poj 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors LCA
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1330
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
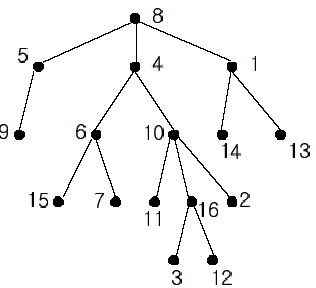
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
题意描述:在一个DAG中,定义节点u是节点v的祖先:节点u是树根到节点v的路径上的一个节点。 给出一些节点之间的关系,求出两个节点的最近公共祖先。
算法分析:最近公共祖先(LCA)的入门题。
最近公共祖先算法的大致思路:
1:求出每个节点的2^k(0<=k<max_log_n)的祖先节点。节点u的2^0(第一代)祖先节点就是u的父亲节点,那么我们可以得到u的第一代、第二代、第四代、第八代...祖先节点。
2:把节点u和v深度大的节点根据1中的算法思想移到和深度小的节点同一深度(树根深度为0,树根的儿子节点深度为1),然后再一起往上移,即可求出LCA。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<cmath> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 #include<vector> 8 #define inf 0x7fffffff 9 using namespace std; 10 const int maxn=10000+10; 11 const int max_log_maxn=14; 12 13 int n,A,B,root; 14 vector<int> G[maxn]; 15 int father[max_log_maxn][maxn],d[maxn]; 16 17 void dfs(int u,int p,int depth) 18 { 19 father[0][u]=p; 20 d[u]=depth; 21 int num=G[u].size(); 22 for (int i=0 ;i<num ;i++) 23 { 24 int v=G[u][i]; 25 if (v != father[0][u]) dfs(v,u,depth+1); 26 } 27 } 28 29 void init() 30 { 31 dfs(root,-1,0); 32 for (int k=0 ;k+1<max_log_maxn ;k++) 33 { 34 for (int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++) 35 { 36 if (father[k][i]<0) father[k+1][i]=-1; 37 else father[k+1][i]=father[k][father[k][i] ]; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 int LCA() 43 { 44 if (d[A]<d[B]) swap(A,B); 45 for (int k=0 ;k<max_log_maxn ;k++) 46 { 47 if ((d[A]-d[B])>>k & 1) 48 { 49 A=father[k][A]; 50 } 51 } 52 if (A==B) return A; 53 for (int k=max_log_maxn-1 ;k>=0 ;k--) 54 { 55 if (father[k][A] != father[k][B]) 56 { 57 A=father[k][A]; 58 B=father[k][B]; 59 } 60 } 61 return father[0][A]; 62 } 63 64 int main() 65 { 66 int t; 67 scanf("%d",&t); 68 while (t--) 69 { 70 scanf("%d",&n); 71 for (int i=0 ;i<=n ;i++) G[i].clear(); 72 for (int i=0 ;i<max_log_maxn ;i++) 73 { 74 for (int j=0 ;j<maxn ;j++) 75 father[i][j]=-1; 76 } 77 int a,b; 78 int vis[maxn]; 79 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); 80 for (int i=0 ;i<n-1 ;i++) 81 { 82 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 83 G[a].push_back(b); 84 vis[b]=1; 85 } 86 scanf("%d%d",&A,&B); 87 for (int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++) if (!vis[i]) {root=i;break; } 88 init(); 89 printf("%d\n",LCA()); 90 } 91 return 0; 92 }