类库探源——System.Delegate
一、MSDN 描述
Delegate 类:表示委托,委托是一种数据结构,它引用静态方法或引用类实例及该类的实例方法。(是不是感觉很像C语言中的函数指针 :) )
命名空间: System
程序集: mscorlib.dll
说到 Delegate 就必须谈 MulticastDelagate
MulticastDelagate类 :表示多路广播委托;即,其调用列表中可以拥有多个元素的委托。
命名空间: System
程序集: mscorlib.dll
继承关系:

备注:
1. Delegate 类是委托类型的基类
2. MulticastDelegate 继承自Delegate(这是废话,上面的继承关系那么明显)
3. MulticastDelegate 拥有一个带有链接的委托列表,该列表称为调用列表(虚函数表 Virtual Method Table)
4. 如果MulticastDelegate 的委托列表中某一个委托执行时发生异常,则在这个委托后面的委托不会执行
5. C# 中 delegate 与 Delegate 和 MulticastDelagate 的关系:
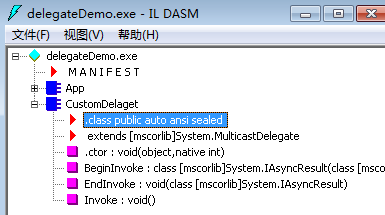
在C#中用 delegate 关键字标示一个方法 编译器将自动生成一个继承自 System.MulticastDelegate 的以方法名为类名的类,且添加 BeginInvoke 和 EndInvoke 方法

using System; public delegate void CustomDelaget(); // 用 delegate 关键字 编译器将自动生成一个继承自 System.MulticastDelegate 的类 /* .class public auto ansi sealed CustomDelaget extends [mscorlib]System.MulticastDelegate { } // end of class CustomDelaget */ class App { static void Main() { CustomDelaget d = new CustomDelaget(Invoke); d.Invoke(); } static void Invoke() { } }
二、用 Action 和 Func 代替自定义委托
Action 表示没有返回值的委托
Func 表示有返回值的委托
话说Action 和 Func 程序集分得有点怪异,Func 和 Action 程序集一样,以 Action 为例
Action(T) --> Action(T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T8) 的程序集为 mscorlib.dll
Action(T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T8,T9) --> Action(T1,T2,T3,...,T16) 的程序集为 System.Core.dll
这给人最初设计折类库的人觉得最多8个参数就够了,后来发现8个参数又不够,又加了8个放在 System.Core.dll 下的感觉
三、异步
1. 基于委托的异步(传统异步)
.NET Framework 运行你用传统异步的方式调用任何方法,只要你定义与你所需要调用的方法具有相同签名的委托,CLR会自动为该委托加上 BeginInvoke 和 EndInvoke
BeginInvoke 方法启动异步调用。
定义:
IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(待异步执行方法的参数表,AsyncCallback 委托,object State)
EndInvoke 方法检索异步调用的结果
如委托有返回值
var 委托的返回值 = EndInvoke(IAsyncResult ar);
如果 委托没有返回值则为
EndInvoke(IAsyncResult ar);
例子:

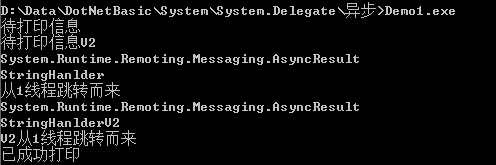
1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; 4 5 // 无返回值的委托 6 public delegate void StringHanlder(string msg); 7 8 // 待返回值的委托 9 public delegate string StringHanlderV2(string msg); 10 class App 11 { 12 static void Main() 13 { 14 StringHanlder handler = new StringHanlder(PrintMsg); 15 handler.BeginInvoke("待打印信息",new AsyncCallback(CallBack),string.Format("从{0}线程跳转而来",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)); 16 17 // 待返回值 18 StringHanlderV2 handler2 = new StringHanlderV2(PrintMsgV2); 19 handler2.BeginInvoke("待打印信息V2",new AsyncCallback(CallBackV2),string.Format("V2从{0}线程跳转而来",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)); 20 21 Thread.Sleep(1000*100); 22 } 23 24 static void PrintMsg(string msg) 25 { 26 Console.WriteLine(msg); 27 } 28 29 static void CallBack(IAsyncResult ar) 30 { 31 AsyncResult result = (AsyncResult) ar; 32 StringHanlder caller = (StringHanlder) result.AsyncDelegate; 33 string formatString = (string) ar.AsyncState; 34 caller.EndInvoke(ar); 35 36 Console.WriteLine(result); 37 Console.WriteLine(caller); 38 Console.WriteLine(formatString); 39 } 40 41 42 static string PrintMsgV2(string msg) 43 { 44 Console.WriteLine(msg); 45 return "已成功打印"; 46 } 47 static void CallBackV2(IAsyncResult ar) 48 { 49 AsyncResult result = (AsyncResult) ar; 50 StringHanlderV2 caller = (StringHanlderV2) result.AsyncDelegate; 51 string formatString = (string) ar.AsyncState; 52 var strRet = caller.EndInvoke(ar); 53 54 Console.WriteLine(result); 55 Console.WriteLine(caller); 56 Console.WriteLine(formatString); 57 Console.WriteLine(strRet); 58 } 59 }
结果:
2. 基于事件的异步
2014-12-29 补充
委托的几种初始化方式(原始方式、方法、匿名方法、Lambda 方式)
using System; public delegate void MyDelegate(); class App { static void Main() { //MyDelegate d = new MyDelegate(Method1); // 原始方式 //MyDelegate d = Method1; // 方法形式 //MyDelegate d = delegate{Console.WriteLine("Method1");}; // 匿名方法 MyDelegate d = () =>Console.WriteLine("Method1"); // Lambda 表达式 d.Invoke(); } static void Method1() { Console.WriteLine("Method1"); } }
未完
