Golang测试func TestXX(t *testing.T)的使用
一般Golang中的测试代码都以xxx_test.go的样式,在命名测试函数的时候以Testxx开头。
以下是我写的一个单元:
package tests
import "strings"
func Split(s, sep string) (res []string) {
i := strings.Index(s, sep)
for i > -1 {
res = append(res, s[:i])
s = s[i+len(sep):]
i = strings.Index(s, sep)
}
res = append(res, s)
return
}
第一种测试方法:
func TestSplit(t *testing.T) {
inputs := Split("a:b:c", ":")
want := []string{"a", "b", "c"}
if !reflect.DeepEqual(inputs, want) {
t.Errorf("inputs:%v, want:%v", inputs, want)
}
}
这种直接定义好输入、期望值,进行对比,这种不适合大量数据比较。
第二种测试方法:
func TestSplit(t *testing.T) {
testCases := []struct {
input string
sep string
want []string
}{
{input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
{input: "a:b:c", sep: ",", want: []string{"a:b:c"}},
{input: "abcd", sep: "bc", want: []string{"a", "d"}},
}
for _, tc := range testCases {
got := Split(tc.input, tc.sep)
if !reflect.DeepEqual(got, tc.want) {
t.Errorf("期望值:%v,实际值:%v\n", tc.want, got)
}
}
}
使用结构体测试,然后使用for range遍历,是比较方便的方式,但是如果我的测试数据很多,但是我其中一个测试出现错误了,我现在需要找到那一个,那么这个方式就有点不适用了。
第三种测试方法(推荐使用):
func TestSplit(t *testing.T) {
testCases := map[string]struct {
input string
sep string
want []string
}{
"one": {input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
"two": {input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
"three": {input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
"four": {input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"a", "b", "c"}},
"five": {input: "a:b:c", sep: ":", want: []string{"b", "b", "c"}},
}
for name, tc := range testCases {
t.Run(name, func(t *testing.T) {
got := Split(tc.input, tc.sep)
if !reflect.DeepEqual(got, tc.want) {
t.Errorf("期望值:%v,实际值:%v", tc.want, got)
}
})
}
}
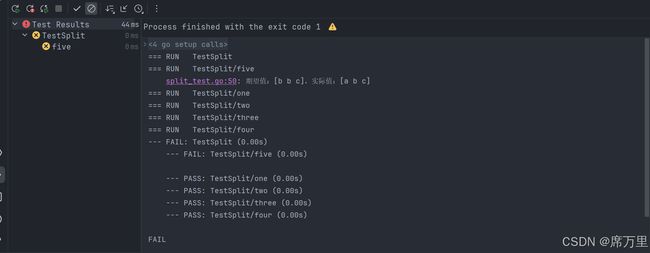
这里我们使用子测试的方法,主要可以看到第五个测试案例直接报错,信息并显示出来。
同样,也有一些其他的测试方法,后续如果了解更多的话,在这里补上。