BindService详解
1 bindService介绍
1.1 bindService介绍
bindService 是 Android 中用于绑定到服务的方法。它的核心功能是建立一个客户端与服务之间的连接,使得客户端可以与服务进行交互。
在解析 bindService 的源码之前,我们需要先了解它的使用方法。bindService 是一个 Activity 的方法,它需要三个参数:
- Intent:这是一个明确指示要启动的服务的对象。
- ServiceConnection:这是一个回调接口,当我们与服务建立连接时,系统将调用这个接口。
- flags:这是一个可选的标志,用于指定绑定服务的额外选项。
1.2 bindService使用
bindService 的例子:
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 当服务连接成功时调用
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// 当服务连接断开时调用
}
};
boolean bindServiceResult = bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
1.3 bindService 的大致流程
bindService 的大致流程:
- 当你调用
bindService方法时,ContextImpl类中的bindService方法会被调用。 - 这个方法会创建一个
ServiceConnection的代理,并通过ActivityManagerNative向ActivityManagerService请求绑定服务。 ActivityManagerService会处理绑定服务的请求,如果服务不存在,它会创建服务的实例。- 服务创建后,
ActivityManagerService会通过ServiceDispatcher回调你提供的ServiceConnection的代理。 - 代理接收回调后,将其转发给你的
ServiceConnection实现。
2 源码解析
2.1 binderService流程
从上面简单使用实例看到,我们一般通过bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE)开始。这个方法会走到ContextWrapper#bindService()
public boolean bindService(@RequiresPermission @NonNull Intent service,
@BindServiceFlags int flags, @NonNull @CallbackExecutor Executor executor,
@NonNull ServiceConnection conn) {
throw new RuntimeException("Not implemented. Must override in a subclass.");
}
继续往下到ContextImpl#bindService()
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, null, mMainThread.getHandler(), null,getUser());
}
这里直接到ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
String instanceName, Handler handler, Executor executor, UserHandle user) {
...
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, instanceName, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
}
ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon前面主要是进行一些条件检查,我们直接跳过,其中关键的是调用到了ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService也就是ActivityManagerService#bindIsolatedService
public int bindIsolatedService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName, String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags,
instanceName, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
bindIsolatedService最后调到了mServices.bindServiceLocked。这个mServices是一个ActiveServices。
final ActiveServices mServices;
public ActivityManagerService(Injector injector, ServiceThread handlerThread) {
...
mServices = hasHandlerThread ? new ActiveServices(this) : null;
...
}
它是在AMS的构造函数里面初始化的。我们继续看ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked里面做了啥。
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String instanceName, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
... //省略一些条件检查
ServiceLookupResult res = retrieveServiceLocked(service, instanceName,
resolvedType,
callingPackage,callingPid,
callingUid, userId,
true,callerFg, isBindExternal,
allowInstant);
...
final ServiceRecord serviceRecord = s;
final Intent serviceIntent = service;
RemoteCallback callback = new RemoteCallback(
new RemoteCallback.OnResultListener() {
@Override
public void onResult(Bundle result) {
bringUpServiceLocked(serviceRecord,serviceIntent.getFlags(),
callerFg, false, false);
}
}
...
try {
if (unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(s, callerApp.info.uid, false)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "BIND SERVICE WHILE RESTART PENDING: " + s);
}
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent,
callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName, callingPackage);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
s.addConnection(binder, c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
activity.addConnection(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
c.startAssociationIfNeeded();
...
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked这个方法分两种情况:
- ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLocked()
- ActiveServices#requestServiceBindingLocked()
为什么分为两种情况,这涉及到 A进程访问B进程时的几种状态:
- 进程B没有启动,即整个B进程都没有启动
- 进程B启动了,但是里面的Service没创建出来
- 进程B启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service没有被绑定过,回调onBind()
- 进程B启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service已经被绑定过,回调onRebind()
状态1、2对应代码中的情况1;状态3、4对应代码中的情况2。
第一种情况ActiveServices#bringUpServiceLockedService启动流程,我们另一篇幅再介绍,这里略去不表。
接着往下看ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked。
这里创建了一个ConnectionRecord对象,传入了服务端和客户端的信息,然后和IServiceConnection的binder对象一起,存入ServiceRecord的connections中,
private final ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> connections
= new ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>>();
然后以binder为key,以ConnectionRecord组成的ArrayList存入mServiceConnections中
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
mServiceConnections中存放的是所有绑定的service连接。
/**
* All currently bound service connections. Keys are the IBinder of
* the client's IServiceConnection.
*/
final ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> mServiceConnections = new ArrayMap<>();
第一次service起来一般不会走下面的connected流程,这里先不看,后面再看。
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately publish the connection.
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
}
}
2.2 onBind流程
我们回过头来继续看ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked后面的流程。
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.d(TAG_SERVICE, "requestBind " + i + ": requested=" +
i.requested + " rebind=" + rebind);
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.getReportedProcState());
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r, e);
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Crashed while binding " + r);
// Keep the executeNesting count accurate.
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bumpServiceExecutingLocked主要是把相关的信息更新到ServiceRecord里面,这里就不看了。
重点来看r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind, r.app.getReportedProcState());
这里r.app的app是ServiceRecord的成员变量ProcessRecord
ProcessRecord app; // where this service is running or null.
而thread是ProcessRecord的成员变量IApplicationThread。
IApplicationThread thread; // the actual proc... may be null only if
// 'persistent' is true (in which case we
// are in the process of launching the app)
IApplicationThread这个我们很熟悉,它的实现是ActivityThread的内部类ApplicationThread
private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub
直接看ApplicationThread#scheduleBindService
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + "
uid="+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
继续看
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
这里调到了handleBindService。
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
这里根据service的token从service的集合中找到对应的service。
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
然后调用service的onBind方法,并将Intent作为参数传递过去了,然后返回服务端的IBinder对象,最后调用ActivityManagerService#publishService发布服务。
2.3 发布服务
AMS的publishService很简单,最终又回到了ActiveServices里面了。
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
publishServiceLocked里面会把前面保存到ServiceRecord里面的相关信息再取出来。
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> connections =
r.getConnections();
for (int conni = connections.size() - 1; conni >= 0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Not publishing
to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Bound intent: " +
c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " +
r.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
2.4 onServiceConnected流程
这里调用 c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
IServiceConnection的实现类是android.app.LoadedApk的静态内部类ServiceDispatcher里面。
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
if (mActivityExecutor != null) {
mActivityExecutor.execute(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else {
doConnected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
这里直接调用了LoadedApk.ServiceDispatche#connected。
connected函数里面三个分支最终都会走到connected里面。
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
...
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is now disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (dead) {
mConnection.onBindingDied(name);
}
// If there is a new viable service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
} else {
// The binding machinery worked, but the remote returned null from onBind().
mConnection.onNullBinding(name);
}
}
这里会将绑定的信息放到mActiveConnections的集合里面,然后回调ServiceConnection#onServiceConnected。这时客户端就收到了onServiceConnected。
2.5 bringUpServiceLocked逻辑
最后来看bringUpServiceLocked的逻辑。
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
如果service没有运行时,就会走bringUpServiceLocked逻辑,然后直接返回。
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode,
mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
...
}
如果APP 已经创建了,即进程已经启动了,就启动service,走realStartServiceLocked。
/**
* Note the name of this method should not be confused with the started services concept.
* The "start" here means bring up the instance in the client, and this method is called
* from bindService() as well.
*/
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
r.setProcess(app);
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final boolean newService = app.startService(r);
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, /* oomAdj= */ false);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(app, OomAdjuster.OOM_ADJ_REASON_START_SERVICE);
...
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackage(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.getReportedProcState());
r.postNotification();
...
}
参数app是一个 ProcessRecord 对象,每启动一个app就创建了一个进程,进程信息就保存在ProcessRecord里面。app.thread就是ApplicationThread对象。
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(),会调用Handler发送一个CREATE_SERVICE消息,然后执行handleCreateService()方法:
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
...
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
// Service resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the application
// context.
context.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
context.setOuterContext(service);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
这里通过类加载器和反射加载的Service,并把它保存到mServices集合中。
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
为什么要将service put到mServices中,因为service只能创建一次,只能bind一次,下次再调用bindService进行绑定服务时,先从mServices中寻找,如果找到了则判断service是否绑定了,如果还没有绑定,则调onBind进行绑定,如果已经绑定了,则调用onRebind。这个过程在handleBindService()中:
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
最后bringUpServiceLocked返回null,继续走ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked后面的流程。
Service的app进程没有启动的逻辑这里就不再展开讨论。
2.6 总结
3 疑问
3.1 onServiceConnected()和onBind()的时机与顺序
我们主要看ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked中下面这段
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
条件1:s.app != null && b.intent.received
s.app != null这个条件一般应该都满足。那么b.intent.received是什么时候设置为true的呢?
答案就在ActiveServices#publishServiceLocked的时候
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
if (r != null) {
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
}
}
}
再来看b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind这个条件。
先来看``b.intent.apps.size() == 1这个条件,它的设置在ServiceRecord#retrieveAppBindingLocked`中
public AppBindRecord retrieveAppBindingLocked(Intent intent,ProcessRecord app) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord i = bindings.get(filter);
if (i == null) {
i = new IntentBindRecord(this, filter);
bindings.put(filter, i);
}
AppBindRecord a = i.apps.get(app);
if (a != null) {
return a;
}
a = new AppBindRecord(this, i, app);
i.apps.put(app, a);
return a;
}
所以,对于已经绑定过service的client来说,这个值应该会是1。
再来看 b.intent.doRebind这个条件
doRebind设置为true的时机,也就是应用端收到UnbindService之后。
void unbindFinishedLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, boolean doRebind) {
if (b != null) {
if (b.apps.size() > 0 && !inDestroying) {
// Applications have already bound since the last
// unbind, so just rebind right here.
boolean inFg = false;
for (int i=b.apps.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord client = b.apps.valueAt(i).client;
if (client != null && client.setSchedGroup
!= ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND) {
inFg = true;
break;
}
}
try {
requestServiceBindingLocked(r, b, inFg, true);
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
// Don't pass this back to ActivityThread, it's unrelated.
}
} else {
// Note to tell the service the next time there is a new client.
b.doRebind = true;
}
}
}
doRebind设置为false的时机:在每一次重新绑定之后,都会把,这个逻辑在前面的requestServiceBindingLocked和移除conn的时候:
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
}
}
void removeConnectionLocked(ConnectionRecord c, ProcessRecord skipApp,
ActivityServiceConnectionsHolder skipAct) {
...
b.intent.hasBound = false;
// Assume the client doesn't want to know about a rebind;
// we will deal with that later if it asks for one.
b.intent.doRebind = false;
}
所以,这里分几种情况:
-
如果service是第一次调用bindService,那么此时received是false,就会直接走
!b.intent.requested分支; -
如果service已经绑定过了,那么直接调用c.conn.connected,客户端收到onServiceConnected回调;
而且,如果之前有unBind过,那么就会再次调用onBind。
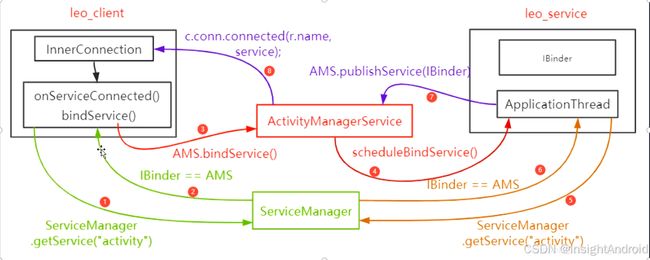
3.2 AMS进程的 conn.connected 是如何调用到app进程的connection.onServiceConnected()方法的?
先看下app进程的ServiceConnection对象是如何转为IServiceConnection对象的,app调用bindService方法进行绑定服务时会在ContextImpl#bindServiceCommon方法中对参数conn对象进行封装,转换为IServiceConnection对象sd,
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
...
}
mPackageInfo时是LoadedApk对象,LoadedApk#getServiceDispatcher方法:
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map =
mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
...
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
...
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
...
}
也就是说客户端进程的bindService方法会把传递进去的ServiceConnection conn参数转为InnerConnection对象sd,InnerConnection实现了IServiceConnection接口,并且是Stub类,而AMS进程的conn对象也实现了IServiceConnection接口,是个Proxy类。
也就是AMS进程调用 conn.connected 方法最终调用到app进程的connection.onServiceConnected()方法的过程是一个Binder机制跨进程调用的过程,这个过程中AMS进程是客户端(IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy),app进程是服务端(IServiceConnection.Stub)。