82 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 83 for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) 84 a[i] = n.a[i]; 85 return *this; 86 } 87 istream& operator>>(istream & in, BigNum & b) //重载输入运算符 88 { 89 char ch[MAXSIZE*4]; 90 int i = -1; 91 in>>ch; 92 int l=strlen(ch); 93 int count=0,sum=0; 94 for(i=l-1;i>=0;) 95 { 96 sum = 0; 97 int t=1; 98 for(int j=0;j<4&&i>=0;j++,i--,t*=10) 99 { 100 sum+=(ch[i]-'0')*t; 101 } 102 b.a[count]=sum; 103 count++; 104 } 105 b.len =count++; 106 return in; 107 108 } 109 ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, BigNum& b) //重载输出运算符 110 { 111 int i; 112 cout << b.a[b.len - 1]; 113 for(i = b.len - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) 114 { 115 cout.width(DLEN); 116 cout.fill('0'); 117 cout << b.a[i]; 118 } 119 return out; 120 } 121 122 BigNum BigNum::operator+(const BigNum & T) const //两个大数之间的相加运算 123 { 124 BigNum t(*this); 125 int i,big; //位数 126 big = T.len > len ? T.len : len; 127 for(i = 0 ; i < big ; i++) 128 { 129 t.a[i] +=T.a[i]; 130 if(t.a[i] > MAXN) 131 { 132 t.a[i + 1]++; 133 t.a[i] -=MAXN+1; 134 } 135 } 136 if(t.a[big] != 0) 137 t.len = big + 1; 138 else 139 t.len = big; 140 return t; 141 } 142 BigNum BigNum::operator-(const BigNum & T) const //两个大数之间的相减运算 143 { 144 int i,j,big; 145 bool flag; 146 BigNum t1,t2; 147 if(*this>T) 148 { 149 t1=*this; 150 t2=T; 151 flag=0; 152 } 153 else 154 { 155 t1=T; 156 t2=*this; 157 flag=1; 158 } 159 big=t1.len; 160 for(i = 0 ; i < big ; i++) 161 { 162 if(t1.a[i] < t2.a[i]) 163 { 164 j = i + 1; 165 while(t1.a[j] == 0) 166 j++; 167 t1.a[j--]--; 168 while(j > i) 169 t1.a[j--] += MAXN; 170 t1.a[i] += MAXN + 1 - t2.a[i]; 171 } 172 else 173 t1.a[i] -= t2.a[i]; 174 } 175 t1.len = big; 176 while(t1.a[len - 1] == 0 && t1.len > 1) 177 { 178 t1.len--; 179 big--; 180 } 181 if(flag) 182 t1.a[big-1]=0-t1.a[big-1]; 183 return t1; 184 } 185 186 BigNum BigNum::operator*(const BigNum & T) const //两个大数之间的相乘运算 187 { 188 BigNum ret; 189 int i,j,up; 190 int temp,temp1; 191 for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) 192 { 193 up = 0; 194 for(j = 0 ; j < T.len ; j++) 195 { 196 temp = a[i] * T.a[j] + ret.a[i + j] + up; 197 if(temp > MAXN) 198 { 199 temp1 = temp - temp / (MAXN + 1) * (MAXN + 1); 200 up = temp / (MAXN + 1); 201 ret.a[i + j] = temp1; 202 } 203 else 204 { 205 up = 0; 206 ret.a[i + j] = temp; 207 } 208 } 209 if(up != 0) 210 ret.a[i + j] = up; 211 } 212 ret.len = i + j; 213 while(ret.a[ret.len - 1] == 0 && ret.len > 1) 214 ret.len--; 215 return ret; 216 } 217 BigNum BigNum::operator/(const int & b) const //大数对一个整数进行相除运算 218 { 219 BigNum ret; 220 int i,down = 0; 221 for(i = len - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) 222 { 223 ret.a[i] = (a[i] + down * (MAXN + 1)) / b; 224 down = a[i] + down * (MAXN + 1) - ret.a[i] * b; 225 } 226 ret.len = len; 227 while(ret.a[ret.len - 1] == 0 && ret.len > 1) 228 ret.len--; 229 return ret; 230 } 231 int BigNum::operator %(const int & b) const //大数对一个int类型的变量进行取模运算 232 { 233 int i,d=0; 234 for (i = len-1; i>=0; i--) 235 { 236 d = ((d * (MAXN+1))% b + a[i])% b; 237 } 238 return d; 239 } 240 BigNum BigNum::operator^(const int & n) const //大数的n次方运算 241 { 242 BigNum t,ret(1); 243 int i; 244 if(n<0) 245 exit(-1); 246 if(n==0) 247 return 1; 248 if(n==1) 249 return *this; 250 int m=n; 251 while(m>1) 252 { 253 t=*this; 254 for( i=1;i<<1<=m;i<<=1) 255 { 256 t=t*t; 257 } 258 m-=i; 259 ret=ret*t; 260 if(m==1) 261 ret=ret*(*this); 262 } 263 return ret; 264 } 265 bool BigNum::operator>(const BigNum & T) const //大数和另一个大数的大小比较 266 { 267 int ln; 268 if(len > T.len) 269 return true; 270 else if(len == T.len) 271 { 272 ln = len - 1; 273 while(a[ln] == T.a[ln] && ln >= 0) 274 ln--; 275 if(ln >= 0 && a[ln] > T.a[ln]) 276 return true; 277 else 278 return false; 279 } 280 else 281 return false; 282 } 283 bool BigNum::operator >(const int & t) const //大数和一个int类型的变量的大小比较 284 { 285 BigNum b(t); 286 return *this>b; 287 } 288 289 void BigNum::print() //输出大数 290 { 291 int i; 292 cout << a[len - 1]; 293 for(i = len - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) 294 { 295 cout.width(DLEN); 296 cout.fill('0'); 297 cout << a[i]; 298 } 299 cout << endl; 300 } 301 int main(void) 302 { 303 int i,n; 304 BigNum x[101]; //定义大数的对象数组 305 x[0]=1; 306 for(i=1;i<101;i++) 307 x[i]=x[i-1]*(4*i-2)/(i+1); 308 while(scanf("%d",&n)==1 && n!=-1) 309 { 310 x[n].print(); 311 } 312 }
维基百科资料:
卡塔兰数
卡塔兰数是组合数学中一个常出现在各种计数问题中出现的数列。由以比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)命名。
卡塔兰数的一般项公式为 另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
前几项为 (OEIS中的数列A000108): 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, ...
[性质]
Cn的另一个表达形式为 所以,Cn是一个自然数;这一点在先前的通项公式中并不显而易见。这个表达形式也是André对前一公式证明的基础。(见下文的第二个证明。)
卡塔兰数满足以下递推关系
它也满足
这提供了一个更快速的方法来计算卡塔兰数。
卡塔兰数的渐近增长为
它的含义是左式除以右式的商趋向于1当n → ∞。(这可以用n!的斯特灵公式来证明。)
所有的奇卡塔兰数Cn都满足n = 2k − 1。所有其他的卡塔兰数都是偶数。
[应用]
组合数学中有非常多.的组合结构可以用卡塔兰数来计数。在Richard P. Stanley的Enumerative Combinatorics: Volume 2一书的习题中包括了66个相异的可由卡塔兰数表达的组合结构。以下用Cn=3和Cn=4举若干例:
- Cn表示长度2n的dyck word的个数。Dyck word是一个有n个X和n个Y组成的字串,且所有的部分字串皆满足X的个数大于等于Y的个数。以下为长度为6的dyck words:
- 将上例的X换成左括号,Y换成右括号,Cn表示所有包含n组括号的合法运算式的个数:
- Cn表示有n+1个叶子的二叉树的个数。
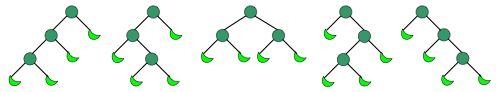
- Cn表示所有不同构的含n个分枝结点的满二叉树的个数。(一个有根二叉树是满的当且仅当每个结点都有两个子树或没有子树。)
证明:
令1表示进栈,0表示出栈,则可转化为求一个2n位、含n个1、n个0的二进制数,满足从左往右扫描到任意一位时,经过的0数不多于1数。显然含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数共有个,下面考虑不满足要求的数目.
考虑一个含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数,扫描到第2m+1位上时有m+1个0和m个1(容易证明一定存在这样的情况),则后面的0-1排列中必有n-m个1和n-m-1个0。将2m+2及其以后的部分0变成1、1变成0,则对应一个n+1个0和n-1个1的二进制数。反之亦然(相似的思路证明两者一一对应)。
从而。证毕。
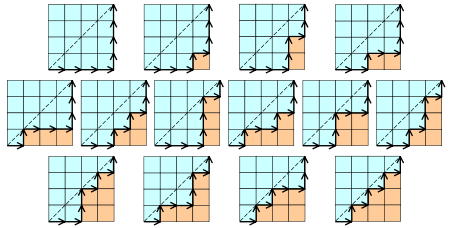
- Cn表示所有在n × n格点中不越过对角线的单调路径的个数。一个单调路径从格点左下角出发,在格点右上角结束,每一步均为向上或向右。计算这种路径的个数等价于计算Dyck word的个数: X代表“向右”,Y代表“向上”。下图为n = 4的情况:
-

- Cn表示对{1, ..., n}依序进出栈的置换个数。一个置换w是依序进出栈的当S(w) = (1, ..., n), 其中S(w)递归定义如下:令w = unv,其中n为w的最大元素,u和v为更短的数列;再令S(w) =S(u)S(v)n,其中S为所有含一个元素的数列的单位元。
- Cn表示集合{1, ..., n}的不交叉划分的个数. 那么, Cn 永远不大于第n项贝尔数. Cn也表示集合{1, ..., 2n}的不交叉划分的个数,其中每个段落的长度为2。综合这两个结论,可以用数学归纳法证明 that all of the free cumulants of degree more than 2 of the Wigner semicircle law are zero. This law is important in free probability theory and the theory of random matrices.
- Cn表示用n个长方形填充一个高度为n的阶梯状图形的方法个数。下图为 n = 4的情况:

百度百科资料:
简介
中文:卡特兰数
Catalan数是组合数学中一个常出现在各种计数问题中出现的数列。由以比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)命名。
原理:
令h(0)=1,h(1)=1,catalan数满足递归式:
h(n)= h(0)*h(n-1) + h(1)*h(n-2) +  + h(n-1)h(0) (其中n>=2)
+ h(n-1)h(0) (其中n>=2)
该递推关系的解为:
h(n)=C(2n,n)/(n + 1) (n=1,2,3, )
)
另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
前几项为 (OEIS中的数列A000108): 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, 
应用
我总结了一下,最典型的四类应用:(实质上却都一样,无非是递归等式的应用,就看你能不能分解问题写出递归式了)
1.括号化问题。
矩阵链乘: P=a1×a2×a3×……×an,依据乘法结合律,不改变其顺序,只用括号表示成对的乘积,试问有几种括号化的方案?(h(n)种)
2.出栈次序问题。
一个栈(无穷大)的进栈序列为1,2,3,..n,有多少个不同的出栈序列?
类似:
(1)有2n个人排成一行进入剧场。入场费5元。其中只有n个人有一张5元钞票,另外n人只有10元钞票,剧院无其它钞票,问有多少中方法使得只要有10元的人买票,售票处就有5元的钞票找零?(将持5元者到达视作将5元入栈,持10元者到达视作使栈中某5元出栈)
(2)在圆上选择2n个点,将这些点成对连接起来,使得所得到的n条线段不相交的方法数。
3.将多边行划分为三角形问题。
将一个凸多边形区域分成三角形区域的方法数?
类似:一位大城市的律师在她住所以北n个街区和以东n个街区处工作。每天她走2n个街区去上班。如果她
从不穿越(但可以碰到)从家到办公室的对角线,那么有多少条可能的道路?
类似:在圆上选择2n个点,将这些点成对连接起来使得所得到的n条线段不相交的方法数?
4.给顶节点组成二叉树的问题。
给定N个节点,能构成多少种形状不同的二叉树?
(一定是二叉树!
先去一个点作为顶点,然后左边依次可以取0至N-1个相对应的,右边是N-1到0个,两两配对相乘,就是h(0)*h(n-1) + h(2)*h(n-2) +  + h(n-1)h(0)=h(n))
+ h(n-1)h(0)=h(n))
(能构成h(N)个)
