python单元测试框架---unittest
仅供个人参考
unittest核心工作原理
四个概念:test case、test suite,test runner,test fixture
test case:
一个测试用例,包括测试前准备环境的搭建(setUp),执行测试代码(run),以及测试后环境的还原(tearDown)
TestSuite:
多个测试用例集合在一起就是TestSuite,而且TestSuite可以嵌套TestSuite。
TestLoader:
用于把Testcase加载到TestSuite中。
loadTestsFrom_()方法:从各个地方寻找TestCase,创建他们的实例,然后add到TestSuite中,再返回一个TestSuite实例。
TextTestRunner:
用于执行测试用例。
run(test)会执行TestSuite/TestCase中的run(result)方法。
测试的结果会保存到TextTestResult实例中,包括运行了多少测试用例,成功了多少,失败了多少等信息。
Test fixture:
对一个测试用例环境的搭建和销毁是一个fixture。
1、执行TestCase
(1)定义一个叫mathfunc.py的模块,写入要测试的函数
# 一些待测方法
def adde(a,b):
return a+b
def minus(a,b):
return a-b
def multi(a,b):
return a*b
def divide(a,b):
return a/b
(2)定义一个叫test_mathfunc.py的模块,用于测试
import unittest
from mathfunc import *
class TestMathFunc(unittest.TestCase):
"""Test mathfunc.py"""
def test_add(self):
"""Test method add(a,b)"""
self.assertEqual(adde(1,2),3)
self.assertNotEqual(adde(2,2),3)
def test_minus(self):
"""Test method minus(a,b)"""
self.assertEqual(1,minus(3,2))
def test_multi(self):
"""Test method multi(a,b)"""
self.assertEqual(6,multi(2,3))
def test_divide(self):
"""Test method divide(a,b)"""
self.assertEqual(2,divide(6,3))
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
在终端执行python test_mathfunc.py
结果:
PS C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest> python .\test_suite.py
test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method add(a,b) ... ok
test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method minus(a,b) ... ok
test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method multi(a,b) ... ok
test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a,b) ... FAIL
======================================================================
FAIL: test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest\test_mathfunc.py", line 23, in test_divide
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
AssertionError: 3 != 2.5
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.002s
FAILED (failures=1)
2、将TestCase都加载到suite中再执行测试用例
创建一个新的模块test_suite.py
(1)有顺序的加载testcase进入suite中:
import unittest
from unittest import runner
from test_mathfunc import TestMathFunc
if __name__ =='__main__':
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
#将所有的测试用例放入一个list中
tests = [TestMathFunc("test_add"),TestMathFunc("test_minus"),TestMathFunc("test_multi"),TestMathFunc("test_divide")]
#将该list中的用例加入到suite中
suite.addTests(tests)
#运行测试用例
# verbosity可以控制输出的错误报告的详细程度,默认是1
# 如果是0则不输出每一用例的执行结果。
# 如果是2,则详细输出执行结果。
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(verbosity=2)
runner.run(suite)
结果:
PS C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest> python .\test_suite.py
test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method add(a,b) ... ok
test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method minus(a,b) ... ok
test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method multi(a,b) ... ok
test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a,b) ... FAIL
======================================================================
FAIL: test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest\test_mathfunc.py", line 23, in test_divide
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
AssertionError: 3 != 2.5
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.002s
FAILED (failures=1)
(2)将testcase无序加入suite中
suite.addTests(unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromName('test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc'))
#或是
suite.addTests(unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromNames(['test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc']))
3、将测试结果输出到文件中
import unittest
from unittest import runner
from test_mathfunc import TestMathFunc
if __name__ =='__main__':
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromTestCase(TestMathFunc))
with open('UnitestTextRepot.txt','a') as f:
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner(stream=f,verbosity=2)
runner.run(suite)
然后就可以在这个.py相同目录下看到自动生成的UnitestTextRepot.txt文件啦!
4、使用test fixture的setUp()和tearDown()
修改test_mathfunc.py
PS C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest> python .\test_suite.py
test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method add(a,b) ... do something before test.Prepare environment.
add
do something after test.Clean up.
ok
test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method minus(a,b) ... do something before test.Prepare environment.
minus
do something after test.Clean up.
ok
test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method multi(a,b) ... do something before test.Prepare environment.
multi
do something after test.Clean up.
ok
test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a,b) ... do something before test.Prepare environment.
divide
do something after test.Clean up.
FAIL
======================================================================
FAIL: test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a,b)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest\test_mathfunc.py", line 33, in test_divide
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
AssertionError: 3 != 2.5
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.004s
FAILED (failures=1)
可以看出,setUp()在每隔测试方法执行前执行一次
tearDown()方法在每个测试方法执行后执行一次。
setUp()用来为测试准备环境
tearDown()用来清理环境,为之后测试做准备
如果在所有case执行之前准备一次环境,在所有case执行结束之后再清理环境,使用setUpClass()与tearDownClass()
class TestMathFunc(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
print("This setUpClass() method only called once.")
@classmethod
def tearDownClass(cls):
print("This tearDownClass() method only called once too.")
5、跳过某个case
1、skip装饰器
class TestMathFunc(unittest.TestCase):
"""Test mathfuc.py"""
...
@unittest.skip("I don't want to run this case.")
def test_divide(self):
"""Test method divide(a,b)"""
print("divide")
self.assertEqual(2,divide(6,3))
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
执行:
test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method add(a, b) ... ok
test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a, b) ... skipped "I don't want to run this case."
test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method minus(a, b) ... ok
test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method multi(a, b) ... ok
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.000s
OK (skipped=1)
skip装饰器共3个:
unittest.skip(reason)skip无条件跳过unittest.skipIf(condition,reason)skipIf当condition为True时跳过unittest.skipUnless(condition,reason)当condition为False时跳过
2、TestCase.skipTest()方法
class TestMathFunc(unittest.TestCase):
"""Test mathfuc.py"""
...
def test_divide(self):
"""Test method divide(a,b)"""
self.skipTest('Do not run this.')
print("divide")
self.assertEqual(2,divide(6,3))
self.assertEqual(3,divide(5,2))
输出:
test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method add(a, b) ... ok
test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method divide(a, b) ... skipped "Do not run this."
test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method minus(a, b) ... ok
test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Test method multi(a, b) ... ok
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 4 tests in 0.000s
OK (skipped=1)
6、导出HTMLReport
实现导出HTMLReport需要使用第三方的HTMLTestRunner.py模块,需要下载(下载文件在本文最下方),放到当前目录下,或是你安装python的目录,C:/Pythonxxx/Lib 下,然后在test_suite.py中导入运行即可。
在test_suite.py中写入:
import unittest
from unittest import runner
from test_mathfunc import TestMathFunc
from HTMLTestRunner import *
if __name__ =='__main__':
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
tests = [TestMathFunc("test_add"),TestMathFunc("test_minus"),TestMathFunc("test_multi"),TestMathFunc("test_divide")]
suite.addTests(tests)
#输出HTML报告
with open('HTMLReport.html','wb') as f:
runner = HTMLTestRunner(stream=f,title='MathFunc Test Report',
description='generated by HTMLTestRunner.',
verbosity=2)
runner.run(suite)
控制台结果:
PS C:\Study\vscode\PythonWorkplace\测试模块unittest> python .\test_suite.py
ok test_add (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
ok test_minus (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
ok test_multi (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
F test_divide (test_mathfunc.TestMathFunc)
Time Elapsed: 0:00:00.001994
输出的HTMLReport.html报告在test_suite.py的当前目录中,view in browse即可看到输出文档。
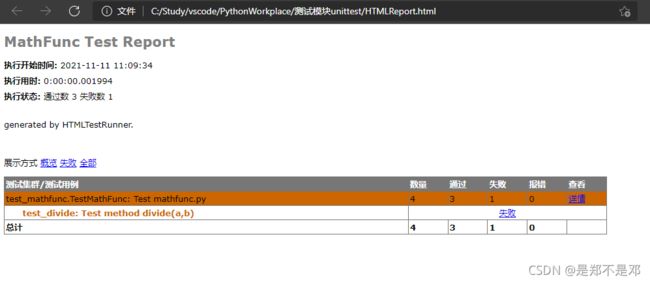
注意点:输出文档出现乱码
需要保证test_suite.py中写文件时是使用的二进制写入还是字符串写入。
二进制写入:
with open('HTMLReport.html','wb') as f:中wb的b表示二进制写入。
则在HTMLTestRunner.py模块中为:
self.stream.write(output.encode('utf-8'))
字符串写入:
with open('HTMLReport.html','w',encoding='uft-8') as f:
则在HTMLTestRunner.py模块中为:
self.stream.write(output)
最后,HTMLTestRunner.py模块源码如下,复制粘贴即可。
"""
A TestRunner for use with the Python unit testing framework. It
generates a HTML report to show the result at a glance.
The simplest way to use this is to invoke its main method. E.g.
import unittest
import HTMLTestRunner
... define your tests ...
if __name__ == '__main__':
HTMLTestRunner.main()
For more customization options, instantiates a HTMLTestRunner object.
HTMLTestRunner is a counterpart to unittest's TextTestRunner. E.g.
# output to a file
fp = file('my_report.html', 'w',encoding='utf-8')
runner = HTMLTestRunner.HTMLTestRunner(
stream=fp,
title='My unit test',
description='This demonstrates the report output by HTMLTestRunner.'
)
# Use an external stylesheet.
# See the Template_mixin class for more customizable options
runner.STYLESHEET_TMPL = ''
# run the test
runner.run(my_test_suite)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Copyright (c) 2004-2007, Wai Yip Tung
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* Neither the name Wai Yip Tung nor the names of its contributors may be
used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without
specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS
IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER
OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
"""
# URL: http://tungwaiyip.info/software/HTMLTestRunner.html
__author__ = "Wai Yip Tung"
__version__ = "0.8.2"
"""
Change History
Version 0.8.2
* Show output inline instead of popup window (Viorel Lupu).
Version in 0.8.1
* Validated XHTML (Wolfgang Borgert).
* Added description of test classes and test cases.
Version in 0.8.0
* Define Template_mixin class for customization.
* Workaround a IE 6 bug that it does not treat
%(heading)s
%(report)s
%(ending)s